What you need to know about mushrooms
Poisoning by poisons of animal or plant origin ranks fourth in frequency of cases. Moreover, 85% of all poisonings are caused by a toxic component, which includes pale toadstool, false porcini mushroom or fly agaric.
Boletus, boletus and boletus are valuable food products, as they contain:
- useful microelements in the form of potassium, phosphorus, calcium, sulfur and magnesium;
- they are rich in vitamins A and B;
- the protein concentration exceeds its content in the egg;
- belongs to products with a low calorie content, due to the reduced concentration of carbohydrates and fats.
In addition, this product has a number of medicinal properties, which are manifested as follows:
- stimulate the production of gastric juice, which has a beneficial effect on the gastrointestinal tract;
- prevent the development of oncological processes;
- prevent the development of atherosclerotic plaques on the vascular walls;
- strengthen the immune status of the body.
You need to know that boletus poisoning is not the only danger that can arise from their consumption. Failure to comply with preservation technology can cause severe poisoning due to botulism in mushrooms. Botulinum toxin is produced by clostridia, which has the peculiarity of developing in the absence of air access.
Where and when do bitterlings grow?
The distribution area of gall mushrooms is quite wide, as well as its edible counterparts - boletus and boletus. They are found in the forests of Europe and Asia, North America. In Russia - in the Caucasus, Western and Eastern Siberia. Gorchak grows in the middle zone, in coniferous, mixed, deciduous forests, is unpretentious and forms mycorrhiza with many tree species.
As a rule, false whites grow singly or in pairs, but can unite in small colonies (5-10 pieces). They prefer sandy soils and can grow on rotten wood - stumps, trunks, especially in the dry season.
The fruiting period of the gall fungus varies depending on the region of growth:
- Fertility occurs throughout the forest zone in June-July (usually in the middle of the summer season), ending in September-October.
- Where autumn comes early, the lifespan of mushrooms decreases, but only slightly. After mid-October you won't see them anymore.
Causes of porcini mushroom poisoning
Many “quiet hunters” ask the same question: “Is it possible to get poisoned by porcini mushrooms?” Doctors have a clear opinion on this matter that this is not only possible, but such cases are not uncommon.
Factors that provoke food poisoning:
- harvesting is carried out in places subject to heavy pollution (near industrial enterprises, highways);
- when using false doubles;
- when the leg is poorly cleaned of soil residues, or in case of insufficient heat treatment;
- during cooking, a portion of edible mushrooms included toadstool, fly agaric, false chanterelles or honey mushrooms;
- improper storage conditions under which there was prolonged contact with insects;
- When preserving and cooking, containers that have visible traces of rust are used.
The question that arises is whether it is possible to eat porcini mushrooms raw or taste them when harvesting, has a clear answer that such actions are unacceptable. Poisoning resulting from them in forest conditions will create obstacles to the provision of emergency qualified care.
Representatives of the boletus family
The white mushroom owes its name to those times when the priority method of processing was drying, which facilitated easy digestion. Its flesh did not lose its attractive color, and no one had any idea whether it was possible to be poisoned by dried porcini mushrooms. In modern unfavorable environmental conditions, you need to be aware of the distinctive features of porcini mushrooms:
- the cap is convex, dome-shaped, has a color from milky to light brown, reaches a diameter of 30 centimeters or more;
- the leg, up to 25 centimeters high, is usually lighter than the cap, has a pear shape and is covered with a network of almost imperceptible veins;
- the pulp is juicy, fleshy, does not darken when cut;
- It has a pleasant mushroom aroma and spicy taste.
The beginning of the boletus collection season depends on the area in which they grow; they need a week to reach full maturity. In southern latitudes they grow from May to October, in northern latitudes - from June to September (harvest in August). The boletus genus is represented mainly by edible mushrooms:
- reticulated white has a brown cap and a short leg of the same color and ocher veins;
- copper (hornbeam) boletus is distinguished by a brown cylindrical leg and a dark bronze cap;
- birch (spike) - a very light (less often cream-colored) mushroom with a small cap diameter (about 15 centimeters) and a thick, low-growing stalk;
- pine (pine) is known for its large reddish-brown cap with a purple tint on a milky white stem, the flesh under the cap is light brown;
- oak mushroom is not as dense as other boletus mushrooms. Its cap is gray-brown and often has light spots;
- The spruce porcini mushroom has a chestnut color and a stem thickened downward.
Symptoms of porcini mushroom poisoning
Symptoms of porcini mushroom poisoning are accompanied by the development of the following conditions:
- development of progressive weakness and dizziness;
- nausea followed by repeated, unrelieved vomiting;
- frequent diarrhea that has a foul odor;
- excessive gas formation, flatulence;
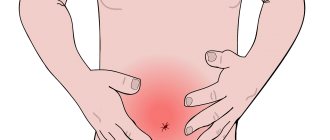
- pain in the lower abdomen is accompanied by intestinal colic;
- rapid breathing;
- drop in blood pressure.
Poisoning with false porcini mushrooms has some differences, since the toxins primarily affect the liver.
Therefore, the patient will experience discomfort from the following manifestations:
- acute pain arising under the rib on the right side;
- mucous membranes, sclera of the eyes and skin become jaundiced;
- the feeling of nausea is accompanied by a frequent gag reflex.
In severe cases, paralysis develops, hallucinations appear, and convulsive syndrome develops.
Necessary pre-medical measures
First aid for porcini mushroom poisoning - an algorithm of actions that must be performed before the arrival of the visiting medical team.
To alleviate the patient’s condition, it is necessary:
- Induce artificial vomiting. This will help clear the stomach of food debris, which will significantly reduce the concentration of toxins in the body. To properly rinse, the patient needs to drink 1 liter of water at room temperature. By placing two fingers in your mouth you need to trigger a gag reflex. It is recommended to repeat this procedure several times until the wash water is clear.
- Cleansing the intestines is done using an enema, to which you can add a decoction of chamomile or calendula inflorescences. The manipulation must be repeated until the wash water becomes clear.
- To neutralize the effects of toxins and pathogenic microorganisms, it is allowed to use a drug from the group of enterosorbents (Polysorb, Enterosgel, Sorbex, activated carbon).
- In order to prevent the clinical picture of dehydration and intoxication syndrome, the patient is recommended to maintain a drinking regime (in small portions). Plain water (still), unsweetened tea, and hydration solutions are suitable for this.
If loss of consciousness occurs, the person must be placed on a flat horizontal surface, with the head turned to the side.
Raise your legs up or bend your knees. Be sure to monitor your breathing and pulse. Pulse monitoring can be done in the area of the side of the neck or on the arm at the bend of the wrist joint. Breathing control is carried out by placing a hand on the surface of the chest. In its absence, it is necessary to begin performing indirect massage of the heart muscle.
It is very important to pay attention to the patient's consciousness. If he is unconscious, has convulsive manifestations or hallucinations, then gastric lavage is contraindicated.
Growing
Porcini mushroom, despite its unsurpassed taste, is not grown on an industrial scale - it is unprofitable. Usually, amateur gardeners are engaged in cultivation. There must be coniferous or deciduous trees on the personal plot. There should be no fruit trees, cultivated shrubs or vegetables nearby. The most difficult thing in growing boletus is creating conditions for the successful creation of connections between tree roots and mycelium.
It is desirable that the site is adjacent to the forest. If this is not possible, you need to have at least a few pine, aspen, birch, oak or spruce trees on your future “plantation.” Trees on the site must be at least 8 years old. There are two ways to grow porcini mushrooms – from mycelium and from caps.
Growing from mycelium
Cultivation begins with the purchase of planting material. You need to buy mycelium in specialized stores. Next, prepare the area and plant the mycelium:
- The soil is exposed near the trunks. The top layer is removed - approximately 20 cm. The diameter of the circle should be approximately 1-1.5 m. The removed soil is saved - it will be needed to cover the crops.
- A layer of peat is applied to the area prepared for planting. Rotted compost can be used. The fertile layer should not be thicker than 2-3 cm.
- Mycelium is placed on top. The interval between adjacent pieces is approximately 30 cm. The pieces are laid out in a checkerboard pattern.
- The mycelium is covered with previously removed soil. Water generously. You need to pour about 3 buckets of water under one tree. Pour carefully so that the soil does not erode.
- Next, mulch the watered soil with straw. The thickness of the layer is 30 cm. This is done to maintain the required humidity - so that the mycelium does not dry out. Crops need to be watered weekly. Be sure to add nutritious fertilizer to the water.
Before frost, areas with mushrooms are covered. For insulation you can use moss, spruce spruce branches, fallen leaves. With the arrival of spring, the insulation is raked using a rake.
A year will pass and the first fungi will be removed. If you properly care for the mycelium, water and feed it on time, the mushroom “plantation” will bear fruit for up to 5 years.
Growing from caps
To implement this method, you will need to get a few mushroom caps. Find mature, or better yet, overripe boletus mushrooms in the forest. The diameter of the cap should be at least 10 cm. It is best that when broken, the cap has a greenish tint - this indicates the maturity of the spores.
When collecting caps, you need to remember what trees the mushrooms grew under. It will be necessary to sow spores under the same trees. If a boletus is found under a spruce, it is unlikely that it will take root under a birch or aspen.
The procedure for preparing the site and planting seed:
- About a dozen caps are soaked in a bucket of water. It is advisable that the water be rainwater. Add one thing per 10 liters:
- alcohol – 3-5 tbsp. l.;
- or sugar – 15-20 g.
Mushrooms should be soaked no later than 10 hours after collection - otherwise they will spoil.
Tea is brewed in 1 liter of boiling water. The second option is to boil oak bark for 1 hour. Water the soil with the cooled solution - 3 liters for each tree.
Boletus mushrooms can reach a yield of up to 250 kg per 1 hectare. Under each tree, during the season, you can collect a bucket of porcini mushrooms.
All that remains is to take care of the crops - water them regularly, sparing no water. If the soil dries out, the mycelium will die before it has time to germinate. For the winter, the area is insulated with spruce branches or leaves. In the spring - they rake. The first mushrooms will appear next summer or autumn.
Growing indoors
You can grow boletus indoors:
- First, the premises are sterilized with a 1% chlorine solution - it kills mold and parasites.
- Creates warm and humid conditions. Place barrels of water or put wet sawdust.
- Prepare a substrate with mycelium. They put it in bags. They make cuts.
- The bags are placed at intervals of 5 cm.
- The temperature is maintained at +23-25 °C, no more. Excess will destroy mycelium.
Treatment of porcini mushroom poisoning
To maintain the functionality of vital organs, medical therapy begins upon the arrival of the ambulance team.
In this case use:
- drugs for drip administration, which replenish the volume of fluid in the body;
- medications are administered intramuscularly or intravenously to stabilize the heart rhythm and lung function;
- using a ventilator to provide oxygen;
- in case of clinical death, resuscitation measures are carried out.
In a hospital setting, therapy is carried out in three stages:
- Initially, the stomach is washed using a probe. The forced diuresis method involves the use of diuretics (Lasix). Ringer's solution or Sodium chloride is used to eliminate the collapsed state. To purify the blood, the hemosorption technique is used, passing it through sorbents.
- During the second stage, it stabilizes blood pressure by administering Mezaton or Norepinephrine. To prevent liver damage, glucocorticosteroids (Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone) are prescribed. Symptoms of heart failure are eliminated by the use of cardiac glycosides (Strophanthin or Korglikon).
- At the end of therapy, a strict diet is prescribed for two weeks, limiting fatty and fried foods. Any types of smoked meats, sausages, and dishes prepared with a large amount of spices and seasonings fall under a complete taboo. Strong tea, coffee and alcoholic drinks of any strength are also prohibited.
The patient is recommended to drink plenty of fluids, mashed mucous porridge and low-fat white meat chicken broth.
Prevention of porcini mushroom poisoning
To avoid porcini mushroom poisoning, you must adhere to the following rules and recommendations:
- When harvesting, collect only familiar mushrooms that do not have damage or visible wormholes;
- do not try to taste the raw mushroom;
- pay attention to the color of the cap and stem, checking it for the presence of a ring;
- Mushroom pickers should not visit contaminated areas near highways or places where industrial waste is stored;
- the harvested crop cannot be subjected to long-term storage without processing;
- it is necessary to adhere to the rules of preservation and storage of ready-made mushroom dishes;
- After contact with false doubles, you must wash your hands thoroughly;
- cooked mushroom dishes cannot be stored in containers made of aluminum, zinc or clay;
- The harvested crop should only be carried in a bucket or basket.
- Before preparing any dishes, be sure to use the method of thorough cooking, draining the first broth.
Mushroom poisoning requires placing the patient in a medical facility. Even if first aid caused an improvement in the patient’s condition, this does not mean that the effect of the poisons was completely neutralized.
Self-therapy and the use of traditional healing recipes can cause dangerous consequences not only for the health, but also for the life of the patient.
Use in cooking
In cooking, boletus mushrooms are used raw, frozen and dried, in the form of canned food and pickles. They are boiled, fried, stewed, baked. Reviews from porcini mushroom lovers on various forums indicate that it is preferable to use dried boletus mushrooms for preparing various mushroom dishes. The most popular dishes among them are porcini mushroom soup and mushroom sauce. It is in these dishes that they reveal themselves, showing all their taste and aromatic qualities.
Porcini mushroom soup
A handful of dried boletus mushrooms are soaked in milk for 30 minutes, washed thoroughly, then boiled for 15-20 minutes. Fry chopped onions and carrots in a frying pan, then add pre-cooked porcini mushrooms. After frying for 10 minutes, the contents of the frying pan along with the chopped potatoes are poured into the pan. Boil until the potatoes are ready. Served with herbs and sour cream.
Mushroom sauce
A handful of dried forest products is poured with water for 1.5 hours, after which the water is drained and the product is thoroughly washed. After this, add 1 liter of fresh water and cook for about an hour. Fry the onion in a frying pan until golden brown, add boiled boletus, and fry covered for about 15 minutes. Stirring with a whisk, add 3 tbsp. spoons of flour, then diluted with mushroom broth to the desired consistency. Add sour cream, herbs and spices to taste. This sauce goes well with pilaf, pasta dishes, buckwheat porridge, and meat.
There are a lot of recipes for boletus dishes in various forms - these include soups, pilaf, roasts, pates, and sauces. All these recipes share a unique aroma with nutty notes and a memorable rich mushroom taste.