Melon is a favorite product not only of adults, but also of children. It has many beneficial qualities and, when consumed, saturates the body with various vitamins. However, you should be careful with it. Overeating this product is not allowed. Especially pregnant women. This is explained by the fact that melon retains fluid in the body, which contributes to the appearance of edema. And during the period of bearing a child, this can cause harm to both the woman and the fetus.
Contraindications
Despite its many beneficial properties, melon is considered a difficult product to digest. It should not be used if you have the following health problems:
- intestinal disorders;
- diabetes;
- urinary tract diseases;
- stomach or duodenal ulcers;
- individual intolerance;
- pregnancy with diagnosed gestosis.
But in other cases, eating this fruit can cause a lot of trouble, in particular, cause poisoning.
Breast-feeding
During lactation it is not recommended to consume a lot of melon. Vegetables are classified as allergenic foods. Substances from melon, getting into milk, cause digestive upset in the child, diathesis, nitrates will provoke poisoning. But melon increases the amount of milk. The product is safe to eat, following the rules:
- Do not eat melons for breakfast or in combination with other foods.
- Try some melon after breakfast.
- Do not abuse the sweet fruit.
A small amount of melon eaten after the morning meal will show during the day how the child will react to the product. In the absence of skin rashes or digestive disorders, it is permissible to eat a melon slice as a snack between main meals.
With breastfeeding, you have to give up confectionery products due to weight gain. Melon will help fill your need for sweets. You should not get carried away, otherwise the effect will be the opposite - the product stimulates appetite.
Causes of poisoning
You can get poisoned by melon in 2 cases. The first of them is the accumulation of nitrates in the pulp, which are often used when growing crops. Once in the body, they are converted into nitrites - dangerous compounds that have a harmful effect on human health:
- disrupt the respiration of cells and tissues;
- lead to problems with the passage of oxygen in the blood;
- settle in the liver, disrupting its functioning;
- cause hypoxia, which negatively affects the functioning of the brain and heart.
Other chemicals - pesticides and ripening accelerators - lead to disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract. Due to the use of these chemicals, many poisonings occur in early summer.
The second case when a melon can cause poisoning is the presence of bacteria in its pulp. They get inside the fruit through a damaged peel, due to violation of storage and care rules during cultivation or transportation, as well as lying on the ground for a long time. Bacteria in the pulp of the fruit multiply, die and rot, and eating a fruit with foulbrood and live pathogens entails poisoning.
But not every case where your health worsens after eating melon can be considered poisoning. Banal overeating of a nourishing fruit sometimes leads to unpleasant manifestations from the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the benefits of melon?
The pulp contains a large amount of vitamins (C, B9, P), carotene, iron, and folic acid. In addition, the chemical composition of the fruit contains fats and pectin substances.
Cases in which melon acts as a natural medicine:
- improved digestion (especially the digestion process);
- treatment of diseases associated with the cardiovascular system;
- help with anemia and atherosclerosis;
- elimination of inflammatory processes;
- fight against diseases of the kidneys, diuretic bladder, and liver;
- constipation, for which just half a glass of melon juice will be enough;
- to remove a person from a state of depression, melon pulp was used, which also helps with any other mental disorders;
- use for preparing tonic face masks.
However, it should be remembered that there are no products that are completely safe for the human body. Is it possible to get poisoned by melon? Doctors say yes, saying that most often people are to blame for this, and not the products themselves. It is known that melon is useful only if it is ripe. Consumption of a green product, on the contrary, can lead to negative consequences, including intoxication. By the way, it is also not recommended to eat melon on an empty stomach or on an empty stomach, because this can cause indigestion.
Differences from overeating
Melon has a laxative effect, so after it the stool becomes somewhat thinner. But if you eat too much (even if the fruit is completely healthy and free of chemicals), symptoms of overeating appear, which people mistake for poisoning:
- heaviness in the stomach;
- diarrhea;
- bloating;
- flatulence;
- occasionally vomiting.
But these signs are actually not so scary. It is enough to give the victim activated carbon, sorbents, plenty of drink and provide the gastrointestinal tract with a rest from heavy food. After these measures, the condition returns to normal on its own.
Preventive measures
In most cases, treatment will not be required if you follow the following precautions:
- buy melon only in season (out-of-season products are a guaranteed source of dangerous nitrates);
- You can eat only high-quality fruits (without damage, cuts, cracks, putrefactive spots);
- the peel should be evenly colored (contrasting spots are a sure sign that the fruit has been treated with nitrates and herbicides);
- Do not eat melon that has been stored cut for more than a day (even in the refrigerator).
Remember that in case of severe poisoning, treatment does not always bring results.
To stay healthy. Be careful when choosing melon. Keep the amount of food you eat in moderation. We recommend:
Symptoms of poisoning
The severity of symptoms following melon poisoning and subsequent treatment will largely depend on the cause of the problem.
Bacterial poisoning
In its manifestations, such intoxication resembles ordinary disruptions in the gastrointestinal tract:
- decreased appetite;
- abdominal pain (mainly in the stomach);
- difficulty digesting food;
- nausea;
- vomiting followed by short-term relief;
- sometimes fever.
Vomiting and fever are even good in case of poisoning. Such symptoms indicate the body's attempts to reject or destroy toxins.
Toxic poisoning
The course of chemical poisoning is characterized by greater severity and slow manifestation. The first symptoms will appear only after 6-8 hours:
- dizziness;
- almost complete lack of appetite;
- weakness, tinnitus;
- sudden sharp pain in the abdomen;
- vomit;
- irritation of the gastric mucosa, causing bitterness in the mouth;
- dark brown stool (a clear indicator of chemical poisoning);
- cyanosis of nails and lips as a result of the effects of poisons on blood vessels;
- pain in the liver area, yellowing of the sclera of the eyes and skin.
If the poisoning is very severe, the victim will suffocate, may lose consciousness, have convulsions and be unable to express thoughts. If these signs are present, you need to urgently consult a doctor. Severe intoxication can lead to dehydration, so don't risk trying to deal with it yourself.
But in any case, severe poisoning is a condition when the patient will need help from people nearby. It is important to provide it while the medical team is still on the way.
First aid
If the victim’s condition is not serious, help will consist of ordinary actions. Here's what you can do in case of poisoning without doctors:
- Clear your stomach. Give the victim warm water (400 ml - 1 l) to drink and induce vomiting. Water can be replaced with weak solutions of salt or potassium permanganate.
- Enema. If you have the skill to carry out such a procedure, it will greatly help the patient. The water should be warm, but slightly below body temperature.
- Sorbents. When the stomach is irritated, it is better to give the victim liquid medications (solutions, gels). Smecta or Enterosgel are suitable here.
- Drink. It is important to give the poisoned person more to drink to remove toxins and avoid dehydration. The best option is water, but you can also give sweet tea.
- Dehydration. To replenish salts and fluids, dissolve Regidron powder and give it to the patient several sips at a time.
- Peace. Place the victim in bed, cover him and provide him with rest for 1-2 days.
- Diet. When the vomiting stops, you can feed the victim semi-liquid food (it is easier to digest). Do not give sweet, peppery, salty foods.
If after these measures there is no relief, but additional symptoms are added, a call to the doctor is required.
During pregnancy, you cannot wait for symptoms to worsen and try to provide help on your own. At the first suspicion of poisoning, you should immediately call an ambulance. In the case of small children, all amateur activities are also prohibited: you can only give the child a weak manganese solution to drink and also immediately call a doctor at home.
Beneficial features
Melon is a berry of the pumpkin family, related to cucumber, rich in vitamins and microelements. If you constantly eat the product in small quantities, the body is cleansed of excess water. Harmful accumulations of toxins will go away, making room for fiber, vitamins A, B, C, E, iron, silicon, sodium, phosphorus, potassium, calcium. One or two slices eaten per day will replenish the supply of folic acid needed during pregnancy. A sweet product consumed between main meals is a source of fiber that normalizes intestinal microflora.
Benefits of melon to the body:
- Increases immunity;
- Maintains high hemoglobin levels;
- Strengthens blood vessels;
- Has a rejuvenating effect on the skin;
- Stimulates growth, prevents hair loss;
- Improves the condition of teeth and gums;
- Strengthens vision;
- Prevents the development of stroke and cancer.
Summer melon has a beneficial effect on the body with hemorrhoids and atherosclerosis.
The fruits are eaten raw, cooked into jam, candied fruits and melon honey are made. Calorie content of 100 g of raw product is 35 kilocalories. 100 g of dried fruit will be 341 kilocalories. Different varieties differ in composition.
Call a doctor, follow-up treatment
A doctor's help will be required if vomiting and loose stools persist for more than a day, or signs of damage to the nervous system appear in the form of loss of consciousness, convulsions, and breathing problems.
Professional medical assistance is also required if a child under 3 years of age or a pregnant woman is poisoned. Measures and medications permitted depending on the age and condition of such victims can only be prescribed and carried out by a specialist.
Treatment
In case of chemical poisoning (nitrates, pesticides, etc.), therapeutic measures will be aimed at reducing oxygen starvation of the body (hypoxia). Hepatoprotectors may also be required to restore normal liver function, which suffers especially acutely during chemical poisoning.
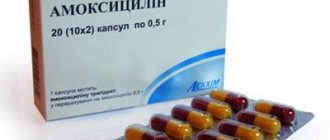
Bacterial poisoning will require antibiotic therapy. But before choosing a specific drug, laboratory tests will determine the susceptibility of the pathogen to several antibacterial agents. This is important for selecting a more effective medicine.
What will doctors do in case of any type of melon poisoning:
- additional cleansing of the stomach using a probe;
- procedures aimed at replenishing water-salt balance and removing toxins from the body.
Intoxication of this kind is not among the most severe, but this does not mean that everything will necessarily pass without consequences for health.
Chemical content
Melon contains toxic substances in the following cases:
- Accumulation of nitrates due to violation of agrotechnical rules.
- Improper storage, leading to the appearance of pathogenic bacteria in the peel and pulp.
- Stimulation of fruit growth using pesticides.
Yellow melon ripens naturally, filled with sunlight. The ripening period is 6 months. Manufacturers speed up the process using chemistry. Remaining on the ground, the melon crop becomes filled with bacteria.
Nitrate is converted into nitrite in the human body. The accumulation of nitrite causes a lack of oxygen, impaired cardiac function, and difficulty breathing. Hypoxia, or oxygen starvation, is detrimental to the brain. Settling in the liver, nitrates affect the gland. Pesticides accumulate in fruits and have a poisonous effect on humans.
Possible consequences
With high-quality first aid provided on time, the body will recover quickly and completely after mild poisoning. If the intoxication was severe or there was no one to help the victim, the following consequences may occur:
- disruption of the respiratory system;
- liver poisoning;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system and brain;
- irritation of the gastric mucosa, etc.
It will be very annoying to treat such serious illnesses just because you once had the unfortunate opportunity to enjoy a delicious fruit. But it’s easy to avoid this, and regular prevention can help.
Prevention
Basic preventive measures are aimed at correct selection and storage of melon:
- do not give the fruit to infants under one year of age as complementary food (such babies do not yet have enzymes that help process this fruit);
- buy melon no earlier than August - early autumn (by this time it ripens on its own, without chemical accelerators);
- do not eat the slice right down to the peel (it is on it and under it that fertilizers accumulate in the greatest concentration);
- choose fruit without damage to the skin (scratches, dents, rotten areas, etc.);
- eat only ripe melon;
- the aroma of the fruit should be pleasant;
- Do not keep the cut-up delicacy even in the refrigerator for more than a day.
Although melon poisoning does not belong to the group of particularly severe ones, you still cannot do nothing about it. Any intoxication can lead to poor health and sometimes dangerous health consequences. Therefore, no one has yet come up with a better option than preventive measures.
Who is contraindicated to eat melon?
It is known that melon is a heavy product, the digestion of which is not easy for the stomach. Therefore, it is advisable for all people not to overuse it, and also not to eat melon before bed. The ideal time for this product is considered to be the period between meals, for example as an afternoon snack.
To prevent melon poisoning, do not drink cold water or eat dairy products immediately after eating this sweet product. And of course, you should not mix melon with any alcohol, since such a mix can lead to quite unpleasant consequences in the form of diarrhea and general weakness.
REMEMBER! You should not buy and consume melon for those people whose body does not accept this product, because even a small amount can lead to an attack or exacerbation of allergies.
The rest of the people need to observe the proportions in consuming melon, since even a completely healthy person can get a little poisoning. However, there are some categories of people whom doctors do not advise eating more than 100-200 grams of melon per day. These include the following groups of people:
- having problems with the gastrointestinal tract and suffering from diseases such as ulcers;
- people with diabetes;
- having diseases associated with the urinary system;
- future mothers who have the possibility of gestosis.
Pregnant women who have no special contraindications are also not recommended to constantly use this product (it is advisable not to exceed 150 grams per day). After all, abuse of this product can lead to the retention of unnecessary fluid in the body, which must be quickly eliminated. Doctors also warn parents who have small children that they should not try melon until they are two years old, because it can cause toxin poisoning.