Bile is a digestive secretion produced by the liver and plays an important role in the digestion and absorption of fats. In certain situations, people vomit bile. This unpleasant symptom is not characteristic of any specific disease and may be present in the clinical picture of a number of pathologies of the digestive tract and other disorders.
The presence of bile in vomit may be a symptom of serious pathologies
How does vomiting with bile manifest?
Vomiting is a natural result of nausea.
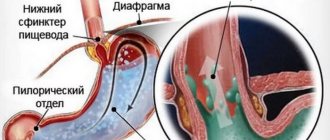
The exception is toxicosis during early pregnancy, when nausea comes on suddenly. Usually, the gag reflex significantly improves the patient's well-being. Vomiting bile is a little different. Liver secretions are detected in vomit if the patient vomits on an empty stomach. This is the result of a sharp contraction of the stomach muscles, which opens the sphincter into the duodenum. Often, vomiting with bile impurities appears after repeated emptying of the stomach, when there is nothing left to vomit. This happens after drinking alcohol.
If bile enters the stomach constantly, the gag reflex does not bring relief to the patient, but alleviates the condition until the next urge. Nausea does not completely disappear, since bile enzymes constantly irritate the gastric mucosa.
Bile gives vomit a specific yellow-green color. After the urge, the patient feels a persistent bitterness in the mouth. As a result of repeated vomiting, the plaque on the root of the tongue turns yellow-green. Associated symptoms include heartburn, in response to bile irritation of the esophageal mucosa, and unpleasant, foul-smelling belching.
Prevention
To avoid vomiting bile, you must follow these rules:
- Limit or eliminate the consumption of alcoholic beverages, which place increased stress on the liver and bile ducts;
- Do not lift heavy objects - a tear in the abdominal press can lead to a hernia and, as a consequence of this injury, to vomiting;
- If there are appropriate recommendations from a gastroenterologist, undergo regular colonoscopy;
- Quit tobacco products – smoking negatively affects the functioning of the digestive organs;
- Do not abuse fatty and smoked foods, dishes containing large amounts of spices, preservatives and dyes, carbonated drinks, sweets;
- Saturate your diet with vegetables, fruits, herbs;
- Do not eat raw meat and fish, avoid dirty or stale foods that can cause intestinal infections, be especially careful with freshwater fish, as they are often contaminated with intestinal parasites;
- Eat regularly, in moderate portions;
- Create a balanced menu to ensure that the body receives the required amount of fiber (to prevent diverticulitis), proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals;
- Treat any diseases of the digestive system in a timely manner.
Following these recommendations will help to significantly reduce the risk of illnesses, the symptom of which is vomiting with bile.
What to do if you vomit bile?
A single vomiting with bile impurities does not mean the development of pathology. More often this is a reaction to eating low-quality, stale or heavy foods. However, the symptom cannot be ignored. The patient should carefully listen to how he is feeling, drink more clean still water and temporarily limit food intake. Children should be fed as desired. This way the body will recover faster.
If you vomit bile several times, this is a reason to take urgent action. The patient should drink water frequently in small sips. Unpleasant sensations and nausea are eliminated by chamomile infusion or mint tea. They are drunk after cooling, in small portions. Rosehip decoction will also help. The drink will refresh, relieve attacks of nausea, and have a mild choleretic effect.
If vomiting does not stop throughout the day and is accompanied by other severe symptoms, you should consult a gastroenterologist. Signs of dangerous conditions:
- uncontrollable vomiting with bile;
- temperature increase;
- clouding of consciousness, dizziness;
- sharp cramps in the abdomen;
- signs of dehydration (dry and sagging skin, sunken eyes, lack of urination, dry mouth);
- icteric syndrome (yellowing of the sclera, mucous membranes, skin, hemorrhagic rash).
These symptoms may indicate serious poisoning, severe diseases of the internal organs, and the development of hepatic colic, which is fraught with painful shock. With such symptoms, the patient should not be left alone. It is necessary to take him to the hospital or call an ambulance.
In addition to sorbents, you should not take other medications before the doctor arrives - they can “blur” the clinical picture and complicate the correct diagnosis.
Vomiting with bile in children requires special attention. If the child vomits a second time, and there are bile impurities in the mass, you should urgently call a doctor at home or take the baby to the clinic. Vomiting for children is dangerous due to the rapid development of dehydration, which causes irreversible changes in the functions of internal organs.
First aid
First of all, you need to stop eating heavy food. At home, you should drink warm water and induce vomiting. To prevent the absorption of toxins, you can take activated carbon at the rate of 1 tablet per 10 kg of weight. Repeated vomiting causes dehydration, so the patient needs to drink in small sips (if you drink too quickly, drinking liquid can again provoke an attack of vomiting) still mineral water, Regidron solution or rosehip decoction.
Saline solution to prevent dehydration and relieve intoxication
If vomiting is accompanied by severe pain, especially girdle pain, you must call an ambulance. When the team arrives, it is imperative to inform health workers about the nature of the food taken the day before, the intake of alcohol, and the measures taken independently. Doctors will lavage the stomach with warm water to remove toxins acting on the mucous membrane, and then, according to indications, the patient will be hospitalized.
A person should not be without control from strangers. If the condition is critical, then loss of consciousness is possible, in which case there is a risk of asphyxia with vomit. You need to take a position on your side.
How to recover from vomiting
Nausea and vomiting debilitate the body, causing fluid loss and electrolyte imbalance. After the symptoms disappear, it is necessary to provide conditions for restoring the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
After vomiting, it is better to drink only liquids. The drinking regime is observed for 6 hours. Then they gradually begin to eat food. It should not irritate the gastrointestinal tract, stimulate gas formation and peristalsis. After vomiting, alcoholic and carbonated drinks, fatty, salty, sour, hard foods, fast food, and sweets are prohibited.
The patient should eat small meals up to 6 times a day for the next 3 days. The diet should contain:
- porridge in water with a small amount of butter;
- boiled vegetable soups without frying;
- low-fat mashed potatoes;
- egg white omelet;
- ground dishes made from boiled meat or products made from lean minced meat, steamed.
You can use berry jelly and bananas as enveloping foods. It is better to hold off on fruits and raw vegetables. Regular bread should be eaten dry.
Bowel obstruction
Intestinal obstruction (intestinal obstruction) can prevent food from passing into the small intestine and lead to vomiting of greenish-yellow bile. Bowel obstructions can be caused by constipation, hernia, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn's disease, or a tumor. In addition to vomiting bile, intestinal obstruction can cause bloating, abdominal pain, constipation, or diarrhea.
What to do
See your doctor immediately if you have a bowel obstruction because the problem can cause a number of complications. In most cases, intestinal obstruction is treated in a hospital setting.
If vomiting stops but symptoms remain
There is a type of vomiting that does not bring relief. This is not uncommon in the case of biliary vomitus. She talks about the development of diseases:
- stomach;
- duodenum;
- pancreas;
- liver.
Treatment of the provoking disease will allow you to completely eliminate the symptoms. It is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based only on vomiting and symptoms. A comprehensive examination by a specialized doctor will be required.
Laboratory tests of blood and urine, hardware diagnostic procedures (ultrasound, MRI, X-ray examinations of the abdominal cavity) help to assess the condition of organs. Based on the confirmed diagnosis, treatment for the underlying problem is selected. After therapy, signs of nausea should completely disappear.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis always begins with a visual examination with mandatory palpation of the abdomen. Then the specialist interviews the patient to collect data about the disease. There are questions about the nature of the ailments, pain, fever and other associated symptoms, as well as about lifestyle and nutrition. The doctor finds out whether the patient has taken any medications or alcoholic beverages.
Further diagnostic measures include:
- general blood analysis;
- blood test for biochemistry;
- general urine analysis;
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- X-ray, MRI or computed tomography of the digestive system.
If necessary, the doctor can prescribe additional tests in order to make the most objective diagnosis and select an appropriate treatment regimen.
What is the problem?
Vomiting, including with impurities of bile, often accompanies food and drug poisoning, alcohol intoxication, infection with viruses or pathogenic bacteria. The final diagnosis will be established on the basis of anamnesis, patient complaints, examination of urine, blood, and feces. Therapy consists of gastric lavage, prescribing sorbents, symptomatic drugs, antidotes (for poisoning), antibacterial or antiviral agents.
If vomiting with bile occurs in a pregnant woman, it is often said to be due to toxicosis. Drug treatment is not prescribed if a woman vomits less than 5 times a day and the general condition of her body is satisfactory. Antiemetic and detoxification drugs will be required for debilitating vomiting, when there is a risk of dehydration and exhaustion of the body. In case of severe toxicosis, temporary hospitalization is possible.
Liver diseases
Vomiting with the release of bile can accompany a number of liver pathologies. It often occurs in people who have undergone cholecystectomy. In them, bile enters the duodenum in a larger volume and, when the sphincter is weak, enters the stomach. The result of its irritating effect is strong vomiting. The risk increases if the patient neglects the doctor's dietary recommendations.
Vomit with bile is a symptom of inflammation of the gallbladder (cholecystitis), cholelithiasis, and the release of stones into the duct. In this case, surgery to remove the gallbladder is often prescribed. Pain in the right hypochondrium that accompanies vomiting, severe cramps, and darkening of the color of urine may indicate liver damage.
Repeated vomiting is possible with cancer. After the stomach is completely emptied, bile appears in the vomit. Such conditions are observed in progressive malignant diseases in the later stages of development. Vomiting is controlled with special medications. The symptom also occurs during radiation and chemotherapy.
Diseases of the upper gastrointestinal tract
Vomiting with bile often accompanies exacerbation of gastritis, when digestion of food is difficult, and bile continues to be secreted reflexively. The most commonly diagnosed cause is ulceration of the gastric mucosa. With the development of a peptic ulcer, the bile in the vomit is replaced by dark brown impurities, which signals gastric bleeding.
Repeated vomiting occurs with psychosomatic and neurological disorders. Sometimes it accompanies stressful conditions and psycho-emotional shocks. The symptom is treated with special drugs that normalize the transmission of nerve impulses in the brain, sedatives and neuropletics.
The release of bile during vomiting is observed during inflammation and ulcer of the duodenum, when its peristalsis is disrupted. Frequent vomiting with copious secretion of bile indicates small intestinal obstruction. Food cannot move along its natural path, and therefore the body sends a signal to remove it through the mouth.
Pancreatic diseases
Vomiting with bile inclusions almost always accompanies pancreatitis. Inflammation leads to nausea, bloating, and bowel dysfunction. If food enters the duodenum that the pancreas cannot digest, a gag reflex occurs. The bolus of food comes out along with bile and pancreatic juice.
A single appearance of bile in the vomit indicates complete emptying of the stomach. If the secretion of bile during vomiting continues, this is a symptom of severe intoxication or a serious illness. Treatment of vomiting is best done under medical supervision. This reduces the risk of complications.
Survey
When a patient complains of vomiting bile, a set of laboratory and instrumental methods is required to assess the condition of the gastrointestinal tract. An examination prescribed by a gastroenterologist is aimed at determining the pathological condition that caused the release of bile-colored vomit. The most valuable diagnostic methods are:
- Endoscopic examination
. FGDS is used to visualize the esophagus, stomach, and upper parts of the duodenum. The method effectively detects inflammatory changes in organs, ulcerative-destructive processes and dysfunction of muscle sphincters. Additionally, a biopsy of pathologically altered tissue areas is performed for histological analysis. - X-ray methods
. Taking X-rays of the gastrointestinal tract with oral contrast is aimed at studying the structure of all parts of the digestive tract, detecting nonspecific signs of inflammatory processes and peptic ulcers. For a detailed study of the hepatobiliary system, percutaneous or retrograde cholangiopancreatography is performed. - Duodenal sounding
. A study of the functional activity of the gallbladder with an assessment of the microscopic properties of bile is often decisive for making the correct diagnosis; it is carried out in all patients with vomiting with impurities of bile acids. If an infectious etiology of the disease is suspected, bacteriological culture is recommended. - Ultrasonography
. Survey ultrasound of the abdominal organs is used as a non-invasive express method that reveals signs of pathology in a specific part of the gastrointestinal tract. In case of biliary diseases, a targeted ultrasound of the gallbladder is performed to study its morphological features and detect possible stones in the lumen of the organ. - Stool analysis
. The appearance of bilious vomiting is often accompanied by various changes in the coprogram. By studying the macroscopic and microscopic properties of feces, the quality of food digestion is assessed, and signs of possible pathology of the biliary system are detected. If the patient has a general infectious syndrome, a bacterial culture of stool is performed.
Laboratory methods are used to clarify the diagnosis: an analysis is often prescribed to determine the content of free and bound bilirubin in the blood, determine the concentration of amylase and lipase, and search for specific antibodies. After excluding organic causes of the symptom, if the disorder is possibly functional, studies of the autonomic nervous system and the patient’s mental state can be carried out.
Ultrasound of the gallbladder
Too much alcohol
Many people, after heavy consumption of alcohol, experience a sharp increase in bile production. Too much alcohol can poison your body, which will try to get rid of it by vomiting. Interesting fact: the human body can only process 28 grams of pure alcohol per hour . Excess alcohol in a person's body irritates the stomach, leading to vomiting, as well as other classic symptoms of excessive drinking.
What to do
In reality, there is no way to speed up the elimination of alcohol from your body, so “two fingers in your mouth” to induce vomiting will not rid your body of alcohol any faster. Moreover, large amounts of alcohol is one of the situations where a person should never induce vomiting, which can cause severe dehydration.
The only way to avoid the consequences of excessive drinking is to drink less and responsibly. Excessive alcohol consumption is the most common cause of liver damage, so it is very important to be aware of the early signs of liver damage.
Treatment
Diseases of the stomach, liver, intestines, gall bladder and other internal organs are treated primarily with diet.
All fatty, fried foods, smoked foods, hot and spicy seasonings, canned food, sausages, heavy foods, alcohol, coffee and sparkling water are excluded from the diet.
Depending on the diagnosis, a therapeutic diet can be selected.
For gastritis or reflux disease, medications that reduce the acidity of gastric juice or antacids are prescribed .
It could be Rennie, Almagel.
antispasmodics (No-shpa, Spazmalgon), antiemetic medications (Motilium, Domrid), and antipyretics (Paracetamol, Ibuprofen) can be prescribed
How to remove? Smecta, Vikalin, Motoricum, and choleretic drugs help normalize the functioning of the stomach and intestines.
If an exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases occurs due to stress, sedatives are prescribed (Motherwort, Valerian).
For diseases of the liver and gall bladder, drugs from the group of hepatoprotectors (Carsil, Essentiale Forte, Gepabene) and enzymes are prescribed .
In advanced cases, surgical methods are resorted to.
Auxiliary methods of treatment for identified diagnoses are physiotherapy and therapy using traditional recipes .
It is imperative to give up bad habits, smoking and drinking alcohol to prevent the condition from worsening and the disease progressing.
In case of dental diseases, teeth are removed or treated is performed . The diet is also adjusted.
Gastroenteritis (stomach flu)
Gastroenteritis is often called stomach flu, although this “folk” term has nothing to do with the influenza virus. However, due to a bacterial or viral infection, the stomach becomes so inflamed and irritated that the symptoms of gastroenteritis resemble those of the flu. Gastroenteritis can cause diarrhea, vomiting of stomach contents and bile.
Stomach flu can be contracted from someone infected with rotavirus, norovirus, or through contaminated food. Additionally, bacteria such as E. coli and salmonella also cause vomiting and diarrhea. If the vomiting is constant and empties the entire contents of the stomach, the body will “supply” greenish-yellow vomit, which is your bile.
What to do
To stop vomiting bile due to gastroenteritis, use peppermint oil, which soothes the stomach and stops the gag reflex. Research has shown that peppermint oil can reduce the frequency and severity of vomiting. ( Bibliography: “Antiemetic Activity of Peppermint Oil” by Z Tayarani-Najaran, E Talasaz-Firoozi, R Nasiri, N Jalali, ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3562057/).