FOS or organophosphorus compounds are toxic substances used as pesticides, herbicides, and for deratization measures. Typical representatives of the group: Dichlorvos, Karbofos, Metaphos. The lethal dose is 2 g when taken orally.
What are the symptoms of damage from phosphorus compounds? Is there an antidote for phosphate poisoning? How to provide first aid to a victim?
Phosphorus poisoning
Phosphorus is a common chemical element, a non-metal.
Free phosphorus does not occur in nature due to its high chemical activity. There are about 180 minerals that contain phosphorus in a bound form; the most important are apatites and phosphates. The bulk of mined phosphorus is transformed into oxide (P2O5) and the corresponding acid (H3PO4), which are actively used in industry for the production of various products:
- phosphate fertilizers;
- mineral feed for livestock;
- pesticides;
- technical salts (phosphates);
- incendiary and smoke shells, fireworks;
- match production;
- alloys of various metals;
- incandescent lamps (as a gas absorber);
- chemical warfare agents (sarin, soman, V-gases).
Phosphorus is the most important biogenic element necessary for the adequate functioning of the body. Present in living cells in the form of orthophosphoric and pyrophosphoric acids and their derivatives, it is part of a number of organic compounds: nucleotides, nucleic acids, phospholipids, coenzymes, etc.
The value of the element, firstly, is due to its ability to form specific bonds in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine phosphate, which are energy accumulators in the body.
Secondly, the presence of a phosphoryl residue in an organic compound (phosphorylation process) allows this substance to be involved in metabolic processes, while the cleavage of the phosphoryl residue (dephosphorylation) excludes the compound from active metabolism.
Thirdly, phosphorus is necessary for the construction of bone (hydroxylapatite) and dental (fluorapatite) tissue.
The daily need for phosphorus is 1–1.2 g, for children and adolescents – 1.5–2.5 g. With intense exercise, the need for the microelement increases.
Elemental phosphorus is represented by several modifications: white (in its crude form it is called yellow phosphorus), red and black.
Red and black phosphorus are fairly stable forms of the substance; they have low volatility, poor solubility in water and, as a result, low toxicity. Black is practically safe, but red phosphorus dust can cause chronic intoxication.
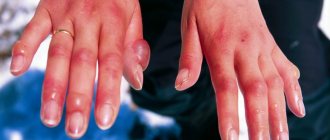
White phosphorus is extremely toxic, has a specific garlic odor, and smolders in air. It can cause poisoning not only when ingested, but also when in contact with the skin. A characteristic feature is the ability to spontaneously combust upon contact with skin (due to high solubility in fats), which leads to the formation of severe damage. The lethal dose of white phosphorus is 50–150 mg.
The ability to spontaneously ignite determines the specific storage of the substance: under a layer of water or an anti-freezing solution in the absence of light.
What is phosphoric acid?
Phosphoric acid is an inorganic mineral acid that is colorless and odorless.
The chemical formula of phosphoric acid is H₃PO₄. It is also called phosphoric acid.
It can be a liquid or a clear crystalline solid that is corrosive to metals as well as human tissue.
Other facts about this acid (especially for science buffs):
- Phosphoric acid p = 1.5
- Density of phosphoric acid = 1.8741
- Boiling point of phosphoric acid = 158°C
- Phosphoric acid charge = 0
Why is phosphoric acid found in cola and other foods we eat? Food and beverage manufacturers like phosphoric acid. Because it is cheap, adds tartness and acts as a preservative.
The food industry continues to include phosphate additives in food products. For example, bottled black tea can become a high phosphate drink due to additives from the manufacturer.
Dark-colored carbonated drinks, such as cola, typically contain more than other carbonated drinks. One container of baking soda can contain up to 500 milligrams of this acid. The exception is dark-colored beer. It usually contains very little of this acid.
Why do food and beverage manufacturers use this chemical in the first place? They use it to give their processed foods a sharper, tangier flavor.
Plus, it also acts as a preservative.
There are many common uses of phosphoric acid. This compound is found in colas, bottled and canned iced teas, coffee drinks, and breakfast cereal bars. Also in non-dairy creamers and improved chicken and meat products.
The use of phosphoric acid in food and drink is legal. It is also allowed to regulate the pH level in processed cheeses and other dairy products.
Phosphoric acid may be indicated on labels as follows:
- E338
- orthophosphoric acid
- phosphoric(V) acid
- pyrophosphoric acid
- triphosphoric acid
- o-phosphoric acid
- hydrogen phosphate
Scientific research confirms that taking this acid may have a number of possible health effects. Although there are many common uses of phosphoric acid.
How does phosphorus poisoning occur?
Phosphorus poisoning is usually industrial in nature and is possible in the following cases:
- emergency situation;
- unprotected industrial contact with vapors and dust;
- obtaining phosphorus by electrothermal sublimation;
- processing of white phosphorus into red;
- violation of safety regulations at the workplace in production where phosphorus compounds are used.
In addition to professional poisoning, household poisoning is possible during the manufacture or use of phosphorus-containing pesticides to control rodents, accidental ingestion (including by children), or the intentional ingestion of phosphorus and its compounds for suicidal purposes.
Removing rust from the surface of bathtubs, toilets and washbasins
Orthophosphoric acid can also be used as household chemicals. It does an excellent job of cleaning traces of rusty water in toilets and enamel bathtubs. This product is not suitable only for acrylic bathtubs.
Application for earthenware and enamel surfaces:
- 100 g of 85% acid should be added to 500 ml of water;
- degrease the surface with any detergent;
- Use a brush with natural bristles to treat the contaminated surface;
- after a few hours (from 1 to 12 - depends on the accumulation of oxides), wash off the acid with a solution of soda - 1 tbsp. spoon per liter of water.
When working with acid, do not forget about safety rules. Do not allow the chemical to come into contact with your skin, and if it does, wash immediately with warm water and soap.
Symptoms of poisoning
Poisoning can occur in both acute and chronic forms. Symptoms of acute intoxication appear within a few minutes, less often - several hours after contact with phosphorus.
Mortality from poisoning is 20–50%; as a rule, parenchymal organs (liver, kidneys), nervous and cardiovascular systems are affected; the prognosis is unfavorable at a dose above 1 mg/kg body weight.
Phosphorus intoxication has three stages, with manifestations varying depending on the severity: from mild to very severe.
At the initial stage of poisoning, the victim complains from the gastrointestinal tract; the second stage lasts several days and is characterized by subsidence of symptoms and a period of imaginary well-being; at the final stage of poisoning, signs of liver, kidney and heart failure appear.
Symptoms of mild poisoning:
- burning and sharp pain along the esophagus and in the stomach area;
- nausea, vomiting, belching;
- vomit glows in the dark and has a pungent odor of garlic;
- headache;
- feeling of general malaise, weakness;
- dryness of the oral mucosa, thirst;
- cramping pain in the umbilical region;
- bowel disorders (diarrhea, often constipation).
In case of poisoning of moderate severity, signs of toxic damage to the central nervous system are added:
- intense motor and emotional excitement;
- as intoxication progresses, excitement is replaced by confusion and depression of consciousness;
- persistent constriction of the pupils, possible anisocoria (different pupil sizes in the right and left eyes);
- delirious syndrome;
- muscle tics, clonic-tonic convulsions.
Severe and extremely severe poisoning, in addition to the listed symptoms, is manifested by diffuse dystrophic damage to the liver and kidneys. Symptoms of liver and kidney failure (yellowness of the skin, mucous membranes and sclera, ascites, vomiting with bile, decreased diuresis) are combined with signs of acute heart failure (general weakness, drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, sharp decrease in pulse, shortness of breath at rest , moist wheezing, cough with pink frothy sputum). Death in this case occurs in the period from the first day (more than 50% of victims) to the end of the first week. If the outcome is favorable, the victim recovers within a few weeks.
In industrial conditions, chronic intoxication with phosphorus and its compounds is more common. They usually manifest themselves as pathological changes in the bones of the jaws (usually the lower ones), starting with a typical toothache. After tooth extraction or treatment, the pain syndrome does not stop, but becomes more diffuse and intense over time, and becomes permanent. X-ray examination reveals areas of bone loss and bone destruction. Subsequently, necrosis of the affected jaw develops, accompanied by symptoms of general intoxication, and a secondary infection may occur.
In addition to damage to the jaw, chronic phosphorism can manifest itself with such nonspecific symptoms as general weakness, decreased appetite, weight loss, systematic headache, chronic laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, anemia.
Symptoms of excess phosphorus in the body
When an element enters the body in large quantities exceeding the required norm, it accumulates in tissues and organs. This causes a number of serious diseases. An excessive amount of it will be indicated by certain signs, which include:
- deposition of phosphates in bone tissue;
- leaching of calcium and development of osteoporosis (bone fragility);
- the appearance of subcutaneous hemorrhages;
- frequent bleeding;
- development of iron deficiency anemia;
- decrease in the number of white blood cells;
- the appearance of kidney stones;
- intestinal inflammation and liver damage.
An excess of phosphorus in tissues affects the body's absorption of calcium, which is removed from bone tissue and deposited in the form of salt in the kidneys, thereby provoking the further development of kidney stones. All this leads to the emergence of a number of diseases affecting the digestive and hematopoietic systems.
An excess of phosphates can occur when there is a predominance of grain products, fish and meat dishes in the diet. In this case, the very first symptom will be a burning sensation in the palms and numbness of the muscles. If these signs appear, it is important to review your diet and reduce your consumption of these foods.
First aid for phosphorus poisoning
- In case of acute phosphorus vapor poisoning, it is necessary to evacuate the victim from the affected area, interrupting contact with the toxin.
- Rinse exposed skin generously with a 5% solution of copper sulfate or a 3% solution of hydrogen peroxide.
- Provide alkaline drinking [still alkaline mineral water, 2% baking soda solution (1 teaspoon of soda per 200 ml of water)].
- Gastric lavage (drink 1-1.5 liters of warm water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate and induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue) is recommended to be carried out repeatedly until the lavage water is clean and the characteristic odor disappears in the vomit.
- Take a saline laxative (Magnesium sulfate).
- Take enterosorbent (Enerosgel, Polyphepan, Lactofiltrum, Polysorb or any other).
- If phosphorus gets on the skin, take measures to extinguish it, remove any remaining substance, apply a damp bandage soaked in a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Effect on the body
The E338 additive is intensively used in the food industry in many countries around the world. However, scientific research has shown that phosphoric acid has a negative effect on the human body and this manifests itself as follows:
TREAT THE CAUSE, NOT THE EFFECT! Nutricomplex, a product made from natural ingredients, restores proper metabolism in 1 month.
- the acid-base balance is disturbed, resulting in an increase in acidity, and this is fraught with the development of early osteoporosis and caries;
- with excessive consumption of food products that contain the E338 additive, an aversion to food may develop and, as a result, weight loss;
- Acute phosphoric acid poisoning causes symptoms such as vomiting, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness and difficulty breathing.
On a note! When phosphoric acid gets on exposed skin, it causes burns, on the mucous membrane of the eyes it causes a burning sensation, and when inhaled, severe coughing attacks begin. Its vapors, with prolonged exposure, irritate the nasal mucosa, which leads to nosebleeds and the initiation of atrophic processes, in rare cases this can lead to changes in the blood formula and tooth decay! However, this is only possible when working with this substance in its pure form. Under domestic conditions, when in contact with food products that contain this additive, such consequences are impossible!
Gaseous water is carbonated water. This causes gastric secretion, increases the acidity of gastric juice and causes flatulence. Filtered tap water is mainly used. Cyclamate is a synthetic chemical that is 200 times sweeter than sugar and is thus used as a sweetener. 200 times sweeter than sugar, contains methyl ester. This makes it difficult for the cardiovascular system to function. It also contains aspartic acid, which can cause irritation to our nervous system and if consumed over a long period of time can lead to addiction.
Prevention
- Complete sealing of production procedures, organization of adequate ventilation.
- Strict compliance with technological process requirements.
- Compliance with safety precautions in the workplace.
- Mandatory regular preventive medical examinations for employees of enterprises in contact with phosphorus and its compounds.
- Refusal to eat and smoke in industrial premises.
- Use of personal protective equipment (respirator, gloves, protective clothing) when working with phosphorus-containing pesticides.
- Storing phosphorus-containing compounds at home out of the reach of children.
Education: higher education, 2004 (State Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “Kursk State Medical University”), specialty “General Medicine”, qualification “Doctor”. 2008-2012 – postgraduate student of the Department of Clinical Pharmacology, KSMU, Candidate of Medical Sciences (2013, specialty “pharmacology, clinical pharmacology”). 2014-2015 – professional retraining, specialty “Management in Education”, Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education “KSU”.
The information is generalized and is provided for informational purposes. At the first signs of illness, consult a doctor. Self-medication is dangerous to health!
source
How to properly store and transport phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid is an aggressive agent, so it is necessary to follow certain rules when transporting and storing this substance. The powder must be placed in an airtight container. To prevent foreign elements from getting into the acid, all containers must be used clean and dry, then the prepared solution will be of high quality.
Preparing a low-quality composition can result in dangerous vapor poisoning or lack of the desired result. Store containers with acid in a dry and warm place where there is no dampness or condensation. There is no need to pour the powder into another container; it is better to leave it in the original packaging. Such cargo is considered dangerous, so special documentation is required to transport it over long distances.
Cleaning is done with care so that the metal surface does not become too thin and holes are formed. During preliminary mechanical cleaning, disks with large elements cannot be used, otherwise significant damage to the surface can be caused.
Before starting the main work, the remaining surface must be covered with film, since exposure to such a strong product may damage the rest of the coating. Therefore, processing must be carried out carefully so that the damaged surface does not have to be restored, which will lead to additional costs.
If the work is done correctly, the result is a reliable and durable surface that does not contain rust stains, which lead to the destruction of metal products.
When applying orthophosphoric acid to a surface, it is necessary to wear gloves and a respirator; they serve as means of protection against the harmful substance. If acid gets on clothing, it must be removed immediately so that the product does not get on the skin and cause a burn.
White phosphorus poisoning
White phosphorus is a colorless, soft, waxy mass that turns yellow in the light, easily oxidizes and spontaneously ignites.
Enters the body through the respiratory system, gastrointestinal tract and skin (for burns). It is excreted through the lungs, gastrointestinal tract and sweat. Acute industrial poisoning (vapors) is very rare.
Strong poison. It has a local cauterizing and general resorptive effect. In acute poisoning, it affects the heart and causes fatty degeneration of internal organs, primarily the liver (acute yellow liver atrophy). Chronic exposure leads to disturbances in mineral metabolism. Phosphorus poisoning occurs in the production of phosphorus bronze and various flammable mixtures. MPC of phosphorus - 0.03 mg/m3.
Phosphorus compounds around us
We will talk about chemicals that in industry and in everyday life are called FOS (FOV). Organophosphorus compounds are a group of complex substances that include phosphoric acids.
Where are organophosphorus compounds used?
- In agriculture for processing orchards, vineyards, vegetables and grain crops.
- To combat animal parasites.
- In service with the army as chemical warfare agents (sarin, soman and V-gases).
- In medical practice (drops in ophthalmology, in surgery, drugs to normalize the functioning of the muscles of the gastrointestinal tract, in the treatment of head lice).
Anyone can encounter one of the phosphorus derivatives in their life without knowing it. Therefore, you need to be fully prepared if FOS poisoning occurs.
Organophosphorus compounds are most often solid or liquid volatile substances, most of which have a specific kerosene-garlic odor. Well soluble in fats and poorly soluble in water. The toxicity of aqueous solutions at a temperature of 35° C per day increases up to 35 times.
Organophosphorus compounds are part of many things that people encounter every day in life. They enter the body mainly through the respiratory tract, digestive system or skin. Poisoning with organophosphorus compounds occurs when consuming contaminated water, food products treated with such substances, or when FOS comes into contact with the skin during the treatment of premises, clothing and linen.
Symptoms
Acute poisoning
In case of vapor poisoning: headache, dizziness, nausea, bradycardia. In severe cases - excitement, followed by depression of the nervous system. Symptoms of myocardial infarction, heart failure, possible collapse. After a few days, hepatitis develops.
When taken orally: dizziness, abdominal pain, vomiting of glow-in-the-dark masses that emit a garlicky odor. Collapse may occur before the development of gastrointestinal disorders. In severe cases, acute yellow liver atrophy develops after 2-3 days. Weakness, subcutaneous hemorrhages, hematuria, nephritis. Excitement, insomnia, hallucinations. Decreased cardiac activity, drop in body temperature, collapse, coma. Death is possible on the 7th day and later. Lethal dose - 0.05-0.15 g.
Chronic poisoning
Headaches, general weakness, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea, pain in the limbs, irritability. Chronic rhinitis, laryngotracheitis, bronchitis, sometimes gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontal disease, caries; chronic gastritis, hepatitis. Functional disorders of the central nervous system. Typical changes in the bones: thickening and loosening of the periosteum, osteoporosis; in adolescents and young adults - transverse striations of the epiphyses.
The old literature described “phosphorus” necrosis of the jaw, beginning as ordinary apical or marginal periodontitis with pain, swelling of the gums and loosening of the tooth, followed by suppuration and periostitis. Currently, “phosphorus” necrosis practically does not occur.
Contact of phosphorus on the skin, due to its rapid ignition, causes severe burns.
Are you one of those millions of women who struggle with excess weight?
Have all your attempts to lose weight been unsuccessful?
Have you already thought about radical measures? This is understandable, because a slim figure is an indicator of health and a reason for pride. In addition, this is at least human longevity. And the fact that a person who loses “extra pounds” looks younger is an axiom that does not require proof.
To prove that cola is not found in the human body, here are 20 practical ways to use cola as a cleanser. Removes greasy stains from clothes and fabrics. Removes rust; Even the rusty screws are loosened. Removes blood stains from clothing and fabric. Cleans oil stains from garage floors; Leave the stain and rinse. Kill the snails; acids kill them. Cleans burnt pots; Let the cola soak into the pan and then rinse it out. Decalcifies the teapot. Cleans the engine; Cola dealers have been using this technique for decades.
Chemical formula: P2O5nH2O. International terminology: phosphoric acid Packaging and delivery: in cans. Price: piecework-negotiable. Concentration: (75.85%)
Orthophosphoric acid is a yellow solution in appearance; at 20 degrees Celsius it behaves like a solid material (colorless hygroscopic crystals), when temperatures above 213° Celsius it turns into pyrophosphoric acid H4P2O7. Orthophosphoric acid is supposed to be considered an 85 percent water-based solution (colorless and odorless liquid).
Makes pennies; Soak old pennies in Coke and they won't work anymore. Removes chewing gum from hair; dip it in a small bowl of cola, let it sit for a few minutes. The gum will flake off. Removes stains from porcelain. Do you have a dirty pool? Add 2 liter bottles of cola and remove rust. You can remove color from your hair by pouring diet coke through it. Removes marker stains from carpet. Clean the toilet; pour in and around the bowl, leave it for a while and rinse it clean.
Cola and aluminum foil add shine to the chrome. Removes paint from metal furniture. Soak the fabric in cola and slide it over the paint surface. In some third world countries it is cheaper and easier to access clean water. The carbonation in Coca-Cola causes calcium to shrink in the bones through a three-step process.
It dissolves well in ethanol, water, and many other solvents.
In the food industry it is used for the production of baking powders, processed cheeses, sausages and sugar. Phosphoric acid is also found in drink flavorings, such as Sprite, Coca-Cola, Pepsi-Cola and many others. Contained as an antioxidant (E338) in sparkling water, cookies and crackers.
First aid and treatment
In case of oral poisoning: give an emetic as quickly as possible (0.2-0.5 g of copper sulfate is dissolved in 0.5 glasses of water, drink in teaspoons until vomiting occurs). Gastric lavage with a 0.1-0.2% solution of copper sulfate (a film of phosphorous copper is formed on the phosphorus particles, which prevents the cauterizing effect).
In case of contact with skin: immediately wash the affected area with a copious stream of water (in the place where phosphorus burns under the flow of water, cut clothing, as phosphorus can burn under the fabric). It is better to immerse the affected hand in a 5% solution of copper sulfate and remove all pieces of phosphorus under a layer of liquid with tweezers or a gauze swab. You can use a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution. Keep your hand in the solution until the affected area stops smoking when you remove your hand from the solution. Examine this place in the dark and remove the luminous points with tweezers. Then apply a wet, dry bandage with a solution of potassium permanganate (1:1000). Ointment dressings are absolutely contraindicated. Butter, milk, eggs, fats, castor oil are contraindicated (they contribute to the dissolution and absorption of the poison).
Precautionary measures
If you need to remove rust chemically, you first need to take care of your safety - prepare a respirator and rubber gloves. Phosphoric acid is an aggressive substance that can cause skin burns, and its fumes can cause burns to the respiratory tract and acute poisoning. In addition, it is fire and explosive. All work must be carried out in well-ventilated areas, and the substance must not come into contact with the skin. If this happens, you need to rinse the affected area under running water. In case of a chemical burn over a large area, you must immediately contact a medical facility.
Poisoning of the body with organophosphorus compounds
Poisoning with organophosphorus compounds is a particularly severe intoxication that leaves behind serious complications.
Organophosphorus compounds (OP) are highly toxic organic compounds containing carbon and phosphorus. Initially, they served for military purposes as chemical weapons, but later they learned to use them for peaceful purposes.
Now organophosphorus substances (OPS) are used:
- in agriculture (soil fertilizers, herbicides, pesticides, insecticides, etc.),
- in the food industry (emulsifier E338),
- in medicine (dentistry, ophthalmology),
- in the production of household chemicals (for example, rust removers).
Phosphorus can be red or black (low toxicity), as well as white (high toxicity, poisonous even in contact with skin).
Any contact with FOS requires special caution, otherwise severe poisoning cannot be avoided.
Healthy Alternatives and Recipes
Carbonated drinks, especially Cola, are the main way people consume phosphoric acid. Instead, drinking pure sparkling water, such as ginger ale, can help reduce your intake. However, it is still a very high sugar option and there are better alternatives to these unhealthy soft drinks.
If you really want to get some bubbles, choose naturally sparkling mineral water. It provides carbonation without any added acids, plus you get healthy minerals into your body without the sugar overload. Check labels before use to ensure it is genuine.
You can also try my homemade switch recipe. It's an easy-to-make, refreshing drink filled with healing ingredients, inflammation-reducing ginger and apple cider vinegar.
Kombucha is another great alternative to soda. You get fizzy bubbles (which come from natural fermentation) along with a powerful hit of probiotics, B vitamins, and enzymes.
You can also try making this kombucha recipe at home. Coconut water is another healthier soda alternative that provides valuable electrolytes.
No one will be surprised by the long list of additives found on food packaging. All of them, to some extent, can have an adverse effect on our body, causing allergic reactions or poisoning. And such an inorganic compound as orthophosphoric acid, used in the food industry as an antioxidant and acidity regulator, is one of them. It is defined as marker E338.
After 40 minutes: caffeine consumption is finally over. The pupils of the eyes dilate. Adenosine receptors are blocked, which prevents drowsiness. After 45 minutes: The body increases production of dopamine hormones, which stimulate the reward center of the brain. Similar to the reaction caused by heroin.
How can you get poisoned?
You can get poisoned by phosphorus and its derivatives by inhaling its fumes, ingesting them, or in case of contact of the substance with the skin. The latter method is especially typical for white phosphorus, which spontaneously ignites when it comes into contact with the skin, which is due to its high solubility in fats.
FOS poisoning occurs for the following reasons:
- industrial accidents where work with phosphorus is carried out,
- violation of safety regulations, work without protective equipment,
- carelessness during production processing of a white modification of an element into a red one, etc.
In everyday life, poisoning with organophosphorus compounds (most often from orthophosphoric acid, which is part of many household chemicals) is possible in the following cases:
- when eating vegetables and fruits treated against pests with preparations containing phosphorus (if the fruits are poorly washed or eaten before the time when insecticides, fungicides and other agents are neutralized on their own),
- from water poisoned by organophosphates,
- from unsterilized milk if the cows ate treated grass,
- after contact with unprotected areas of the skin with chemical cleaning agents, fertilizers, etc.,
- due to inhalation of toxic fumes of phosphorous compounds contained in household products of the same name,
- accidental ingestion (possible in children) or intentional use (suicidal purposes).
The lethal dose of phosphorus is 1 mg/1 kg. This is how FOV poisoning ends in 20–50% of cases.
Characteristics of the substance
Orthophosphoric acid, or additive E338, is colorless crystals. Its main characteristics will be as follows:
- complete absence of oxidizing and reducing properties;
- highly soluble in water and ethanol;
- hazard class of orthophosphoric acid - 2;
- at a temperature of 42.35°C, the process of its melting begins, as a result of which the crystals are transformed into a viscous, colorless, transparent liquid;
- boiling point is 158°C;
- when the temperature rises to 213°C and above, it is converted into pyrophosphoric acid.
Signs of poisoning
Symptoms of OP poisoning depend on the form received - acute or chronic. The acute form appears almost immediately, in extreme cases - after a few hours. Chronic poisoning develops over time when phosphorus constantly and little by little accumulates in the body and affects human health gradually.
Acute form
Signs of acute poisoning will depend on its stage. There are three of them:
- Initial. The greater impact here falls on the gastrointestinal tract. With such intoxication with phosphorus and its compounds, a person feels a burning sensation and pain in the esophagus and stomach, headache, severe weakness and general malaise. The poisoned person vomits, and the vomit smells like garlic and glows in the dark. There are cramping pains in the navel area, dry mouth and severe thirst, diarrhea or constipation.
- Average. Signs of central nervous system damage are added to the gastrointestinal symptoms. The poisoned person becomes overexcited emotionally, and physical activity increases. Then the excitement gives way to foggy consciousness. There is a different degree of pupil constriction in each eye. Nervous muscle tics appear, turning into convulsions. Delirium develops (a mental disorder accompanied by hallucinations, confusion, sometimes even coma).
- Heavy. In addition to all of the above symptoms in case of severe phosphorus poisoning, dystrophic changes in the liver and kidneys are added. This manifests itself in the form of yellowing of the skin, mucous membranes and eye sclera, vomiting with bile, and decreased diuresis. In addition, acute heart failure develops: weakness, rhythm disturbances, decreased blood pressure, and a rare pulse are observed. The respiratory system is not far behind: wheezing is heard when inhaling, shortness of breath appears at rest, and a cough with sputum in the form of pink foam appears.
If a lethal dose of a phosphorus compound is received, then if help is not provided, the person will die within one week from the moment of poisoning.
Chronic form
People who work in industries where phosphorus is used are mainly susceptible to the development of chronic poisoning. Over time, they begin to show the following symptoms:
- pathological changes in the jaw bones, accompanied by diffuse pain, similar to toothache, and which does not go away after a visit to the dentist (the x-ray will show areas of sparse bone tissue, which is the initial stage on the path to necrosis and general intoxication),
- general persistent weakness,
- anemia,
- poor appetite
- constant headaches,
- weight loss,
- chronic diseases of the respiratory system (laryngitis, tracheitis, bronchitis, etc.).
Health Hazards from Phosphoric Acid
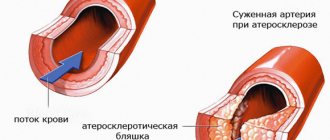
Research has linked phosphoric acid to decreased bone density in humans. A 2000 study linked cola consumption to increased rates of bone fractures in physically active girls in ninth and tenth grades.
Another study published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition suggested that
The researchers measured BMD in the spine and hips of 1,413 women and 1,125 men.
For women, they found that cola consumption was associated with significantly lower BMD at the hips, but not at the spine. Overall, the average BMD of daily cola drinkers was 3.7% lower at the femoral neck. This is a bony bridge that connects the ball of the thigh to the top of the thigh. And 5.4% lower in the Ward-neck area than those who consumed less than one serving of cola each month.
The researchers found similar results for diet cola consumption and similar but weaker results for decaffeinated cola. They saw no relationship between non-cola soda consumption and BMD.
The study's conclusion is that cola consumption is associated with low bone mineral density, especially in women.
Non-cola drinks did not have a negative effect on bone density. And the fact that even without caffeine Coke had a negative effect points to phosphoric acid as an enemy of bone health.
Consumption of colas rich in phosphoric acid has been linked to changes in urination, chronic kidney disease, and kidney stones. Healthy kidneys rid the body of excess phosphorus, but excess phosphoric acid can be hard on the kidneys. Especially for people with chronic kidney disease, who are generally advised to avoid foods high in phosphorus.
Phosphorus is found naturally in many foods. Therefore, it is not difficult for us to obtain it, but it becomes problematic when there is an excess of it in the body. Phosphoric acid, found in colas and other processed foods, is problematic. Because it can easily lead to phosphorus overload in our body.
The study, published in the journal Epidemiology, assessed the eating habits of 465 people with chronic kidney disease and 467 healthy subjects.
What did the researchers find? Drinking 2 or more colas per day, whether regularly or dietaryly, is associated with twice the risk of developing chronic kidney disease.
Most people easily meet their daily phosphorus needs through their diet. Especially if they eat foods high in phosphorus. In fact, an excess of phosphorus in the body is more common than a lack of it.
Excess phosphorus in the diet can reduce calcium levels in the body, and studies have even linked daily cola consumption to hypocalcemia.
In addition, it can lead to an excess of phosphorus. This can affect the body's use of vital nutrients such as iron, magnesium and zinc. A deficiency in any of these nutrients can lead to various health problems.
In food, phosphoric acid is literally used to acidify foods and drinks.
Many acids (such as omega-3 fatty acids) can be beneficial, but phosphoric acid is not one of them.
Phosphoric acid makes cola drinks extremely acidic. In fact, according to a study conducted by Southern Illinois University of Dental Medicine,
The pH of cola products ranges from 2.5 to 4.2. The most acidic cola product is classic Coca-Cola with a pH of 2.5.
To put these numbers into perspective, 7 is a neutral pH level and 0 is the most acidic, so you should stay away from cola.
Phosphoric acid is used in the purification and refining of metals and in the production of fertilizers. It is also found in disinfectants and detergents.
How to determine that poisoning has occurred
You can understand that a person is poisoned due to the effects of organophosphates on his body by the following symptoms:
- slight (at first) muscle twitching,
- convulsions that develop approximately half an hour after poisoning (in severe form),
- complaints of visual impairment,
- hypersalivation (excessive salivation),
- disruptions in intestinal function.
You can also inspect the place where the victim was poisoned. If there is a clear garlic-kerosene smell, the room is poisoned with organophosphorus compounds. There is no need to stay there for further research, since you can inhale the vapors and “inherit” the fate of an already poisoned person.
How does it get inside the body?
Organophosphorus compounds have two ways of entering the body:
- By inhaling volatile particles of toxic substances;
- Together with products or accidentally eating products containing FOS;
- Through the pores of the skin.
The causes of intoxication are as follows:
- The water used for drinking is contaminated with a toxin;
- Fruits and vegetables treated with pesticides are not washed well;
- Dairy products collected from animals that ate poisoned grass were not heat-treated;
- Carrying out work on treating trees and plants against pests without a respirator or other protective equipment. As a result, volatile compounds enter the lungs and negatively affect the body.
Relief measures
In case of poisoning with phosphorus and its compounds at any stage, you should immediately call an ambulance. It is not always possible to independently determine how severe the intoxication is due to the lack of special education, so it is not worth the risk. In addition, there is unlikely to be a special antidote at home, without which treatment of such poisonings is impossible.
First aid for poisoning with organophosphorus compounds should be provided as follows:
- immediately evacuate the victim from the room where he could inhale toxic phosphorus fumes,
- if the substance gets on your skin, take measures to extinguish the fire, remove any remaining chemical,
- wash the burn generously with hydrogen peroxide 3% or copper sulfate 5%, then bandage with a damp bandage soaked in a weak solution of potassium permanganate,
- if there is evidence of ingestion of phosphorous compounds, rinse the poisoned stomach with 1-1.5 liters of water and then induce vomiting (repeat the procedure until the waste water is clear and the garlic smell disappears),
- Give the person who swallowed the phosphorus compound a drink with alkaline mineral water without gas or a solution of soda at the rate of 1 tsp. for 200 ml of water,
- give a saline laxative,
- connect any sorbents.
After this, all that remains is to wait for the doctors to arrive and provide professional assistance that will give the victim a chance to live.
Application
Phosphoric acid has found application in various industries, but it has become most popular in the medical and food industries.
In small quantities, this substance is added to mixtures that are used to whiten tooth enamel. However, it is most often used before the filling procedure, using it to etch the tooth surface.
Acesulfame is poorly soluble and is not recommended for children or pregnant women. A sugar additive for diabetics, it is unstable at elevated temperatures and decomposes into methanol and phenylalanine. Methanol is very dangerous because it takes 5-10 ml to destroy the optic nerve and leads to irreversible blindness. In warm soft drinks, aspartame turns into formaldehyde, which is a very potent carcinogen. Symptoms of aspartame poisoning include: loss of consciousness, headache, fatigue, dizziness, nausea, rapid heartbeat, weight gain, irritability, anxiety, memory loss, blurred vision, fainting, joint pain, depression, infertility, hearing loss and more.
Important! But even during dental procedures, orthophosphoric acid can cause harm - if this substance, even in small quantities, remains on the surface of the tooth, this can lead to the formation of a so-called acid mine, when some time after treatment the tooth simply splits into small pieces!
The substance was later originally illegal due to its dangers, but was suspiciously re-legalized. This may cause eye and skin irritation. It is used for the production of phosphoric acid salts of ammonia, sodium, calcium, aluminum, as well as in organic synthesis for the production of charcoal and foil. It is also used in the production of fireproof materials, ceramics, glass, fertilizers, synthetic detergents, medicines, metalworking, textiles and petroleum industries.
Phosphoric acid is known to interfere with the body's absorption of calcium and iron and can therefore lead to weakened bones and osteoporosis. Other side effects include thirst and rash. It is widely used in the pharmaceutical and food industries. Salts of citric acid are used in the food industry as acids, preservatives, stabilizers and in the medical field to preserve blood.
Inpatient therapy
The main tasks of doctors are the rapid removal of organophosphorus compounds from the body of a poisoned person and the restoration of his affected organs. The patient will be seen by toxicology, since it is this department of the hospital that can quickly provide the most qualified assistance.
A person with phosphorus poisoning will undergo a number of procedures:
- professional cleansing of the stomach and intestines (if the poisoned person has swallowed a chemical mixture),
- intravenous glucose administration,
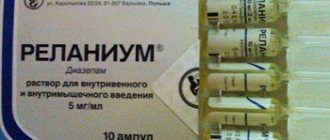
- neutralization of phosphorus with the main antidote - Atropine sulfate (sometimes the drugs Isonitrosine or Diazepam are used as antidotes),
- drugs and procedures for the speedy restoration of respiratory and cardiac functions,
- anticonvulsant and antishock therapy,
- vitamins and medications to prevent further damage to the nervous system as a result of poisoning,
- forced diuresis and hemodialysis if necessary.
After stabilization of the condition, the patient will be prescribed a special diet for poisoning based on dairy and fatty products, which contribute to the rapid breakdown of FOS.
Purification of elements by complete immersion in phosphoric acid
If you have a sufficient amount of the product, you can use the full immersion method to remove rust. To do this, you first need to degrease the element to be cleaned using a detergent composition, and then wash it thoroughly. After this, pour 100 grams of an 85% acid solution into the prepared container and add 1 liter of water. The element to be cleaned is immersed in the solution for one hour, stirring the product periodically. Then the product must be removed and washed well. After such cleaning, the product is washed with another solution consisting of 50% water, 2% ammonia and 48% alcohol. Then the product is washed again with plain water and dried. All stages must be performed in strict sequence. If you do not degrease the product, the cleaning will be uneven, since the product may not corrode normal stains, and additional cleaning will be required. In this way, you can clean any products with varying degrees of rust, but the thicker the coating, the more time you need to keep the element in the solution. If the element is not dried after washing, hydroxide appears on it. Drying can be done using any method.
Complications after poisoning
Sometimes even mild food poisoning leaves behind a number of consequences. And if we are talking about severe chemical intoxications, it is almost impossible to avoid complications.
If a person is poisoned by phosphorus compounds, this will certainly affect his health even after high-quality and quickly treated treatment. The victim is likely to:
- toxic damage to the central nervous system,
- heart, kidney or liver failure,
- coma,
- fatal outcome.
Any of these consequences, which can cause organophosphate poisoning, is extremely dangerous and sometimes irreparable. This is why it is so important to be careful in any interaction with these chemicals.
Have you ever had organophosphate poisoning?
- Yes they were
- No, it was not
- Now there are symptoms of intoxication
ResultsPoll Options are limited because JavaScript is disabled in your browser.
- No, there was no 84%, 313 votes 313 votes 84% 313 votes - 84% of all votes
- Yes, there were 9%, 35 votes 35 votes 9% 35 votes - 9% of all votes
- Currently there are symptoms of intoxication 7%, 25 votes 25 votes 7% 25 votes - 7% of all votes
Total votes: 373 10/19/2017 You or from your IP have already voted.
- Yes they were
- No, it was not
- Now there are symptoms of intoxication
You or from your IP have already voted. results
Applying acid to the surface
If the part is large, there is no suitable container or there is not enough acid, you can apply it to the metal surface using a sprayer, roller or brush with natural bristles. In this case, it is necessary to take into account the degree of corrosion. If the rust layer is large, you will have to use a combined method and first remove the surface layer of the loose mass mechanically. This can be done manually or using a grinder, on which an attachment is put on - a metal brush or a flap circle.
After mechanical cleaning, you need to degrease and apply an aqueous acid solution, being careful not to make any gaps. Two hours after application, you can rinse with a neutralizing solution, and then perform a final rinse and drying. For minor corrosion, mechanical repairs may not be necessary, although reapplication may be required.
An inhibitor, catapine, can be added to the acid solution, which inhibits the chemical process and prevents the reaction with the unoxidized metal. It is added in an amount of 1-2 g per liter of water.
Preventive measures
All rules of prevention boil down to maximum care when working with FOS both at work and at home. This requires:
- strictly adhere to safety regulations (this includes the correctness of technological processes and the need for special protective uniforms),
- undergo regular medical examinations in order to timely detect the onset of chronic intoxication,
- do not eat or smoke when working with phosphorus,
- work with fertilizers and pest control products only in special equipment (mask, gloves, protective suit),
- also, do not use household cleaning products containing phosphorus without protective equipment and do not leave them open for a long time,
- Keep any phosphorus-containing preparations away from children.
Only caution and attentiveness can truly protect against poisoning. And in the case of such dangerous compounds as phosphorus, it is doubly important to observe prevention. The main thing here is to always remember that phosphorus intoxication in almost half of the cases results in the death of the victims.
source
What dose of FOS can cause poisoning?
The degree of toxicity of various organophosphorus preparations is assessed by the severity of the impact on animals, since it is impossible to accurately determine these indicators in relation to the human population due to the impossibility of conducting the necessary tests. In accordance with the results of studies conducted on animals, the following doses of FOS are considered toxic:
- low toxic – less than 15 mg/kg;
- moderately toxic – from 15 to 150 mg/kg;
- highly toxic – from 150 to 1500 mg/kg;
- extremely toxic with a high risk of death - more than 1500 mg/kg.