Radiation is the propagation in air space or vacuum of a certain kind of particles or waves of an electromagnetic nature. It should be said that radiation can be either ionizing or non-ionizing.
Non-ionizing radiation is any type of radiation that is not dangerous to the human body and can be detected by thermal radiation, ultraviolet light and radio waves. The first type of ionizing radiation differs from the previous one in that during its operation, electrons are gradually separated from the atom and begin to exist separately, forming ions. What is the lethal dose of radiation for humans? The ions appear due to increased energy and can often cause harm to the human body.
It should be said that when talking about radiation, we mean ionizing radiation. This will be discussed later in this article.
Types of radiation doses and what is equivalent dose rate
The concept of dose was introduced to assess the degree of impact of ionization radiation on various objects. To determine the intensity of permissible radiation doses, the concept of dose rate was introduced.
- Exposure dose.
The amount of positive ions of x-rays and gamma rays in a certain volume of air is usually called the exposure dose. The system unit of measurement is the coulomb divided by kilogram (C/G), not the system unit Roentgen (R). 1 C/G = 3876 R. - Absorbed dose.
The amount of radioactive energy received per unit mass of the irradiated substance is called the absorbed dose. The system unit of measurement is Gray (Gy), not the system Rad. 1 Gy = 100 rad. - Equivalent dose.
The concept of equivalent dose shows the absorbed dose of ionizing radiation, adjusted by the coefficient of relative biological effectiveness of various types of radioactive radiation. The system unit of measurement is the sievert (Sv), not the system rem (rem). 1 Sv = 100 rem. - Effective dose.
Different body tissues have different sensitivity to radiation. Therefore, to calculate the effective dose, a radiation hazard coefficient was added. It is measured in the same way as the equivalent dose in Sieverts (Sv). - Equivalent dose rate.
The radiation dose received by the body in a certain period of time (for example, within an hour) is called the dose rate. Rate is calculated as the ratio of dose to exposure time and is measured in Roentgen per hour, Sievert per hour and Gray per hour. Household dosimeters usually measure equivalent dose rate (microSievert per hour) or exposure dose rate (micro-Roentgen per hour). The ratio is easy to remember - one Sievert is one hundred Roentgen.
Permissible radiation dose or safe dose rate
Permissible radiation doses (natural background power level) from 0.05 µSv/hour to 0.5 µSv/hour are harmless. But with constant exposure to radon in the human body, the risk of various diseases, including cancer, increases. Therefore, the premises must be ventilated. When building a house or renovating an apartment, you need to check the building materials used with a household dosimeter or radioactivity indicator.
Human activity increases the natural radioactivity of nature. And this is not just nuclear weapons or the nuclear industry. Conventional combustion of gas, oil or coal changes the background radiation. Permissible radiation doses are significantly exceeded in areas of oil wells. Unsafe salts of thorium 232, radium 226 and potassium 40 are deposited on the ground near wells and on drilling equipment. Therefore, used pipes are considered radioactive waste and must be disposed of in a special way.
Today the issue of background radiation has become very acute. A huge number of devices that surround a person can harm him. That is why sanitary inspectors, as well as radiation safety workers, often check houses, streets, and businesses, because the radiation level exceeds the permissible values.
What is ionizing radiation
Ionizing radiation can be present in the space around us throughout our lives.
The appearance of such particles in the atmosphere is a consequence of both natural processes and artificial ones created by human hands. A person can receive the highest possible doses of ionizing radiation and a lethal dose of radiation due to radioactive accidents or explosions at nuclear power plants, as well as due to nuclear attacks or space disasters. An increased level of ionizing substances in the atmosphere of a certain area, and a lethal dose of radiation for humans in roentgens, is considered radiation contamination that is dangerous for human habitation or presence in this area.
Norms for humans
Radiation standards are those values that are used by scientists to designate a safe environment when exposed to various devices. Radiation standards are established by higher authorities, who try to regulate the strict observance of them at one or another enterprise, as well as in everyday life.
It is not uncommon to hear radiation levels discussed. The norm sometimes exceeds the permissible values. Inflated levels are mainly observed at chemical industry enterprises, where workers wear special suits to avoid exposure to radiation.
Review
Of all the radiation diagnostic methods, only three: X-ray (including fluorography), scintigraphy and computed tomography, are potentially associated with dangerous radiation - ionizing radiation. X-rays are capable of splitting molecules into their component parts, so their action can destroy the membranes of living cells, as well as damage the nucleic acids DNA and RNA.
Thus, the harmful effects of hard X-ray radiation are associated with cell destruction and death, as well as damage to the genetic code and mutations. In ordinary cells, mutations over time can cause cancerous degeneration, and in germ cells they increase the likelihood of deformities in the future generation.
The harmful effects of such types of diagnostics as MRI and ultrasound have not been proven. Magnetic resonance imaging is based on the emission of electromagnetic waves, and ultrasound studies are based on the emission of mechanical vibrations. Neither is associated with ionizing radiation.
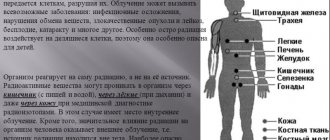
Ionizing radiation is especially dangerous for body tissues that are intensively renewed or growing. Therefore, the first people to suffer from radiation are:
- bone marrow, where the formation of immune cells and blood occurs,
- skin and mucous membranes, including the gastrointestinal tract,
- fetal tissue in a pregnant woman.
Children of all ages are especially sensitive to radiation, since their metabolic rate and cell division rate are much higher than those of adults. Children are constantly growing, which makes them vulnerable to radiation.
At the same time, X-ray diagnostic methods: fluorography, radiography, fluoroscopy, scintigraphy and computed tomography are widely used in medicine. Some of us expose ourselves to the rays of an X-ray machine on our own initiative: so as not to miss something important and to detect an invisible disease at a very early stage.
But most often the doctor sends you for radiation diagnostics. For example, you come to the clinic to get a referral for a wellness massage or a certificate for the pool, and the therapist sends you for fluorography. The question is, why this risk? Is it possible to somehow measure the “harmfulness” of X-rays and compare it with the need for such research?
Acceptable standards
It is impossible to say exactly what the norm of radiation is for humans. Scientists have only identified some correspondences between radiation and everyday moments of life. First of all, it should be noted that all indicators are measured in microsieverts per hour (this determines the level of exposure to gamma radiation and background radiation).
It is believed that the norm of radiation, which is acceptable for the common man, should not be more than 5 mSv per year. Moreover, the indicators are calculated in aggregate for five years. If the level is elevated, then radiologists will find out the cause, and first of all, look for it in the air, and check the operating chemical plants in the city.
Types of radiation
The natural radiation background is influenced by the number of elementary particles that previously hit the area or object and continue to come from various sources.
Modern science distinguishes between types of radiation that directly affect the natural radiation background:
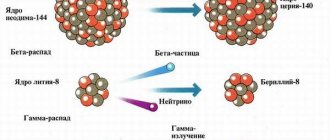
- Gamma radiation. It is a flow of microparticles with a neutral charge. Has high penetrating ability. This type of radiation is the most destructive to all living things. Materials with heavy nuclei provide protection against X-rays. They trap gamma particles, becoming a source of radiation.
- Beta radiation. Its carrier is larger particles with average penetrating ability. Potentially dangerous to humans, beta rays are trapped in a thin layer of metal, wood and stone.
- Alpha radiation. It is a stream of heavy positively charged particles. They carry a powerful ionic charge that has a destructive effect on living tissue cells. In humans, alpha particles only affect the outer layer of the skin. Even clothing is a barrier for them.
On earth, sources of radiation that create natural and artificial background radiation are the sun, stars, rocks and industrial facilities built by man. The level of contamination is created by isotopes of chemical elements such as iodine, uranium, radium, strontium, cobalt, cesium and plutonium.
Knowing what radiation is, you can successfully protect yourself from such a phenomenon dangerous to life and health.
Effects at different doses of radiation
Separately, it is necessary to say what effect this or that radiation dose will have:
- 11 µSv per hour - this is the dose that is considered dangerous and increases many times the likelihood of cancer tumors appearing in the human body.
- 10,000 mSv per hour - with this exposure, a person immediately becomes ill and dies within two or three weeks.
- 1000 mSv per year - with this dose of radiation, a person feels a temporary malaise, which manifests itself as symptoms of radiation sickness. But it does not lead to death or deterioration of the condition to such an extent that a person cannot lead a normal life. The main danger is that the risk of cancer becomes so great that annual examinations will be required to monitor cell mutations.
- 0.73 Sv per hour - with such short-term exposure, a change in blood composition occurs, which will pass over time. But, as a rule, this will affect a person’s well-being in the future.
Diagnostics
The appearance of radiation sickness is detected based on primary symptoms. Close attention is paid to patients who have been in a situation where the safe dose of radiation was exceeded.
The severity of the injury is determined by examining blood samples from the victim.
The presence of anemia, reticulocytopenia, leukopenia, and ESR is determined. The presence of radiation sickness is indicated by signs of bleeding in the myelogram .
In addition to blood tests, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Taking scrapings of skin ulcers and performing microscopy.
- EEG.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal cavity.
- Ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
- Ultrasound of the pelvic organs.
At the same time, consultations are held with specialized specialists: hematologist, endocrinologist, neurologist and gastroenterologist . They carefully study the clinical picture of the disease and the results of all examinations.
What to do if background radiation increases
The main reason that the permissible radiation level is too high is the objects surrounding a person. Today, all household appliances irradiate the inhabitants of the globe. If the background radiation is significantly increased, you need to pay attention and check:
- batteries in the house, especially those that were produced in the USSR;
- furniture;
- tiles, which are usually laid in the toilet and bathroom;
- some food products, especially imported fish (even now fish that have been in poisoned waters are transported across the border).
The radiation rate is such an important indicator that it cannot be ignored. True, the current pace and lifestyle of many people, as well as the universal prevalence of technology, do not allow it to be reduced. And this happens because not a single person can do without a cell phone, computer, or the Internet, since our whole life is built on this! So we hear in the news that more people are dying from cancer!
Cosmic radiation from the Earth, as well as man-made and natural radionuclides, participate in the formation of background radiation. Background radiation is radiation from man-made and natural sources that a person is exposed to.
Therapy for radiation sickness
The disease can be successfully treated if the dose threshold for infection is exceeded slightly . Among the main therapeutic techniques are:
- Timely provision of first aid. This is especially important for people who have been to a place of severe radiation contamination. All clothing is removed from the victim, as it accumulates radiation. Wash the body and stomach thoroughly.
- Drug therapy. It includes the use of sedatives, antihistamines, antibiotics, and agents for restoring the gastrointestinal tract. In addition, treatment is carried out aimed at restoring the immune system. At the third stage of the disease, antihemorrhagic drugs are prescribed, among other things.
- Blood transfusion.
- Physiotherapy. The most common method of breathing is using an oxygen mask.
- Exercise therapy.
- In some cases, specialists perform a bone marrow transplant.
- Proper nutrition. First of all, an optimal drinking regime is organized. The victim should drink at least two liters of water per day. His diet should also include juices and tea. However, you should not drink at the same time as eating. The consumption of fatty, fried and overly salty foods is minimized. There should be at least five meals a day. The consumption of alcoholic beverages is strictly prohibited.
Only full compliance with all the recommendations of specialists gives the victim a chance for recovery. A period of 12 weeks is considered critical . If the victim managed to overcome it, then recovery will most likely occur.
General information
After the Chernobyl disaster, about 40 types of artificial radionuclides were released into the atmosphere. The greatest danger to humans are substances such as strontium, cesium, plutonium, and iodine. The half-life of some of them reaches 25 thousand years.
According to an organization that deals with environmental issues, radionuclides are recognized as the most toxic substances. For a long time, nuclear test sites existed on the territory of the former USSR, where nuclear weapons were tested and hazardous waste was stored. The most famous are “Mayak” and the training ground in the city of Semipalatinsk.
Preventive actions
In order to avoid becoming a victim of radiation treatment, you must adhere to the following recommendations:
- Avoid potentially hazardous areas . At the slightest suspicion that there is a maximum dose of radiation in the area, you should immediately leave this place and contact specialists.
- People employed in hazardous industries are advised to take vitamin and mineral complexes, as well as other medications that support the immune system. The choice of specific medications should be made in conjunction with your doctor.
- When contacting radioactive objects, it is necessary to use specialized protective equipment: suits, respirators, and so on.
- Drink as much water as possible. The liquid helps flush out radioactive substances from the body .
The lethal dose of radiation in sieverts is only 6 units. Therefore, at the first suspicion of an increased background, it is necessary to conduct a study using a dosimeter.
Sources of radioactive radiation
A person receives a dose of radiation from external, cosmic sources, also under the influence of internal radionuclides present in the body. The average radiation dose from external and internal sources is about 200 mrem/year.
Human industrial activity directly affects the formation of radionuclides and isotopes in the atmosphere. They are extracted from the bowels of the earth during the extraction of coal, oil, gas, and mineral fertilizers.
It is possible to be exposed to natural radionuclides even at home. Materials such as brick, wood, and concrete emit small amounts of radon.
Being in an unventilated room for a long time, a person runs the risk of receiving a large dose of this radionuclide. Potassium-40, radium-226, polonium-210, radon-222, -220 have a negative effect on health.
The degree to which a person is exposed to cosmic radiation depends on the area in which he lives. People living in the mountains have a higher risk of radiation exposure than those living in the lowlands. It is known that those who live low above sea level receive about 300 μSv/year. The reason for this is the screening properties of water. The average amount of radiation coming from space to which a person is exposed per year is 350 μSv.
How to measure
In 1895, Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered radiation with unique properties, the action of which on photographic plates, like the action of light, activated the glow of fluorescent screens. This radiation easily penetrated through opaque barriers. Roentgen carried out his experiments with a working Crookes tube.
After some time, the world was surprised to learn that the source of such radiation was not only the Crookes tube, but also substances containing uranium, which produced radiation not only invariably and continuously, but also without supplying energy from the outside.
This discovery, like the discoveries of polonium, radium and other radioactive elements, shocked the whole world! In a short period of time, scientists were able to establish a connection between radioactive decay and the transformation of one radioactive element into another and carry out the first nuclear reactions. In the process of conducting experiments, the need arose for measuring instruments and units of measurement.
To measure radiation, you need to take a certain volume of air and determine the number of ions collected in it. This can be done using an ionization chamber or a pencil-type cumulative dosimeter created on its basis. To measure the absorbed dose of radiation, you need to measure the amount of energy released in the substance. This energy is very difficult to measure directly, since most often it is released in very small quantities.
In the modern world, there are many household and professional instruments for measuring background radiation. To measure radiation using a household device that can be purchased at a specialized store, you need to turn it on and start moving around your apartment, office, cottage or any other room. The device should be brought as close as possible to granite or marble countertops, walls, interior items, tiles, radiators, etc.
Measurements can be made either on the ground or, if the measurement is carried out for medical purposes, in the tissues of the body.
They are measured with dosimeters, which after a few minutes show the power of various types of radiation (beta and gamma), as well as the absorbed dose per hour. Household appliances do not capture alpha rays.
A professional will be required; when measuring, it is necessary that the device be located near the source (difficult if you need to measure the level of radiation from the ground on which a structure is already built). To determine the amount of radon, household radon radiometers are used.
Radiation background and its types
Background radiation of natural origin includes cosmic radiation, as well as natural radionuclides that fill the water surface, the earth’s crust, and the atmosphere as a whole. Its size remained unchanged for many thousands of years. There are several areas where the magnitude of human exposure to radiation is significantly higher. This is explained by the fact that thorium or uranium ore lies shallow in the soil, and radon springs emerge.
The natural background radiation is radiation that comes from space as a result of the processing of radioactive elements located in the bowels of the Earth, in building materials, and food. The greatest danger is represented by radionuclides 40K and 222Rn. The natural radiation background formed and developed simultaneously with the development of the biosphere. Cosmogenic radionuclides participated in the formation of the Earth's crust. Shifts and depressions in it are places where radionuclides were released onto the earth's surface, the power of ionizing radiation increased. Over time, the degree of radioactivity decreased.
The natural background radiation can become technologically altered due to the transformation of ionizing radiation. The artificial radiation background is a consequence of the decay of nuclear energy waste.
Impact of radiation pollution on the human body
Any radiation that leads to the formation of electrical particles with different signs in the environment is considered ionizing. Scattered radiation background constantly accompanies a person; it is created by cosmic radiation, the influence of the sun, natural sources of radionuclides, and other components of the biosphere.
To work in hazardous conditions, personnel are protected with special suits and comply with safety standards. The body receives radiation at the workplace during physical and chemical experiments, flaw detection, medical research, geological surveys, etc.
Stories from our readers
Vladimir, 61 years old,
I clean my blood vessels every year. I started doing this when I turned 30, because the pressure was too low. The doctors just shrugged their shoulders. I had to take charge of my health myself. I tried different methods, but one helps me especially well... Read more >>>
The degree of exposure to artificial sources of radiation is illustrated in the table:
Which examination is the most dangerous?
To compare the “harmfulness” of various types of x-ray diagnostics, you can use the average effective doses given in the table. This is data from methodological recommendations No. 0100/1659-07-26, approved by Rospotrebnadzor in 2007. Every year the technology is improved and the dose load during research can be gradually reduced. Perhaps in clinics equipped with the latest devices, you will receive a lower dose of radiation.
| Body part, organ | Dose mSv/procedure | |
| film | digital | |
| Fluorograms | ||
| Rib cage | 0,5 | 0,05 |
| Limbs | 0,01 | 0,01 |
| Cervical spine | 0,3 | 0,03 |
| Thoracic spine | 0,4 | 0,04 |
| Lumbar spine | 1,0 | 0,1 |
| Pelvic organs, hip | 2,5 | 0,3 |
| Ribs and sternum | 1,3 | 0,1 |
| Radiographs | ||
| Rib cage | 0,3 | 0,03 |
| Limbs | 0,01 | 0,01 |
| Cervical spine | 0,2 | 0,03 |
| Thoracic spine | 0,5 | 0,06 |
| Lumbar spine | 0,7 | 0,08 |
| Pelvic organs, hip | 0,9 | 0,1 |
| Ribs and sternum | 0,8 | 0,1 |
| Esophagus, stomach | 0,8 | 0,1 |
| Intestines | 1,6 | 0,2 |
| Head | 0,1 | 0,04 |
| Teeth, jaw | 0,04 | 0,02 |
| Kidneys | 0,6 | 0,1 |
| Breast | 0,1 | 0,05 |
| X-ray | ||
| Rib cage | 3,3 | |
| Gastrointestinal tract | 20 | |
| Esophagus, stomach | 3,5 | |
| Intestines | 12 | |
| Computed tomography (CT) | ||
| Rib cage | 11 | |
| Limbs | 0,1 | |
| Cervical spine | 5,0 | |
| Thoracic spine | 5,0 | |
| Lumbar spine | 5,4 | |
| Pelvic organs, hip | 9,5 | |
| Gastrointestinal tract | 14 | |
| Head | 2,0 | |
| Teeth, jaw | 0,05 | |
There is no safety threshold; this was established by the scientist R. Siewert back in 1950. Specific numbers can describe a range; their impact can only be predicted approximately. Even a small, permissible dose can cause somatic or genetic changes.
The difficulty is that it is not always possible to see damage immediately; they appear some time later.
All this complicates the study of the issue and forces scientists to adhere to cautious, approximate estimates. That is why the safe level of radiation for humans is a range of values.
Human activity as a source of radiation manifestation
Since the middle of the 20th century, the level of radiation from man-made impacts has increased to 15 μR/h. This happened for a number of reasons:
- conducting nuclear weapons tests;
- combustion of fossil fuels;
- redistribution of minerals that are extracted from the earth;
- emissions of harmful substances due to accidents at nuclear power plants and enterprises.
Technogenic sources include various sources of penetrating radiation:
- medical diagnostic devices;
- X-ray equipment;
- energy and research installations;
- radiation flaw detection.
As a result of nuclear reactions, transuranium radionuclides are formed. They are characterized by increased toxicity. The most dangerous are plutonium and americium.
According to the degree of toxicity, radionuclides are divided into 4 groups:
- particularly high toxicity;
- high toxicity;
- average toxicity;
- low toxicity (do not pose a serious danger to humans).
Methods of personal protection in case of radiation contamination of the area
Standard actions have been defined for the population if there is radiation in the area. A lethal dose of radiation is life-threatening, therefore, to reduce fatalities, people are evacuated to structures, which, according to the degree of protection, are divided into permanent bomb shelters, basements, wooden buildings and cars. The first type of structure protects best; the rest are considered as emergency temporary shelters.
Effective measures include protection of respiratory organs, water and food supplies. Covering essential items is done in advance if there is a danger of release or explosion. They use anti-radiation medications and do not use fresh milk for nutrition.
Regular sanitization and disinfection of the area is carried out; at any opportunity, people are evacuated outside the contaminated area. Reducing internal exposure by eliminating dust entrapment is ensured by respirators, which are effective in 80% of cases. A four-layer gauze bandage gives a lower indicator, but use all available protective equipment. Water-repellent raincoats or, in extreme cases, plastic film are used as a cape.
In conclusion, it should be mentioned that radiation contamination of the area does not decrease; the risk of human infection is minimized by the use of personal protective equipment and monitoring the received radiation dose using dosimeters.
Radiation exposure measurement
The concept of “background radiation norm” appeared in the 20s of the last century. The permissible exposure level was 600 mSv/year. By the middle of the 20th century, this value dropped to 50 mSv/year, and in 1996, 20 mSv/year. The norm indicator was introduced for the examination of medical personnel, especially radiologists.
Man experiences the influence of radiation everywhere. A radioactive dose in a certain amount is always present in the body. When the norm of radiation in the body is exceeded many times, death can occur.
The permissible rate of radiation for humans (exposure to natural background) ranges from 0.05 μSv/hour to 0.5 μSv/hour. It is especially dangerous to be exposed to large amounts of man-made radiation. Radionuclides and isotopes accumulate in the human body, causing diseases, primarily cancer.
The radiation level is the maximum allowable dose of background ionizing radiation (measured in microsieverts). The permissible level of radiation indoors is 25 μR/h. The unit of radiation exposure is microsieverts per hour. The likelihood of developing cancer increases sharply if a person is exposed to a dose of radiation exceeding 11.42 µSv/hour. More than half of people exposed to a dose of more than 570.77 μSv at one time die within 3-4 weeks. The maximum permissible level of radiation from sources of natural origin is considered normal within the range of up to 0.57 μSv/hour. Normal background radiation, excluding the influence of radon, is 0.07 microns/hour.
Radiation poses a particular danger to persons whose professional activities involve constant exposure to radiation. Measures to prevent radiation exposure among medical personnel come down to establishing an acceptable radiation limit.
The maximum permissible concentration (MPC) of radioactive radiation is calculated based on data on the type and decay period of ionizing particles.
If a person regularly comes into contact with radioactive elements, he needs to know how to protect himself. Acceptable levels of contamination of clothing and protective equipment after disinfection have been developed and put into practice. The maximum permissible level of contamination is shown in the table below.
There is an average daily requirement for a person. It is equal to 0.0027 mlSv/day.
Where can you encounter radiation?
Radiation follows people everywhere. The earth itself has a natural radiation background. It may vary depending on the region. The highest level of radiation in our country is observed in the Altai Territory . But even it is so small that it is considered completely safe. Much more dangerous are artificially created sources of ionizing radiation, which we encounter quite often:
- X-ray equipment in hospitals. Every year we undergo fluorographic examination and are exposed to radiation. The dose of radiation in x-rays is small and a single procedure does not cause any harm to health.
- Scanning devices at airports. They work similarly to medical x-rays. The rays pass through the human body, so the radiation dose is extremely small.
- Screens of old televisions equipped with cathode ray tubes.
- Nuclear power plant reactors. This is the most powerful source. As long as it is intact, it does not pose any particular danger. But any damage to it threatens a global catastrophe.
- Radioactive waste. If they are disposed of incorrectly, the environment may be contaminated, which poses a potential danger.
A normal dose of radiation does not pose a great danger to human life or health . If it is slightly exceeded, radiation sickness develops. If a person is exposed to a large dose of radiation, instant death occurs.
Why are X-rays dangerous?
There is no safety threshold; this was established by the scientist R. Siewert back in 1950. Specific numbers can describe a range; their impact can only be predicted approximately. Even a small, permissible dose can cause somatic or genetic changes.
The difficulty is that it is not always possible to see damage immediately; they appear some time later.
All this complicates the study of the issue and forces scientists to adhere to cautious, approximate estimates. That is why the safe level of radiation for humans is a range of values.
Radiation standard is a professional term that denotes the flow of ionizing radiation to which a person is exposed in everyday life or in an emergency situation. Acceptable standards may vary, if only because the source of such a flow can be alpha particles, fragments of destroyed atoms, elementary particles or photons.
At nuclear power plants
The role of ionizing radiation is played by flows that trigger a certain reaction, which is accompanied by the release of thermal energy and the release of electrons (radiation).
The level of radiation is the breakdown of tissue under the influence of free electrons, which is accompanied by the formation of free radicals. Even more precisely, it is an indicator of the intensity of the process, its ability to lead to emissions of varying strength and direction when deviating from the norm:
- Not all types of radiation are dangerous to humans. Under natural conditions, radiation simply does not have enough energy to lead to the final destruction of the strong cellular structure provided by nature with protective mechanisms.
- Studies have shown that ultraviolet and infrared rays, visible light and radio waves, although they are streams, under natural conditions cannot cause significant harm to humans (within normal limits). To do this, it is necessary either to exceed the permissible amount, or to increase the intensity - a deviation from the norm.
- The dose of radiation is always a consequence of the passage through living tissue of electromagnetic or x-ray radiation, ions, neutrons, protons and other types of particles formed during the fission of the atomic nucleus.
Near the power plant
When we talk about radiation, we mean ionizing radiation, leading to the destruction of cells, their loss of their usual functionality and degeneration. Humanity creates reservoirs and uses them for its own purposes, for example, at nuclear power plants, in engines. There, in extreme situations, radiation doses are immediately dangerous and deviating from the norm.
In these cases, the level of radiation exposure (which does not pose a danger to tissues) is regulated using simple and accessible means of protection.
If we take into account that unstable atoms of a substance are capable of disintegrating in individual elements and leading to the appearance of ionizing radiation (radiation), then only those that are capable of causing a flow with high energy should be considered the most dangerous. Weak ones do not destroy living cells, which means they are not dangerous to humans and do not exceed the norm.
The famous Swedish scientist Sievert, after whom the unit of measurement is named, argued that there is no point in discussing the permissible level if living cells do not undergo destruction and dangerous transformations during irradiation. Radiation level is mentioned when it leads to damage and death, exceeding the permissible norm.
Emblem
Amateurs confuse these two concepts with a similar sound and a common root, although they have different meanings. Radiation is radiation, but in professional circles this term refers only to strong, charged flows that have a pronounced ability to destabilize or negatively transform the cellular structure.
Level of radiation pollution in Japan
Radioactivity is not radiation yet, it is only the potential ability of a substance to emit strong or weak streams of ionizing particles mixed with strong electromagnetic radiation, which exceeds the permissible norm for humans.
This occurs when a relatively stable system is disrupted as a result of any influences. So in order for irradiation to occur, two conditions are necessary - destabilization of the substance with the subsequent release of a flux and the entry of this flux into a living cell.
Possible consequences of exposure
Radioactivity is the existing potential, radiation is a consequence of its implementation, and irradiation is the direct effect of ions on the tissues of a living organism when the norm is exceeded.
The cell can easily withstand the permissible norm. Radiation is obtained during a medical examination in the city, during certain professional activities. Much in the development of events depends on the type and ability of ionizing particles to penetrate, release energy and form free radicals, and deviate from the permissible norm.
Safety standards
Humanity relatively recently acquired the first knowledge in this area, but types of radiation have long been the subject of study in the school curriculum. Alpha particles were first produced artificially through the ionization of helium.
Permissible doses throughout the year
They penetrate the atmosphere from space and are not dangerous to humans. Only where the protective earth's shell ends (high in the mountains, for example), can they lead to the development of radiation sickness, getting into important vital systems.
Artificially created flows can lead to radiation exposure if safety measures are not followed or at high intensity.
Beta particles move at high speeds, act both outside and inside the body, and can be positive or negative. Irradiation with gamma particles causes neoplasms and radiation damage. For neutron radiation to become dangerous, certain conditions are required.
Sources of radiation
However, it is necessary to ensure that it does not exceed the permissible limit. Irradiation with the maximum permissible dose can also lead to irreversible consequences, regardless of whether it is hard or soft.
Radiation of natural origin is created by nature without the provoking influence of man. It arrives by overcoming the protective layer - the atmosphere. Some mineral deposits have the ability to deposit radiation.
Medical effects of radiation
In different settlements, the increased level can be explained by location, artificial sources that appeared as a result of human activity. In apartments it is less than on the streets, due to the protective abilities of the walls and roof.
However, being in residential premises does not always help to escape from a lethal dose in the event of a man-made disaster or mass destruction. There are cases when the level in a residential area increased even within an hour.
Anything that exceeds the upper limit of the norm is already classified as dangerous. If it continues from year to year, the person habitually does not attach importance to the symptoms. The immediate threat is a level of 3 thousand mSv. A person goes bald, loses the ability to procreate, and already a thousand can lead to radiation sickness. Against the background of 3.5–5 thousand, you can die in a month.
In the forest,
the ten thousand mSv/hour mark means a guaranteed lethal dose. Although this concept is conditional, since it was noted that this figure of excess of the norm may depend on the individual characteristics of the human body.
During the procedure, X-rays, penetrating tissues and organs, can cause changes in the cellular structure. The consequences of radiographs are expressed in the development of diseases, including those of genetic origin.
The x-ray method has the greatest impact on the body’s circulatory system and in particular on the red bone marrow.
Exceeding the permissible radiation dose, you may encounter the following problems:
- Leukemia. Otherwise, the disease is called “blood cancer” and is characterized by a decrease in the number of leukocytes in the body, as well as a change in their composition. This has a detrimental effect on human immunity, resistance to various diseases decreases, all organs suffer, and basic vital processes are disrupted.
- Reversible processes. Appear when the radiation dose is higher than the minimum permissible.
- Erythrocytopeia. The disease manifests itself through an acute lack of oxygen in the tissues and is provoked by a sharp decrease in the number of red blood cells.
- Hemolytic irreversible processes. In this case, the harmfulness reaches its peak and can lead to human death.
After exposure to X-rays, the following processes may occur:
- Oncology. By changing the structure of cells, x-rays provoke the development of cancer. A single dose of radiation increases the chance of tumor formation by 0.001%.
- Eye problems. Each, even minimal dose of radiation disrupts the condition of the eye lens, which in the future may result in cataracts and other ophthalmological pathologies.
- Aging. One of the main reasons why you should not take x-rays often is considered to be premature aging. And this process concerns not only the cells of the epidermis, which is expressed in external changes, internal organs also age.
X-ray for children
Radiology is prescribed for a child as a last resort, when there is no access to other diagnostic methods, and the time to establish a diagnosis is running out.
The permissible x-ray dose for a child depends on the nature of the disease and the frequency of examination. Some doctors do not recommend X-raying children under 14 years of age, and in case of emergency, using radiation more than once a year.
Pros, cons and other aspects associated with performing x-ray examinations for children. Filmed by the Doctor Komarovsky channel.
X-rays do not have such a detrimental effect on an adult body as they do on a child’s body. Functional X-ray examination may cause side effects and impair the patient's functioning only if used frequently.
Causes of radioactive contamination
The action of various factors and circumstances causes increased background radiation:
- the fallout of a radioactive substance from a nuclear cloud during an explosion;
- when induced radiation occurs, obtained by the formation of radioactive isotopes during the instantaneous action of gamma rays and neutrons released during a nuclear explosion;
- exposure to external radiation of gamma and beta rays;
- fatal is manifested by internal irradiation after radioactive isotopes enter the human body from the air or with food;
- is provoked in peacetime by man-made disasters at nuclear facilities, improper transportation and disposal of nuclear waste.