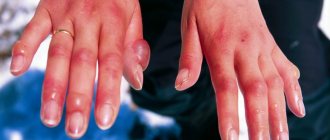
Chlorine is a gaseous substance that has a disinfecting effect. It is included in various detergents and cleaning products. The oldest are bleach and bleach. Chlorine and substances containing it are widely used in industry, medicine and everyday life. However, it should be remembered that when using this substance, safety rules and precautions must be followed. Otherwise, there is a high risk of poisoning.
What to do if you inhaled bleach: what are the symptoms and consequences of poisoning, how to provide first aid - you will learn about this and much more in our article.
How can you get poisoned with acetone?
This solvent is widely used, which is why it is not difficult to poison yourself with it. Intoxication occurs by exogenous (the intake of a substance from the outside) and endogenous (the formation of acetone inside the body) pathway.
In case of exogenous poisoning, a substance can enter the body in several ways:
- Through the respiratory tract (inhalation of solvent vapors);
- By mouth (when swallowing the solution).
The most common causes of exogenous intoxication are:
- Poisoning by acetone vapor occurs when the rules for using liquids that contain this substance are not followed. This is observed both in everyday life and at work;
- Accidental use of solvent. More often this happens to children and people under the influence of alcohol and drugs;
- Using a drug to achieve a state of euphoria (substance abusers);
- Intentional use of a toxic substance for the purpose of suicide.
Endogenous poisoning occurs when intensive breakdown of fats occurs in the body. Since in this case a large number of ketone bodies are formed.
Causes of endogenous poisoning:
- Low carbohydrate diet;
- Diabetes mellitus (untreated or incorrectly selected dose of insulin).
Is it possible to rinse your eyes with peroxide?
In some cases, diluted peroxide with a concentration of 0.5-1% is used to wash the organs of vision in case of inflammatory diseases, for example, conjunctivitis. To do this, the substance purchased at the pharmacy is diluted with clean water in a ratio of 1:5 or 1:6. The resulting mixture is instilled under the eyelids for disinfection.
It is believed that a weak solution will not cause irritation and does not harm the organs of vision. However, many are interested in whether it is possible to wipe their eyes with peroxide, or whether it is better to use special drops. Doctors strongly recommend the use of modern medications to treat conjunctivitis and other eye diseases. They are more effective and safe because they have a combined and gentle composition. You can wash your eyes with these products without fear for their health, as is the case with peroxide.
The effect of acetone on the human body
The toxicity of acetone is low-hazard (4th degree of danger). It should be remembered that poisoning can result from exceeding the content of this substance in the atmosphere by more than 0.07 mg/m³.
The greatest toxicity of this substance occurs when it penetrates through the digestive tract. In this case, the substance quickly penetrates into all tissues of the body.
Pathological changes in the body during poisoning:
- Burns and severe swelling of the mucous membranes;
- Stagnation of blood in the pulmonary and systemic circulation;
- Death (necrosis) of tissues of internal organs;
- Severe pathology of the cardiovascular and nervous system.
Penetration of the substance through the respiratory tract negatively affects the following systems:
- Nervous, brain cells are primarily affected. They undergo irreversible changes;
- Cardiovascular;
- Digestive (changes in the liver parenchyma during chronic poisoning).
Stages of visual damage
Depending on how strongly the substance affected the functions of the ocular apparatus, several degrees of damage are distinguished:
- Easy stage. It is characterized by minor damage to the conjunctiva. In this case, the connective membrane of the eye acquires a bright red hue.
- Average degree of burn injury. The substance acts on the cornea of the eye. Defects form on its surface.
- Severe form. The pathology is characterized by the appearance of foci of necrosis in the deep layers of the organ of vision. The cornea takes on a matte tint, and severe swelling is observed.
- A particularly severe type of burn. The process of necrosis at this stage is deep. It covers the entire connective membrane, sclera, and conjunctiva. Scabs of a yellow, grayish or brown hue form on the surface of the organ.
Symptoms of poisoning
Symptoms of poisoning with acetone and its vapors depend on the route of penetration of the substance into the body. So, when this substance is ingested, the following pathological signs are observed:
- Swelling and hyperemia of the oral cavity and upper digestive tract;
- Hypotension – decreased blood pressure . In this case, the pressure drop can be quite rapid, and collapse develops;
- Abdominal pain accompanied by nausea and vomiting;
- The smell of acetone from the patient's mouth;
- Head pain and dizziness;
- Drowsiness;
- Impaired speech and coordination of movements;
- In severe cases, lack of consciousness and coma.
If poisoning with acetone vapor occurs, then a slightly different clinical picture is observed.:
- The mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract are primarily affected. Their swelling develops, which is manifested by severe shortness of breath;
- The mucous membrane of the eye becomes irritated, which leads to the development of conjunctivitis;
- Severe dizziness and headache;
- Pain and aches in the body;
- Loss of consciousness.
Follow-up treatment after first aid
The need and content of further therapy is determined by the ophthalmologist . At home, it is only allowed to provide first aid according to the algorithm.
If the chemicals in the paint have a harmful effect, the following procedures are prescribed.
- Local impact. Removing residual substances from the mucous membrane.
- Taking antibiotics to prevent infection (Ciprofloxacin drops, Levomycetin ointment).
- Cycloplegic drugs. The goal is to relieve pain and prevent scarring. The most commonly used solution is Atropine.
- Tear fluid substitute (Lakrisin).
- Means for lowering intraocular pressure (Timolol).
- Vitamins, citrates to improve calcium metabolism in the affected eye.
First aid and removal of solvent from the body
Acetone poisoning is a dangerous condition that requires timely first aid and adequate treatment. Therefore, you need to call an ambulance.
First aid includes a number of manipulations:
- Stop exposure to the toxic substance on the body. In case of vapor poisoning, the victim is taken out or taken to fresh air. If the poison gets into the stomach, then it is washed;
- To lavage the stomach, take 1 - 1.5 liters of water with salt . After the patient has drunk the entire solution, it is necessary to induce vomiting. It is better to perform this procedure several times. Washing is carried out only if the patient is conscious;
- After washing, you can give an adsorbent: Activated carbon, Polysorb and others;
- If the patient is unconscious, then you can try to revive him with ammonia (let him sniff cotton wool soaked in ammonia). Give it a stable lateral state;
- Wait for paramedics to arrive with the victim.
In the hospital, various procedures are carried out aimed at removing toxic substances from the body.:
- Gastric lavage using a tube;
- Oxygen therapy is a treatment aimed at enriching the blood with oxygen. In this case, the substance is removed from the blood faster;
- Forced diuresis . In this case, the patient is given intravenous drops of saline and other solutions in large quantities, and in parallel with this, diuretics are prescribed;
- In severe cases, hemodialysis is prescribed.
First aid at home
This is a rinse - a tea compress - eye drops for disinfection - an examination by an ophthalmologist.
For an adult
The first mandatory action is rinsing . Clean water at room temperature will do. The paint is viscous, so you need to wash it out of your eyes as quickly as possible.
You can put water in your palm and rinse your eye, or you can put it in a rubber bulb and direct a thin stream into the affected eye.
The duration of the procedure is 10-20 minutes or until the doctor arrives.
Then you should make a tea compress . It will stop inflammatory processes.
Disinfection is shown next . Drop any drops with an antibacterial effect - Albucid, Levomycetin, Tobrex, Colbiotsin or analogues.
Instead of drops, you can apply a little eye gel to the eyelid - Oftagel, Korneregel.
Consequences and complications
The solvent has a detrimental effect on all internal organs. This pathology has a lot of complications, the most common consequences of acetone poisoning are:
- Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract . This complication occurs due to the traumatic effect of this substance on the mucous membranes of the digestive organs;
- Acute and chronic renal failure . This pathology is characterized by impaired renal function, since the bulk of the toxic substance is excreted from the body in the urine;
- Acute liver failure . The solvent destroys the liver parenchyma. It becomes swollen and painful. On palpation, there is pain in the right hypochondrium and an increase in the size of the organ;
- Acute pancreatitis – inflammation of the pancreas with disruption of its functionality;
- Brain damage can lead to the development of mental pathologies;
- Convulsions;
- Decreased memory and intellectual abilities;
- Decreased levels of red blood cells and iron in the blood (anemia).
What to do in case of an iodine burn and how to properly provide assistance
In highly developed Western countries, the use of iodine has already been abandoned. This is explained by its high toxicity and the possibility of causing complications. In the countries of the post-Soviet space, this drug continues to be widely used, without thinking about the dangers. As a result, many patients receive burns not only to the skin, but also to the mucous membranes, even the organs of vision.
Photo 1. Iodine is an aggressive and dangerous agent. Source: Flickr (Utherian)
Why does iodine cause chemical burns?
Iodine is a fairly aggressive substance that has qualitative characteristics that provide it with versatile biological activity. However, these very properties make the drug dangerous for the tissues of the human body, especially if used incorrectly. In large quantities, iodine oxidizes the skin, corrodes the mucous membranes , and this is how burns occur.
The main reasons why iodine causes burns to different parts of the body:
Skin burn
Skin burns occur as a result of:
- Long-term exposure of the drug to areas of the skin. This most often happens if an iodine solution is used for lotions and compresses .
- Applying the product to an open wound .
- Repeated application of the drug without observing the time intervals recommended by the instructions.
Eye burn
Occurs most often due to careless handling of the drug. The product can get into the eye, for example, if it is applied in the periorbital area of the face.
Throat burn
You can burn the mucous membrane of the throat with:
- An attempt to treat dental or ENT diseases with iodine.
- An attempt to eliminate iodine deficiency by taking an oral solution of the drug.
Also, those people who are allergic to this product are likely to get a burn from iodine. Even if you follow the instructions for use.
Symptoms of an iodine burn
Signs of damage may not appear immediately after contact of body tissue and the solution, but after some time:
- The appearance of large and small blisters is a common symptom of an iodine burn.
- The appearance of spots similar to pigment spots.
- Peeling of the skin.
- A burning and itching sensation in the area where the drug was applied.
Symptoms of mucosal burn:
- Severe pain, burning at the point of contact.
- Difficulty breathing and swallowing.
- Reflex cough, urge to vomit.
Burns from iodine to the organs of vision are manifested by a burning sensation, profuse lacrimation, redness of the eyes, decreased visual acuity, and even an increase in general temperature.
Photo 2. Trying to cure mouth ulcers with iodine can cause new ones. Source: Flickr (tom.ontheroad).
Incorrect use of the drug in combination with the occurrence of characteristic clinical symptoms is an indication for immediate seeking medical help.
First aid
While the ambulance has not yet arrived, the patient must be given first aid. It is aimed at alleviating the human condition and reducing the degree of damage caused to tissues.
First of all, the affected area should be rinsed with cool water . The water procedure should last at least 20-30 minutes.
Apply a paste of a product containing starch to the skin - potatoes, pumpkin, oatmeal.
A blister , if it occurs, cannot be opened to prevent secondary infection.
If the solution gets into the oral cavity and nasopharynx, you should also rinse with water, then with milk or jelly.
If the patient swallowed the drug, milk will help .
There is no need to induce vomiting , since the reverse movement of iodine through the digestive tract can cause additional damage.
If iodine gets into your eyes, they should be rinsed with plenty of water.
Diagnostics
To diagnose skin lesions, only anamnesis data and an external examination of the patient by a specialist are required. If the solution gets inside, additional diagnostic measures may be required:
- Instrumental methods for studying the esophagus and lung tissue. These are X-ray , CT , laryngoscopy , thoracoscopy .
- Laboratory research methods. These are blood and urine tests .
In case of damage to the mucous membrane of the organs of vision, a specialist will conduct an examination, analyze the clinical picture and the nature of its manifestation. In most cases, consultation with an ophthalmologist is required.
Complications
In case of severe iodine burns, complications cannot be avoided. However, superficial damage to the skin and mucous membranes, with proper treatment and compliance with the rules of the recovery period, give many chances for a complete cure.
The main complications after a burn with iodine are:
- Impaired function of affected tissues and/or organs.
- Scars.
- Changes in skin pigmentation.
- The addition of an infection, accompanied by a constant inflammatory process.
Rehabilitation period
If a patient receives adequate treatment after an iodine burn and is prescribed restorative procedures, then the return to normal will occur much faster.
Rehabilitation after an iodine burn involves the use of various methods of physiotherapy . They are aimed at improving trophism and blood supply to tissues, improving recovery, preventing purulent formations, and pain relief. The most popular methods of physiotherapy:
- Darsonvalization.
- UV irradiation.
- Ultrasound or UHF therapy.
- Electrophoresis.
- Laser therapy.
- Magnetotherapy.
- Aeroionotherapy.
Prevention of burns with iodine
Prevention of burns with iodine solution consists of following the following recommendations:
- Keep the drug out of the reach of children.
- Do not use iodine to treat organs covered with mucous membranes.
- Follow the instructions for use.
If you doubt the correctness of treatment, it is better to consult a doctor than to resort to the advice of unqualified specialists.
Source: https://glavtravma.ru/ozhogi/ot-ioda-102
What to do if acetone gets into your eye?
When the solvent gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes, a chemical burn occurs, which is accompanied by pain, pain, lacrimation and signs of inflammation (mucosal hyperemia). In this case, there is a high risk of vision loss, which is why it is necessary to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
If solvent gets into your eye, you should:
- Rinse eyes with plenty of water. It is better to use boiled chilled water. Rinsing is carried out using a large syringe or syringe. If a syringe is used, the needle must be removed so as not to injure the visual apparatus;
- After rinsing, you can drip your eyes with Albucid drops, 1 – 2 drops into each eye;
- You can make a cold compress with chamomile infusion or black tea;
- If there is a feeling of discomfort, pain and cutting in the eye, as well as changes in vision, you should immediately contact the ophthalmology department. The doctor will assess the condition and prescribe adequate treatment.
When should you consult a doctor?
If we are talking about a child, you need to see a doctor in any case .
The fact is that the effect of the chemical must be neutralized.
Means for neutralizing burns on the skin are not suitable for those on the cornea, and special solutions are used that are only available in medical institutions.
Adults also need to see a doctor, even if a small drop of iodine gets on the cornea.
Sometimes it seems that after washing the discomfort has disappeared and no alarming symptoms are bothering you anymore.
With the help of a doctor, healing and further rehabilitation are accelerated.
A child drank acetone: what to do?
If this toxic substance enters the child’s body, he will develop severe intoxication. Acetone poisoning in children is much stronger and more dangerous than in adults due to:
- Rapid heartbeat (more often than in adults);
- Intensive blood supply to internal organs;
- Intensive metabolism.
If the child becomes drowsy, lethargic and smells of acetone, then this indicates poisoning with this substance. In this case it is necessary:
- Call an ambulance;
- Provide a flow of fresh air;
- Rinse the stomach;
- Rinse mucous membranes and contaminated skin;
- Give Activated carbon;
- Provide plenty of fluids.
If the child does not have a pulse or breathing, then resuscitation measures (artificial respiration and cardiac massage) are required.
Victor Systemov – expert of the 1Travmpunkt website
What happens if you drink acetone? The consequences in this case can lead to a number of complications incompatible with life. To save a person, a whole range of urgent measures must be taken.
How can you get poisoned with acetone?
It is not difficult to get poisoned by acetone. The most common route is exogenous intoxication. In this case, acetone enters the body from the outside: through inhalation of vapors, after ingestion by ingestion. Dimethylketone poisoning can occur at work or at home. Toxic vapors can be inhaled accidentally.
If a person swallows acetone, the consequences are extremely sad. Often people do this deliberately, committing suicide. Drug poisoning is possible among drug addicts who use such toxic substances to obtain euphoria by inhaling large amounts of vapor.
Young children or people who drink alcohol excessively may accidentally swallow the liquid. The toxic compound is quickly absorbed into the blood, causing severe intoxication. Poisoning can also occur when acetone accumulates in the body due to diabetes and other serious diseases.
Symptoms of poisoning
When the solvent penetrates inside, a burn occurs in the mucous membranes of the mouth and gastrointestinal tract, which is accompanied by severe swelling. If you take 50 ml of acetone, death cannot be avoided - this is a lethal dose for the human body.
When the substance is ingested, tissue necrosis occurs, the heart and blood vessels are damaged. Poisoning is accompanied by severe dizziness, loss of consciousness, respiratory depression, vomiting and nausea. The person's tongue turns red. Blood pressure drops sharply, which provokes collapse. A strong solvent odor can be smelled from a person's mouth. There are complaints of severe abdominal pain. There are disturbances of consciousness, signs of drowsiness and confusion of speech.
Poisoning through the respiratory system manifests itself with other symptoms. The signs are less pronounced. When inhaling acetone vapor, lacrimation, inflammation of the bronchi and lungs occur, which can result in coughing and shortness of breath. In severe cases, severe headaches, joint aches, swelling of the oral mucosa and loss of consciousness occur.
If the substance gets into the eye, lacrimation occurs. The mucous membrane turns red, a vessel may burst, and pain occurs.
If a large amount of solvent gets in, vision impairment may occur, which will be difficult to eliminate on your own.
Chemical burn to the eye: symptoms, risk factors, first aid measures, prohibited actions, treatment
Eye injuries are a common injury that causes vision impairment and can lead to blindness. A chemical burn to the eye poses a great danger. It can easily be obtained by careless handling of toxic substances. If you find yourself in such a situation, you need to know how to provide first aid. Correct actions reduce the damaging effects of chemicals and can preserve vision.
Description of injury
According to statistics, about 10% of damage to the visual organ is caused by chemicals. Most often, local damage occurs upon contact with acid and alkali. The degree of severity directly depends on the number of aggressive agents that have reached the mucous membrane and on the duration of the dangerous influence.
Penetrating into the eye, liquid chemicals immediately mix with tears and act more slowly. Solid agents quickly dissolve, forming a concentrate that destroys the structure of the organ.
Acid
An acid burn is similar to a thermal injury. It injures the cornea and creates coagulative necrosis. A film of dead tissue prevents the substance from penetrating deep into the eyeball. The following acids pose a serious danger:
- vinegar, salt;
- chlorine, nitrogen;
- sulfuric, hydrogen fluoride.
Under the influence of acids, nerve endings are irritated, so a person feels acute pain.
Alkali
Alkali burns pose a serious threat. The substance tends to penetrate deep into the eye and continue its destructive effect for a long time. If the chemical is not removed immediately, the burn will worsen and may cause blindness. Large-scale damage is caused by concentrated hot alkaline solutions. Common substances that can burn the eye:
- caustic soda;
- caustic potassium;
- slaked and quicklime;
- ammonium hydroxide;
- ammonia;
- Magnesium hydroxide.
Symptoms of damage by various substances
The main signs of a chemical burn of the cornea and conjunctiva of the eye are:
- burning;
- lacrimation;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- swelling;
- blurred vision.
When exposed to acids, the color of the conjunctiva changes. Chromium provokes the appearance of a brown tint, nitrogen - yellow. A substance in the eye promotes excessive tear production. It becomes difficult to open the eyelids, they hurt, vision becomes blurred, and a feeling of a foreign body appears.
Characteristic symptoms of an alkaline burn are photophobia, swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. The chemicals destroy nerve fibers, so the victim rarely feels severe pain. Sometimes this causes a person to underestimate the injury.
Acid and alkali burn the skin around the eyes. It becomes inflamed, red, and blisters form.
Emergency help
There are 4 degrees of damage for chemical burns of the eye with acid and alkali. Help needs to be provided as quickly as possible. This will minimize damage and improve the prognosis for recovery.
- First of all, you need to rinse the affected area. This must be done no later than half an hour after injury.
- You will need saline solution, potassium permanganate slightly diluted in water, or 0.9% sodium chloride solution. You can use regular cool water.
- The procedure should be carried out for 20 minutes, washing the mucous membrane from the inner corner of the eye to the outer.
- If the cause of the burn is a solid substance, you must first remove it with tweezers or a sterile cloth..
- To provide qualified emergency care, it is important to find out what exactly caused the injury, because the effect of chemicals can be neutralized.
- When alkali gets into the eye, rinsing should be done with a three percent acetic solution or two percent boric acid.
- Acid burns should be washed with a solution of baking soda - 25 g of the substance is dissolved in 0.5 liters of water.
To prevent the development of infection, you can instill a solution of Furacilin. Then you should cover the eye with sterile gauze, secure it with a bandage and go to the hospital. It is advisable to take with you a bottle of the reagent that caused the injury. Studying the contents will help doctors prescribe the right therapy.
What not to do
Chemical eye damage should not be treated independently. You should definitely contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible.
In order not to aggravate the situation, first aid should be carried out in strict compliance with hygiene rules.
Forbidden:
- rub your eyelids;
- leave solid chemicals on the mucous membrane;
- try to reach particles of the aggressive substance with your fingers;
- apply warm compresses;
- use medications without a doctor's permission.
First aid and removal of solvent from the body
If you are poisoned by acetone vapor and the compound gets inside, it is important to immediately call an ambulance. Otherwise, you can waste time and provoke cardiac and respiratory arrest. First of all, you need to rinse your stomach with plenty of water. If severe poisoning occurs due to inhalation of chemical vapors, the victim should be taken to fresh air.
Gastric lavage when swallowing the solution is carried out only if the person is conscious.
You need to take 1.5 liters of water, add a little salt, mix everything thoroughly and give the victim a drink. Then induce vomiting by pressing on the root of the tongue. It is advisable to repeat the washing 2 times.
Consequences and complications
Poisoning can lead to the following serious consequences and complications:
- Bleeding from the gastrointestinal tract. Occurs when solvent gets inside. Damage occurs to the gastric mucosa and blood vessels.
- Impaired kidney function. This occurs due to the fact that these organs perform an excretory function - all toxic substances pass through them.
- Severe liver damage. Occurs when a solvent is accidentally ingested. The liver parenchyma is damaged, the organ swells and increases in size.
- Inflammation of the pancreas. The chemical compound destroys the organ, causing swelling and functional failure.
- Brain disorders. A person who survives poisoning may suffer from impaired intellectual abilities and memory, and develop mental disorders.
- The appearance of seizures and a decrease in hemoglobin in the blood, which provokes the development of anemia.
Main characteristics of injury
A chemical burn is an injury to the eye caused by exposure to aggressive chemicals. First of all, there is damage to the conjunctiva - a thin connective membrane that covers the outer surface of the eye and the back surface of the eyelid. It performs an important function because it releases a special liquid that lubricates the eye and prevents it from drying out. Its damage often leads to impairment and even loss of vision.
Damaging substances
Chemical burns of the conjunctiva are not uncommon these days. According to statistics, 10% of all eye burns are of chemical origin. Most often, damage occurs when aggressive substances come into contact with the ocular surface. Among them are:
Acids. Most often, burns occur with the following acids:
- hydrochloric acid (HCl);
- sulfuric (H2SO4);
- acetic (HC, COOH);
- hydrofluoric(HF).
An acid burn is similar to a thermal burn. It affects the conjunctiva and cornea without spreading into the eyeball. The degree of damage is influenced by the concentration of acids and the duration of their exposure. At the site of acid entry, a necrotic area appears, which is separated from healthy tissue (coagulation). In this case, a very strong pain syndrome appears, since the optic nerves are irritated.
Alkali. The most common alkalis that cause burns are:
- ammonia (ammonium hydroxide);
- caustic soda (sodium hydroxide);
- magnesium hydroxide;
- potassium hydroxide;
- slaked lime (calcium hydroxide).
Burns from alkaline substances are considered more dangerous because the damage extends deep into the eye, from where it is not easy to remove. At the same time, the time of negative impact increases.
This occurs due to the fact that alkali provokes liquefaction necrosis in the proteins, which leads to their melting (myomalacia) and spreading throughout the eye. In this case, the optic nerves are damaged by alkali, which leads to their loss of sensitivity. That is why a person with alkaline burns practically does not feel pain. This often leads to underestimation of damage.
Risk factors
How do chemical eye burns occur? This occurs through direct contact with acids or alkalis, when, due to carelessness or failure to comply with safety measures, these aggressive substances first enter the area of the conjunctiva of the eye, causing its necrosis (death). Among the risk factors contributing to the occurrence of such burns are:
- Construction or repair manipulations. These types of work often use chemicals that can cause burns.
- Using aggressive substances in everyday life without following safety rules. For example, improper or careless use of ammonia, household chemicals containing dangerous acids or alkalis. It is also risky to leave such substances within the reach of children.
Work involving frequent use of chemicals. This may be the production of concentrated acids and alkalis or other types of work where such substances are used.- Careless behavior with car batteries that contain sulfuric acid concentrate. This is especially true for car enthusiasts who do not have professional skills in working with cars.
- Alcohol abuse. In this state, very often people do not follow safety rules, which leads to unpleasant consequences.
Any type of burn is potentially dangerous. Therefore, first of all, a person needs emergency care for a chemical burn to the eyes.
The sooner it is provided, the more favorable the forecasts will be.
Prevention
To prevent intoxication, it is recommended to keep acetone away from children and in places where food is not stored. During work that involves the release of large amounts of solvent vapor, it is necessary to use personal protective equipment.
When engaging in hazardous work conditions, you need to drink more fluids and go out into fresh air more often. Work only with gloves. If one of the family members is addicted to alcohol or drugs, varnish thinners and other similar products should be kept in a secluded place.
Acetone (dimethylketone) is a substance belonging to the ketone group. It is a precursor to narcotic substances, the circulation of which in a concentration of over 60% is under control. Since acetone is added to many household liquids, poisoning with it is a fairly common type of intoxication.
Let's look at the main signs of acetone poisoning in adults and children, as well as methods for treating this condition.
ethnoscience
The use of natural medicines in the fight against iodine burns shows good results. The damage goes away more slowly than when exposed to pharmaceutical drugs, but the risk of side effects is minimal.
Top recommendations:
- Apply mashed potatoes for a while (grind the fresh root vegetable into a pulp).
- Use aloe juice to speed up healing.
- Treat iodine burns with a decoction of oak bark and chamomile.
- Prepare a paste of starch or oatmeal porridge to soften the dermis.
Of course, such treatment should be discussed with your doctor first. Traditional medicine does not always give the desired result.
Briefly about acetone
Acetone is a colorless liquid with a sharp, characteristic odor. You can be poisoned by this substance if you take it internally (that is, orally) or by inhaling its vapors. When inhaled, it has an irritating and mild narcotic effect. The lethal dose of acetone for internal use is from 50 to 200 milliliters. The substance is quickly absorbed into the blood, thereby causing poisoning.
Once the substance enters the bloodstream, it is eliminated from the body rather slowly. In high doses, dimethyl ketone causes drooling, nausea, and skin irritation. The harm is aggravated by the fact that the substance contributes to the development of delusional states and causes confusion. Some studies indicate that this substance causes the destruction of male sperm. Inhalation of vapors causes irritation of the mucous membranes of the respiratory system.
Inhalation of acetone vapor is often used by drug addicts to achieve a euphoric effect. In this case, there is a pronounced effect on the central nervous system, its inhibition.
Symptoms of acetone poisoning
Signs of acetone poisoning are similar to those observed during alcohol intoxication. Loss of consciousness during dimethyl ketone poisoning is not as long as with alcohol intoxication.
When the substance enters the body, the following symptoms are observed:
- lowering blood pressure;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the mouth, pharynx, as well as swelling of these organs;
- presence of a strong odor of acetone in the exhaled air;
- nausea and vomiting;
- presence of a sweetish taste in the mouth;
- abdominal pain;
- fainting;
- drowsiness;
- headache, hallucinations;
- irritation of the oral mucosa;
- severe redness of the eyes;
- When a large amount of dimethyl ketone enters the body, incoherent speech, stupor, and coma are observed.
Causes of burns and dangers
Most injuries and burns from medications occur due to improper and careless use or storage. Burns can occur if the substance is not carefully diluted or neighboring areas are damaged if the medicinal liquid is carelessly applied. Getting iodine into the eye area or another place is dangerous because the alcohol solution, when left for a long time, penetrates into the deep tissues. If you neglect first aid and do not go to the clinic, serious damage to the visual organ and a significant deterioration in its function may occur.
In some situations, due to iodine burns, complete loss of vision and even removal of the eye were noted.
First aid for acetone poisoning
A person who has been poisoned by this toxic substance must receive professional medical assistance. Successful treatment saves the patient's life.
First aid for this type of poisoning should be carried out smoothly, without panic and according to clear rules.
- If poisoning occurs indoors, it is urgent to take the patient out into fresh air.
- If acetone is taken orally, immediately rinse the stomach with saline solution and induce vomiting.
- The patient must be given activated charcoal.
- If the patient is unconscious, they are brought to life with a cotton swab dipped in ammonia.
- The poisoned person must be given warm tea and put to bed.
Treatment of poisoning
One of the most effective ways to treat acetone vapor poisoning is oxygen inhalation. Breathing oxygen cleanses the blood of poison. However, most doctors note significant improvement in the patient's condition just a few days after starting oxygen inhalation.
Gastric lavage is used to remove poison from the digestive tract. This is done in a hospital setting: the doctor inserts a special tube through the throat into the stomach, where water is supplied, which is then pumped out. This procedure is done until the stomach is completely cleared of the toxic substance.
Infusion therapy is common: the patient is injected intravenously with alkalizing solutions that help quickly remove dimethyl ketone from the blood.
If treatment is started in a timely manner, the patient’s chances of recovery are very high.
Acetone poisoning in children
Parents should explain to their child from a very early age that acetone is a toxic substance that can cause severe poisoning if used improperly.
In children, acetone is absorbed into the blood much faster and spreads throughout the body. The rapid absorption of the toxic substance is due to the fact that the child’s heartbeat is faster, which is why the organs are supplied with blood more intensely. Metabolism in children is also much more intense. So, their health and sometimes their lives will depend on how quickly medical care is provided to young patients.
Acetone poisoning in children has more pronounced symptoms. The lethal dose per kilogram of a child’s weight is 2–3 milliliters. The most typical symptoms of dimethyl ketone poisoning in children:
- unsteadiness of gait and severe dizziness;
- severe weakness;
- dyspnea;
- pungent odor of acetone in exhaled air;
- ulceration of the oral mucosa;
- severe drowsiness, coma.
A rapid increase in drowsiness indicates a sharp drop in cardiac activity in children, and therefore requires urgent therapeutic measures.
Parents should remember a clear algorithm of actions in case of such poisoning.
- Call emergency medical assistance.
- Rinse the stomach with plenty of water. However, this should only be done if the child is conscious.
- Give the child any enterosorbent - activated carbon, Smecta, etc.
- In case of acetone vapor poisoning, it is very important to provide a supply of fresh air.
- If the poison gets on the skin, it should be washed with plenty of water.