Vomiting in childhood is often associated with immaturity of the immune and digestive systems. Bowel movement of stomach contents occurs both after meals and on an empty stomach. An unpleasant condition appears as a reaction of the child’s body to stimuli (external and internal).
Normally, there should be no bile in the stomach. Its casting is permanent or one-time in nature. To alleviate the child’s condition, it is necessary to call a doctor who will conduct a diagnosis and help find out the reason for the emptying of the stomach. Until then, you need to know how to provide first aid.
The main reasons why a child vomited bile?
Causes of vomiting bile in children can be:
- liver diseases;
- stomach diseases;
- gallbladder pathology;
- eating spicy, fatty, fried foods in the evening;
- various types of poisoning;
- appendicitis (in rare cases);
- alcohol poisoning (in adolescents);
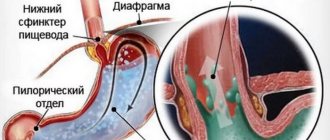
- In newborn infants, regurgitation of bile may indicate intestinal obstruction or pyloric spasm.
Vomiting of bile in a child can also be provoked by stress and mental overload. In most cases, this type of vomiting occurs once or twice and is not dangerous.
Very often, repeated vomiting with bile is caused by poisoning. It is often accompanied by symptoms such as diarrhea, chills, fever and abdominal pain.
Folk recipes for restoring digestion in a child
You can restore a child’s digestive system when vomiting bile using traditional medicine methods. However, do not forget that the treatment is carried out on very young children, and such methods also have contraindications. Therefore, you should first consult with your pediatrician.
These treatment methods include:
- juice from vegetables. It is recommended to combine potato, cabbage and carrot juice;
- pumpkin seeds. They help normalize bile production. Children over three years old can be given up to five seeds every day;
- flax seeds. Restores digestion and pancreatic function. The decoction will require 50 g of seeds. Pour water over them and boil for 45 minutes over low heat. Drink 1 teaspoon before meals every morning;
- dill infusion Pour 250 ml of boiling water over a spoon of grated greens and let it brew for 3 hours. Regular intake will relieve the baby from bloating;
- beet juice Eliminates bile stagnation, improves the condition after repeated vomiting. Grind the boiled beets and squeeze through cheesecloth. Drink juice 1 tsp. twice a day half an hour before meals.
Vomiting of bile in infants
The most common cause of vomiting in infants is improper feeding and attachment to the breast. When feeding, the baby swallows excess air, which leads to such a stomach reaction.
If the child is bottle-fed, overeating can provoke vomiting. Parents need to calculate the correct dosage of artificial formula.
First aid for a child
The main principle of normalizing the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is to adjust the diet so that the stomach is restored. If the parent knows the causes of stomach problems, they need to be eliminated. With occasional vomiting, dietary nutrition and increased fluid intake are necessary.
Tips on how to help your baby:
- Calm the child, wash his face with cool water, give a small amount of liquid to rinse the mouth.
- Provide increased fluid intake (1-1.5 liters) of cold drinks. In small quantities and often. Suitable drinks are bottled mineral water, sweetened water (20 g of sugar per liter), children's tea, rehydration solution.
- Create an optimal diet. Do not feed anything other than liquids for the first few hours. Later add unsweetened cookies, rice, potatoes, pasta, ripe banana, meat broth (without fat). Eliminate milk, fatty foods, mixed juices.
- Don't force your child to eat. Offer food often and in small portions.
- Monitor the general condition of the baby and body temperature.
- Follow your child’s daily routine to restore his mental state. A psychological disorder may indicate problems with the nervous system. Stress can cause angina pectoris, which provokes gag reflexes.
- If the condition worsens, seek medical help immediately.
In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor immediately?
Vomiting can cause great harm to the baby's health. Properly prescribed treatment and doctor’s recommendations will help improve the baby’s well-being and relieve him of the feeling of nausea and eliminate the cause of vomiting.
Mandatory medical assistance, hospitalization may be required if vomiting:
- Bloody, yellow discharge appears.
- Associated with head trauma, possible concussion.
- The child has increasing abdominal pain, spasms at intervals, the abdomen is hard, inflamed, and painful.
- The baby is apathetic, sleepy, if his eyes are flooded.
- Rejects fluid and stops urinating.
- Often nausea, a sudden attack of vomiting appears.
- Poor health is accompanied by a headache with fever.
- There is diarrhea (possibly green).
- The diet does not help, the baby continues to vomit, food comes out.
- Accompanied by a temperature above 38C.
- A dangerous symptom is dehydration (dry mouth, decreased salivation, accelerated pulse, irregular breathing rhythm, disorientation, lost gaze, no tears when crying, the child is irritable, quiet, if babies have a slightly swollen large fontanelle, daytime sleep lasts more than 4 hours , while the baby may not have a temperature).
A child is vomiting bile: what to do?
If a child vomits bile, parents should take the following measures to relieve the child's condition:
- First of all, remain calm and calm the child;
- completely empty the stomach of all contents, rinse the stomach;
- let the child take activated charcoal or another absorbent drug;
- You can also give a little water with mint drops to drink, the water should be cold.
- put the child to bed and provide him with peace;
- if the temperature rises, give an antipyretic;
- under no circumstances leave the child alone in this state;
- do not give food for 6 hours, but at the same time give water periodically to avoid dehydration.
But the most important step any parent should take if their child is vomiting bile is to first seek medical help from a doctor. If, in the opinion of the doctor, the child needs to be admitted to hospital, it is best to follow the advice of a qualified medical professional. In the hospital, you can quickly cope with intoxication of the body and conduct the necessary examination.
In order to prevent and prevent vomiting of bile in children, it is necessary to provide the child with a balanced healthy diet, a healthy lifestyle, of course - maintain hygiene, undergo timely medical examinations for preventive purposes and promptly seek medical help in case of any diseases.
Treatment
If your child starts vomiting, it is better to call a doctor. Before his arrival, first aid must be provided. To begin with, you need him to be in bed in a reclining position with his chest raised. Horizontal laying of children can lead to repeated vomiting, which ensures the penetration of bile into the stomach area.
The danger of vomiting is the onset of dehydration. To prevent this consequence, it is necessary to give the child fluids to drink. In addition to water, you are allowed to give your child something to drink:
- juice diluted with water;
- weak warm tea;
- compote;
- saline solution (Regidron).
Saline solution
Saline solution is sold at the pharmacy. It can be prepared at home. To do this, you need to dissolve the following ingredients in a liter of boiled water:
- baking soda - 6 g;
- salt - 12 g;
- sugar - 24 g.
The resulting solution is given warm. The optimal temperature is 37 degrees. It is important to remember that if taken incorrectly, the drink causes nausea. To avoid its appearance, “homemade Regidron” is given to the baby to drink in small sips, but often.
It is not recommended to feed the child until the doctor arrives. If the baby is breastfed, then mother's milk is not contraindicated.
Drugs
If the condition is caused by food poisoning, then it will be enough to relieve the child’s digestive system by not feeding him for 5 hours and provide him with fluids. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes:
| Drug groups | Action | Names of drugs |
| Antacids | Eliminate irritation of the gastric mucosa | Gaviscon (suspension allowed from 6 years), yellow and green Almagel (from 1 month of life), Phosphalugel (from birth) |
| Antidiarrheals | Stop diarrhea (if any) | Phthalazole (from birth), Smecta (infants), Imodium (from 6 years old) |
| Antispasmodics and painkillers | Eliminate spasms of the walls of the stomach and bile ducts | Nurofen (from 3 months from birth), No-shpa (from 6 years) |
In more severe cases, when the child vomits bile, symptomatic and antibacterial treatment is prescribed in a hospital setting. To normalize the functions of the gastrointestinal tract, you need to contact a pediatric gastroenterologist.
Before giving your child any of the drugs, you should consult your doctor. It is important to study the side effects and contraindications indicated in the instructions for use for each medicine. It is recommended to follow the dosages prescribed in the instructions for the medications and adhere to age restrictions.
News MirTesen
Fever, vomiting and skin rash
This combination of symptoms occurs in the following cases:
- Viral infections (measles, chickenpox, rubella, enteroviral disease).
- Bacterial infections (scarlet fever, chicken pox, measles).
- Meningococcal infection (causing meningitis and blood poisoning).
- Allergic reactions.
A child may develop a rash from a high fever due to a cold or flu.
In any case, rash, fever and vomiting are dangerous symptoms, and it is important to know what to do so as not to miss a serious illness. If, in addition to the above, the baby has convulsions, photophobia, headache and muscle stiffness, there is a possibility of inflammation of the brain and you should call a doctor without delay.
Diagnostics
To establish the cause, it is necessary to examine the patient and carefully collect anamnesis. The doctor determines why the vomiting occurred and its relationship with the intake of food, medications, and alcohol. Finds out the presence of other symptoms - pain, fever.
The patient may require additional studies:
- blood and urine tests;
- biochemical study of venous blood;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray of the stomach and intestines.
Further tactics are determined based on the results of observation and identified pathology.
Vomiting and diarrhea (diarrhea)
The cause of these symptoms is often an intestinal infection, the causative agents of which are salmonella, Escherichia, enteroviruses, cholera and dysentery bacilli, and rotaviruses. The temperature rises to 39-40°C, the child vomits repeatedly, and has greenish diarrhea with mucus. This condition lasts several days if left untreated.
Rotavirus under a microscope
Rotavirus infection is most common among children, especially under 2 years of age. Infection occurs through unwashed hands, unboiled water, and through household contact. The disease begins with weakness, sore throat, runny nose, headache, and a gradual increase in temperature; later nausea, vomiting, stomach pain and loose stools appear.
Principles of pathology therapy
If vomiting bile was sporadic, you can do nothing - the condition will stabilize on its own. But if the attacks become more frequent, you need to visit a doctor and undergo the recommended examinations with your child. Based on their answers, the specialist diagnoses a functional disorder of the digestive organ. For treatment, the child will be prescribed suitable choleretic medications:
- Holaflux;
- Flamin;
- Holagogum;
- Berberine et al.
From folk remedies, children are recommended to make herbal teas, the components of which have choleretic properties. Immortelle, mint or angelica should be taken in the amount of 1 tsp, pour 200 ml of boiling water and cover for 15 minutes. Give the child 4 rubles. per day before meals. Single dosage – ½ cup. Course – 10 days.
How else can you help your child? Nutritionists advise giving the patient cool lime and cranberry juices. For frequent episodes of bilious vomiting, tea with ginger and cinnamon is helpful. You should not feed your baby products with caffeine during therapy. It is also necessary to abstain from tomatoes and citrus fruits - they irritate the gastric mucosa.
Daily meals should be portioned, that is, the child should eat little and often. You can’t have dinner right before bed, drink black tea, soda, or coffee. It is important to eliminate spices from your diet. It is advisable to sleep on your side.
- If a teenager is poisoned by alcoholic drinks, in addition to gastric lavage, sorbents are recommended (the drugs will remove toxic substances), a sufficient number of hours of sleep and a short-term fasting diet.
- Do not give fatty broths to a child who is vomiting. The first course should be dietary. You can prepare it from young chicken.
- To prevent dehydration, give your baby a decoction of rose hips, mint leaves and dried chamomile flowers. Give non-carbonated mineral waters.
Do not try to treat your child on your own without consulting a doctor. If the baby vomits, but there is no temperature, this condition is still dangerous. With repeated episodes, it causes dehydration and loss of consciousness. In this case, you cannot stay at home - the child requires hospitalization.
What to feed your baby
Eating until vomiting completely disappears is not advisable, with the exception of infants, whom it is recommended to continue feeding. When the child develops an appetite, you need to start with rice or oatmeal porridge with water, crackers, and hard-boiled eggs.
Food and drink should be taken little by little, but often, so as not to overload the stomach . After the symptoms disappear, low-fat cottage cheese and dietary meat can be added to the diet; the transition to the usual menu should be carried out gradually. For the first time after illness, you will have to limit sweets, fatty foods, and carbonated water.
Symptoms such as vomiting and fever in a child are not always safe. Every parent should know what to do when they occur. With timely treatment of some diseases, complications can be avoided.
What a temperature condition may indicate
Yellow vomiting with elevated body temperature, accompanied by chills, pallor and stickiness of the skin, pain and cramping in the abdomen, and loose frequent stools indicates acute infections. Salmonellosis, escherichiosis, and dysentery disrupt the process of bile outflow and provoke its reflux into the stomach.
Viral hepatitis A is manifested by yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and yellowness of the skin, and the reflux of bile into the stomach.
The symptoms of intestinal disorders of an infectious nature are pronounced, making a diagnosis is not difficult.
What information is missing from the article?
- Methods for eliminating vomiting in children
- Doctors' opinion
- Medicine Reviews
- Traditional recipes for vomiting
What are some ways to relieve a child’s condition?
There are simple methods that need to be done first. First, the child is washed and given water at room temperature to rinse his mouth. During these manipulations, you need to calm the baby down. Then he is placed in bed on his side so that the chest is higher than the pelvis. Then they measure the temperature and ask about general well-being, clarify what else hurts, and also try to find a possible cause of vomiting.
If the baby continues to feel sick, you can give him up to 750 ml of boiled, cooled water to drink. A large amount of liquid will provoke repeated vomiting. Together with the released mass, the stomach will be cleansed, which will ease the general condition.
Signs that indicate bile in the stomach
Vomiting is always preceded by nausea. Small reflux of bile is accompanied by systematic belching. In infants, this condition affects overall physical development - stunted growth, poor weight gain, restless sleep.
Gagging is caused by sharp contractions of the diaphragm, and for children this is a painful process. The discomfort is intensified by a feeling of bitterness in the mouth, heartburn, and heaviness in the iliac region. Children constantly experience a feeling of thirst, general weakness and loss of strength. Physical activity decreases sharply. Periodically, the child vomits bile.
What does it look like?
The secretion of bile with vomit gives it a yellowish or greenish color. The contents of the stomach are thrown out through the mouth due to a sharp contraction of the muscles of the diaphragm, the stomach itself and the abdominal wall.
Before vomiting occurs, the child usually feels an attack of nausea, turns pale, and may experience chills. The more episodes of vomiting a child has, the more weakened he becomes and the higher the risk of developing dehydration.
Bend of the gallbladder
A substance called bile is concentrated in the gallbladder and is actively involved in digestion, and in particular in the breakdown of fats. Bile enters the duodenum through the common bile duct, where it performs its functions.
Often the cause of vomiting with a small amount of bile is a bend in the gallbladder. This pathology has become increasingly common in children aged 6-10 years in recent years. It is often asymptomatic, but if the bend completely blocks the bile ducts, the disease can be accompanied by acute pain, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting. If a set of such symptoms appears, you should immediately go to the hospital. The doctor will prescribe treatment and determine a diet. If a child has been diagnosed with a bent gallbladder, there is no need to panic.
As a rule, the child outgrows this pathology. The internal organs also grow and the gallbladder usually levels out. Diet is important to ensure that the gallbladder does not work with overload, does not produce more bile than it can dump into the intestines, and that stones do not form.
What is vomiting? The reasons for its occurrence
A healthy child will not vomit!
Vomiting occurs in the following cases:
- Poisoning.
- An inflammatory process in the stomach caused by infection.
- Diseases of the pancreas, liver, gastrointestinal tract.
- Increased intracranial pressure due to birth trauma.
Vomiting can occur in both adults and small children. She doesn't just appear. There are always reasons, and this is a serious cause for concern. Especially if the child is vomiting.