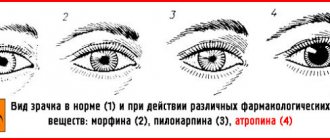
Stages of poisoning:
- Mild poisoning. Stunned, asleep, in a state of stupor, the victim makes contact. Muscle hypotonia, decreased reflexes, ataxia. Miosis or sharp constriction of the pupil. Nystagmus or involuntary eye movement.
- Moderate poisoning. The pupils react to light, residual tendon reflexes are recorded. Development of superficial coma.
- Severe poisoning. The functions of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems are severely impaired. Renal failure is registered. The pupil is maximally dilated (mydriasis), there is no reaction to light. The victim falls into a deep coma with areflexia.
Benzodiazepines themselves rarely provoke complications associated with drug overdose. According to statistics, deaths from benzodiazepine poisoning when taken independently led to death in 3.8% of cases. The remaining 96.2% of deaths are caused by mixing benzodiazepines with alcoholic beverages, opioids and tricyclic antidepressants - drugs that significantly increase their toxic properties.
Relanium
An overdose of Relanium can cause the following symptoms in a patient: craving for sleep, disturbance of brain activity, which can be more or less pronounced, overexcitation of nervous activity.
Complete suppression of reflexes may occur, as well as a complete absence of pain responses. In some cases, dysarthria occurs, various deterioration in the functioning of the visual organs, sometimes trembling of the limbs, and a sharp drop in blood pressure. In particularly severe conditions, collapse, cardiac arrest, respiratory arrest, and coma may occur. In case of overdose, the following manipulations must be urgently performed: complete rinsing of the digestive system, giving large quantities of absorbents, powerful and urgent diuresis. In addition, it is necessary to carefully monitor the patient's condition and, if necessary, introduce supportive therapy. Particular attention should be paid to the state of blood pressure and normalization of the functioning of the respiratory system. If necessary, the patient should be connected to a ventilator. Relanium has an antidote - flumazenil. This drug is used only in a hospital. This is due to the fact that the drug has a number of contraindications and warnings for use. If used to treat patients with epilepsy, it may increase epileptic seizures, especially in cases where treatment with benzodiazepines was carried out.
Elderly patients should be especially careful when using Relanium, since it is for this group of patients that a reduced dosage is prescribed.
Relanium affects the functioning of almost all human organs and systems. In elderly patients, in the first days of taking the drug, there may be an increased desire to sleep, lethargy, poor coordination, impaired ability to concentrate, staggering, slow reactions, and memory impairment. In some cases, the appearance of migraine-like pain, trembling of the limbs, too much gaiety or vice versa, melancholy, blurred thoughts, impaired control of the limbs, mental disorders such as anger, fear, attempts at suicide, visions, nervousness, poor sleep are possible.
Relanium can also cause disturbances in blood production, increased body temperature, fever, weakness, a decrease in the number of red blood cells in the blood, and a violation of the platelet count.
The effect of this drug on the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract is the appearance of hiccups, impaired saliva production, vomiting, stomach pain, anorexia, and difficulty defecating. Yellowness of the skin and mucous membranes may develop, and liver function will deteriorate.
Relanium also has an effect on the cardiovascular system. The heart rhythm may be disturbed and blood pressure may drop sharply. When using the drug, the functioning of the organs of the genitourinary system may be disrupted: difficulties of any kind with urination, deterioration of kidney function, changes in sexuality in one direction or another.
The use of relanium can cause hives on the skin, as well as scabies. When used as an injection, a blood clot may form at the injection site.
When treating acute alcohol poisoning, a certain number of manipulations are required that will simultaneously stop the absorption of alcohol by the body, help evacuate it from the body more quickly, and prevent the harmful effects of alcohol on many organs and systems.
The number of procedures and medications used during a patient's treatment depends on the patient's condition. During treatment, physical methods are also used, such as washing the digestive organs, and the use of certain medications that rid the body of alcohol and act against alcohol.
Medicines used include glucose, sodium chloride, vitamin C, cordiamin, and magnesia. In the event that withdrawal syndrome is accompanied by mood swings, hysteria or agitation, the use of four milliliters of Relanium intramuscularly is prescribed. All manipulations must be done until the patient feels better. At the same time, doctors constantly monitor heart function, measure pulse rate, blood pressure and respiratory function.
Ukrainian scientists have conducted studies on the effectiveness of using Relanium and other drugs in the treatment of withdrawal symptoms. Riboxin, sodium thiosulfate, was used in these studies. The drug was used at a dose of twenty milligrams as an intramuscular injection at bedtime, as well as thirty milligrams per day orally.
Based on the results of the study, it was concluded that the use of Relanium accelerates the relief of patients from symptoms such as fear, dysphoria, anxiety, and motor agitation.
Relanium what is it?
Relanium is a drug, a tranquilizer common in medical practice.
It is a derivative of diazepam, which the World Health Organization classifies as a necessary drug for society with a proven effect. However, due to the strong impact on the body, the danger of psychological addiction, comparable to dependence on a “real” drug, the Federal Drug Control Service equates it to psychotropic drugs, the release of which is strictly controlled. This is understandable: diazepam, the key active component of the drug, was included in the list of narcotic substances practically equivalent to morphine by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 78 of April 4, 2013. Relanium belongs to the group of benzodiazepines; it is obtained by combining the main substance with benzyl alcohol. Therefore, one of its properties is to enhance the effect:
- alcohol;
- analgesics;
- sleeping pills;
- neuroleptics and narcotics.
The drug is taken in “severe” stages of addiction to enhance the effect, which increases the craving for it and turns into an independent, separate problem. As a second-generation anxiolytic, it depresses the central nervous system and has a number of dangerous side effects, so it must be taken strictly as prescribed by a doctor.
The main forms in which Relanium is produced are tablets, coated dragees and solutions. They are used for intravenous and intramuscular administration and are produced in ampoules (standard 10 mcg) of 5, 10 or more units. The volume of active substance in 1 ml of solution is 5 mg. Drug analogues - diazepam, Valium, alaurin and so on.
As prescribed by a doctor, Relanium is used intravenously, depending on the indications, at certain intervals (usually from 2 to 8 hours).
- for anxiety and agitation - 10-20 mg;
- for tetanus or when epileptic seizures are repeated one after another for 30 minutes or more, 10-20 mg is prescribed;
- for muscle spasms before surgery - 10 mg;
- for infants from 5 weeks - the drug is administered slowly (drip) up to a maximum dose of 5 mg;
- in obstetrics during childbirth - 10-20 mg;
- for children over 5 years of age, the maximum dosage is 10 mg.
Exceeding the dose of Relanium causes the following symptoms:
- drowsiness, the person is less and less aware of what is happening;
- agitation from sedatives;
- lack of response to stimuli, including pain;
- violation of pronunciation, speech;
- decreased heart rate;
- inconsistency of movements;
- hands, head or whole body are shaking;
- depressed respiratory and cardiac functions, loss of consciousness, coma (risk of death).
This is an overdose. To treat it, doctors prescribe gastric lavage and use activated charcoal. If necessary, artificial ventilation is performed and pressure is maintained. Hemodialysis is not very effective. Flumazenil is used as an “antidote”, but not for epilepsy.
Interaction with other drugs and special instructions
Relium should be used with extreme caution simultaneously with phenothiazine derivatives, narcotic analgesics, hypnotics and antidepressants.
Such combinations enhance the effect of the main component of Relium - diazepam. It is prohibited to consume alcohol and drugs during treatment with Relium, since in such a situation the nervous system is significantly depressed and a syndrome of pathological intoxication occurs, which does not depend on the amount of alcohol consumed. This condition is quite often fatal.
Oral contraceptives (COCs) inhibit the effect of the medication. The process of smoking during the treatment period has the same effect.
Concomitant use with other drugs does not cause significant changes in the pharmacodynamics of Relium. However, clinical trials on this matter are ongoing.
Any treatment with this medicinal product should be carried out under the strict supervision of medical personnel.
Prescribed with caution for the treatment of depressive disorders, since there is a high probability of suicidal tendencies in the patient’s behavior
Clinical and laboratory parameters of the blood and urine system should be monitored periodically during therapy.
Particular attention should be paid to changes in liver function tests. The drug is gradually withdrawn
Application of relanium in medicine and effects on the body
In medicine, Relanium in tablets and ampoule form is used to relieve psychomotor excitability in neuroses, panic attacks, fears, anxiety and emotionally unstable conditions. It is a strong sedative and hypnotic with anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects. It provokes an addictive effect, which is dangerous for Relanium. Feedback from patients indicates the development of dependence, primarily psycho-emotional.
The drug reduces the excitability of the “subcortex” of the brain, inhibits the cells of its reticular formation. By prescribing Relanium (the dosage is determined individually), doctors fight convulsions and epilepsy, tetanus, withdrawal syndrome and alcoholic delirium, and paroxysmal anxiety. As a means of relieving emotional stress, it is used in premedication before medical diagnostics, preoperative preparation associated with unpleasant sensations for the patient.
Relanium has many negative effects. Honored Scientist, Doctor of Medical Sciences Professor E. Belozerov, in a study of drug complications, notes that the drug has a teratogenic effect, and its use during pregnancy provokes abnormalities and hypotension in the fetus. Women taking the medicine (even in tablets) note ovulation disorders and gynecomastia. Other dangerous consequences of its use:
- dizziness and regular headaches;
- dysarthria and ataxia;
- tremor and muscle hypotonia;
- apathy, emotional disturbances;
- shortness of breath, apnea, decreased blood pressure, and so on.
Consequences
When regularly taking large doses of the drug, the body is exposed to severe disorders such as:
- Pronounced apathy;
- Dysarthria and speech slowness;
- Depression;
- Hand tremors;
- Emotionality;
- Amnestic memory disorders;
- Disorders of cardiovascular and genitourinary activity.
Abuse of the drug leads to the development of persistent sleep disorders; the patient can fall asleep only after a large dose of the drug. If there is no next dose, the patient will not be able to feel fully. Only treatment and rehabilitation will help improve the situation.
How to get rid of addiction
Dependence is rather psycho-emotional in nature, so traditional drug withdrawal in the case of Relanium is ineffective. Unlike substitution rehabilitation, the Narconon program is aimed at eliminating mental and psychological cravings for the drug and returning the patient to a healthy perception of himself and life. To do this, the following steps are used sequentially:
- non-pharmacological weaning with the help of specially trained staff;
- methods for restoring communication skills “Objective processes”;
- ways to eliminate the consequences of the toxic effects of drugs on the body (“New Life”) - exercises, special nutrition, taking mineral complexes, oils, niacin;
- support techniques for leaving a dangerous circle of friends, realizing one’s responsibility and liberation from the past - “Personal Values” and “Overcoming the Ups and Downs in Life”;
- procedures that develop the skill of creatively dealing with problems and classes for final drug cessation - “Changing conditions in life” and “Life skills”.
After the program, which usually lasts up to 10 weeks, the patient is freed from addiction and returns to a healthy life without relapses or breakdowns.
Poisoning with toxins of bacterial and animal origin
| Poisons and toxins | Antidotes and antidotes | Methods of application |
| Karakurt toxin | Antivenin, magnesium sulfate or calcium chloride | Antivenin is administered in an amount of 2.5 ml intramuscularly or intravenously. Magnesium sulfate is administered in the form of a 25% solution, and calcium chloride is 10%. |
| Wasp and bee stings | Metasone, adrenaline or Prednisolone | Metazone is administered intravenously using a dropper in the form of a solution. Adrenaline is administered subcutaneously; it can be replaced with ephedrine. |
| Snake bites | Antivenin or heparin | Antivenin is administered intravenously 20-150 ml. The exact amount of antivenom depends on the severity of the symptoms. Heparin is administered in a volume of 10,000 units. |
| Botulinum toxin | No antidote |
Relanium
Relanium (active ingredient - diazepam) is one of the most commonly used drugs in neurology.
The mechanism of action is to enhance the action of the inhibitory mediator (gamma-aminobutyric acid) involved in the transmission of nerve impulses. It is used for a dozen diseases of different types, as it is a benzodiazepine tranquilizer.
In this article we will look at why doctors prescribe Relanium, including instructions for use, analogues and prices for this drug in pharmacies. Real REVIEWS of people who have already used Relanium can be read in the comments.
General information about the drug Relium
Relium is a standard psycholeptic of European quality. It is produced in Warsaw (Poland) at the Polfa pharmaceutical concern. The medication has a combined effect, providing anticonvulsant and sedative effects. The drug is on the list recommended for availability in medical institutions compiled by the World Health Organization.
Drug group, INN, scope of application
Relium belongs to the pharmacological group of psycholeptic drugs, a subgroup of anxiolytics, benzodiazepine derivatives. A special feature of this group is that all drugs included in its composition are sold strictly according to prescription. International nonproprietary name (INN) is Diazepam.
The drug is actively used in psychiatric, neurological and drug addiction practices. It can also be used in selected clinical cases of infectious diseases.
Release forms
Available in the form of film-coated tablets. Each tablet is round, biconvex, yellow in color. Dosage is exclusively 5 mg.
The price of medicine in Russian pharmacies differs slightly.
| A drug | Pharmacy name, city | Price in rubles |
| Relium 5 mg, No. 20 | APTEKA LLC, St. Petersburg | 40 |
| Pharmaceutical Leasing LLC, St. Petersburg | 39 | |
| WER.RU, Moscow | 31.9 | |
| Farmalizing LLC, St. Petersburg | 27.5 | |
| Apteka.ru, Smolensk | 31 | |
| Low price pharmacy, Moscow | 33 | |
| Apteka.ru, Orel | 3410 | |
| Laboratory of beauty and health, Moscow | 38 | |
| Online pharmacy GORZDRAV, Moscow and region | 30 |
Composition of Relium
The active substance of the drug is diazepam. This component is a chemical derivative of 1,4-benzodiazepine. It has the ability to influence the GABAergic system, changing its sensitivity. The amount of diazepam in a tablet is directly proportional to its dosage. Auxiliary components are:
- potato starch;
- dry gelatin;
- yellow quinoline dye (E 104);
- talc;
- magnesium stearate;
- sodium starch glycolate.
The coating covering the tablet consists of cellulose acetate phthalate, polyethylene glycol 6000.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The basis of the mechanism of action of Relium is the pharmacodynamic effects of diazepam. The medication has a direct effect on all components of the central nervous system. While taking the medication, changes occur especially actively in the centers of the brain responsible for emotionality - these are, directly, the limbic system and the hypothalamus.
Relium has an inhibitory effect on neurons of the GABAergic system located in the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, and cerebellum. As a result of this, there is a change in the activity of various groups of neurons: dopamine, norepinephrine, serotonin and cholinergic. Against the background of all these processes, the sensitivity and susceptibility to stimuli of the GABA receptor changes, which leads to an increase in its affinity for gamma-aminobutyric acid, which itself is an internal inhibitory transmitter.
Thanks to the combination of these processes, complex sedative effects occur: feelings of fear and anxiety are eliminated, muscle tension is reduced, and sleep improves.
Relium is absorbed by the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract. Metabolism occurs in the liver. Here the active component begins to be divided into two components - N-desmethyl-diazepam and N-methyloxazepam. These, in turn, are converted to oxazepam, which has an affinity for glucuronic acid. Its half-life is a day or two. In the form of these metabolites, the drug is excreted from the body in the urine.
The peak concentration of the drug in the circulatory system occurs an hour after taking the tablet. Relium has the ability to penetrate the blood-brain and placental barrier.
Why is Relanium prescribed?
The drug Relanium is prescribed in the following cases:
- severe anxiety states (paroxysmal anxiety);
- states of anxiety and tension occurring with motor agitation in patients with psychosis:
- status epilepticus;
- withdrawal syndrome in alcoholics - to eliminate acute agitation, muscle tremors; menacing or acute delirium and hallucinosis;
- symptomatically with tetanus;
- preparation for operations;
- premedication during diagnostic procedures;
- uncontrollable vomiting;
- in cardioversion - intravenously;
Additionally, Relanium is used to soften muscle spasms caused by the spasm reflex in local pathology (secondary myositis or arthritis, after injury).
pharmachologic effect
Relanium is a tranquilizer with a benzodiazepine active ingredient. The anxiolytic effect manifests itself in the relief of anxiety, anxiety, fear and emotional stress.
There are three groups of anxiolytics. The drug in question belongs to the second generation anxiolytics. To date, their effect has not been fully studied. But the main manifestations of the drug’s work are expressed in the effect on the subcortical areas of the human brain. The hypothalamus and thalamus, in particular, are responsible for emotional reactions in the human body.
The drug is prescribed against seizures, as a sedative, as a hypnotic and a muscle relaxant.
Effect
Due to its therapeutic effect, Relanium is often used by drug addicts as an independent drug or to enhance the effect of other drugs.
After using Relanium, drug addicts experience the following sensation:
- Carefree;
- Emotional uplift;
- A warm wave spreading over the body;
- Floating and lightness;
- Muffled color and sound perception;
- Weakness of motor coordination.
Such sensations are similar to drug euphoria, although they cannot be compared with the pleasure from opiates or various types of stimulants. However, Relanium brings relief and prevents the onset of drug withdrawal, which is especially important for experienced drug addicts. Some drug addicts even take the drug intravenously in the hope of getting rid of drug addiction, however, in reality they fall under an even stronger relanium addiction.
Instructions for use
According to the instructions for use, Relanium is intended for intravenous or intramuscular administration. The exact dosage is calculated depending on the response to the drug, the indication, the clinical picture of the underlying and concomitant diseases, and the patient’s condition.
- To relieve spasms of skeletal muscles - 10 mg IM 1-2 hours before surgery.
- In order to relieve psychomotor agitation associated with anxiety, 5-10 mg IV is prescribed slowly; if necessary, after 3-4 hours the drug is re-administered in the same dose.
- For status epilepticus, 10-20 mg is prescribed IM or IV; if necessary, after 3-4 hours the drug is re-administered in the same dose.
- In obstetrics, 10-20 mg is prescribed intramuscularly when the cervix is dilated by 2-3 fingers.
- For tetanus, 10 mg IV is prescribed slowly or deep IM, then 100 mg of diazepam is administered IV drip in 500 ml of 0.9% sodium chloride solution or 5% glucose solution at a rate of 5-15 mg/h.
For children over 5 years of age, slow IV injections of 1 mg every 2-5 minutes are indicated until the maximum allowable dose of 10 mg is administered. The administration is repeated at intervals of 2-4 hours if necessary.
Slow IV infusions are also recommended for children from one month of age to 5 years of age. The maximum dose is 5 mg, administered in parts of 100-300 mcg/kg of the child’s weight. Depending on the clinical symptoms, repeated administration is possible with a break of 2-4 hours.
Release form and composition
The dosage form of Relanium is an injection solution, produced in ampoules of 2 ml (5 ampoules in plastic holders, 1, 2 or 10 holders in a cardboard box).
The active ingredient of the drug is diazepam; 1 ml contains 5 mg (10 mg in one ampoule).
Excipients:
- 96% ethanol;
- Propylene glycol;
- Glacial acetic acid;
- Sodium benzoate;
- Benzyl alcohol;
- Injection water;
- 10% acetic acid (to obtain pH 6.3-6.4).
Contraindications
The drug should not be used in the following cases:
- Shock;
- Angle-closure glaucoma;
- Lactation;
- Pregnancy;
- Severe myasthenia gravis;
- Coma;
- Dependence on drugs, alcohol;
- Sleep apnea syndrome;
- Hypersensitivity to benzodiazepines;
- Acute intoxication with sleeping pills, narcotic and psychotropic drugs;
- State of alcoholic intoxication of varying degrees of severity;
- Acute respiratory failure.
Overdose
Symptoms:
drowsiness, depression of consciousness of varying severity, paradoxical excitation, decreased reflexes to areflexia, decreased response to painful stimuli, dysarthria, ataxia, blurred vision (nystagmus), tremor, bradycardia, decreased blood pressure, collapse, cardiac and respiratory depression (up to apnea) activity, coma.
Treatment:
gastric lavage, forced diuresis, administration of activated charcoal, symptomatic therapy (maintaining breathing and blood pressure), artificial ventilation. Flumazenil is used as a specific antagonist in hospital settings. Hemodialysis is ineffective.
Flumazenil is not indicated for patients with epilepsy being treated with benzodiazepines. In such patients, flumazenil can cause the development of epileptic seizures.
Side effects
Thanks to reviews of Relanium, the following side effects of the drug and Relanium analogues were identified:
- Hematopoietic system: thrombocytopenia, anemia, agranulocytosis (weakness or severe fatigue, sore throat, hyperthermia, chills), neutropenia, leukopenia;
- From the digestive system: hypersalivation or dry mouth, liver dysfunction, hiccups, nausea, vomiting, constipation, gastralgia, heartburn, loss of appetite, jaundice, increased activity of liver transaminases and alkaline phosphatase;
- Cardiovascular system: tachycardia, arterial hypotension;
- From the urinary system: urinary retention or incontinence, impaired renal function.
- Reproductive system: dysmenorrhea, decreased or increased libido;
- Respiratory system: respiratory depression (if the drug is administered too quickly);
- Allergic reactions: skin itching, rash;
- Local reactions: venous thrombosis or phlebitis at the injection site;
- From the central and peripheral nervous system: at the beginning of treatment (especially in older people) - increased fatigue, dizziness, impaired concentration, drowsiness, ataxia, slowed mental and motor reactions, dulled emotions, disorientation, anterograde amnesia; rarely - catalepsy, tremor, confusion, depression, dystonic extrapyramidal reactions (uncontrolled movements), hyporeflexia, muscle weakness, euphoria, dysarthria, asthenia, headache; in some cases - paradoxical reactions (sleep disturbances, psychomotor agitation, muscle spasms, anxiety, fear, confusion, outbursts of aggression, hallucinations, suicidal tendencies); Other: drug dependence, addiction; rarely - weight loss, bulimia, diplopia, depression of the respiratory center.
In cases of a sharp reduction in the dose of Relanium or discontinuation of its use, withdrawal syndrome may occur.