Views: 42791
Atomic energy is quite actively used for peaceful purposes, for example, in the operation of an X-ray machine and an accelerator installation, which made it possible to distribute ionizing radiation in the national economy. Considering that a person is exposed to it every day, it is necessary to find out what the consequences of dangerous contact can be and how to protect yourself.
What is ionizing radiation?
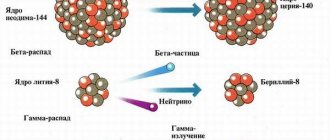
The release of harmful ionizing radiation occurs after the chemical decay of radioactive elements. The most common are gamma, beta and alpha rays. When radiation enters the body, it has a destructive effect on humans. All biochemical processes are disrupted under the influence of ionization.
Types of radiation:
- Alpha rays have increased ionization, but poor penetrating ability. Alpha radiation hits human skin, penetrating to a distance of less than one millimeter. It is a beam of released helium nuclei.
- Electrons or positrons move in beta rays If a person appears near the source, beta radiation will penetrate deeper than alpha radiation, but the ionizing ability of this species is much less.
- One of the highest-frequency electromagnetic radiations is the gamma-ray variety , which has increased penetrating ability but very little ionizing effect.
- X-rays are characterized by short electromagnetic waves that are produced when beta rays come into contact with matter.
- Neutron - highly penetrating beams of rays consisting of uncharged particles.
Features of radiation registration
The characteristics of ionizing radiation show that they are invisible, odorless and colorless, so they are difficult to notice.
For this purpose, there are methods for recording ionizing radiation. As for the methods of detection and measurement, everything is done indirectly, using some property as a basis.
The following methods for detecting ionizing radiation are used:
- Physical: ionization, proportional counter, gas-discharge Geiger-Muller counter, ionization chamber, semiconductor counter.
- Calorimetric detection method: biological, clinical, photographic, hematological, cytogenetic.
- Luminescent: fluorescent and scintillation counters.
- Biophysical method: radiometry, calculation.
Dosimetry of ionizing radiation is carried out using instruments; they are able to determine the radiation dose. The device includes three main parts - a pulse counter, a sensor, and a power source. Radiation dosimetry is possible thanks to a dosimeter or radiometer.
Sources of ionizing radiation
Sources of ionizing radiation can be air, water and food. Harmful rays occur naturally or are created artificially for medical or industrial purposes. There is always radiation in the environment:
- comes from space and makes up a large part of the total percentage of radiation;
- radiation isotopes are freely found in familiar natural conditions and are contained in rocks;
- Radionuclides enter the body with food or by air.
What happens to the human body when exposed to ionizing radiation?
The destructive effect of ionizing radiation on the human body is explained by the ability of radioactive ions to react with cell components. It is well known that eighty percent of man consists of water. When irradiated, water decomposes and hydrogen peroxide and hydrate oxide are formed in cells as a result of chemical reactions.
Subsequently, oxidation occurs in the organic compounds of the body, as a result of which the cells begin to collapse. After a pathological interaction, a person’s metabolism at the cellular level is disrupted. The effects can be reversible when exposure to radiation was insignificant, and irreversible with prolonged exposure.
The effect on the body can manifest itself in the form of radiation sickness, when all organs are affected; radioactive rays can cause gene mutations that are inherited in the form of deformities or severe diseases. There are frequent cases of degeneration of healthy cells into cancer cells with the subsequent growth of malignant tumors.
Consequences may not appear immediately after interaction with ionizing radiation, but after decades. The duration of the asymptomatic course directly depends on the degree and time during which the person received radiation exposure.
The concept of “non-ionizing radiation”
It is well known from the physics course that energy propagates in the form of small particles and waves, the process of emission and propagation of which is called radiation .
There are 2 main types of radiation based on their effects on objects and living tissues :
- Ionizing radiation . These are streams of elementary particles formed as a result of the fission of atoms - radioactive radiation, alpha, beta, gamma, x-rays. This type of radiation includes gravitational radiation and Hawking ;
- Non-ionizing radiation . In essence, these are electromagnetic waves with a length greater than $1000$ nm and released energy less than $10$ keV. Radiation occurs in the form of microwaves, releasing light and heat.
Non-ionizing radiation, unlike the first, does not break the bonds between the molecules of the substance it affects. But, it must be said that there are exceptions here, for example, UV rays can ionize a substance. Electromagnetic radiation includes high-frequency X-rays and gamma rays, only they are harder and ionize matter.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Non-ionizing fields and radiation 450 rub.
- Abstract Non-ionizing fields and radiation 250 rub.
- Test work Non-ionizing fields and radiation 220 rub.
Get completed work or advice from a specialist on your educational project Find out the cost
The rest of the electromagnetic radiation is non-ionizing and cannot interfere with the structure of matter, because there is not enough energy for this. Visible light and UV radiation are also non-ionizing, and light radiation is often called optical radiation . It is formed when bodies are heated and its spectrum is close to infrared rays.
Infrared radiation is widely used in medical practice. It is used to improve metabolism, stimulate blood circulation, and disinfect food. However, excessive heating leads to drying of the mucous membrane of the eye, and the maximum radiation power can destroy the DNA molecule.
Ultraviolet radiation, which is close to X-rays, may have the ability to ionize UV rays can cause various mutations, burns of the skin and cornea of the eyes. Medicine synthesizes vitamin D3 in the skin using UV rays. With their help, water and air are disinfected and equipment is sterilized.
Non-ionizing electromagnetic radiation can be of natural or artificial origin. The natural source is the Sun, which sends out all types of radiation. They do not reach the surface of the planet in full. Thanks to the Earth's atmosphere, the ozone layer, humidity, and carbon dioxide, their harmful effects are mitigated. Lightning and space objects can become natural sources of radio waves. Any body heated to the required temperature is capable of emitting thermal infrared rays, despite the fact that the main radiation comes from artificial objects. In this case, the main sources include heaters, burners, and incandescent lamps found in every home.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
Since radio waves are transmitted through any electrical conductors, all electrical appliances become artificial sources .
The strength of electromagnetic radiation depends on wavelength, frequency and polarization. Longer waves transfer less energy to an object and are therefore less harmful.
Human exposure to non-ionizing radiation has two sides: long-term exposure is harmful to health, moderate doses can be beneficial .
Biological changes in the human body under the influence of rays
Exposure to ionizing radiation entails significant biological changes in the human body, depending on the extent of the area of skin exposed to radiation energy, the time during which the radiation remains active, as well as the condition of organs and systems.
To indicate the strength of radiation over a certain period of time, the unit of measurement is usually considered to be the Rad. Depending on the magnitude of the missed rays, a person may develop the following conditions:
- up to 25 rad – general health does not change, the person feels good;
- 26 – 49 rad – the condition is generally satisfactory; at this dosage, the blood begins to change its composition;
- 50 – 99 rad – the victim begins to feel general malaise, fatigue, bad mood, pathological changes appear in the blood;
- 100 – 199 rad – the exposed person is in poor condition, most often the person cannot work due to deteriorating health;
- 200 – 399 rad – a large dose of radiation, which develops multiple complications and sometimes leads to death;
- 400 – 499 rad – half of the people who find themselves in a zone with such radiation values die from frolicking pathologies;
- exposure to more than 600 rad does not give a chance for a successful outcome, a fatal disease takes the lives of all victims;
- a one-time exposure to a dose of radiation that is thousands of times greater than the permissible figures - everyone dies directly during the disaster.
Impact of electromagnetic fields on humans
Electromagnetic fields, one way or another, have an effect on humans.
This impact is due to:
- electric and magnetic field strength;
- energy flux density;
- vibration frequency;
- irradiation mode;
- size of the irradiated body surface;
- individual characteristics of the body.
Compounding the danger of exposure to radiation is the fact that the human senses cannot detect it. A person is exposed to an electrostatic field (ESF) in the form of a weak current of several microamps passing through him, without observing electrical injuries. But people may have a reflexive reaction to electric current, in which case mechanical injury , for example, you can hit structural elements located nearby. The central nervous system, analyzers, and cardiovascular system are quite sensitive to electrostatic fields. Irritability, headache, sleep disturbances are the manifestations that are observed in people working in the area exposed to ESP.
Magnetic fields (MF) can operate continuously or intermittently, the degree of impact of which depends on how strong the field is in the space near the magnetic device. The dose received depends on where the person is located in relation to the MP and his work schedule. Visual sensations are noted under the influence of an alternating magnetic field , but when the influence ceases, these sensations disappear. Serious violations occur in conditions of chronic exposure to MPs exceeding the maximum permissible levels. In this case, dysfunction of the central nervous system, cardiovascular and respiratory systems, and digestive tract is observed, and changes occur in the blood. The rhythm is disrupted and the heart rate slows down with constant exposure to industrial frequency EMF.
The human body, consisting of atoms and molecules, is polarized under the influence of electromagnetic fields in the radio frequency range, and the following occurs:
- Polar molecules, for example, water molecules, are oriented in the direction of propagation of the electromagnetic field;
- After exposure, ionic currents appear in electrolytes, and these are the liquid components of tissues and blood;
- Human tissues heat up, which is caused by an alternating electric field. This occurs both due to the variable polarization of the dielectric and due to the emerging current conductivity.
A consequence of the absorption of electromagnetic field energy is the thermal effect . With increasing tension and exposure time, these effects become more pronounced.
Electromagnetic fields have a stronger and more intense effect on organs containing large amounts of water and will be approximately $60$ times higher compared to the impact on organs with low water content. If the length of the electromagnetic wave is increased, then the depth of its penetration increases. Tissues are heated unevenly as a result of differences in dielectric properties, macro and micro thermal effects with temperature differences occur. An underdeveloped vascular system will experience shock, which will manifest itself in insufficient blood circulation to the eyes, brain, kidneys, stomach, gallbladder, and bladder.
One of the few specific lesions that are caused by electromagnetic radiation is the eyes and the possible development of cataracts. This damage is caused by electromagnetic radiation of radio frequencies in the range of $300$ MHz... $300$ GHz at an energy flux density above $10$ mW/sq. see. Characteristic of long-term exposure to EMFs of various wavelength ranges are considered to be functional disorders in the central nervous system with often pronounced changes in endocrine metabolic processes and blood composition; performance, as a rule, decreases. The changes are reversible only at an early stage.
What are the dangers of the human body being exposed to ionizing rays?
One-time or regular exposure of radiation to the human body has the property of accumulation and subsequent reactions over a period of time from several months to decades:
- inability to conceive a child, this complication develops in both women and men, making them sterile;
- the development of autoimmune diseases of unknown etiology, in particular multiple sclerosis;
- radiation cataract, leading to vision loss;
- the appearance of a cancerous tumor is one of the most common pathologies with tissue modification;
- diseases of an immune nature that disrupt the normal functioning of all organs and systems;
- a person exposed to radiation lives much shorter;
- the development of mutating genes that will cause serious developmental defects, as well as the appearance of abnormal deformities during fetal development.
Remote manifestations may develop directly in the exposed individual or be inherited and occur in subsequent generations. Directly at the sore spot through which the rays passed, changes occur in which the tissues atrophy and thicken with the appearance of multiple nodules.
This symptom can affect the skin, lungs, blood vessels, kidneys, liver cells, cartilage and connective tissue. Groups of cells become inelastic, harden and lose the ability to fulfill their purpose in the body of a person with radiation sickness.
Fallout
A serious problem of our time associated with recent tragedies at nuclear power plants is the spread of radioactive rain. Emissions of radiation into the atmosphere result in the accumulation of isotopes in the atmospheric liquid - clouds. When there is an excess of liquid, precipitation begins, which poses a serious threat to crops and humans.
The liquid is absorbed into agricultural lands where rice, tea, corn, and cane grow. These crops are typical for the eastern part of the planet, where the problem of radioactive rain is most pressing.
Ion radiation has less of an impact on other parts of the world because precipitation does not reach Europe and the island nations in the UK area. However, in the USA and Australia, rain sometimes exhibits radiation properties, so you need to be careful when purchasing fruits and vegetables from there.
Radioactive fallout can fall over bodies of water, and then the liquid can enter residential buildings through water treatment channels and water supply systems. Treatment facilities do not have equipment sufficient to reduce radiation. There is always a risk that the water you take is ionic.
How to protect the human body from radiation?
Determining effective protection from harmful rays is the basis for preventing damage to the human body in order to avoid the occurrence of negative consequences. To save yourself from radiation exposure you must:
- Reduce the time of exposure to isotope decay elements: a person should not stay in the danger zone for a long period. For example, if a person works in a hazardous industry, the worker’s stay in the place of energy flow should be reduced to a minimum.
- To increase the distance from the source, this can be done by using multiple tools and automation tools that allow you to perform work at a considerable distance from external sources with ionizing energy.
- It is necessary to reduce the area on which the rays will fall with the help of protective equipment: suits, respirators.
Natural sources of radiation
Mineral rocks pose the main danger to humans. In their cavities, the largest amount of radioactive gas, radon, invisible to human receptors, accumulates.
It is naturally released from the earth's crust and is poorly recorded by testing instruments. When supplying building materials, contact with radioactive rocks is possible, and as a result, the process of ionization of the body.
You should be wary of:
- granite;
- pumice;
- marble;
- phosphogypsum;
- alumina.
These are the most porous materials that best retain radon. This gas is released from building materials or soil.
It is lighter than air, so it rises to great heights. If, instead of the open sky, an obstacle is found above the ground (canopy, roof of a room), the gas will accumulate.
High saturation of air with its elements leads to irradiation of people, which can only be compensated for by removing radon from residential areas.
To get rid of radon, you need to start simple ventilation. You should try not to inhale the air in the room where the infection occurred.
Registration of the occurrence of accumulated radon is carried out only with the help of specialized symptoms. Without them, a conclusion about the accumulation of radon can only be made on the basis of non-specific reactions of the human body (headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, darkening of the eyes, weakness and burning).
If radon is detected, a team from the Ministry of Emergency Situations is called to eliminate the radiation and check the effectiveness of the procedures performed.