Everyone knows that poisonous mushrooms are dangerous to humans and pose a threat to their health and life. But not everyone knows that the same effect can be expected from edible mushrooms. Today we will talk to you about oyster mushrooms.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms? This is a question to which there would seem to be an obvious negative answer. But this is another misconception.
Oyster mushroom is the queen among edible mushrooms. Oyster mushrooms are edible mushrooms that have a very pleasant taste and smell. They grow in groups and have a characteristic appearance, so it is almost impossible to confuse them with other mushrooms.
They don't even have poisonous "twin brothers." But, nevertheless, poisoning with oyster mushrooms does occur. What is their reason? We will tell you about this. And the photos and videos in this article will help you better understand the material you read.
What are oyster mushrooms?
Oyster mushrooms are widely consumed mushrooms with excellent taste. They are considered healthy dietary products because they are enriched with vitamins and beneficial microelements:
- calcium and potassium;
- iron and phosphorus;
- cobalt and copper;
- fructose and sucrose;
- types of amino acids;
- polysaccharides.
In terms of value, they can be compared with meat, seafood and vegetables . In addition to all this, oyster mushrooms have medicinal properties and are used as a therapeutic agent in the treatment of certain pathologies.
But you should know that not all varieties of these fungi are beneficial. There are 7 known wild varieties of oyster mushrooms, but only 5 of them belong to the edible group:
- the most useful is the oyster mushroom;
- Poisonous species include plated and oak oyster mushrooms, which have a fibrous and hard structure.
Causes of poisoning
Any mushrooms are heavy food for the human body; they are among the difficult to digest foods. Therefore, they are contraindicated for people suffering from chronic pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract or liver. Even edible mushrooms, including oyster mushrooms, can cause intoxication.
Let's consider why poisoning occurs with oyster mushrooms grown in artificial conditions or growing in the wild.
Causes of poisoning from artificially grown oyster mushrooms:
- Failure to comply with growing technologies. For example, over-treating mushrooms with pesticides to prevent pests from multiplying.
- Growing mushrooms in areas located next to a highway where many cars pass, or near industrial facilities. Under such conditions, oyster mushrooms absorb all toxic fumes and exhaust gases, becoming a harmful product with a high content of toxic substances.
- Violation of the rules for canning (pickling) oyster mushrooms. For example, insufficient heat treatment.
Causes of poisoning from wild oyster mushrooms:
- Mushroom picking in environmentally polluted areas.
- A poisonous mushroom that was accidentally picked ended up in a basket of edible oyster mushrooms. Even one small toxic mushroom can ruin a dish prepared with oyster mushrooms and cause intoxication.
The ability of mushrooms to absorb, like a sponge, and accumulate toxic compounds and heavy metals from everywhere (from soil, air, precipitation) leads to the fact that the most harmless mushrooms can become toxic and lead to poisoning.
Therefore, even oyster mushrooms grown in artificially created conditions can turn out to be dangerous if all the rules for organizing their production are not followed.
Properties of mushrooms
Oyster mushroom is an edible mushroom. Its large specimens reach 15 cm in diameter of the cap, which has a convex and round shape with curved edges. It is cultivated on an industrial scale and grows in deciduous forests.
The chemical composition of oyster mushrooms is a unique combination of substances necessary for the human body: vitamins, minerals and antioxidants. Nutritional value: 38 calories per 100 g of product.
Useful properties, including medicinal:
- antitumor effect;
- lowering blood cholesterol;
- strengthening the immune system;
- removal of toxins.
Oyster mushrooms can be considered an environmentally friendly product, but poisoning with them is still possible. More often this occurs in people who have contraindications to eating mushrooms:
- Children under 3 years old. Oyster mushrooms are rich in chitin, a substance difficult to digest in the gastrointestinal tract. The body of a small child cannot digest any mushrooms, which may result in signs of intoxication.
- People suffering from high acidity of gastric juice. Excessive consumption of oyster mushrooms negatively affects the health of such a patient.
- Persons with kidney disease. Mushrooms contain hydrocyanic acid and phosphorus - components that provoke intoxication and the development of problems with the urinary system.
Oyster mushrooms are not contraindicated for other people, but it is not recommended to abuse them.
Symptoms of poisoning
Signs of oyster mushroom poisoning may vary in different cases. What symptoms will appear depends on what led to the intoxication.
If poisoning occurs after eating improperly canned mushrooms, the victim will experience the following symptoms:
- a strong increase in body temperature (occurs sharply and suddenly);
- nausea and vomiting;
- loose stools;
- convulsions or disturbance of consciousness. Such signs may develop against the background of dehydration caused by repeated vomiting.
If intoxication occurs as a result of botulism caused by a violation of the technology for preparing and storing dishes with oyster mushrooms, the patient will experience the following symptoms:
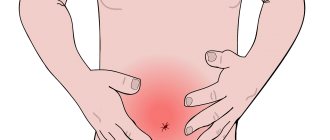
- the appearance of increasing abdominal pain, concentrated in the navel area;
- after half an hour, nausea and the urge to vomit are added to the pain syndrome;
- vision temporarily deteriorates, objects are seen blurry and indistinct;
- joint and muscle pain is observed;
- swallowing becomes painful.
In cases where poisoning has occurred with oyster mushrooms that grew in a polluted environmental environment and absorbed chemical fumes and exhaust gases, the following symptoms are observed:
- severe feeling of nausea or repeated vomiting;
- drowsiness;
- feeling of pressure or squeezing in the back of the head;
- headache.
How to provide first aid?
The purpose of emergency care is to cleanse the stomach and intestines of toxins and prevent them from spreading throughout the body. Therefore, it is important to provide it as early as possible.
Let's consider how and in what sequence it is recommended to provide first aid for oyster mushroom poisoning.
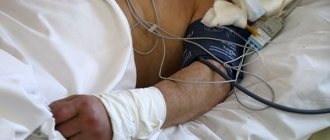
- It is necessary to perform a gastric lavage to cleanse it of residual fungi and toxins. The victim is given about 1-1.5 liters of liquid to drink (it is preferable to give slightly warm boiled water). After this, induce vomiting by gently pressing on the very root of the tongue. The procedure can be repeated 2-3 times until the liquid coming out of the stomach becomes clear.
- The victim is given absorbents - drugs that absorb toxins (poisons and waste) and remove them out. They are safe and are not absorbed into the bloodstream. You can take any sorbent from the medicine cabinet, for example: Activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel, Laktofiltrum.
- It is necessary to feed the patient, since repeated vomiting and the procedure of cleansing the stomach cause severe dehydration. But you need to drink in small portions, 1-2 tablespoons (tablespoon) every 10-15 minutes. Drinks such as plain water, Regidron, decoction of dried fruits, water with lemon juice and honey will be useful.
- If more than 2 hours have passed after eating spoiled mushrooms, you should perform an enema to cleanse the intestines. It is necessary to fill the bulb with warm boiled water, lubricate the end with Vaseline and introduce the contents into the small intestine.
- In cases where the victim has a fever, he should be given an antipyretic drug: Nurofen, Aspirin, Paracetamol, Ibufen.
Possible consequences
- If the intoxication turned out to be mild and the patient was given first aid correctly, negative consequences can be avoided. After 1-2 days, digestion will improve, weakness will recede and the functioning of the whole body will normalize;
- Poisoning caused by a poisonous mushroom found among the oyster mushrooms will be more severe. In advanced cases, jaundice or pancreatitis may develop;
- Poisoning from canned oyster mushrooms containing botulism toxin poses a particular danger. This can lead to problems with the kidneys, liver or heart.
Summarizing the above, we can say with confidence that even edible oyster mushrooms can be poisoned. But this condition can be avoided if you collect them in an ecologically clean forest area, adhere to all technologies for preparing dishes with mushrooms and eat only properly preserved oyster mushrooms. Collect and choose mushrooms correctly, this will help you avoid intoxication.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms?
Everyone knows that poisonous mushrooms are dangerous to humans and pose a threat to their health and life. But not everyone knows that the same effect can be expected from edible mushrooms. Today we will talk to you about oyster mushrooms.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms? This is a question to which there would seem to be an obvious negative answer. But this is another misconception.
Oyster mushroom - the queen among edible mushrooms
Oyster mushrooms are edible mushrooms with a very pleasant taste and smell. They grow in groups and have a characteristic appearance, so it is almost impossible to confuse them with other mushrooms.
Two strains in one room
Growing two strains in the same chamber that do not coincide in incubation/fruiting periods, with different optimum temperatures and humidity, can also lead to a change in the appearance of mushrooms of one of the strains.
The photo on the right shows two strains in one growth chamber. Strain K-17 (on the block on the left) develops quite well at a carbon dioxide concentration of 900 ppm. He has a dense, thick hat and strong small legs.
But for the K-15 strain, such a concentration is destructive: the oyster mushroom pulls the stem, the caps are light, thin, and fragile. it is designed for summer cultivation. In summer, work is carried out only in the fresh air, and it grows normally at a CO2 level of up to 600, maximum 700 ppm.
Causes of poisoning
There are 7 varieties of oyster mushrooms. The most common, tasty and healthy is oyster mushroom. It contains many nutrients and minerals.
Conditionally edible varieties include oak and covered oyster mushrooms. They are characterized by a rigid structure of the cap and stem, but their taste does not differ from edible ones. Poisoning by these types of oyster mushrooms is possible in case of insufficient heat treatment.
There are also wild and artificially grown oyster mushrooms. There is an opinion that mushrooms grown on so-called “mushroom farms” do not cause any harm to the human body. But this is far from true.
You can also be poisoned by oyster mushrooms grown in artificial conditions. The most common reason is non-compliance with technology, excessive and irrational use of pesticides and fertilizers.
Growing oyster mushrooms in artificial conditions
The likelihood of poisoning from wild oyster mushrooms is much higher. The cause of intoxication can be mushrooms collected along highways, near industrial enterprises, and garbage dumps.
Mushrooms accumulate salts of heavy metals, poisons and toxins, which are not completely destroyed during heat treatment. It is the breakdown products of harmful substances that cause gastrointestinal disorders.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of intoxication from poisoning with conditionally edible, wild and artificial oyster mushrooms will be the same. Manifestations are nonspecific; gastroenteritis comes first: nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea.
Sometimes there may be an increase in temperature. Gastrointestinal disorders can lead to dehydration, which will be manifested by dry skin, increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure, and dizziness.
In case of mushroom poisoning, symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders come to the fore
If the mushrooms were collected along the highway, then most likely their pulp contains a large amount of heavy metal salts. Then the above symptoms will be accompanied by more severe disorders - convulsions and breathing problems, a decrease in the amount of urine, which indicates a deterioration in kidney function.
Treatment of oyster mushroom poisoning
Oyster mushroom poisoning is not difficult to treat, and anyone without medical education can cope with it.
Basic principles of therapy:
- It is necessary to try to rinse the stomach . The easiest way is to rinse the stomach using the “restaurant method” - drink about 1000 ml of water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate and induce vomiting by pressing two fingers on the root of the tongue. Repeat this procedure until the rinses are clear. Do not be too zealous when lavaging the stomach, as repeated vomiting can lead to ruptures of the esophageal mucosa and bleeding.
- If possible, give the victim an enema . An alternative may be to take enterosorbents and laxatives - activated carbon, smecta, enterosgel, duphalac. These drugs prevent toxins from being absorbed into the blood. When using medications, you must follow the instructions.
- After washing the stomach and intestines, it is necessary to replenish the body’s water losses so as not to cause dehydration. The victim is given plenty of salted and sweetened water, rosehip decoction, dried fruit compote, or balanced pharmaceutical solutions (Regidron).
- Under no circumstances should the victim be given strengthening or antiemetic drugs ! This will only worsen the intoxication.
Symptoms of gastroenteritis usually resolve within 24-36 hours. If the victim's condition has not improved and continues to worsen, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Enterosgel removes toxins from the body Rosehip decoction is rich in vitamins and promotes better recovery after dehydration
Prevention
Preventive measures to avoid oyster mushroom poisoning are very simple:
- Do not collect mushrooms along highways, near factories, or in garbage dumps.
- Cook the mushrooms thoroughly. First, boil them for about two hours in salted water, and only then fry.
- Be careful when hunting mushrooms so as not to accidentally cut off a specimen that is unsuitable for food.
- Do not buy mushrooms from hand, especially dried ones. It is easy to disguise a poisonous one under their appearance.
Dried mushrooms are more dangerous than raw ones
Poisoning from canned oyster mushrooms
A jar of canned mushrooms may be deadly.
Also, we should not forget about poisoning from canned oyster mushrooms. When consuming canned mushrooms, a serious disease develops - botulism. The likelihood of contracting botulism is higher when consuming homemade preserves.
The cause of this disease is the bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It lives in the ground and can end up in a can due to insufficient heat treatment or insufficient pickling of the mushrooms.
Symptoms of botulism can be divided into:
- dizziness ;
- dry mouth;
- discomfort when swallowing;
- vomit;
- blurred vision (blurred vision);
- bloating.
- muscle weakness, paralysis, paresis;
- frequent shallow breathing;
- increased heart rate, hypertension;
- swallowing disorder;
- double vision, drooping eyelids, dilated pupils;
- lack of facial movements due to facial nerve paralysis;
- urinary retention.
If you experience one or more of the above symptoms after eating canned mushrooms, you should seek medical help immediately! The treatment of severe poisoning and botulism is carried out by a resuscitator together with an infectious disease specialist.
Treatment
Treatment of botulism includes gastric and intestinal lavage, administration of anti-botulinum serum, hyperbaric oxygenation, restoration of water-electrolyte and acid-base balance disorders, and, if necessary, hemodialysis.
Prevention of botulism
When making canned food, maintain cleanliness, cook the mushrooms until cooked, and under no circumstances eat canned food with a swollen lid (the so-called “bombage”).
Prevention
Mushroom poisoning can be avoided by taking precautions before consuming them. Let's list the main points:
- collect mushrooms in natural conditions strictly under the supervision of an experienced person;
- do not eat or taste raw oyster mushrooms;
- do not eat the product if there are signs that it has deteriorated, for example, a white coating has formed on the oyster mushrooms, there are moldy areas on the cap and legs, there is a foreign smell, etc.;
- the preparation of homemade mushroom preparations should be carried out in compliance with canning technology and the cleanliness of the containers used;
- You should purchase ready-made canned mushrooms only from trusted retail outlets, taking into account their expiration date and storage conditions, the integrity of the jar, and the transparency of the brine.
Unfortunately, sometimes it is not possible to avoid poisoning. If the initial symptoms of intoxication develop, you must immediately provide first aid to the person and consult a doctor.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms: 4 main causes, symptoms
When inexperienced gatherers go into the forest for a “silent hunt,” they run the risk of cutting up inedible mushrooms, which can cause serious health problems.
Surely you have heard more than once that poisonous mushrooms pose a great danger? However, the “catch” can also be hidden in edible representatives of forest delicacies.
Today we will talk about whether it is possible to be poisoned by oyster mushrooms, because any safe mushroom can become toxic under certain circumstances.
Nutritional value of fruits
Before discussing the dangers of the crop we are considering, let us pay attention to the beneficial properties and rich chemical composition of this mushroom variety.
Of course, oyster mushrooms are considered one of the most healthy, dietary, tasty, and also budget mushrooms. In addition to the mild taste and pleasant aroma, the fruiting bodies are enriched with a huge amount of minerals and vitamins.
When consuming oyster mushrooms, our body receives:
All of the listed microelements are necessary for the proper functioning of vital systems of the body, primarily the cardiovascular and gastrointestinal tract.
The high value of the product allows mushrooms to replace all kinds of vegetables and even meat and seafood, which is very attractive for vegetarians, as well as those who adhere to religious, health or sports diets. Another huge advantage of oyster mushrooms is that even a small amount of fruit eaten quickly makes you feel full, although the mushrooms themselves are low in calories - only 43 kcal per 100 grams of raw product.
The chemical composition of the product has medicinal properties; decorative cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, as well as all kinds of tinctures and extracts used in alternative medicine are created on the basis of mushrooms.
It is important to know! People concerned about their health should know that only a few varieties of oyster mushrooms are healthy, and some of them are considered conditionally edible, which means they can cause serious food poisoning.
If the mushroom picker is not confident in his knowledge, it is worth preparing in advance for the outing and studying what the safest and most popular, edible members of the family – oyster mushrooms – look like. The rest are not worth collecting.
If you didn’t find it in the forest, you can find it in the nearest store.
Causes of possible poisoning
Absolutely any mushroom is considered a difficult to digest food, which means it is contraindicated for young children, the elderly and those who suffer from serious disorders of the digestive system. An edible and high-quality fruit can cause intoxication if the human body is weakened or is in an active stage of formation.
Even if a lover of forest gifts does not fit into any of the listed groups, there is always a risk of poisoning, especially if the mushrooms are bought and not collected independently. There may be several reasons for the problem:
- Artificial cultivation of crops occurs in unfavorable conditions or with violations of cultivation technology: plants are treated with chemical fertilizers or anti-parasite agents, the plantation is maintained improperly.
- Mushrooms are grown near industrial and production buildings, near dusty roads, etc. Oyster mushrooms have the interesting property of absorbing substances from the environment, that is, they can absorb toxic gases and fumes from the air, becoming poisonous.
- If canned rather than fresh mushroom bodies are purchased, the cause of poisoning may be improper heat treatment or failure to follow the rules according to which the delicacy should be salted or pickled.
Causes of toxicity of edible oyster mushrooms
Frivolous mushroom pickers who harvest in the wrong area can also become poisoned by oyster mushrooms. It is always worth remembering the golden rule - the pulp of oyster mushroom is like a sponge - it absorbs everything it comes into contact with.
If you decide to go for forest gifts, carefully study each cut specimen - one poisonous mushroom in a basket can spoil the entire catch, becoming the culprit of serious intoxication.
The safest way to enjoy your favorite product is to “hunt” only in a proven, environmentally friendly area, having previously prepared for the outing.
How to recognize poisoning
Since there is always at least the slightest risk of mushroom poisoning, it is necessary to know the symptoms by which a person can quickly understand that his body needs immediate help.
The negative experience of people poisoned by poorly preserved forest fruits makes it possible to identify a number of manifestations, the presence of which requires medical intervention. Here are the main ones:
- A sharp increase in body temperature to 38 - 40 degrees.
- Abdominal pain, abnormal stool.
- Nausea, dizziness, vomiting.
- Convulsive states, clouding of consciousness, hallucinations.
If the cause of poisoning is in mushrooms that are “saturated” with chemicals and poisons from the environment, the following types of ailments may occur:
- Acute pain in the middle of the abdomen, gradually increasing nausea followed by vomiting.
- Joint discomfort, discomfort in the muscles or even the throat so much that it hurts to swallow.
- A sharp deterioration in vision, resulting in a headache.
- Severe weakness throughout the body, drowsiness, a feeling that something is pressing on the head from the inside.
This is how toxins enter the blood from the stomach. A person with the described symptoms needs urgent help, otherwise the consequences can be unpredictable.
Article on the topic: Did you know that the Svinushka mushroom is classified as poisonous?
How to provide first aid for oyster mushroom poisoning
It should be remembered that each organism is individual and can react in its own way to the same stimulus. To make a diagnosis, it is not necessary to wait until all the described symptoms begin to appear; one or two are enough.
Help for someone who has been poisoned should include a set of measures:
- First of all, it is necessary to get rid of the source of poison in the stomach by washing it. The simplest and most effective way is for the patient to drink a large amount of warm water (about two liters), after which artificially induce vomiting.
- Once the stomach is cleansed, it is important to take absorbent pharmaceuticals; they will “suck in” the remaining toxins and toxic substances. Such medications include Smecta, activated carbon, Enterosgel, etc. If poisoning is accompanied by high fever, you cannot do without antipyretic medications.
- If the spoiled mushroom fruits were eaten more than 120 minutes ago, you can give the patient an enema to cleanse the intestines (using a simple warm liquid and a pear).
- It is very important to ensure that the poisoned person constantly drinks water or chamomile decoction - a little, but often. This will avoid serious dehydration.
If you ignore the manifestations of illness, serious consequences may arise - disruptions in the functioning of the heart, kidneys, liver, digestive system and even the brain. Timely assistance will help you get rid of the problem without consequences, within a few days.
Prevention of oyster mushroom poisoning
If you do not want to be poisoned by oyster mushrooms or any other mushrooms, treat purchasing, collecting and consuming mushrooms with the utmost caution.
- Try not to buy mushrooms from strangers. It’s better to find a proven, official “point” of implementation with good reviews. It is advisable that the supplier is a well-known manufacturer of treats.
- If you purchase canned fruits, pay attention to the brine with mushrooms - it should be transparent and liquid.
- Harvest forest products only in environmentally safe places (there should be no industries, factories, roads, wastewater treatment plants, etc. nearby).
- Check each mushroom before you start preparing the planned dish. Do not eat a product unless you are sure of its variety or freshness.
As you can see, even a teenager can take precautions.
Be careful what you consume, because we are what we eat.
(2
Bacteriosis
The topic of bacteriosis is overblown on the Internet, especially on forums.
Any infectious lesion of dead sprouts is unknowingly declared bacteriosis. And many beginners also think that they brought it with mycelium.
There is a separate article about real bacteriosis, which is caused by bacteria of the genus Pseudomonas. If you click here, it will open in a new window.
And I will tell you what happened to this sprout in the image, why it is moldy. There was a lack of moisture - the mushroom in the center was dry, with a lifeless brown cap. The two mushrooms above and slightly to the left began to develop later, when the moisture was raised. But they raised it too high, or too quickly. So they turned the caps up and exposed the plates so that they could evaporate their own liquid. But the changes destroyed them and the splice died. Condensation began to settle on this dead mass, and mold grew on it.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms: symptoms and signs, reviews, first aid
It is impossible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms if you follow the technology for collecting and preparing them. However, we must remember that mushrooms are difficult for the digestive system. They can harm the body of elderly people and children, as well as any person with unlimited use.
Is it possible to get poisoned by oyster mushrooms?
Oyster mushrooms are considered edible mushrooms. Experienced mushroom pickers can eat the fruiting body even raw without any special consequences. If we look at it in general, you can even get poisoned by bread if you use it incorrectly.
As for oyster mushrooms, the main problem is the difficulty of digestion by the gastrointestinal tract. In other words, mushrooms create heaviness in the stomach when consumed in excess.
Oyster mushrooms will cause intoxication in people with chronic liver or gastrointestinal disease.
Why do oyster mushrooms not fully develop a bunch?
There are several reasons:
— the impact of condensation, more on this below.
— the nutritional value of the substrate is low, read here.
— insufficient flow velocity near the floor.
If the air ducts are properly routed, part of the mushroom drusen begins to wither if the air duct sags (or bends) and/or the nozzles (cups) fall out of the holes in the air duct.
This phenomenon is also observed in chambers without air ducts, if only the supply and exhaust fans are running. In this case, the flows are distributed unevenly and chaotically.
They cannot fulfill the main task of ventilation - to promptly remove CO2 and moisture directly from the mushroom cluster.