Paracetamol today is found in almost every home medicine cabinet. This medical drug is actively used as an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic agent for both adults and children. However, incorrect dosage and non-compliance with the rules of administration can lead to the fact that this universal medicine turns into a real poison, rapidly destroying the entire body. To avoid this, it is worth learning more about what is a lethal dose of paracetamol, how to recognize poisoning and provide emergency medical care.
The effect of paracetamol on the body
Paracetamol is a white, light creamy, crystalline powder that is not completely soluble in ordinary water and has high absorption. Up to 98 percent of the drug is metabolized in the liver, and the average half-life is 2-3 hours.
The basic pharmacodynamics of paracetamol is associated with the blocking of cyclooxygenase enzymes and inhibition of prostaglandin production. Being one of the metabolites of phenacetin, the drug is close to it chemically, but at the same time, having a pronounced analgesic and antipyretic effect, it has a relatively weak anti-inflammatory effect, which in turn is compensated by low toxicity, weak formation of methemoglobin even at high concentrations and the possibility of use for all age groups. groups of patients, including infants.
Side effects
In general, if the dose of paracetamol is within the normal range, the drug is slightly toxic. But with prolonged use, side effects develop. Paracetamol has a particularly noticeable effect on the liver and kidneys.
Paracetamol has been used for quite some time. From time to time its safety is called into question and research is carried out. For example, a teacher at the University of Illinois stated that taking paracetamol in children caused a 41% increase in the incidence of asthma. She conducted her research from 1970 to 1990, when America massively switched from aspirin to paracetamol.
The use of paracetamol by pregnant women also has its risks. Analgesics from this series can cause disruption of the development of the genital organs in boys. Therefore, paracetamol is contraindicated in pregnant women in the third trimester and in newborns up to one month old.
Causes of paracetamol overdose
The direct cause of an overdose of paracetamol is a significant excess of the dosage of the drug, both one-time and over a certain period of time. Causes of poisoning:
- Simultaneous use of several drugs with different trade names containing paracetamol . A typical situation associated with a drug overdose is caused by poor medical literacy of the population - to relieve pain and lower the temperature, drugs with similar effects that contain paracetamol are purchased, which, when taken simultaneously, can cause pathology;
- Concomitant use of certain groups of medications . The simultaneous use of phenobarbital, ethacrynic acid, glucocorticosteroids, antihistamines and other drugs along with paracetamol significantly enhances the toxic effect of the latter and provokes the classic symptoms of overdose;
- Alcohol consumption . Paracetamol, even in small concentrations, consumed together with alcohol, causes severe toxic damage to the liver.
The maximum permitted dosage of paracetamol is 1 gram at a time or 4 grams per day for adults and adolescents over twelve years of age. It is not recommended to use the drug for more than 5 days.
The lethal dose of paracetamol is 20 grams once or 40 grams throughout the day.
When using 4-5 grams of the medicine at a time, which corresponds to 8-10 tablets. Moderate-level hepatotoxicity most often develops. Severe degrees of toxic damage are formed with a single dose of 7.5 to 10 grams of the drug.
Application area
The medicine is prescribed for the treatment of fever accompanying infectious, viral infections. Paracetamol relieves various pains:
- Migraine;
- Toothache;
- Neuralgia;
- Myalgia;
- Algodismenorrhea;
- Traumatic, rheumatic pain.
The main symptom that the medicine fights is high fever. The substance relieves painful menstruation - algodismenorrhea, joint pain - arthralgia. Myalgia, muscle pain due to infections, injuries is treated with paracetamol.
The substance is used as the main, additional component of anti-inflammatory and cold remedies. They produce suppositories, tablets, over-the-counter syrups for children and adults. The substance is part of complex powder preparations against colds - Fervex, Coldrex, Coldrex.
Stages and symptoms of paracetamol overdose
Signs of an overdose of paracetamol significantly depend on both the volume of the drug taken and the time elapsed after this event. Conventionally, the symptoms of the pathological process can be divided into 4 stages.
Signs of the first stage of overdose
General signs of poisoning develop in the form of malaise, weakness, nausea and vomiting. Often these manifestations are associated with side effects of the drug, as well as poor tolerability of paracetamol in general.
The above symptoms may be completely “lost” against the background of the development of a disease or syndrome, to neutralize the manifestations of which paracetamol was taken.
It is also worth noting that basic laboratory parameters may be normal within 1 day after poisoning.
Second stage of poisoning
At the next stage of administration of paracetamol, 1 day after the onset of the pathology, the general symptoms of intoxication begin to progress and increase in intensity.
When conducting a biochemical blood test, an increase in the concentration of liver enzymes is clearly observed, in particular ALT and AST - in some cases the indicators exceed the threshold of 1000-1200 units per liter.
Third stage
The third stage is characterized by an avalanche-like formation of new symptoms - the liver can no longer cope with the load during poisoning, the stage of decompensation begins with the potential development of parenchymal necrosis.
Laboratory studies show very high concentrations of liver enzymes in the blood (from 10 thousand units per liter and above), the level of glucose and total blood pH decreases significantly, the content of lactic acid and bilirubin increases - the diagnostician clearly determines the presence of acidosis.
The destructive processes described above are characteristic of severe levels of paracetamol ingestion, starting from 3 days after the development of pathology.
The peak of acute symptoms occurs on days 4-5 and is expressed in the following conditions (severe and especially severe paracetamol poisoning):
- Nervous and mental disorders. Typical manifestations include weakness of the entire body, confusion, drowsiness or extreme agitation, dizziness, regular loss of consciousness, sometimes convulsions and coma;
- Pain syndrome . It is usually localized in the right hypochondrium and is very acute;
- Dyspeptic disorders . The classic list of diarrhea, nausea, vomiting is accompanied by ascites and swelling;
- Cardiovascular pathologies . Multiple heart rhythm disturbances, sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- Manifestations of blockade of the liver and urinary canals. Includes a pronounced sweetish odor from the mouth, yellowing of the mucous membranes, skin and sclera of the eyes, general hypothermia of the body with a significant drop in body temperature;
- Bleeding . Expressed in nasal, oral and subcutaneous hemorrhages, less often bleeding is diagnosed in the abdominal cavity, stomach, intestines and other internal organs;
- Actual liver destruction . Usually diagnosed by instrumental research techniques (for example, ultrasound of the liver), it is expressed in a decrease in the size of the organ;
- Other multiple organ failure of adjacent systems.
Symptoms of stage 4 paracetamol poisoning
The last stage of paracetamol overdose in cases of extremely severe degrees of toxic poisoning occurs 4-5 days after the onset of the pathological process.
Generalized bleeding, cerebral edema, liver destruction, sepsis, complex failure of a number of systems and organs lead to death.
It should be noted that according to modern medical statistics, about 4 percent of patient deaths are diagnosed among all patients who have been diagnosed with an overdose and paracetamol poisoning.
Lethal doses LD50
Coffee helps us perk up, improves concentration and is completely safe in moderation. But in high concentrations, caffeine causes insomnia, dizziness, vomiting, headaches and heart problems.
.
The risk of overdose is greatest with powdered caffeine. Just one tablespoon of caffeine powder is equal to approximately 120 cups of coffee. In the summer of 2014, two young men died after drinking a mixture of pure caffeine powder and water.
Water regulates the shape of cells in our body. Excess water in and around cells is called water intoxication or hyponatremia
. If you drink too much water, which sometimes happens accidentally to athletes during exercise, this condition can occur.
In severe cases of water intoxication, the brain can be damaged and a range of neurological problems can occur, ranging from headaches to confusion, seizures and, rarely, death.
.
A famous case of water intoxication occurred in 2007, when 28-year-old Jennifer Strange drank 6 liters of water in less than 3 hours during a competition and died a few hours later.
First aid for overdose
According to modern research, the toxicity of paracetamol is associated with a significant depletion of glutathione reserves in the body and the dynamic accumulation of unprocessed intermediates of metabolic products in the form of cytochrome P450 - in high concentrations during hydroxidation it has a hepatotoxic effect on the liver.
Providing first aid for an overdose of paracetamol significantly depends on the amount of the drug consumed, as well as the age group - this allows the number to assess the potential degree of poisoning, from mild (no special therapy required) to severe (immediate administration of an antidote and transportation to an inpatient intensive care unit is required) .
Basic simple activities include:
- Gastric lavage with a large volume of liquid;
- Consumption of activated carbon or other sorbent at the rate of 1 gram of product per 10 kilograms of body weight;
- Call an ambulance.
It should be noted that the above actions are effective only in the first 15-30 minutes after an overdose of paracetamol , when the bulk of the active substance has not yet had time to dissolve and be absorbed through the gastrointestinal tract - in this situation, washing will mechanically remove the tablets from the stomach, and activated carbon will not will allow the already half-dissolved drug to act.
The next stage of primary care is the use of the antidote paracetamol . The most effective in this regard are methionine (moderate poisoning) and acetylcysteine (severe poisoning) - the first and second are sources of glutathione, which naturally binds and removes intermediates in the metabolism of paracetamol and neutralizes the danger of hepatotoxic effects on the liver.
The optimal time to use the antidote is up to a maximum of 8 hours after an overdose.
Dosage of acetylcysteine antidote (for severe overdoses):
- Oral – initial 140 mg per kilogram of body weight, repeated every 4 hours with a dosage reduced by 2 times (in total, the course is calculated for 1 day);
- Infusions . A similar starting dosage is diluted in 200 milliliters of glucose and saline, after which it is gradually reduced throughout the day.
The dosage of the methionine antidote (for medium and mild overdoses) is 2.5 grams every 4 hours during the day.
Treatment methods
The first therapeutic measures for paracetamol poisoning are provided by emergency physicians. First, they take a medical history and do a quick examination of the patient. After this, primary treatment of paracetamol poisoning begins. It includes the following components:
- the use of droppers with solutions to reduce symptoms of intoxication;
- taking medications to regulate breathing and heart function;
- oxygen supply through a face mask.
After normalization of vital signs, the patient is hospitalized in the toxicology department. In difficult cases, the patient is placed in the intensive care unit.
In case of excessive use of paracetamol tablets, the following therapy is carried out:
- The antidote for paracetamol, Acetylcysteine, is administered.
- Symptomatic medications are used - painkillers, antispasmodics, antiemetics.
- Droppers are used to eliminate symptoms of intoxication. For this purpose, all kinds of solutions are used - in particular, Disol, glucose.
- A diet is prescribed - this allows you to restore the functioning of the liver and stomach.
- Hemodialysis is performed - indicated in complex cases of poisoning. This procedure helps cleanse the blood of toxic substances.
Symptomatic treatment
When the situation returns to normal, the doctor will select further therapy. An overdose of paracetamol requires the following recommendations:
- diet - indicated for liver pathologies;
- intravenous administration of glucose;
- the use of gliclazide - in the development of heart failure.
If paracetamol poisoning has caused dangerous consequences, surgery may be necessary. It involves kidney removal or liver transplantation.
When should you see a doctor?
If you know exactly the dosage of paracetamol used, then you can roughly estimate the potential risk to the body - about 5 grams of the drug at a time can cause a mild form of poisoning.
You will be interested...
Signs and consequences of valerian poisoning From 7 to 9 grams of paracetamol consumed at a time often provokes the development of moderate or severe poisoning.
A single dose of more than 10 grams is an indication for immediate hospitalization.
In case of moderate and severe overdose of paracetamol, you should seek qualified medical care, even if first aid measures have been carried out promptly and fully.
The dosages described above take into account only the “pure” use of paracetamol - often the potential danger is underestimated due to the simultaneous use of several drugs containing this active substance, as well as the administration of alcohol, glucocorticosteroids, phenobarbital, antihistamines, ethacrynic acid, etc., due to induction them of the toxic pathological effect of the main drug.
Contraindications
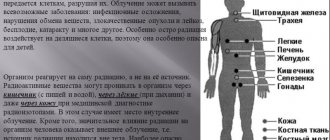
Paracetamol is not toxic in standard dosage. Dangerous in high doses, the drug damages the liver, kidneys, heart, stomach, intestines, and central nervous system.
Chronic liver and kidney diseases do not allow you to cope with low doses of paracetamol. You cannot combine drinking alcohol with treatment with the substance due to the increased load on the liver. Other contraindications:
- Allergy to analgesics;
- Gilbert's syndrome;
- Alcoholism;
- Anemia.
Consequences of an overdose of paracetamol
Severe forms of paracetamol overdose can cause serious complications for the body, both in the short term (up to 5 days after poisoning) and long term (up to several months).
An overdose of paracetamol has typical consequences associated primarily with the development of acute renal failure:
- Coagulopathy. Systemic disorder of blood clotting with the formation of multiple foci of bleeding;
- Encephalopathy . Organic brain damage with the formation of edema;
- Respiratory distress syndrome . Severe breathing disorder;
- Blood sepsis . Entry into the blood of pathogens of secondary bacterial infections;
- Kidney failure . The syndrome of impaired renal function is formed as a consequence of generalized pathologies throughout the body;
- Death. In the terminal stages of paracetamol poisoning with massive necrosis of parenchymal tissue, there is a high probability of death.
Diagnosis of poisoning
If an overdose is suspected, the level of paracetamol in the blood should be analyzed. To determine whether an antidote is needed, the Rumak-Matthew nomogram is used. Thanks to this, it is possible to predict the degree of complexity of liver damage.
The study is performed 4 hours after consuming the drug. To do this, you need to determine the exact time of intoxication. In the absence of clinical symptoms and concentrations less than 150 mcg/ml, there is no threat to health. If the body contains more harmful substances, the risk of liver damage is very high. In such a situation, an antidote must be urgently administered.
If there is a dangerous level of toxic substance in the blood, it is necessary to monitor the level of liver enzymes, glucose, and bilirubin daily. Blood clotting is of no small importance.
Features of overdose in children
As modern clinical practice shows, children, along with older people, are at particular risk for an overdose of paracetamol - as a rule, they require a smaller dosage compared to adults to form a toxic lesion.
Recent global medical studies show that children under 6 years of age tolerate an overdose of paracetamol more easily than other age categories of the population.
A dose of 150 milligrams of the drug per 1 kilogram of a child’s weight is considered potentially dangerous, while obvious signs of liver failure appear only in 4 percent of cases (that is, general intoxication and non-specific forms of poisoning on 1 day are not replaced by the characteristic symptoms of a severe stage of development of the pathology).
Principles of first aid for paracetamol overdose in children include:
- Gastric lavage, forced induction of vomiting and use of sorbents in the first 15-40 minutes after a recorded case of excessive use of the drug;
- The use of an antidote in the form of acetylcysteine (from 1 to 8 hours after an overdose) is infused at the rate of 70 mg/kg body weight when diluted in 150 milliliters of saline;
- Prohibition on taking antihistamines , phenobarbital, glucocorticosteroids, ethacrynic acid, and any medications containing alcohol;
- Hospitalization in a hospital and, if necessary, complex supportive therapy.
Lethal dose of alcohol
13 shots of alcohol in quick succession
As you know, alcoholic drinks can blur your vision, confuse your speech, play tricks on your memory, and slow down your reactions. But all of these consequences can be deadly if you drink too quickly.
.
Alcohol poisoning is when excess alcohol in the blood shuts down areas of the brain that control certain functions, such as breathing and consciousness. Typically, it occurs when someone drinks a large amount of alcohol in a short period.
For the average person, 13 drinks in a short period of time is enough to kill, but this figure varies depending on the size of the drink, gender and other factors.
Lethal doses of substances
85 chocolate bars
Although chocolate is delicious, it contains quite a lot of the toxic substance theobromine.
to kill a small animal. That is why it is not recommended to give it to pets.
This ingredient can kill humans, but because we metabolize it so much better than cats and dogs, we would need to eat much more chocolate to experience serious health effects.
In humans, the potentially harmful dose of theobromine is 1000 mg per kg
or about 85 chocolate bars. For cats, for example, even a few pieces can be dangerous.
We all know that apples are healthy and tasty. However, their seeds contain small amounts of a compound that turns into the dangerous toxin hydrogen cyanide
or hydrocyanic acid when digested.
It is estimated that an apple contains about 700 mg of hydrogen cyanide per kilogram of dry weight, and about 1.5 mg of cyanide per kilogram of the human body can kill.
This means you need to chew and swallow half a cup of apple seeds.
in one sitting or about 19-24 apples.
Symptoms of mild cyanide poisoning include confusion, dizziness, headache and vomiting. Large doses can lead to breathing problems, kidney failure and, in rare cases, death.
If you're worried about poisoning, remember it's best to swallow the apple seeds whole
. This will allow them to pass through the digestive system without causing harm.