Scientists from the University of Manchester (UK) announced a connection between rice consumption and the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. According to scientists, this risk is higher in those who consume rice in large quantities and for a long time.
A study published in the journal Science of the Total Environment found a link between rice consumption in England and Wales and cardiovascular disease caused by arsenic exposure. The findings show that the 25% of people in England and Wales who eat the most rice are at greater risk of cardiovascular mortality, compared with the 25% of those who eat the least. Researchers also note that long-term exposure to arsenic increases the risk of other dangerous diseases, including cancer.
Q&A Is arsenic in shrimp dangerous?
As scientists have found, over the past few years, the concentration of arsenic in the soil and water of regions where rice is grown has increased significantly. Experts suggest that arsenic in rice may be responsible for more than 50,000 premature deaths annually. Despite a number of useful substances, scientists advise consuming this product in moderation and eating a varied diet.
What is arsenic and how does it work?
Arsenic (arsenicum) is element No. 33 of the periodic table of Mendeleev, which is a deadly poison (we recommend reading: how many days can you walk with arsenic in your tooth?). This semimetal has a gray-silver color and a brittle structure. For medical use, arsenic acid (anhydride) is used, which has the form of a white powder. When it enters the human body, it simultaneously affects the cardiovascular system, liver, and kidneys.
The composition of arsenic-containing dental pastes for pulp devitalization includes:
- arsenic anhydride (30 mg),
- novocaine hydrochloride,
- thymol, camphor, engenol,
- fibrous former and paste-forming components.
The most common arsenic-containing pastes are Devit-ARS, Pulpocid, Arsenic Paste, Caustinerf arsenical, Septodont, Pulparsen, etc. Despite the different manufacturers, their composition is almost identical.
Consequences
Poisoning with this toxin can have a variety of consequences. First of all, it depends on the form of intoxication and the timeliness of its detection. The acute form is much easier and simpler to detect, since it manifests itself immediately and is accompanied by pronounced symptoms, which means that treatment will be carried out on time and will allow the body to fully recover.
Chronic poisoning is more difficult to identify. It slowly, almost imperceptibly affects the organs, gradually worsening their functioning, negatively affecting digestion, appetite, and general well-being. However, in such cases, treatment is also usually effective.
Indications and contraindications in dentistry
The indication for using the paste is the need to necrotize the pulp for subsequent depulpation of the tooth. The permitted residence time of arsenic-containing substances in the dental cavity is no more than 72 hours.
Contraindications:
- individual intolerance or hypersensitivity to the drug,
- allergy to lidocaine,
- childhood, baby teeth,
- pregnancy and breastfeeding,
- violation of root integrity,
- renal and liver failure,
- increased eye pressure,
- athletes (a positive doping test result is possible),
- driving a car or working with various mechanisms that require increased attention.
Causes of intoxication
Arsenic poisoning is, as a rule, a consequence of an accident, inattention and careless handling of various toxic substances and products. After all, it is found everywhere:
- in seafood;
- in food preservatives, dyes;
- in pest control products: rodents, parasites, insects, weeds, plant diseases;
- in antifungal products;
- in various industries;
- in rocks, earth;
- in smoke resulting from the combustion of chemical waste, coal, ore smelting.
The causes of intoxication may be:
- Attempted suicide.
- Accident at work.
- Drinking water or other products containing this poison.
- Failure to comply with safety requirements and standards.
- Murder.
Why does a toothache with arsenic hurt?
In the first few hours after the filling is installed, the pain is quite severe, despite the presence of lidocaine. This happens because during its installation, actions were performed with an open pulp, the nerve endings are irritated, and the effect of the drug has not yet occurred. In this case, it is recommended to take a painkiller: Ibuprofen, Paracetamol, Ketanov, etc.
If after a day the pain does not subside, but, on the contrary, intensifies, you must urgently contact a dental clinic. The reasons for this pain may be:
- necrosis or inflammation of periodontal tissues,
- periodontitis (periodontal disease),
- violation of root integrity,
- The tooth cavity is not open enough, so the paste does not work,
- small amount of drug
- poor quality filling,
- allergic reactions.
Methods of poisoning
The poison can enter the body through the skin, respiratory system, and can be eaten with food or drunk with water. It combines with blood plasma and quickly spreads throughout all systems and internal organs. Poisoning can occur when:
- Living in contaminated areas.
- Eating contaminated water and seafood.
- Production (in case of violation of safety regulations for working with poisons).
There are quite a few places where arsenic is found in nature; however, whether poisoning occurs depends on the concentration of the poison that has entered the body.
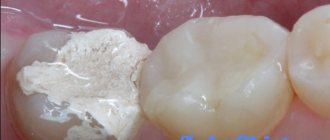
What to do if arsenic falls out of a tooth?
In the process of eating, a rather fragile temporary filling can break and expose the arsenic layer. In such cases, it is necessary to close the cavity with cotton wool and go to the dentist, where everything will be restored and a new date will be set for the visit.
If it so happens that arsenic paste is accidentally swallowed, do not panic. The dose of arsenicum in it is so small that it cannot do any harm. You can drink a glass of milk as an antidote. The casein contained in it reacts with arsenic anhydride, neutralizes it, and precipitates. You can also eat beaten egg whites. Of the medicinal antidotes, injections of Unitol (Dimercaprol) are used.
To prevent the temporary filling from falling out, you must:
- do not eat or drink after filling for 2 hours, but when you are very thirsty, you are allowed to drink warm water through a straw no earlier than 30 minutes after installation (see also: why does a tooth hurt after root canal filling? ),
- Carry out hygienic procedures very carefully, do not use toothpicks, floss,
- try to chew food on the opposite side of the jaw or eat soft foods.
READ ALSO: what to do if a temporary filling falls out, given that the canals were sealed?
Areas of application
Arsenic is used in various fields and purposes:
- In everyday life - for rodent control.
- Dentistry – for dental treatment.
- Electronics industry - for the manufacture of semiconductor devices, when alloyed with silicon it allows to increase conductivity.
- Non-ferrous metallurgy - to impart strength to certain metals: lead, copper and others.
- Agronomy - to eliminate pests and weeds.
- Glassmaking.
- Shipbuilding - for impregnation of wood.
- In the production of hunting shot.
- Finishing skins - as an antiseptic.
- Sanitary and Epidemiological Services.
- Veterinary medicine.
- Bearing alloys to improve their thermal properties, increase corrosion resistance, and hardness.
Is it possible to remove arsenic yourself?
If inflammation has developed in the mouth around a tooth with a temporary filling, unbearable pain that does not decrease throughout the day, the periodontal tissues have begun to bleed, or 72 hours have passed after the filling, and it is not possible to visit the dentist, you can remove the temporary filling and arsenic paste yourself. Next, you need to thoroughly rinse the resulting cavity with infusion (chamomile, sage or oak bark), soda-salt solution or warm boiled water. Then close the cavity with cotton wool.
READ ALSO: How many hours can you not eat after having a filling installed?
First aid
Typically, a mild form of poisoning does not require treatment in a hospital, but the severity of the condition can only be determined by a specialist after conducting the necessary examination. As soon as the poison has entered the body, you should call an ambulance. While waiting for a doctor, it is necessary to help the victim at home:
- Gastric lavage. Give the patient plenty of lightly salted water and induce vomiting.
- A solution of hydrogen sulfide water (100 ml) can be used as an antidote for arsenic poisoning. It neutralizes the poison by converting it into a safe compound - arsenic sulphide.
- Give the victim some sorbent (Polysorb) to drink.
- To prevent dehydration, give the victim small amounts of water frequently.
- If poison gets on the surface of the skin, you should immediately wash it off with soap and water.
Read also: Signs, symptoms and treatment for household gas poisoning
It is unlikely that every home has a first aid kit containing an arsenic antidote. Therefore, after carrying out possible manipulations at home, the victim should be given to the hands of doctors.
Notes
- Michael E. Wieser, Norman Holden, Tyler B. Coplen, John K. Böhlke, Michael Berglund, Willi A. Brand, Paul De Bièvre, Manfred Gröning, Robert D. Loss, Juris Meija, Takafumi Hirata, Thomas Prohaska, Ronny Schoenberg, Glenda O'Connor, Thomas Walczyk, Shige Yoneda, Xiang-Kun Zhu.
Atomic weights of the elements 2011 (IUPAC Technical Report) // Pure and Applied Chemistry. — 2013. — Vol. 85, no. 5. - P. 1047-1078. — DOI:10.1351/PAC-REP-13-03-02. - Arsenic: electronegativities (English). WebElements. Retrieved August 5, 2010.
- Editorial team: Knunyants I. L. (chief editor).
Chemical encyclopedia: in 5 volumes - Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1992. - T. 3. - P. 157. - 639 p. — 50,000 copies. — ISBN 5—85270—039—8. - Arsenic. Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
(2000). Retrieved January 30, 2014. - Frisk H.
Griechisches etymologisches Wörterbuch, Band I. - Heidelberg: Carl Winter's Universitätsbuchhandlung. - 1960. - P. 152. - Lavoisier, Antoine.
Traité Élémentaire de Chimie, présenté dans un ordre nouveau, et d'après des découvertes modernes. - Paris: Cuchet, Libraire, 1789. - P. 192. - JP Riley and Skirrow G. Chemical Oceanography V. 1, 1965
- Online Encyclopedia Around the World. Arsenic.
- Inorganic chemistry: In 3 volumes. /ed. Yu. D. Tretyakova. T. 2: Chemistry of intransition elements: textbook for students. institutions of higher education education / A. A. Drozdov, V. P. Zlomanov, G. N. Mazo, F. M. Spiridonov - 2nd ed., revised. - M.: Publishing House, 2011. - 368 p.
- Knizhnikov V.A., Bochkarev V.V., Zimina L.N., Marchenko E.N., Rubtsov A.F., Serebryakov L.A.
Arsenic // Great Medical Encyclopedia: in 30 volumes / chapter. ed. B.V. Petrovsky. — 3rd ed. - Moscow: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1981. - T. 16. Museums - Nile. — 512 s. — 150,800 copies. - Pharmacology prof. Nikolaev. 1943 1st edition
- McDiarmid, 2020, p. 8.
- Wolfe-Simon F, Blum JS, Kulp TR, et al.
(December 2010).
"A Bacterium That Can Grow by Using Arsenic Instead of Phosphorus." Science
. DOI:10.1126/science.1197258. PMID 21127214. - Arsenic-eating microbe may redefine chemistry of life. naturenews. Retrieved January 26, 2011. Archived February 24, 2012.
- An astrobiological discovery leads a poison-filled life (Russian). membrane Retrieved January 26, 2011. Archived February 24, 2012.
- Reaves, Marshall Louis; Sunita Sinha, Joshua D. Rabinowitz, Leonid Kruglyak, Rosemary J. Redfield (2012-07-27). "Absence of Detectable Arsenate in DNA from Arsenate-Grown GFAJ-1 Cells." Science 337
(6093):470-473. DOI:10.1126/science.1219861. ISSN 1095-9203 0036-8075, 1095-9203. Retrieved 2012-12-25. - Detoxification of arsenic-contaminated soils with natural sorbents, their mixtures and modifications
- N. V. PETROVSKAYA “NATIVE GOLD. GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS, TYPOMORPHISM, QUESTIONS OF GENESIS, PUBLISHING HOUSE "NSCHKL, MOSCOW, 1973
- Gold mining as a poison for the environment - WAR and PEACE
MORPHOLOGY
Arsenic is usually observed in the form of crusts with a sintered kidney-shaped surface, stalactites, shell-like formations, which reveal a crystalline-granular structure when fractured. Native arsenic is quite easily recognized by the shape of the deposits, blackened surface, significant specific gravity, strong metallic luster in a fresh fracture and perfect cleavage. Under the blowpipe it evaporates without melting (at a temperature of about 360°), emitting a characteristic garlic odor and forming a white As2O3 coating on the coal. It turns into a liquid state only at increased external pressure. In a closed tube it forms a mirror of arsenic. When struck sharply with a hammer, it emits a garlicky smell.
PROPERTIES
The color on a fresh fracture is zinc-white, tin-white to light gray, quickly fades due to the formation of dark gray tarnish; black on a weathered surface. Hardness on the Mohs scale 3 - 3.5. Density 5.63 - 5.8 g/cm3. Fragile. Diagnosed by the characteristic smell of garlic when struck. Cleavage is perfect along {0001} and less perfect along {0112}. The fracture is grainy. Ud. weight 5.63-5.78. The line is gray, pewter-white. The luster is metallic, strong (when freshly fractured), quickly fades and becomes dull on an oxidized surface that has become blackened over time. Is diamagnetic.
PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Mineral color | pewter-white, fading to dark gray or black on the surface |
| Stroke color | grey |
| Transparency | opaque |
| Shine | semi-metallic, dull |
| Cleavage | perfect by {0001} and less perfect by {0112} |
| Hardness (Mohs scale) | 3,5 |
| Kink | uneven |
| Strength | fragile |
| Density (measured) | 5.63 – 5.78 g/cm3 |
| Radioactivity (GRapi) | 0 |
Literature
- Val McDermid.
Anatomy of a crime: What insects, fingerprints and DNA can tell. = Val Mcdermid: “Forensics: The Anatomy of Crime.” - M.: Alpina Non-fiction, 2020. - 344 p. — ISBN 978-5-91671-591-0.
H
| Periodic table of chemical elements by D. I. Mendeleev | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| He | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Li | Be | B | C | N | O | F | Ne | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Na | Mg | Al | Si | P | S | Cl | Ar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| K | Ca | Sc | Ti | V | Cr | Mn | Fe | Co | Ni | Cu | Zn | Ga | Ge | As | Se | Br | Kr | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rb | Sr | Y | Zr | Nb | Mo | Tc | Ru | Rh | Pd | Ag | Cd | In | Sn | Sb | Te | I | Xe | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cs | Ba | La | Ce | Pr | Nd | Pm | Sm | Eu | Gd | Tb | Dy | Ho | Er | Tm | Yb | Lu | Hf | Ta | W | Re | Os | Ir | Pt | Au | Hg | Tl | Pb | Bi | Po | At | Rn | ||||||||||||
| Fr | Ra | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | MD | No | Lr | Rf | Db | Sg | Bh | Hs | Mt | Ds | Rg | Cn | Nh | Fl | Mc | Lv | Ts | Og | ||||||||||||
| Uue | Ubn | Ubu | Ubb | Ubt | Ubq | UBP | Ubh | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alkali metals | Alkaline earth metals | Lanthanides | Actinoids | Superactinoids | Transition metals | Other metals | Semimetals | Other non-metals | Halogens | Noble gases | Properties unknown | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Hospital treatment
If the ambulance team determines the patient’s condition as serious, he is indicated for urgent hospitalization. The attending physician will prescribe the necessary tests that will help in making an accurate diagnosis. The classic treatment regimen for arsenic poisoning includes:
- A course of injections with calcium chloride to prevent dehydration and maintain blood pressure at the required level.
- If there is blood in the urine (renal failure has developed), novocaine with glucose is used.
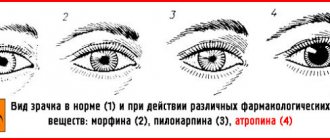
- If the victim suffers from pain in the gastrointestinal tract, injections of morphine with atropine are indicated.
- Administration of the antidote. In case of arsenic poisoning, Unithiol is used (intravenously), which converts the poison into a safe compound and removes it from the body along with urine. Chronic poisoning is relieved with a course of injections of D - penicillin (1 g / 4 times a day).
- Blood transfusion, hemodialysis or forced diuresis (depending on the condition of the kidneys).
- In case of arsenic vapor poisoning, oxygen inhalation is used.
If the poisoning was so severe that it affected the condition of the internal organs and the body’s life support system, the duration of its recovery can be up to 24 months. Therefore, after discharge from the hospital, it is important to follow all rehabilitation standards: adhere to a special diet, take alkaline baths, and do not violate the recommended drinking regime.
STRUCTURE
The crystal structure of arsenic is ditrigonal-scalenohedral symmetry. Trigonal syngony, c. With. L633L23PC. The crystals are extremely rare and have a rhombohedral or pseudocubic habit.
Several allotropic modifications of arsenic have been identified. Under normal conditions, metallic or gray arsenic (alpha arsenic) is stable. The crystal lattice of gray arsenic is rhombohedral, layered, with a period a = 4.123 A, angle a = 54° 10′. Density (at a temperature of 20° C) 5.72 g/cm3; temperature coefficient linear expansion 3.36 • 10 degrees; specific electrical resistance (temperature 0° C) 35 • 10-6 ohm • cm; NV = f 147; coefficient compressibility (at a temperature of 30° C) 4.5 x 10-6cm2/kg. The melting point of alpha-arsenic is 816 ° C at a pressure of 36 atmospheres.
Under atm. Arsenic sublimes under pressure at a temperature of 615° C without melting. Heat of sublimation 102 cal/g. Arsenic vapors are colorless, up to a temperature of 800°C they consist of As4 molecules, from 800 to 1700°C - from a mixture of As4 and As2, above a temperature of 1700°C - only from As2. With the rapid condensation of arsenic vapor on a surface cooled by liquid air, yellow arsenic is formed - transparent soft crystals of a cubic system with a density of 1.97 g/cm3. Other metastable modifications of arsenic are also known: beta-arsenic - amorphous glassy, gamma-arsenic - yellow-brown and delta-arsenic - brown amorphous with densities of 4.73, respectively; 4.97 and 5.10 g/cm3. Above a temperature of 270° C, these modifications turn into gray arsenic.
Scale of the problem
Arsenic contamination of groundwater is widespread, and a number of areas have significant levels of arsenic contamination in drinking water. Today, at least 140 million people in 50 countries are known to drink water with arsenic concentrations above the WHO guideline level of 10 µg/liter (4).
After in the 1990s. In Bangladesh, widespread arsenic was found in well water, and the issue of arsenic exposure in that country has received a lot of attention. Since then, significant progress has been made, and the number of people exposed to arsenic levels above the Bangladesh Drinking Water Quality Standard has decreased by approximately 40%. Despite these efforts, it is estimated that in 2012, approximately 19 million and 39 million people in Bangladesh were exposed to arsenic levels above the national standard of 50 μg/liter and the WHO guideline of 10 μg/liter, respectively (5 ). In areas of Bangladesh where the problem is particularly acute, 21.4% of all deaths were caused by arsenic concentrations in drinking water greater than 10 µg/liter (6). A similar dose-response relationship was observed in other parts of Bangladesh: these results were combined with those of a national survey, and the combined analysis yielded an annual arsenic-related mortality rate of 43,000 (7). The US National Research Council has noted that lifetime consumption of drinking water containing 50 µg/liter arsenic (8) may be responsible for up to 1 in 100 additional cancer deaths.
Symptoms and signs caused by long-term exposure to elevated concentrations of inorganic arsenic vary between individuals, populations, and geographic areas. Therefore, there is no general definition of the disease caused by arsenic. This makes it difficult to estimate the burden of disease associated with arsenic.
There is also no method for distinguishing between cancers caused by arsenic and cancers caused by other factors. As a result, there is no reliable estimate of the extent of the problem worldwide.
In 2010, the Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) re-evaluated the health effects of arsenic exposure in the light of new evidence. JECFA concluded that for selected areas of the world where levels of inorganic arsenic in drinking water exceed 50-100 µg/litre, there is some evidence of adverse effects. For other areas where elevated levels of arsenic in water (10-50 µg/litre) are observed, the committee noted that while adverse effects may occur, the prevalence is low and would be difficult to detect in epidemiological studies.
Safety regulations
When buying rice, you should remember that it may contain traces of a toxic substance. Therefore, purchased rice in bulk should be thoroughly washed and dried. Another way to protect your body from the effects of harmful impurities is to increase the water when cooking rice, in a ratio of 1:6. An effective, albeit unconventional, method is to cook the rice using a coffee maker. This idea came from American scientists. The device allows you to evaporate rice, thereby destroying toxic components.
Considering the harmfulness of arsenic present in rice, it is worth reducing its daily consumption and partially replacing it with other products. Nutrition experts recommend amaranth, barley, and whole wheat pasta. Obviously, you should not obsessively get rid of rice reserves, since eating the product in small quantities will not harm the body at all. You just have to observe moderation and maintain common sense. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!