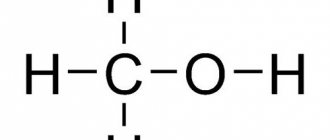Home / Preparations and fertilizers
Back
Published: 06/05/2019
Reading time: 8 min
0
1130
Substances containing copper are widely used in various areas of human life. Gardeners and gardeners are familiar with copper sulfate, which is used as an antiseptic and fungicide for the prevention and control of diseases and pests. But we must remember about its possible harm to humans, and follow the rules of use and take precautions.
- 1 Why is copper sulfate dangerous?
- 2 Copper sulfate poisoning 2.1 Signs of poisoning
- 2.2 Consequences of intoxication
Intoxication
To ensure proper functioning of the body, the daily dosage of copper is about three milligrams. Its reserves can be replenished independently if you eat products that are rich in such microelements, namely:
- oats;
- buckwheat grain;
- potato;
- spinach;
- some offal - liver and kidneys.
In such cases, poisoning is impossible.
Copper sulfate poisoning can occur in the following situations:
- Inhalation method - a person inhales dust in the process of violating safety precautions associated with grinding and processing a metal surface that contains copper;
- With food, when cooking utensils that may contain this toxic substance are used;
- Infection through the skin. If the patient has large and severe burns, then a special compress containing a solution of copper salt can be used.
Such poisoning causes enormous harm and damage to health and life.
Safety regulations
The basic safety precautions are contained in the following rules:
- before starting to prepare a solution (or work with a substance), put on rubber gloves, secure a gauze bandage or a respirator, put on safety glasses, and choose long-sleeved workwear;
- when working with the drug, exclude the possibility of drops of the solution getting into the eyes and mucous membranes, drinking water and food is prohibited, and you must stop smoking;
- After treatment, ventilate the room, take a shower, rinse your mouth, nose, eyes with running water, and go out into the fresh air.
Symptoms and signs of poisoning
Poisoning with a toxic copper substance causes significant harm to health, life and the general condition of the body.
Symptoms that occur due to the penetration of copper sulfate with food products may be as follows:
- severe kidney failure;
- impaired and complicated breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing;
- there is significant harm to the activity of the gastrointestinal tract: blue or red vomiting, heartburn, severe diarrhea, prolonged attacks of nausea, there is a metallic taste in the oral cavity, burning, increased salivation;
- liver failure develops, and then jaundice;
- Particular harm is caused to the cardiovascular system: a sharp drop in blood pressure, acute tachycardia appears;
- convulsions.
When inhaled into the body, particular harm is caused to the respiratory system, manifested by the following symptoms:
- tears flow;
- severe redness of the eyes;
- irritation of the eyeball is observed;
- frequent sneezing;
- damage to the nasopharynx;
- development of dry cough, runny nose;
- increase in body temperature up to 39 degrees Celsius;
- severe chills;
- difficulty breathing, wheezing, shortness of breath;
- severe muscle weakness;
- profuse sweating;
- allergic reaction in the form of a rash.
The next method of poisoning is through the skin, which is very rare. The substance in dry form does not cause any particular harm, and if the solution gets on the skin, it must be washed off with running water as quickly as possible.
First aid
Proper medical care depends on how the poisoning occurred. If a toxic substance enters the human body through food, the following important actions will be required:
- Rinse the stomach and induce vomiting so that there is clean water.
- Then prepare the solution: take water into a glass and dilute the activated carbon. You need to drink it in one gulp.
- To quickly cleanse the body, you need to use a saline laxative, namely magnesium sulfate or Glauber's salt.
- Drink plenty and frequently.
- If you have cramps in the abdominal area, apply a warm heating pad.
When poisoning occurs by inhalation, if symptoms of copper fever appear, do the following:
- you need to drink a lot of liquid;
- use diuretic and antipyretic medications.
If copper sulfate gets on your skin, rinse the area under running water.
Treatment is as follows:
- you need to introduce an antidote - Unithiol;
- an antiemetic drug is administered intravenously, it is very effective, namely Aminazine;
- you will need painkillers: Morphine, Atropine;
- hemodialysis is performed;
- vitamin therapy is carried out;
- if necessary, antibacterial agents are used.
All of the above activities are performed in a hospital under the supervision of the attending physician. Follow safety precautions and be careful!
Copper poisoning has become a common occurrence quite recently, although people have known this metal since ancient times. Today, without it, it is impossible to produce gadgets, televisions and computers, but copper compounds can also be dangerous - in particular, copper sulfate can harm the body if safety precautions are violated when working with it or due to deliberate ingestion of the substance.
On the other hand, copper is a biogenic, vital microelement for humans, animals and plants, playing a key metabolic role in metabolism:
- it is part of the enzymes that synthesize red and white blood cells, ensure the absorption and transport of iron, and participate in the construction of bone tissue, collagen and elastin;
- Without copper, the functioning of the brain and nervous system is impossible, because it is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses along nerve fibers;
- it is the main component for the normal functioning of the immune system and the activity of the endocrine glands.
However, this valuable metal can also bring a lot of trouble to a person - taking it in excess quantities will inevitably cause poisoning.
Application of copper compounds
The main consumers of copper are heavy industry, communications and transport, and its compounds are indispensable in the textile, engineering, aviation and electrical industries, as well as in agriculture.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the properties of copper sulfate and silver-copper compounds are used to produce:
- antifungal ointments and creams that combat foot odor;
- eye drops, ointments and pencils;
- medicines for the treatment of phosphorus burns;
- drugs, sorbents and dressings for antibacterial therapy.
The most famous copper compound that people encounter in everyday life is copper sulfate. Harm to humans can occur if safety instructions are not followed, or if large quantities of the substance are accidentally or intentionally ingested.
A few facts about copper sulfate:
- despite the fact that the color of copper itself is red, vitriol granules have different shades from white to deep blue;
- the powder and its aqueous solution do not have a distinct odor, but have a bitter-tart taste characteristic of metals;
- the solution has antiseptic, disinfectant and astringent properties;
- food preservative and color stabilizer food additive E-519 is nothing more than the same copper sulfate powder. However, its use in the food industry is limited by its nauseating metallic taste;
- It is used as an antiseptic in medicine, plant growing, woodworking and construction industries, and is widely used against mold and fungi.
Precautionary measures
Copper sulfate and compounds based on it have been used by gardeners and gardeners for decades. It is difficult to do without the drug, since the product is convenient and effective to use, economical, and affordable.
- Use special containers (not made of metal) to prepare solutions.
- Maintain the dosage of the product according to the instructions.
- When diluting solutions and processing, wear special clothing, gloves, goggles, a respirator or mask.
- To better dissolve the powder, use warm (not hot) water.
- Prepare formulations immediately before use. Do not store solutions; discard any remaining solution. When water in solutions cools, the substance crystallizes and such compositions are not suitable for use.
- When storing the substance, keep it away from food, indoors in places inaccessible to small children and animals. Store in plastic or glass containers.
- Treat plantings in the evening or in the morning. It is advisable to choose a windless day and not spray immediately after rain.
- After work, be sure to clean and rinse sprayers and containers for solutions.
- Do not work with the compounds when gardens are flowering, otherwise the plants will get burned.
- After treatments, take a shower, wash overalls, and rinse personal protective equipment.
To prevent copper from accumulating in the soil, alternate planting of crops on the site. It is also recommended to treat trees alternately with various fungicides to avoid intoxication, including for plants. The substance contains impurities of sulfuric acid, so in large quantities the composition is dangerous for living organisms.
The inorganic compound copper sulfate (copper sulfate) is indispensable in gardening and gardening as a means to combat fungal diseases and to protect against pests. It is necessary to follow the instructions for use of the compositions, otherwise the beneficial substance may be harmful to human health.
Copper sulfate, as an essential element of everyday life, is sure to be found by any summer resident. It is used to feed and treat plants. Using copper sulfate, you can perfectly clean home pools, which are also not uncommon in dachas. Vitriol even fights mold on the walls - verified! Of course, the use of a useful solution of a beautiful blue color does not at all imply its ingestion.
Mortality is quite high in severe cases. A comprehensive review of the clinical presentation and treatment of copper sulfate poisoning was performed. Key words: acute swallowing, copper sulfate, poisoning. Copper sulfate forms bright blue crystals containing five water molecules. It is commonly known as "Blue Vitriol" or "Blue Stone". It is used mainly for agricultural purposes as a pesticide and in the leather industry. It has also been used as a precipitant for heavy metal poisoning and has been used to treat gastric and topical phosphorus exposure.
However, neither you nor your children are insured against accidents, so you need to know how copper sulfate poisoning occurs and what to do if it happens.
How copper compounds act on the body
Copper is very dangerous for the body - when inhaled, it irritates the mucous membranes of the pulmonary system, and when swallowed, it irritates the gastrointestinal tract. After this, the metal enters the blood and destroys the membrane of red blood cells - blood, enriched with released hemoglobin, has a detrimental effect on the cells of the lungs and nervous system.
Copper not bound to protein molecules poses a great danger. It accumulates in the tissues of the kidneys and liver and leads to functional disruption of their work.
The toxicity of copper sulfate is not great and is classified as hazard class IV. However, copper sulfate poisoning is not only possible, but can also be fatal:
- contact with skin is safe, but requires hygienic treatment;
- contact with the mucous membrane of the eyeballs can cause deep burns and requires immediate thorough rinsing with plenty of running water;
- acute toxic dose: if swallowed – 0.5 g, if inhaled – 11 mg/kg;
- The lethal dose if swallowed depends on age, body weight and health status - from 45 to 125 g.
Options for accidental poisoning
Accidents can occur both at home and in copper processing industries.
Because some clinicians face unfamiliarity when challenged to manage cases of copper sulfate poisoning, we attempted to conduct a comprehensive review of the clinical presentation and treatment of copper sulfate poisoning. The kinetics of copper during overdose differs from the kinetics of copper during normal dosage. Gastrointestinal absorption is affected by copper intake and may be as high as 12% in patients with high copper intake. However, in the presence of damaged mucosa after acute overdose, fractional absorption is likely to be higher.
Causes and symptoms of copper poisoning
People who abuse vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements containing copper or follow a diet with a large amount of copper-containing products are at risk of poisoning.
The daily intake of copper for a healthy adult is 2 mg.
Copper poisoning can occur at work or at home by violating safety precautions when working with copper-containing compounds. In this case, the routes of entry into the body will influence the manifestation of symptoms.
| Inhalation of vapors of copper compounds or its dust – foundry fever | Accidental or intentional ingestion, food overdose, medical intoxication with copper-containing drugs, regular use of copper utensils |
|
|
General signs of poisoning:
| |
In most cases, acute poisoning is caused by inhalation of vapors or dust. The first 2 symptoms from the table appear immediately, more severe disorders appear after 4-48 hours. The acute course is also characterized by hemolysis of the blood, jaundice and the appearance of blood in the urine.
On a note! Symptoms of foundry fever are similar to adenovirus infection. This is important for providing adequate first aid.
In the chronic course of the disease, hand tremors, poor coordination of movements, yellowness of the skin, allergic rashes on the skin, and protein in the urine are added to the general symptoms. Ignoring chronic copper poisoning increases the harmfulness of its effects by an order of magnitude and increases the risks of developing atherosclerosis and cirrhosis of the liver.
Separately, we note that the symptoms of copper sulfate poisoning will also depend on the route of its entry into the body:
- if the lesion occurred during the spraying of copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture, these will be signs of foundry fever;
- if the powder or solution is swallowed - symptoms of “food intoxication with copper”.
Cautions
Today there is a list of countries where copper sulfate is officially registered as a food additive, but this indicator is not clear. Contact with copper sulfate is strictly prohibited for pregnant women, during lactation and children under 12 years of age. People in these categories need therapy with safe means under the supervision of a specialist.
Until recently, it was believed that most people consumed sufficient amounts of copper. However, modern research has shown that this is not the case. For example, in the United Kingdom and the United States, many typical foods have been analyzed for their metal content.
They are considered the lowest intakes likely to cause the slightest biochemical evidence of adverse effects in all but a small number of members of the population. Those suffering from childhood cirrhosis or hereditary diseases such as Wilson's disease retain excessive amounts of copper in the body and suffer liver damage, often with fatal consequences. Symptoms of acute copper poisoning include nausea, vomiting, abdominal and muscle pain. Excess body copper can be removed using specific chelating agents or by consuming high levels of zinc.
Laboratory studies have established that a small dose of powder, if ingested, can be fatal to humans. If undiluted vitriol gets on the skin, it will lead to a burn, and if it is inhaled, it can damage lung tissue. Therefore, before using the powder, it is recommended to clear the room of food and tableware. It is better to put a gauze bandage on your face.
Some foods are especially rich in copper. These include most nuts, seeds, chickpeas, liver and oysters. Natural foods such as grains, meats and fish generally contain enough copper to provide up to 50% of the required copper intake in a balanced diet. In addition, an additional proportion of daily consumption in the United Kingdom can be obtained from drinking water transmitted through copper pipes. However, in most areas, the copper content of water is insufficient to balance the required normal daily intake of this element.
Security measures:
- when interacting with vitriol, use latex gloves;
- It is recommended to protect your eyes with glasses and wear closed clothing;
- during any actions with powder, children and animals must not be nearby;
- containers that were used to dilute the solution are strictly prohibited from being used for food in the future;
- After completing manipulations with the powder, you must wash your face and hands with soap.
If the instructions are not followed, copper sulfate can lead to intoxication of the body: a metallic taste will appear in the mouth, the stomach will ache, all this will be accompanied by vomiting, loose stools, headaches and yellowing of the skin. If all instructions are followed, copper sulfate is not capable of harming humans.
Impact on the body
Additionally, be aware that some water filters claim to remove metals, including the main element copper, from drinking water.
Copper has been used as a medicine for thousands of years, including treating chest wounds and purifying drinking water. Recently, studies have shown that copper helps prevent inflammation in arthritis and similar diseases. Research is being conducted on anti-ulcer and anti-inflammatory drugs containing copper and its use in radiology and for the treatment of seizures and epilepsy. Copper is considered one of the metals that has been known since ancient times. Despite the fact that many are familiar with this element of the periodic table (abbreviated Cu) only because of frequent mentions of copper poisoning, it is capable of providing benefits in minimally acceptable quantities.
Metal is one of the fundamental microelements that are necessary for the normal functioning of the human body. The reason lies in the fact that it acts as a constituent element in tissue respiration as an oxidative enzyme. In addition, it is considered a fundamental factor in the production of melanin, which is responsible for the formation of pigmentation. The formation of hemoglobin cannot occur without copper.
Although there is no epidemiological evidence that copper can prevent arthritis, wearing copper bracelets has been claimed to improve symptoms. Acute copper poisoning is a rare event that is largely limited to accidental ingestion of copper nitrate or copper sulfate solutions, which should be kept out of the home. These and organic copper salts are potent emetics, and occasional large doses are usually rejected by vomiting. Chronic copper poisoning is also very rare, and a few reports relate to patients with liver disease.
That is why doctors insist that people do not give up Cu in their daily diet, replenishing its reserves with enviable regularity. At the same time, violating the maximum permissible norms is prohibited, since an excess of the substance can lead to serious functional problems in the body.
First aid and treatment
Regardless of how the poisoning was obtained, the first thing to do is call an ambulance, and only then provide first aid yourself.
A person who has “inhaled copper” must be given antipyretic and diuretic tablets and forced to drink as much water as possible.
If copper enters the body through the gastrointestinal tract, the following algorithm should be followed:
- rinse the stomach thoroughly (up to clean water);
- give a laxative (preferably saline);
- make you drink a lot of water;
- After 10 minutes, take any sorbent.
Attention! In case of copper poisoning, it is forbidden to drink sour juices, milk or fermented milk drinks!
Treatment of toxic damage in a medical institution will be carried out according to the following scheme:
- introduction of an antidote – Unithiol;
- specific treatment - penicillamine;
- providing assistance according to indications, as a rule, these are painkillers, antiemetics, antipyretics, antimicrobials and expectorants;
- if necessary, hemodialysis is possible;
- in cases aggravated by hemolysis - droppers with sodium bicarbonate;
- for foundry fever - aminophylline.
What to do before the doctor arrives
Treatment of stranding intoxication should begin immediately after the first symptoms appear. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate: you must immediately call a medical team and provide first aid to the victim. The future life of a person depends on the literacy of decisions made at the initial stage of intoxication.
First of all, you need to thoroughly rinse the person’s stomach with plenty of water with the addition of activated carbon.
It should be remembered that in case of copper sulfate poisoning, you should not give acidified fruit drinks, compotes, teas or milk drinks to drink. In such an environment, copper dissolves well, which significantly aggravates the course of poisoning and contributes to the development of complications.
It is necessary to offer the victim to take a diuretic or laxative, preferably with a saline composition. This promotes the rapid removal of poison from the body. It is useful to drink any absorbent - Smecta, Polysorb, Enterosgel.
Prevention
To prevent copper poisoning at work, you should strictly follow safety instructions. For domestic use, you must follow the following rules:
- Do not store food in copper containers. Use copper utensils only for cooking and only if this is provided for by the technology;
- Store the powder and solution of copper sulfate out of the reach of children;
- When processing a garden plot, take all necessary precautions - wear protective clothing, gloves, respirator glasses;
- Do not work with copper and its alloys in the room where products are stored. After carrying out the work, it is necessary to clean the room with a vacuum cleaner and carry out a thorough wet cleaning.
If symptoms of acute copper poisoning are detected, you should urgently call an ambulance, and if chronic symptoms occur, contact an endocrinologist or toxicologist.
Copper belongs to 7 metals that were already known to ancient people. Scrapers, arrowheads, armor, knives, utensils... Until now, any self-respecting housewife must have a copper basin among her kitchen utensils, in which jam is wonderfully prepared. Without this metal, it is impossible to produce modern gadgets, televisions and computers, because copper is the best conductor material for the manufacture of circuit boards and microcircuits.
On the other hand, copper is a biogenic, vital microelement for humans, animals and plants, which plays a key metabolic role in metabolism . In the human body, copper is part of the enzymes that synthesize red and white blood cells, ensure the absorption and transport of iron, and participate in the construction of bone tissue, collagen and elastin. Without copper, the functioning of the brain and nervous system is impossible, because it is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses along nerve fibers. Copper is the main component for the normal functioning of the immune system and the activity of the endocrine glands.
However, this metal, valuable for its properties, can bring a lot of trouble to a person. Taking an excess amount of it orally through ingestion or inhalation will inevitably cause poisoning.
Poisoning: what to do
Medical reference books claim that copper sulfate in quantities of more than 0.6 g threatens intense vomiting. And in a dose of more than 2 g it leads to severe poisoning with a fatal outcome (in some cases). This often refers to the accidental, careless ingestion of copper sulfate orally.
Each of us is faced with the need to use this substance. The main thing is to adhere to safety standards and rules. Do not use copper sulfate in food areas. Should be stored in a tightly closed container away from children.
In case of acute symptoms (vomiting, allergic reactions, fever), calling an ambulance is inevitable. Only she will quickly take you to the intensive care unit of a local hospital for examination by a toxicologist and resuscitator.
In case of mild poisoning (refusal to hospitalization), the main specialist will be the local internist (family doctor), who will issue sick leave, refer you for tests, prescribe medication, and consult with a specialist.
Application of copper compounds
The main consumers of copper are heavy industry, communications and transport. Copper compounds are indispensable in the textile, engineering, aviation and electrical industries, as well as in agriculture.
In the pharmaceutical industry, the properties of copper sulfate and silver-copper compounds are used to produce:
antifungal ointments and creams that combat foot odor; eye drops, ointments and pencils; medicines for the treatment of phosphorus burns; drugs, sorbents and dressings for antibacterial therapy.
The most famous “copper” liquid that people encounter in everyday life is copper sulfate. Harm to a person and his vital body processes can be caused if safety instructions are violated, as well as if a large amount is accidentally or intentionally ingested.
Copper sulfate is an aqueous solution of 5-aqueous sulfate of 2-valent copper. Although the color of copper itself is red, copper sulfate granules have different shades from white to deep blue. The powder and its aqueous solution do not have a distinct odor, but have a bitter-tart taste characteristic of metals. Copper sulfate has antiseptic, disinfectant and astringent properties.
By the way, food preservative and color stabilizer - food additive E-519, is nothing more than the same copper sulfate powder. However, its use in the food industry is limited by its nauseating metallic taste.
Copper sulfate is used as an antiseptic in medicine, crop production, woodworking and construction industries. Copper sulfate is widely used against mold and fungi.
Is copper sulfate harmful to humans and why is it dangerous to the body?
What is the harm of copper sulfate to the human body?
Copper sulfate is a hygroscopic (moisture-absorbing) powder of bright blue or dark blue crystals. The substance is toxic, hazard class 4, harmful if it affects mucous membranes and is ingested.
Compliance with safety rules is appropriate and necessary here, since careless use can even lead to death . Extremely dangerous for fish. Anhydrous copper sulfate (CuSO4) when dissolved in water (H2O) forms crystals of copper sulfate (CuSO4 5H2O).
The action is based on the reaction of copper ions to fungal or bacterial cells, causing irreversible changes in them.
How copper compounds act on the body
When copper enters the body, it irritates the mucous membranes of the pulmonary system when inhaled and the gastrointestinal tract when swallowed. After which it enters the blood and destroys the red blood cell membrane. Blood enriched with released hemoglobin has a detrimental effect on the cells of the lungs and nervous system. Copper not bound to protein molecules poses a great danger. It accumulates in the tissues of the kidneys and liver and leads to functional disruption of their work.
Excessive copper content in the body can be caused by a hereditary pathology - Wilson-Konovalov disease or be a consequence of frequent hemodialysis.
The toxicity of copper sulfate is not too great and is classified as hazard class IV. However, copper sulfate poisoning is not only possible, but can also be fatal:
contact with skin is safe, but requires hygienic treatment; contact with the mucous membrane of the eyeballs can cause deep burns and requires immediate thorough rinsing with plenty of running water; acute toxic dose: if swallowed – 0.5 g; inhalation – 11 mg/kg; The lethal dose if swallowed depends on age, body weight and health status - from 45 to 125 g.
How to use against fungus on walls
The effectiveness of copper sulfate largely depends on proper surface treatment before applying the composition. You cannot skip one of the steps:
careless operation will worsen the results of mold control.
Preparation of concrete walls:
- remove decorative coating;
- remove the plaster from the walls using a spatula;
- if the mold has penetrated deeply into the pores of the concrete, you will have to use a gas burner;
- carefully rub the treated areas with sandpaper to remove the mycelium;
- before applying copper sulfate, it is advisable to wash the walls with a soapy solution, then dry well;
- the next stage is applying the anti-fungal composition;
- After the first layer has dried, repeat the treatment 3-4 more times. The longer the mold was on the site, the more layers will be required (no more than five);
- After the fungicide has completely dried, plaster the surfaces or apply a finishing material.
Causes and symptoms of copper poisoning
People who abuse vitamin-mineral complexes and dietary supplements with copper, adhere to a diet with a large amount of copper-containing products, or simply transmit: liver, oysters, chocolate, cocoa, seafood, legumes, nuts are at risk of copper poisoning.
The daily intake of copper for a healthy adult is 2 mg.
Copper poisoning can occur at work or at home by violating safety precautions when working with copper-containing compounds. In this case, the ways in which copper enters the body will influence the manifestation of symptoms.
| Inhalation of vapors of copper compounds or its dust – foundry fever | Accidental or intentional ingestion, food overdose, medical intoxication with copper-containing drugs, regular use of copper utensils |
| lethargy, decreased performance dry mouth, unquenchable thirst abdominal and headache attacks of dry cough chills and fever tightness and pain in the chest increased reflex function of the brain | metallic taste in the mouth increased salivation abdominal pain and diarrhea, blue feces speech impairment (common) epileptic seizures (rare) symptoms of kidney and liver failure |
| General signs of poisoning: impaired urine production, redness of the eyeballs, attacks of nausea and vomiting, aches and pain in the muscles, depression due to increased irritability | |
In most cases, acute poisoning is caused by inhalation of vapors or dust. The first 2 symptoms from the table appear immediately, the next, more severe disorders appear after 4-48 hours. The acute course is also characterized by hemolysis of the blood, jaundice and the appearance of blood in the urine.
On a note! Symptoms of foundry fever are similar to adenovirus infection. This is important for providing adequate first aid.
In the chronic course of poisoning, trembling of the hands, impaired coordination of movements, yellowness of the skin, allergic rashes on the skin, and protein in the urine are added to the general but mild symptoms. Ignoring chronic copper poisoning increases the harmfulness of its effects by an order of magnitude and increases the risks of developing atherosclerosis and cirrhosis of the liver.
Separately, we note that the symptoms of copper sulfate poisoning will also depend on the route of its entry into the body. If poisoning occurs while spraying copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture, these will be signs of foundry fever, and if the powder or solution is swallowed, these will be symptoms of “food poisoning with copper.”
Chronic poisoning
Sclera color during poisoning
The situation is very sad. Not only does it greatly harm your health, it also spoils your appearance. Signs of chronic copper poisoning are as follows. Skin lesions - eczema, dermatitis. The color of the skin and even the sclera becomes greenish-yellow, and sometimes the hair changes color. A characteristic red border appears on the mucous membrane of the gums. Teeth deteriorate, trophic changes occur in the nasal septum. Chronic gastritis develops, affecting the kidneys and liver. The nervous system suffers. Treatment of these pathologies lasts for years. Copper production is considered extremely harmful.
There are studies that prove the dependence of life expectancy on the experience of working with copper.
Copper sulfate, which is a corrosive acid, causes caustic burns of the esophagus and superficial and deep ulcers in the stomach and small intestine. Changes in acute gastritis, intestinal mucosal hemorrhage, intestinal mucosal necrosis, and perforation have been reported.
Gastrointestinal: Immediate symptoms following ingestion of copper sulfate are universally gastrointestinal in the form of nausea, vomiting and cramping abdominal pain. Vomiting usually occurs within 15 minutes after ingestion. Hemorrhagic gastroenteritis may occur, associated with mucosal erosion, metallic taste, epigastric burning, and diarrhea. In severe cases, hemethenis and malena occur.
One year of work in hazardous conditions shortens a person’s life by an average of 4 months.
The statistics are sad, so always think about whether you really need the notorious additional payment “for harmfulness”.
First aid and treatment
Regardless of how the poisoning was obtained, the first thing to do is call an ambulance, and only then provide first aid yourself.
A person who has “inhaled copper” must be given antipyretic and diuretic tablets and forced to drink as much water as possible.
If food poisoning occurs, you should proceed according to the following algorithm:
rinse the stomach thoroughly (up to clean water); give a laxative (preferably saline); make you drink a lot of water; After 10 minutes, take any sorbent.
Attention! In case of copper poisoning, it is forbidden to drink sour juices, milk or fermented milk drinks!
Treatment of copper toxicity in a medical facility will be carried out according to the following scheme:
introduction of an antidote - unitol; specific treatment - penicillamine; providing assistance according to indications, as a rule, these are painkillers, antiemetics, antipyretics, antimicrobials and expectorants; if necessary, hemodialysis is possible; in cases aggravated by hemolysis - droppers with sodium bicarbonate; for foundry fever - aminophylline.
Treatment at home
Treatment at home is possible only for mild copper sulfate poisoning and consists of drinking plenty of fluids, fresh air, and following the therapist’s recommendations.
If complications arise that cause disruption of the internal organs, a specialist will treat these manifestations. Therapy should be carried out exclusively in a medical facility under the supervision of a doctor.
Prevention
To prevent copper poisoning at work, you should strictly follow the safety instructions, and for domestic use the following rules will help:
Do not store food in copper containers. Use copper utensils only for cooking and only if this is provided for by the technology. Keep copper sulfate powder and solution out of the reach of children. When processing a garden plot or when working with copper parts, take all necessary precautions - wear protective clothing, gloves, and respirator glasses. Do not work with copper metal and its alloys in the room where products are stored. After work, copper shavings or dust must be removed with a vacuum cleaner and a thorough wet cleaning must be carried out.
And in conclusion, we would like to add that if symptoms of acute copper poisoning are detected, you should call an ambulance, and if chronic symptoms occur, contact an endocrinologist or toxicologist.
Views: 115849
Copper sulfate or copper sulfate is a special blue pentahydrate that has a crystallized form. It is used in almost all spheres of human activity, namely: agriculture, medicine, crop production, paint and varnish industry, as well as construction. This is due to its universal and effective properties: astringent, antiseptic, disinfectant.
Despite the fact that many claim that such a drug is harmless to human health and life, there are many factors that refute such an opinion. Many experts believe that copper sulfate can cause significant damage and harm to human health, under certain circumstances. This drug has a fourth class of danger. Also read here about how to cleanse your body with baking soda.
Characteristics of meat breeds
Meat varieties of sheep are suitable for the production of lamb and mutton. Despite such a succinct name, animals also provide milk and wool.
Meat productivity is determined by the choice of breed
The following subspecies are considered the most productive:
- Meat-fat or fat tail. A popular category in dry Asian countries. Typical representatives are Edilbaevskaya and Gissarskaya.
- Meat and wool. A popular group in the Russian Federation. Romanovskaya, Kuibyshevskaya, Gorkovskaya.
Representatives of meat breeds are precocious and quickly gain weight
General characteristics:
- strong physique;
- graceful skeleton;
- well-formed muscle mass;
- thin skin with a dense layer of fatty tissue;
- good slaughter yield indicators;
- early maturity and fertility;
- possibility of 12-month pasture maintenance;
- ease of care.
Females have a high milk yield. Young animals raised on suckling demonstrate excellent survival rate.
Sheep and rams of the meat line are hardy and have strong immunity
Sheep quickly gain weight, which is why a large number of livestock farmers choose these animals to keep. Already by 4 months, the lamb has half the weight of an adult ram, and by the end of the first year its weight reaches 90% of the weight required for slaughter. These animals are unpretentious in keeping; for some breeds, only a small pen with free access to water and food is enough.
When choosing meat, you should pay attention to the following characteristics of the animal:
- the physique should be strong, with voluminous muscle mass;
- the skeleton is thin, the internal organs are smaller;
- The skin of meat breeds is thin, due to which a thick layer of subcutaneous fat is formed under it;
- increased productivity, faster lamb maturation;
- endurance and the ability to live on pasture all year round.
For those who also practice shearing sheep for wool harvesting, it is worth learning more about what types of sheep shears there are.
When choosing a sheep, it is important to take into account not only its health, appearance, resistance to disease, but its ancestry. It is the breed that will determine the productivity characteristics of the animal, on which profit largely depends.
Domestic
Sheep farming in Russia has a long history.
In addition to the selection achievements of Soviet breeding farms, such as Kuibyshevskaya, Gorky and North Caucasus, obtained through the active infusion of the European gene pool, it was possible to preserve older ones, for example, Romanovskaya.
Intoxication
To ensure proper functioning of the body, the daily dosage of copper is about three milligrams. Its reserves can be replenished independently if you eat products that are rich in such microelements, namely:
oats; buckwheat grain; potato; spinach; some offal - liver and kidneys.
In such cases, poisoning is impossible.
Copper sulfate poisoning can occur in the following situations:
Inhalation method - a person inhales dust in the process of violating safety precautions associated with grinding and processing a metal surface that contains copper; With food, when cooking utensils that may contain this toxic substance are used; Infection through the skin. If the patient has large and severe burns, then a special compress containing a solution of copper salt can be used.
Such poisoning causes enormous harm and damage to health and life.
Prevention during frequent use of the product
In production workshops, copper sulfate poisoning is avoided by observing safety standards and regulations. After work, you need to take a shower and change clothes. At home, the substance must be stored in a closed container, away from children, in a well-ventilated room without food.
When working, use gloves, goggles, a respirator, and follow safety rules. After work, carry out wet cleaning, change clothes, and perform water procedures. Drinking plenty of fluids is recommended. If you feel unwell, consult your doctor.
Inorganic copper sulfate is in demand and popular due to its low price and less danger to the environment than the latest developments of pesticides from organic components. However, in order to avoid health problems, you must adhere to personal safety rules.
Symptoms and signs of poisoning
Poisoning with a toxic copper substance causes significant harm to health, life and the general condition of the body.
Symptoms that occur due to the penetration of copper sulfate with food products may be as follows:
severe kidney failure; impaired and complicated breathing, shortness of breath, wheezing; there is significant harm to the activity of the gastrointestinal tract: blue or red vomiting, heartburn, severe diarrhea, prolonged attacks of nausea, there is a metallic taste in the oral cavity, burning, increased salivation; liver failure develops, and then jaundice; Particular harm is caused to the cardiovascular system: a sharp drop in blood pressure, acute tachycardia appears; convulsions.
When inhaled into the body, particular harm is caused to the respiratory system, manifested by the following symptoms:
tears flow; severe redness of the eyes; irritation of the eyeball is observed; frequent sneezing; damage to the nasopharynx; development of dry cough, runny nose; increase in body temperature up to 39 degrees Celsius; severe chills; difficulty breathing, wheezing, shortness of breath; severe muscle weakness; profuse sweating; allergic reaction in the form of a rash.
The next method of poisoning is through the skin, which is very rare. The substance in dry form does not cause any particular harm, and if the solution gets on the skin, it must be washed off with running water as quickly as possible.
Where does mold come from and why it needs to be dealt with
The appearance of mold not only spoils the overall appearance of the walls in the premises, but also negatively affects the health of people who spend a lot of time in them. Mold can cause constant weakness, headaches, and general malaise. It can cause an allergic reaction and provoke an asthma attack. Constant exposure to fungal secretions can lead to various upper respiratory tract diseases.
The main reason for the appearance of this fungus is most often high humidity and ineffective ventilation. Mold spores are found almost everywhere. They move freely through the air, settling on objects. When placed in a favorable environment, they germinate and, growing, form a colony, which we observe in the form of dark spots. It is clear that it is advisable to get rid of this uninvited “tenant” as quickly as possible.
First aid
Proper medical care depends on how the poisoning occurred. If a toxic substance enters the human body through food, the following important actions will be required:
Rinse the stomach and induce vomiting so that there is clean water. Then prepare the solution: take water into a glass and dilute the activated carbon. You need to drink it in one gulp. To quickly cleanse the body, you need to use a saline laxative, namely magnesium sulfate or Glauber's salt. Drink plenty and frequently. If you have cramps in the abdominal area, apply a warm heating pad.
When poisoning occurs by inhalation, if symptoms of copper fever appear, do the following:
you need to drink a lot of liquid; use diuretic and antipyretic medications.
If copper sulfate gets on your skin, rinse the area under running water.
Treatment is as follows:
you need to introduce an antidote - Unithiol; an antiemetic drug is administered intravenously, it is very effective, namely Aminazine; you will need painkillers: Morphine, Atropine; hemodialysis is performed; vitamin therapy is carried out; if necessary, antibacterial agents are used.
All of the above activities are performed in a hospital under the supervision of the attending physician. Follow safety precautions and be careful!
How dangerous is copper sulfate ? Is it absorbed by plants?
The answer to this question will consist of two parts. Which point of view to adhere to on your site - choose for yourself.
Official opinion
Answer from a candidate of agricultural sciences in a popular science magazine.
Copper is one of the most important trace elements required in very small doses for plant development. Its absence or deficiency can cause plant diseases.
Copper sulfate belongs to the second hazard class (use of gloves is required). Widely used in gardening as a component of Bordeaux mixture. The fungicidal properties of copper-containing preparations are expressed in the sterilization of spores of fungal diseases and the prevention of the development of diseases.
The use of all copper-containing preparations requires compliance with the concentrations of working solutions when working on various crops, since upon contact with green leaves, copper inhibits the work of chlorophyll grains and the synthesis of organic matter during photosynthesis.
To this day, Bordeaux mixture remains one of the most effective preparations for preventive treatments, recommended before and after the end of the growing season (over the crown without leaves) in early spring and late autumn. One such treatment allows in some years to avoid the need to combat fungal diseases in the summer, which increases the environmental friendliness of products and working conditions.
In a number of stone fruit crops (plum, apricot), leaf-by-leaf treatment with copper-containing preparations can cause leaves to desiccate (fall off), so it is not recommended during the growing season.
Opinion of a practicing soil scientist
From the book by Pavel Trannoy “The Gardener’s Golden Book”
If you had to use copper sulfate, Bordeaux mixture, copper oxychloride and other copper-containing preparations on your site, then consider that your soil is provided with copper for centuries to come, no longer necessary, no matter what smart books write about your peat bog or other copper-poor soil.
The very name “micro” says a lot: microelements in large quantities no longer bring benefit, but harm to plants. This also applies to copper.
Breed classifications
There are 2 basic principles for separating sheep.
Table 1. Zoological principle of separation.
| Illustration | Description |
| Short-skinny-tailed | The tail is short, skinny, and does not reach the hock joints in length. |
| Long-skinny-tailed | An oblong process without fatty deposits. |
| Short-fat tailed | Instead of this organ, sheep grow a fat pad. |
| Fat tail | Layers of fat are located near the underdeveloped tail. |
| Long-fat-tailed | A plump, elongated appendage with a characteristic narrowing at the tip. |
Table 2. Production principle of separation.
| Illustration | Description |
| Fine-fleece | Wool consists of thin, uniform fibers. |
| Semi-coarse-haired | Heterogeneous fleece with soft and elastic downy fibers. |
| Semi-fine fleece | Due to the low concentration of grease, the color of the coat is not only white, but also black, gray, and brown. |
| Fur coats | This category includes sheep of coarse wool breeds, the area of the skins after cutting is at least 18 dm², and the length of the fibers is more than 1.5 cm. |
| Smushkovye | Smushka is the skin of a newborn lamb. Coarse-haired varieties bred to produce smushkas of various shapes. |
| Meat-fat | Owners of coarse hair. They have good meat productivity. |
| Meat-wool-dairy | Universal breeds that produce meat, wool and milk. |
The production classification is considered the most common in the post-Soviet space. It takes into account the following aspects:
- specifics of basic productivity;
- ratio of wool and meat productivity;
- wool quality.
In terms of numbers and bioproductivity indicators, fine-wool sheep are in first place. They are followed by semi-fine wool, coarse wool and semi-coarse wool.
Sheep in the fields