Govorushka is a genus of edible cap mushrooms from the Ryadovkov family and the Agarikov order. Sometimes it is also called clitocybe or nail plate. Forms a symbiotic association with pines and oaks. It grows in mixed forests with a temperate climate, mainly in Russia, Austria, Canada, Hungary, Belgium, Ukraine and the Czech Republic. The color of talkers varies from white to light brown. The diameter of the mushroom cap reaches 4-6 cm, it is dry and concave in the center. The pulp has a dense consistency and a spicy-sweet taste. Characterized by a pineapple aroma. The legs are thin and cylindrical in shape. The spore powder has a creamy tint. The talker is found from the beginning of May to the end of July. There are about 250 varieties. The mushroom is often used in cooking and in skin care products.
How does mushroom poisoning occur?
Biologists have described over 3,000 species of various fungi. Of these, only 400 species are edible; all the rest pose a serious health hazard. Several species are permanently poisonous, and all the rest become poisonous when consumed raw or with improper preparation technology and therefore are called conditionally edible.
The most severe poisonings can be caused by pale, white and spring toadstools. If you accidentally eat just one quarter of their cap, severe poisoning occurs that can lead to the death of an adult. Toadstools are dangerous in any form, since the poison amanitin they contain does not lose its toxicity either when dried or when exposed to high temperatures.
Muscarine, which is contained in fly agarics and whitish talker, is also very dangerous for humans.
In addition to the above, severe poisoning is caused by the following types of fungi:
- stinky mushroom;
- pig;
- false honey mushrooms;
- parterre mushroom;
- satanic mushroom.
Incorrect cooking technology can cause poisoning from mushrooms, morels, strings and milk mushrooms.
Useful properties of talkers
Edible types of talkers are used to prepare soups, sauces, and are also consumed fried or stewed. The smoky govorushka can even be salted or dried. The fruiting bodies of mushrooms of this genus are used as low-calorie products, without which almost no professional diet is unthinkable.
- The caps of young edible talkers contain B vitamins, as well as macro- and microelements, being real storehouses of copper, zinc and manganese.
- The pulp of the talker helps remove accumulated toxins from the body.
- The optimal ratio of plant proteins, vitamins, fiber, amino acids and minerals helps reduce the risk of various diseases. Talker mushrooms reduce the content of cholesterol plaques in blood vessels; eating them has a beneficial effect on the condition of the digestive system.
- In addition, the antibacterial properties of talkers are used in folk and official medicine. Decoctions of talkers are used to relieve tuberculosis manifestations, and the substance they contain, clitocybin, is included in drugs for the treatment of epilepsy.
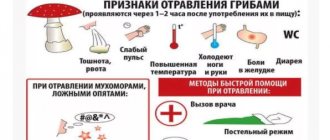
Symptoms of mushroom poisoning
The first signs of mushroom poisoning usually appear several hours after eating them. The duration of the latent period depends on the type of poisonous mushrooms, their quantity, age, body weight, alcohol consumption and other reasons. For example, in case of poisoning with toadstool, the incubation period can last up to 6-7 hours, and when eating lepiot or cobweb, it extends to several weeks.
When poisoning with mushrooms, regardless of their type, some general symptoms are observed that are similar to those of other foodborne diseases. These include:
- cramping abdominal pain;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea.
In addition, there are signs characteristic of mushroom poisoning.
In case of poisoning with toadstool, diarrhea and vomiting are profuse, they can occur up to 30 times per day. Due to disturbances in the hemostatic system, blood is often present in the stool, and vomit takes on the appearance of coffee grounds. Victims experience convulsions and increased cardiovascular and respiratory failure. The functions of the kidneys and liver suffer, up to the development of renal and liver failure, which is the cause of a coma, and subsequently the death of patients.
In addition to the general symptoms, poisoning with talkers and fly agarics is characterized by the following signs:
- lacrimation;
- increased salivation;
- constriction of the pupils;
- increased sweating;
- bronchospasm accompanied by shortness of breath;
- bradycardia;
- hypotension;
- convulsions;
- delusions and hallucinations;
- coma.
In case of panther fly agaric poisoning: dilated pupils, tachycardia, dry skin and mucous membranes.
Poisoning with morels and strings is characterized by the presence of convulsive syndrome, the development of toxic hepatitis, and damage to the spleen and kidneys. In the blood of patients, the membranes of red blood cells are destroyed (hemolysis), as a result, the urine becomes red.
Symptoms of mushroom poisoning in children are more pronounced, since the children's body is more sensitive to the effects of toxins.
Taxonomy
In the literature, two species were often distinguished - Clitocybe rivulosa
with a pinkish cap and plates and a short stalk and
Clitocybe dealbata
with a grayish color and a longer stalk. These factors turned out to be insufficient for separation; the color of hygrophanic talkers significantly depends on the degree of wetting. Molecular genetic studies also concluded that there is one polymorphic species.
Synonyms
- Agaricus dealbatus Sowerby, 1799, nom. dub.
- Agaricus dealbatus var. agrestis Pers., 1828
- Agaricus rivulosus Pers., 1801basionym
- Agaricus rivulosus var. neptuneus Berk. & Broome, 1883
- Clitocybe dealbata (Sowerby) P.Kumm., 1871, sensu auct., nom. dub.
- Clitocybe dealbata subsp. sudorifica (Peck) HEBigelow, 1982
- Clitocybe dealbata var. minor Cooke, 1883
- Clitocybe dealbata var. rivulosa (Pers.) P.Kumm., 1871
- Clitocybe dealbata var. sudorifica Peck, 1911
- Clitocybe rivulosa var. gracilis Métrod, 1939
- Clitocybe rivulosa var. neptunea (Berk. & Broome) Massee, 1893
- Clitocybe sudorifica (Peck) Peck, 1912
- Omphalia dealbata (Sowerby) Quél., 1886, nom. dub.
- Omphalia rivulosa (Pers.) Quél., 1886
First aid for poisoning
The appearance of signs of mushroom poisoning is the basis for immediately providing first aid to the poisoned person.
- Rinse the stomach thoroughly. To do this, the patient should be given at least one liter of water to drink, and then, by pressing on the root of the tongue, induce vomiting. Repeat this procedure several times until the rinsing water is clear. This will help to cleanse the stomach as completely as possible of mushroom toxins that have entered it.
- If mushroom poisoning occurs without diarrhea, then the victim should be given 1 tablespoon of castor or vaseline oil.
- To bind toxic substances that have already entered the small intestine, you must take any sorbent, for example Polysorb MP, Smecta or Activated Carbon.
- Place the patient in bed, wrap him warmly, and apply a heating pad to his feet.
- Provide plenty of fluids. You can give strong black tea, mineral or regular water without gas.
When is medical attention required?
In case of any mushroom poisoning, self-medication is unacceptable. If you feel even a slight discomfort after eating mushrooms, you must urgently call an ambulance or take the victim to the hospital on your own.
Treatment of mushroom poisoning is carried out in toxicology departments. It includes:
- gastric lavage through a thick tube;
- prescribing a saline laxative;
- carrying out forced diuresis.
In case of poisoning with talkers and fly agarics, the patient is injected with atropine, which is an antidote to muscarine. The dosage of this drug and the frequency of its administration are determined by the doctor.
If necessary, hemosorption is performed using a carbon column.
In addition, therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating damage to the liver, kidneys, nervous and other systems.
Possible consequences
The consequences of mushroom poisoning, especially if the patient does not see a doctor in time, can be very serious. Thus, mortality from poisoning with toadstool occurs in 50-90% of cases. Delayed medical care for fly agaric poisoning causes the death of every second poisoned person.
Severe mushroom poisoning can cause chronic liver or kidney failure, which requires transplantation of these organs.
Mushroom poisoning in pregnant women is dangerous, since toxins from inedible mushrooms can penetrate the uteroplacental barrier and cause damage to the fetus and contribute to spontaneous miscarriage or premature birth.
Prevention
To prevent mushroom poisoning, it is important to follow the following rules:
- You should collect only those mushrooms that are familiar to you;
- do not eat wormy or overripe mushrooms;
- do not taste raw mushrooms;
- collect mushrooms only in the basket;
- do not collect mushrooms growing along roads, near large industrial enterprises, or in the protected zone of radiation facilities;
- cook mushrooms as quickly as possible after picking; long-term storage is unacceptable;
- when preparing mushrooms, they should first be boiled once and the resulting broth should be drained;
- do not prepare any types of canned mushrooms at home;
- When in the forest, do not leave children unattended.
Video from YouTube on the topic of the article:
Education: graduated from the Tashkent State Medical Institute with a degree in general medicine in 1991. Repeatedly took advanced training courses.
Work experience: anesthesiologist-resuscitator at a city maternity complex, resuscitator at the hemodialysis department.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
Research shows that women who drink several glasses of beer or wine per week have an increased risk of developing breast cancer.
Many drugs were initially marketed as medicines. Heroin, for example, was originally brought to market as a cure for children's coughs. And cocaine was recommended by doctors as an anesthesia and as a means of increasing endurance.
Human bones are four times stronger than concrete.
People who eat breakfast regularly are much less likely to be obese.
Our kidneys are capable of purifying three liters of blood in one minute.
It was previously believed that yawning enriches the body with oxygen. However, this opinion has been refuted. Scientists have proven that yawning cools the brain and improves its performance.
You are more likely to break your neck if you fall off a donkey than if you fall off a horse. Just don't try to refute this statement.
An educated person is less susceptible to brain diseases. Intellectual activity promotes the formation of additional tissue that compensates for the disease.
According to WHO research, talking on a mobile phone for half an hour every day increases the likelihood of developing a brain tumor by 40%.
The human stomach copes well with foreign objects without medical intervention. It is known that gastric juice can even dissolve coins.
The rarest disease is Kuru disease. Only members of the For tribe in New Guinea suffer from it. The patient dies of laughter. The disease is believed to be caused by eating human brains.
Most women are able to derive more pleasure from contemplating their beautiful body in the mirror than from sex. So, women, strive to be slim.
Dentists appeared relatively recently. Back in the 19th century, pulling out diseased teeth was the responsibility of an ordinary hairdresser.
Even if a person's heart does not beat, he can still live for a long period of time, as the Norwegian fisherman Jan Revsdal demonstrated to us. His “engine” stopped for 4 hours after a fisherman got lost and fell asleep in the snow.
The liver is the heaviest organ in our body. Its average weight is 1.5 kg.
Malignant tumor diseases of the female reproductive system include cervical cancer, breast cancer, ovarian cancer, endometrial cancer.
A mushroom picker, like a sapper, makes one mistake. Although this saying is somewhat exaggerated, there is still a great deal of truth in it. Poisonous mushrooms can cause severe poisoning and even death, which is why you need to know their photos and names.
Types of poisonous mushrooms
Mushrooms are divided into poisonous and conditionally edible. The latter contain substances that can be destroyed, for example, during prolonged heat treatment, after which they can be eaten.
A medium-sized forest mushroom, distinguished by a specific purple color, especially bright in young mushrooms. You can eat the violet row only after boiling for at least 20 minutes.
It is found in coniferous forests, as well as under birch trees, forming mycorrhizae with trees. Bittersweet has a specific bitter taste, which is why it got its name. In order to get rid of bitterness, the mushroom must be soaked for several hours before cooking.
A small mushroom growing in coniferous and small-leaved forests. Information about toxicity is contradictory - in many countries (USA, France) it is considered edible with the caveat that eating large quantities of mushrooms can cause food poisoning.
A large mushroom, the cap of which reaches 30 cm in diameter. Grows in moist deciduous forests. Eating aspen milk mushrooms is possible only after preliminary soaking.
It grows on the edges of coniferous and mixed forests, along paths. It is considered conditionally edible due to the content of the substance nebularin, which causes acute gastrointestinal upset. Use after boiling for at least 15 minutes.
It is most often found in coniferous forests, on rotten stumps. It has a specific bitter taste, which only intensifies during heat treatment.
It grows only in coniferous forests, preferring acidic and poor soils. The mushroom is inedible due to its very pungent taste.
A mushroom that was previously classified as conditionally edible, but after a series of fatal food poisonings, it was classified as deadly poisonous. In addition to the toxins it contains, which are not always destroyed when boiled, it accumulates radioactive isotopes.
The mushroom is found in coniferous and deciduous forests, on the edges. A characteristic feature is the presence of scales on the cap. Even in small quantities, tiger grass can cause severe poisoning. It is especially dangerous because it has a pleasant smell and is similar in appearance to edible rows.
Grows in deciduous forests. In its raw form it is very toxic - 1 g of mushroom consumed can lead to severe gastrointestinal upset.
It includes several varieties of honey mushrooms, which are very similar in appearance to the edible species - summer and autumn honey mushrooms, but differ from them in the absence of a ring on the stem.
A mushroom with a specific appearance - a bright red cap with white flakes. Contains toxic compounds that cause a psychotropic effect, as well as vomiting, nausea, decreased blood pressure, and suffocation.
It grows in coniferous and mixed forests; the time of active growth is autumn. According to some sources, the inverted talker is an inedible mushroom due to its poor taste; according to others, it is poisonous because it contains toxins.
A fairly large mushroom, the cap of which grows up to 25 cm in diameter. It grows in mixed forests, most often under oak and hornbeam. Entoloma causes food poisoning with disruption of the gastrointestinal tract and dizziness. Possible death.
The most poisonous mushroom in the world. Externally, the pale toadstool can be confused with some types of champignons and russula. It grows in deciduous forests with fertile soil, where it can be found very often. In case of poisoning, the first symptoms appear from 8 hours to 2 days after consumption. The poison contained in the mushroom is not destroyed during prolonged processing. In most cases, poisoning ends in death.
Characteristic features of talkers
Govorushki belong to the type of cap mushrooms and the family of row mushrooms. They also have some differences between themselves, which need to be studied in order to distinguish edible varieties from inedible ones. There are also poisonous species in the genus, so collecting this species is recommended only for experienced mushroom pickers.
Appearance and photo
All representatives have fruiting bodies of medium or small size. The average diameter of the cap is 3-7 cm. The cap is mostly light in color, sometimes grayish, and has a small depression in the center - it is funnel-shaped.
The cap is smooth and dry to the touch. The mushroom stem is thin and tall. On the back of the cap there are thin, white plates that extend to the upper part of the stem. The spore powder of the fungus is light, sometimes creamy.
Place of distribution
You can meet talkers most often in deciduous forests. This is where they form mycorrhizae with trees. Organisms grow in groups, often called a witch's circle. This phenomenon is accompanied by the growth of a large number of mushrooms in a circle, with an empty space in the center.
In addition to forests, this species can also be found in grassy areas, for example, in meadows or parks. In Russia, mushrooms are common in temperate climates, and can also be found in the forests of Siberia and the Primorsky Territory.
Collection rules
Experienced mushroom pickers recommend collecting talkers from mid-August to October. Their yield peaks in mid-September. Many varieties of talkers grow in groups, which makes collection much easier.
The place where talkers are collected depends on the characteristics of the variety, however, most of them grow in forests near trees, where a large number of fallen leaves or moss predominate.
What to do if you eat a poisonous mushroom
If you suspect mushroom poisoning, you must immediately call an ambulance or get to the nearest hospital yourself. In no case should you hope for the results of self-medication, even if your general well-being improves.
In case of mushroom poisoning, the following symptoms may be observed, which vary depending on the type of mushroom that caused them:
- disruption of the gastrointestinal tract - sharp abdominal pain, nausea with vomiting, diarrhea;
- disruption of the central nervous system - hallucinations or psychomotor agitation, anxiety, confusion;
- disruption of the cardiovascular system - low blood pressure, rapid pulse.
Symptoms can appear either half an hour after consumption or after a long time.
First aid for mushroom poisoning is to rid the body of the remaining harmful substances. Self-medication is unacceptable. As soon as you notice the first symptoms, call an ambulance immediately. Before the team arrives, it is necessary to rinse the stomach.
The poisoned person should be given a large amount of water or a weak saline solution to drink, and then vomiting should be induced by pressing on the root of the tongue. Carry out the procedure until the stomach is washed out of all food remnants, then give some sorbent and provide the patient with peace.
Like an adult, the child must be given plenty of fluids, a weak solution of potassium permanganate can be used, followed by inducing vomiting to remove toxins. After this, you can give activated carbon or another sorbent.
The dog needs to rinse the stomach with a solution of potassium permanganate, and then also induce vomiting. It is necessary to take the animal to the veterinary clinic as soon as possible.
The insidiousness of mushroom poisoning is that after the initial symptoms of malaise, there may be an improvement in well-being, and then it sharply worsens again. Also, in case of poisoning with certain types of mushrooms, treatment is effective only in the first 2 days after eating the mushrooms. Therefore, it is absolutely impossible to delay the provision of qualified medical care in these cases.
Poisoning with poisonous mushrooms is called sudorin syndrome in medicine; it is provoked by the toxin muscarine. Not all talkers are poisonous, among them are:
- edible mushrooms, such as goblet goblet, fragrant, anise,
- conditionally, or relatively edible - smoky, club-legged,
- poisonous - waxy gray, whitish, brindle, reddish.
Even an experienced mushroom picker can get confused in such a variety of mushrooms; poisonous talkers are difficult to distinguish from edible ones, since they look and smell very attractive.
In case of poisoning by talkers, competent first aid saves the patient’s life. If this is not provided in time, death is possible.
Mushroom diets
In order to go on a mushroom diet, in which the daily diet will consist of nutrients and talkers, you need to know in advance how to cook these mushrooms. The cooking method is simple. Fruit bodies must be cleaned of leaves, debris and other forest contaminants.
Then you need to rinse the mushrooms under running cold water. Pour the required amount of water into the pan so that it completely covers the nutritious talkers and add salt (1 teaspoon per 1 liter). When the water boils, set aside for 25-30 minutes and cook over medium heat. After such processing and preparation, the mushroom can be used in any diet.
Losing excess weight with the help of a mushroom diet is simple; this is possible due to the low calorie content of talkers and their ability not to linger in the stomach. This food prevents fat deposits in the body. Nutritionists prescribe mushroom diets if there are no diseases of the kidneys, intestines, stomach or liver. This is due to the fact that the pulp contains a substance called chitin, which is difficult to digest. Therefore, it is best to consult with a specialist before testing a new diet.
A mushroom diet with vegetables will help you get rid of extra pounds in a short period of time. You need to eat 400 grams of talkers per day and the same amount of any vegetables. You need to eat mushrooms in three doses. You are allowed to drink mineral water, juices, green tea and a glass of rye kvass. For a variety of tastes, you are allowed to enjoy one or two teaspoons of honey. The results of the diet will be noticeable after one and a half to two weeks.
A mushroom diet, in which mushrooms completely replace meat and become the main ingredient of dishes.
Daily diet
Breakfast: 200 grams of mushroom salad and 100 grams of stewed vegetables, 200 milliliters of green tea.
Snack: salad of 1 kiwi with an apple and 1 teaspoon of honey, 200 milliliters of vegetable juice.
Muscarine is a dangerous toxin
Poisonous talker mushrooms seem to specially lure people, because some of them, for example, whitish and waxy, have a pleasant, mealy smell.
At a young age, it is almost impossible to distinguish an edible mushroom from a poisonous one; they all have a white, slightly grayish color.
Here's what happens when muscarine enters the human body:
- muscarine acts on M-receptors, causing them to be excited,
- the brain recognizes this as commands and transmits impulses to smooth muscles,
- the latter begin to actively, uncontrollably contract and/or relax.
This malfunction of smooth muscles can lead to death, because they line many of our organs: intestines, heart, pancreas and other glands.
Unlike the fly agaric, the talker does not contain hallucinogens, but it contains much more muscarine. Therefore, poisoning by this type of rowing is much more dangerous than from fly agaric. During heat treatment, muscarine does not decompose, so neither boiling nor boiling can get rid of it.
Where do talker mushrooms grow?
The growing area of talkers is very extensive and includes all countries of the Northern Hemisphere with a temperate climate. Talker mushrooms grow among meadows, fields and park areas. The genus forms stable mycorrhizae with deciduous or coniferous trees in forests of the European part of Russia, France, Italy, Portugal, Poland, Germany, Denmark, Belarus, Spain and other European countries. Found in Western and Eastern Asia. Populations of talkers have been recorded in Turkey, China, and the Primorsky Territory. Some species grow throughout the North American continent.
How does talkative poisoning manifest itself?
When a person has eaten a poisonous talker, symptoms can appear literally immediately - after 15-30 minutes; sometimes later, but this happens extremely rarely.
- abdominal pain due to cramps,
- nausea, vomiting, diarrhea,
- heavy sweating,
- intense salivation and mucus from the nose,
- lowering blood pressure,
- disturbance of the heart, expressed in a decrease in the frequency of contractions - less than 60 beats per minute,
- confusion, euphoria, aggression,
- difficulty breathing, asthmatic attacks,
- visual impairment.
- frequent urination,
- heat,
- muscle tremors, cramps.
Among all these signs, the most characteristic is the so-called narrow pupil, or spasm of accommodation. It looks just as it is written - the patient’s pupil becomes smaller than a match head, vision is impaired, and false myopia appears.
The second most common and striking symptom is confusion and unreasonable fear. The person does not understand where he is, does not recognize others, behaves aggressively towards them or falls into euphoria. Moreover, these two states can alternately change each other.
Two to three hours after poisoning, the symptoms may lose their brightness and a false impression is created that everything will go away on its own. This is dangerous, since severe breathing problems may subsequently occur and the patient dies. This violation is accompanied by:
- Wheezing in the lungs, whistling when inhaling/exhaling. Such manifestations are provoked by spasm of the smooth muscles of the bronchi, as well as strong secretion of bronchial mucus.
- Then there is severe shortness of breath and cyanosis (lips and skin turn blue).
- Impaired breathing causes oxygen starvation, subsequently hypercapnia, or an increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide in the blood, appears, and death occurs.
Talker poisoning does not have a direct effect on the nervous system. Unreasonable fear, anxiety, and aggression manifest themselves against the background of the patient’s general condition. Having noticed the first signs of poisoning, you should immediately call an ambulance.
What to do first in case of poisoning
So, the first step in case of talker poisoning is to call an ambulance. Next you can take the following actions:
- If you have a medicine in your medicine cabinet that belongs to the group of M-anticholinergics, give the victim an injection. It is an antidote to muscarine, and this will stop the development of poisoning.
- When there is no such medicine, make sure that the patient is in a horizontal position, lying down.
- You cannot prevent vomiting or diarrhea by giving any medications for this. In these ways, the body is cleansed of toxins.
- You can induce vomiting yourself by placing two fingers down your throat. However, you should not drink liquid for this purpose, as it will promote better absorption of the poison by the walls of the stomach and intestines. For the same reason, you should not do an enema.
- Give the patient some kind of sorbent, for example, activated carbon.
When the victim is unconscious, place him on his side. This way he will not choke on vomit that may enter the respiratory tract. If there are convulsions, hold the patient so that he does not hit nearby objects.
How to treat poisoning with talkers
Right in the ambulance, the poisoned person is injected with an M-anticholinergic blocker, which removes irritation from the M-receptors. In the hospital, the patient is prescribed a course aimed at removing muscarine from the body and supporting the functioning of the bronchi, lungs and heart.
To remove muscarine do the following:
- wash out the stomach
- an enema or castor oil is prescribed,
- in case of confusion, infusion therapy is carried out, after which medications are prescribed that remove excess fluid from the body, along with which muscarine also comes out.
To maintain heart function, medications are prescribed that contain caffeine and camphor. And to help the lungs, they give oxygen to breathe; in some situations, tracheal intubation is required (insertion of a special tube to ensure patency of the airways).
It is also necessary to help the gastrointestinal tract recover, so corrective therapy is carried out. Drugs are prescribed individually, depending on the severity of the patient’s condition.
Particularly severe cases of talker poisoning are observed in children and people under the influence of alcohol. However, with timely assistance, the prognosis is always favorable. If everything is done correctly, then on the third or fourth day the victim’s condition improves so much that he can be discharged from the hospital.
Application in medicine
Funnels are widely used in the medical field. Based on talkers, various medical preparations are made - extracts, creams, ointments, powders, which make it possible to treat various skin diseases and fight epileptic manifestations.
- They have a pronounced analgesic, antibacterial and wound-healing effect, which allows the use of mushroom-based medicines:
- for the treatment and prevention of tuberculosis;
- removing stones from the kidneys and bladder;
- treatment of respiratory tract infections;
- reducing the level of “bad” cholesterol;
- cleaning and strengthening blood vessels;
- restoring normal functioning of the digestive tract.
What to do to avoid getting poisoned
- Having trouble identifying a mushroom? Give it up!
- Be sure to review the collected mushrooms again.
- Do not buy canned mushrooms from unfamiliar sellers.
- Don't feed your children mushrooms.
- Do not mix the consumption of mushrooms and alcohol.
Govorushki are mushrooms that belong to the family Tricholomataceae.
Representatives of this family number more than 2.5 thousand species - about 1/3 of all agaric mushrooms. Of these, about 250 are talkers. Among them there are edible and poisonous, which are difficult for an inexperienced mushroom picker to distinguish.
Poisoning by poisonous species of talkers has a similar clinical picture to intoxication caused by consumption of fly agaric mushrooms.
Literature
- Kuyper, T. W.
Flora Agaricina Neerlandica. - Rotterdam, 1995. - Vol. 3. - P. 48. - 183 p. — ISBN 9-054-10616-6. - World of Plants: in 7 volumes / Ed. Academician A.L. Takhtadzhyan. T. 2. Slime molds. Mushrooms - 2nd ed., revised. - M.: Education, 1991. - 475 pp. (p. 269).
- Aurel Dermek. Mushrooms. - Bratislava: Slovart, 1989. - p. 74.
- "Mushrooms". Directory. / lane from Italian F. Dvin - Moscow: AST. Astrel, 2004. - 303 s (p. 82)
- Lesso, Thomas. Mushrooms. Determinant. / lane from English - Moscow: AST, 2007. - 304 pp. (p. 34)
- Serzhanina G.I.
Hat mushrooms of Belarus. - Mn.: Science and Technology, 1984.
Brief description of the species
The talkers have small caps (Æ3-6 cm), convex in young mushrooms and funnel-shaped in old ones.
The color varies from light white, beige, gray to brownish. The stem of the mushroom is cone-shaped, tapering downwards. The exception is the club-shaped talker.
The plates at the bottom of the cap darken when pressed. Many species have a distinct odor and specific taste, due to which mushrooms are classified in the 4th taste category. Poisonous species include the following types of talkers:
- brown-yellow (synonyms - golden row, water-spotted, brown-yellow);
- waxy (leaf-loving talker, waxy, grayish);
- leafy;
- inverted (red-brown talker);
- pale-colored (gray talker);
- whitish (whitened talker, reddish, grooved, discolored).
Toxic properties are due to a toxic substance - muscarine. In bleached govorushka, for example, its amount exceeds the muscaine contained in fly agarics. Talkers are used not only in the preparation of various dishes, but also in folk medicine as part of ointments, decoctions for the treatment of diseases of the respiratory system, kidneys and rapid scarring of wounds.
Talkers: benefits and harms
This type of mushroom has many beneficial properties because it combines plant and animal protein. Fiber, vitamins, active minerals, amino acids - this is an incomplete list of what mushrooms are rich in. Properly prepared fruiting bodies will have a positive effect on the functioning of the digestive system, strengthen the immune system, and reduce the likelihood of malignant formations and tumors.
You can cleanse and renew the entire body (remove toxins, heavy metal salts) with the help of Clitocybe. For vegetarians, these mushrooms are an indispensable product of the diet, because in terms of the total amount of nutrients and beneficial substances they are in no way inferior to meat products.
Some doctors and practitioners of traditional medicine use the pulp, stems and caps of edible fruiting bodies to treat diseases. Ointments and decoctions of clitocybe heal and disinfect wounds. Mushrooms are used to treat respiratory tract and bladder diseases.
Govorushka is a low-calorie product, the energy value of which is only 30 kilocalories (per hundred grams).
Composition of the talker: ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates
| Compound | Grams |
| Squirrels | 3,7 |
| Fats | 1,7 |
| Carbohydrates | 1,1 |
Almost all types of mushrooms are low-calorie, for example, 100 grams of champignons contain 27 kilocalories, 100 grams of butter mushrooms contain 9 kilocalories, but 100 grams of dried porcini mushrooms contain as many as 152 kilocalories. Govorushki are not just a low-calorie product, but also a very useful product for the human body.
Varieties of talkers that are considered edible cannot harm, but if you try inedible fruiting bodies, you are likely to get food poisoning. You should also remember that mushrooms should not be collected near roads and polluted areas, because they absorb and accumulate toxins from the external environment.
Composition and mechanism of action of the poison
Poisonous mushrooms contain muscarine, muscazone and muscaridine - alkaloids that are found only in mushrooms. In the fly agaric, after which the alkaloid muscarine is named, its content does not exceed 0.0005-0.02%.
Muscarine selectively acts on receptors located on the membranes of synapses of nerve cells, which is why they are called M-receptors or acetylcholine muscarinic receptors, which are widely represented in all organs:
- in the brain;
- in the ciliary bodies of the iris;
- lacrimal and salivary glands;
- heart;
- gallbladder;
- stomach;
- large intestine;
- bladder.
Muscarinic receptors transmit the slow effects of acetylcholine - inhibitory and excitatory. The mechanism of action of the poison is similar to the action of atropine. Like other neurotoxic substances, muscarine blocks the binding of acetylcholine to receptors.
Acetylcholine is a mediator of nerve signal transmission in the presynaptic space, slows down the contraction of the myocardium and muscles that provide wave-like contractions of the intestines. The antagonists of muscarine are atropine and decamethonium.
Common Misconceptions
| Myth | Reality |
| a cut onion or a silver spoon will darken if the boiled mushrooms contain poisonous | Darkening is caused by certain enzymes, for example, tyrosinade, which are found in both edible and poisonous mushrooms. But toadstool does not change the color of silver cutlery. |
| Worms, snails, insects do not damage poisonous types of mushrooms | Many poisonous mushrooms, such as the satanic mushroom, are happily eaten by worms and slugs. But they avoid the fox. |
| Poisonous mushrooms all emit an unpleasant odor and have a bitter taste | Poisonous talkers smell pleasantly of fresh flour, and the pale toadstool has a pleasant smell. |
| Only overripe, old mushrooms are poisonous | Poisonous mushrooms have a toxic effect at all stages of development |
| The poison accumulates only in the skin of the mushrooms | In the toadstool, all parts of the mushroom are poisonous, even the spores. This is true for all types of poisonous mushrooms. |
If you focus on these signs when collecting talkers, then poisoning will be very likely.
Who can the poisonous Talker be confused with?
This mushroom has a close relative, Govorushka Bleached Clitocybe rivulosa - the same poisonous muscarine mushroom, which also cannot be collected. It is much more dangerous to confuse the Waxy Talker with edible mushrooms:
- Cherry Edible Clitopilus Prunulus - very similar in appearance to the poisonous talker, but has a characteristic smell of spoiled flour.
- Talker Bent Clitocybe Geotropa - similar, but twice as large, and has a pronounced tubercle on its cap.
- Saucer-shaped talker Clitocybe Catinus - has a matte surface of the cap and more descending plates.
Never, NEVER eat a mushroom unless you are 100% sure it is edible. It’s better to play it safe and lose a delicious mushroom dish than your health or life.
Like all creations of nature, Waxy Talker has its place in the cycle of life, but for the sake of one’s own safety, it is better for a person to avoid it.
Signs of poisoning by poisonous species
Poisoning with poisonous talkers has a local stimulating effect.
The manifestation of poisoning by poisonous species of talkers is characterized by muscarinic syndrome:
- increased secretion of saliva - hypersalivation;
- profuse sweating;
- facial redness;
- feeling of chills and cold sweat;
- violation of the sinus rhythm of the heart - bradycardia;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- dysfunction of the visual analyzer - false myopia;
- pinpoint pupils;
- intense intestinal peristalsis, accompanied by pain;
- urine separation is difficult, urine is dark, with an unpleasant odor;
- In lactating women, milk is intensively secreted from the mammary glands.
Severe poisoning is accompanied by:
- impaired blood supply to vital organs, a sharp decrease in blood pressure (collapse);
- depression of respiratory function;
- pulmonary edema;
- convulsions.
The first symptoms of poisoning appear 0.5-2 hours after consuming poisonous talkers.
As an antagonist of the slowing receptors of neuromuscular fibers, muscarine and other talker poisons stimulate strong muscle contraction.
For example, by acting on intestinal muscarinic receptors, poisons provoke such strong peristalsis that intestinal movements are visible even through the abdominal wall. Then all hollow organs are involved in the process.
Talker poisons do not have a direct effect on the brain, since muscarine cannot cross the blood-brain barrier.
Providing emergency first aid
If signs of mushroom poisoning appear, it is necessary to call an ambulance and, before its arrival, provide the patient with all possible assistance in cleansing the intestines of toxins:
- give the patient 500-1000 ml of warm water with a small amount of salt;
- irritating the root of the tongue, inducing vomiting;
- Continue washing until clean wash water appears;
- give the patient a laxative, cleansing the intestines;
- ensure binding and removal of toxins, and reduction of their absorption with the help of enterosorbents;
- when the heart rate decreases, give stimulating drinks - strong sweet tea, coffee. You can put mustard plasters;
- If you have difficulty breathing, provide a supply of fresh air.
If the symptoms indicate a severe degree of poisoning, the patient is hospitalized to provide care and monitor the condition in a hospital setting.