Do you want to be like a cucumber in the morning after a fun feast? Looking for a healthy and simple recipe with the least amount of money and effort? For this you will need an antidote. Let's try to find out what an antidote is, and what medications can affect the removal of alcohol from the body, how to use them correctly, and much more.
In general, an antidote means an antidote that neutralizes all bad substances; this remedy neutralizes the effects of alcohol.
The most popular and easily accessible antidote is activated carbon. It perfectly removes ethanol from the body. There are a number of other means that are also capable of removing alcohol well, but more on that below.
What is an antidote?
An antidote is usually called a drug that acts as an antidote. When it is used in the human body, the so-called alcohol rejection occurs, which we will talk about a little later.
Do not think that it is always used when a person drinks alcohol. Since it can not only relieve alcohol intoxication, but also has a lot of side effects.
But if a person allows himself to drink when he has already taken the antidote, then he will create a huge number of problems for himself.
Content
- 1 Physical properties
- 2 Receipt
- 3 Reactivity 3.1 Condensation reaction
- 3.2 Acetal derivatives
- 5.1 Tobacco addiction
Antidotes for alcohol poisoning
This is not a universal cure for alcohol poisoning. And not everyone can accept them. Let's look into this further.
Disulfiram
Disulfiram is a polysorb for alcohol poisoning. This medicine helps a person stop drinking any alcoholic beverages that contain ethyl alcohol.
This drug increases the amount of alcohol metabolite in the human body. It is this factor that causes the feeling that a person has already consumed a large dose of alcohol. He develops tachycardia, hypotension, bradycardia, and so on. And with such symptoms, you don’t want to drink alcohol at all, you want to lie down and rest.
Neutralization of Disulfiram
It is worth noting that this drug has its own antidote. This was created for the purpose that not all people can use antidotes, so doctors were forced to create a means for forcibly decoding a person.
As a rule, the relatives themselves ask to decode their friend, relative, or loved one, since a person immediately giving up alcohol falls into depression and apathy. At this moment he realizes that he urgently needs to take something containing alcohol. That is, the whole meaning of life is now focused around alcohol.
Antidotes are fundamental substances. Therefore, a person with a weak psyche is unlikely to take such drugs.
Colma
Colme drops are a unique alternative to the drug that was described earlier. If we compare Colme drops, they are much weaker in strength than Disulfiram. And the treatment period for these drugs is much longer than the previous ones.
The effect of the same drops is exactly the same as that of other antidotes. When drinking alcohol, it causes tachycardia, pain in the heart, bradycardia and much more.
Polysorb
The first thing to do after alcohol poisoning is to take Polysorb powder. If you take it during a hangover, then after an hour the signs of withdrawal will stop ruining your life.
First of all, after drinking libations, you need to think about cleansing the body of the breakdown elements of alcohol and harmful substances. Polysorb ensures that it completely absorbs all the alcohol and acetaldehyde.
Activated carbon
The most common tablets for alcohol poisoning are activated carbon. The principle of its action is that it prevents alcohol from being absorbed into the blood.
It also helps eliminate alcohol from the body slowly but surely. It must be taken three times a day at the rate of one tablet per ten kilograms of weight.
Dosage forms
The active ingredients of the drugs that provide chemical protection against alcoholism are disulfiram or calcium urea. The first provokes a strong pharmacological effect, completely blocking the alcohol enzyme. It acts almost instantly and causes vivid symptoms of intolerance. Urea has less harsh properties, but is not inferior in efficiency to its analogue.
Types of drugs used to create chemical protection:
- torpedoes sewn under the skin of the person being coded: periodically release a portion of the active substance into the blood;
- gel solutions administered intramuscularly or intravenously.
Trade names of medicines: Torpedo, Teturam, Tetlong, Antabuse, Esperal, Lidevin. The validity period of a portion of the medicine is 3, 6 and 12 months.
Antidotes for acute alcohol poisoning
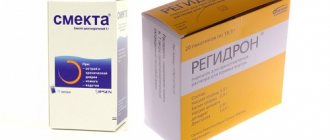
You can easily choose an adsorbent; there are a lot of them. There are actions that are weak in strength and more powerful. Among the most famous are: Enterosgel, Neosmectin, Polyphepan, Algisorb. Smecta is very often used for alcohol poisoning, since its effect is safe and there are no complications from it, except in very severe cases, when there are disturbances in the functioning of internal organs and systems.
Pharmacists also separately highlight REKITZEN-RD. It is used both for the prevention and prevention of withdrawal syndrome, that is, a hangover, and in cases of existing alcohol intoxication.
This drug also contains various groups of vitamins, including E, B, PP, K and D. This remedy should be taken three times a day, about two tablespoons, thirty minutes before meals. A very good result can be obtained if you mix the medicine with half a glass of kefir. This drug is prescribed in courses of one month.
There are times when tablets and powders may not help. More serious therapy is required. In this case, all kinds of solutions that are injected directly into the blood come to the rescue.
What do you use for alcohol intoxication?
- A solution of electrolytes and sugars. These are sodium bicarbonate, Ringer's solution and Panangin.
- In order to cleanse the blood of alcohol breakdown elements, Reogluman, Polygluconin, Rondex are used.
- Vitamins. These may be Ascorbic acid, Thiamine and Pyridoxine.
Contraindications
The specificity of the action of disulfiram and analogues does not allow the use of these drugs in the presence of significant health problems. Contraindications for the use of chemical protection include:
- severe diseases of the liver, kidneys, heart, blood vessels, central nervous system;
- disorders of hematopoietic functions;
- oncological processes;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases;
- withdrawal syndrome;
- age over 60 years.
The treatment method is not used for exacerbation of any chronic pathology, and is prohibited for pregnant women and adolescents.
Formed alcoholism requires radical methods of treatment. Unfortunately, gentle methods of therapy - symptomatic methods of influence and psychotherapy - sometimes have only a temporary therapeutic effect. Under certain conditions, alcoholic behavioral patterns re-emerge, which lead to breakdowns and relapses. That is why radical methods of treatment are so in demand - drug coding for alcohol or chemical protection.
How do antidotes work?
The antidote is used when it is necessary to get rid of alcohol addiction. It affects the liver. These drugs form an enzyme that breaks down the elements of ethanol.
The antidote is administered intravenously into the human body. There is no discomfort or discomfort.
Discomfort begins when a person takes even a drop of alcohol into his mouth. A person loses even the slightest desire to try alcohol, as pain and other similar sensations appear.
Receipt
In 2003, global production was about a million tons per year.
The main production method is ethylene oxidation (Wacker process):
2 CH 2 = CH 2 + O 2 → 2 CH 3 CHO {\displaystyle {\mathsf {2CH_{2}{\text{=}}CH_{2}+O_{2}\rightarrow 2CH_{3}CHO}} }
Palladium chloride is used as an oxidizing agent in the Wacker process, which is regenerated by oxidation with copper chloride in the presence of atmospheric oxygen:
CH 2 = CH 2 + P d C l 2 + H 2 O → CH 3 CHO + P d + 2 HC l {\displaystyle {\mathsf {CH_{2}{\text{=}}CH_{2}+PdCl_ {2}+H_{2}O\rightarrow CH_{3}CHO+Pd+2HCl}}} P d + 2 C u C l 2 → P d C l 2 + 2 C u C l {\displaystyle {\mathsf {Pd+2CuCl_{2}\rightarrow PdCl_{2}+2CuCl}}} 4 C u C l + 4 HC l + O 2 → 4 C u C l 2 + 2 H 2 O {\displaystyle {\mathsf {4CuCl +4HCl+O_{2}\rightarrow 4CuCl_{2}+2H_{2}O}}}
Acetaldehyde is also obtained by hydration of acetylene in the presence of mercury salts (Kucherov reaction), with the formation of enol, which isomerizes into aldehyde:
C 2 H 2 + H 2 O → H g 2 + , H + CH 3 CHO {\displaystyle {\mathsf {C_{2}H_{2}+H_{2}O{\xrightarrow[{}]{Hg^ {2+},H^{+}}}CH_{3}CHO}}}
Another method dominated until the discovery of the Wacker process. It consisted of the oxidation or dehydrogenation of ethyl alcohol on a copper or silver catalyst.
C 2 H 5 OH → A g , o CCH 3 CHO + H 2 {\displaystyle {\mathsf {C_{2}H_{5}OH{\xrightarrow[{}]{Ag,^{o}C}}CH_ {3}CHO+H_{2}}}} 2 C 2 H 5 OH + O 2 → A g , o C 2 CH 3 CHO + 2 H 2 O {\displaystyle {\mathsf {2C_{2}H_{5 }OH+O_{2}{\xrightarrow[{}]{Ag,^{o}C}}2CH_{3}CHO+2H_{2}O}}}
Ethanol toxemia
Ethyl alcohol poisoning is possible not only when taking excessive amounts. They can occur with the simultaneous use of drugs or other pharmacological preparations. Among them are analgesics, tranquilizers, antidepressants.
Such liquids are rightfully classified as strong narcotic substances. About 80% of alcohol is converted into acetic acid in the liver. It, in turn, is eliminated with 20 percent unsplit in the urine.
Conditions for toxemia
Ethanol poisoning is possible if the concentration in the bloodstream exceeds 3 g (5 ppm) per 1 kg of human weight.
An overdose entails not only acute toxemia, but also death. A lethal dose corresponds to 250-400 ml of alcohol of 95% concentration, consumed within 0.5-1.5 hours.
Clinical picture
The dynamics and level of toxicity largely depend on the good quality of food products, general physical condition, the percentage of gastric acidity, emotional background and other factors.
If ethyl alcohol poisoning occurs, the symptoms increase and develop very dynamically within an hour. Signs and their severity will depend on the level of intoxication.
Easy degree
With a mild degree of intoxication, one feels relaxed and euphoric
It is characterized by a content of 0.2 ppm to 0.29 ppm of alcohol-containing liquid in the bloodstream. At the same time, there are no visible changes or functional disorders in the victim’s behavior. It is possible to observe any changes in the body only with the use of special tests. If we assume that about 0.15 ppm is eliminated within an hour, then perfect sobriety with a similar concentration of the substance in the bloodstream can be expected only after 4 hours.
In the case when a person continues to increase the dose, and it reaches 0.30-0.59 ppm, then alcohol toxemia does not develop, but behavioral signs begin to progress. The victim feels relaxed, becomes overly talkative, and unrestrained. A slight euphoria develops.
0.6-0.9 ppm makes a person a pronounced extrovert. He ignores social behavioral norms and becomes very impulsive. His pain threshold decreases.
The manifestation of symptoms at this stage increases. Among them:
- loss of judgment;
- peripheral vision decreases;
- the reaction of the pupils to changes in light decreases;
- the degree of reaction to external stimuli decreases.
Average degree
It is characterized by a number per mille in the range of 1-3. This is an important factor, because the line between
Loss of balance when walking in moderate intoxication
moderate and severe degrees are negligible.
From 1.5 to 2.9 ppm changes in behavior are pronounced. Moreover, it becomes changeable. Expressive fun gives way to crying, and sometimes anger. A person ceases to navigate in space and time. Loss of consciousness or stupor is possible.
Characteristic symptoms for this stage:
- slurred, confused speech;
- loss of balance when walking;
- decrease or loss of memory.
If timely assistance is not provided in such a situation, then a severe degree of toxemia develops.
Severe degree
Severe symptoms are diagnosed already at 3 ppm, when death is not excluded.
Dangerous ppm levels are from 3 to 5. If the concentration of alcohol in the bloodstream is above 5 ppm, then death is almost inevitable, even if assistance is provided to the victim.
The external symptoms that appear in this case are:
- unnatural shine of the eyes;
- skin hyperemia;
- excessive sweating;
- grimacing;
- lack of coordination in movements.
Symptoms rapidly increase and become more complex. There is a disorder of the central nervous system, alcoholic coma. Its symptoms are:
In severe cases of poisoning, alcoholic coma occurs
- sudden constriction of the pupils;
- involuntary urination;
- defecation;
- profuse, continuous vomiting;
- decrease in blood pressure;
- thready weak pulse;
- noisy and shallow breathing.
Literature:
- Physical chemistry: coursework: textbook / Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation, Ural Federal University named after the first President of Russia B. N. Yeltsin. - Ekaterinburg: Ural University Publishing House, 2014. - 185 p.
- A short course in organic chemistry for doctors and biologists / P. P. Shorygin. - Leningrad; Moscow: State. publishing house, 1925. – 399 p.
- Chemical foundations of life processes / K. Oppenheimer; translation edited by S. Ya. Kaplansky. - Moscow ; Leningrad: State. Publishing house of biological and medical sciences. Literature, 1934. - Hardcover, 309 p.
Authorship and editing of the text:
Head of the Department of Psychiatry and Narcology of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist Popov A.G., psychiatrist-narcologist Serova L.A.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 744-85-28
Call! We work around the clock!
First aid
In case of acute alcohol poisoning, emergency measures are taken. Before the arrival of the emergency medical service, you must:
- Induce artificial vomiting.
- Give the victim 1–2 glasses of warm water to drink.
- If it is not available, offer sweets in the form of regular sugar.
In case of loss of consciousness, ammonia should be used. Soak a gauze swab in it and bring it to your nose. Absence of pulse and breathing is an indication for resuscitation.
First aid is carried out independently. At the pre-medical stage, a person can be given sorbents. It is recommended to take white charcoal. It adsorbs substances contained in ethanol.
Causes of intoxication
Death without treatment due to ethyl alcohol poisoning occurs due to:
- consumption of low-quality products;
- use for oral administration of substances that are intended for application to the skin;
- excessive use of alcohol-containing medications;
- improper use of substances containing wine alcohol;
- neglect of safety rules when working with ethanol.
The greatest danger is not so much ethanol poisoning, which in modern conditions is quite easily dealt with, but rather its surrogates.
Treatment methods
It is carried out in a hospital. Upon admission with alcohol poisoning:
- Detoxification of the body. They put in IVs with glucose and vitamins.
- Correction of respiratory dysfunctions.
- Prescription of antiemetics and laxatives.
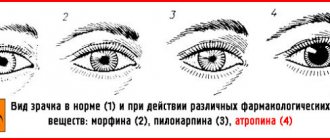
According to indications, drugs are used to restore heart function. Oxygen is supplied. If necessary, atropine is given to reduce the secretion of the salivary glands. It is advisable to use analeptics. The development of a serious condition requires hemosorption.
Antidote
There is literally no antidote for ethyl alcohol. Poisoning is treated with symptomatic and pathogenetic therapy. Patients with chronic intoxication are prescribed long-term intake of vitamins and disulfiram.
Prevention
To prevent poisoning with methyl alcohol, this substance and liquids containing it should be stored in a locked cabinet. The packaging must be clearly marked to indicate that the liquid is toxic.
In industries that use methyl alcohol, to prevent poisoning, they usually add special substances to it that either cause it to color or give it a sharp, unpleasant odor.
Methyl alcohol can be found in toxic concentrations in alcohol surrogates, as well as in counterfeit alcoholic beverages produced by handicraft. Therefore, to prevent methanol poisoning, you should buy alcoholic beverages only at official retail outlets whose activities are licensed.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Fluconazole and alcohol: compatibility, how long after you can drink
on the topic of the article:
Reactivity
In terms of its chemical properties, acetaldehyde is a typical aliphatic aldehyde, and the reactions of this class of compounds are characteristic of it. Its reactivity is determined by two factors: the activity of the carbonyl of the aldehyde group and the mobility of the hydrogen atoms of the methyl group, due to the inductive effect of the carbonyl.
Like other carbonyl compounds with hydrogen atoms at the α-carbon atom, acetaldehyde tautomerizes to form enol - vinyl alcohol, the equilibrium is almost completely shifted towards the aldehyde form (the equilibrium constant is only 6 10−5 at room temperature [3]):
Condensation reaction
Due to its small molecular size and availability as an anhydrous monomer (as opposed to formaldehyde), acetaldehyde is a common electrophilic agent in organic synthesis[4]. As far as condensation reactions are concerned, the aldehyde is prochiral. It is used primarily as a source of the “CH3C+H(OH)” synthon in aldol and related condensation reactions. Grignard reagent and organolithium compounds react with MeCHO to form hydroxyethyl derivatives. In one condensation reaction, three equivalents of formaldehyde add and one reduces the resulting aldehyde, forming pentaerythritol (C(CH2OH)4) from MeCHO.
In the Strecker reaction[5], acetaldehyde condenses with cyanide and ammonia, forming the amino acid alanine[6] after hydrolysis. Acetaldehyde can condense with amines to form imines, as the condensation of cyclohexylamine gives N-ethylidene cyclohexylamine. These imines can be used for direct downstream reactions such as aldol condensation[7].
Acetaldehyde is also an important building block for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds. An outstanding example is the conversion by ammonia to 5-ethyl-2-methylpyridine (“aldehyde-collidine”)[8]
The aldol condensation reaction is caused by the mobility of hydrogen in the alpha position in the radical and is carried out in the presence of dilute alkalis. It can be considered as a reaction of nucleophilic addition of one aldehyde molecule to another:
CH 3 - CHO + CH 3 - CHO → CH 3 - CH ( OH ) - CH 2 - CHO {\displaystyle {\mathsf {CH_{3}{\text{-}}CHO+CH_{3}{\text{ -}}CHO\rightarrow CH_{3}{\text{-}}CH(OH){\text{-}}CH_{2}{\text{-}}CHO}}}
Acetal derivatives
Three molecules of acetaldehyde condense to form “paraldehyde,” a cyclic trimer containing single C-O bonds. The condensation of four molecules produces a cyclic compound called metaldehyde.
Acetaldehyde forms stable acetals when reacting with ethanol under dehydration conditions. The product CH3CH(OCH2CH3)2 is called an "acetal"[9], although the term is used to describe a broader group of compounds with the general formula RCH(OR')2.
Neutralization during a feast
We continue to look at how to quickly neutralize alcohol. One of the important rules is to follow simple instructions directly during the feast:
- Do not drink alcoholic beverages (especially strong ones) in their pure form.
- Be sure to take a bite of the alcohol you drink.
- Watch what you eat - snack food must be low-fat.
- Remember to drink clean drinking water.
- Avoid carbonated drinks.
- Move as much as possible - dance, take part in active competitions, periodically go out into the fresh air for a walk.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with Paxil and alcohol: compatibility, how long it takes, consequences
All these simple rules taken together will help alcohol decompose faster in your body and exit with excretory products more quickly.