Detoxification therapy is a set of methods that is aimed at cleansing the body and ridding it of the influence of various toxic substances that come from outside or are formed in it due to certain processes.
This treatment is used for endogenous intoxication, when metabolic products are not completely removed from it, as well as for various poisonings.
There are two types of poisoning for which detoxification therapy is prescribed:
- Intoxication is when the body reacts painfully to various poisons. This reaction is protective and is aimed at combating the effects of the toxin in the body.
- Toxicosis is a perverted, nonspecific reaction of the immune system to the effects of viruses and microbial toxins. Toxicosis occurs due to too rapid transition of adaptive reactions into pathological ones.
Content:
- Indications for detoxification therapy.
- Possible options for detoxifying the body.
- Means for detoxification therapy: 2.1. Use of medications. 2.2. Hardware detoxification therapy.
- Is it possible to detoxify on your own?
Detoxification therapy is necessary to cleanse tissues of narcotic compounds and ethanol. For this purpose, various medications are used, and hardware methods of detoxification of the body are practiced in hospital settings. In this way, withdrawal symptoms can be alleviated and the addict prepared for further treatment.
Etiotropic treatment
It is necessary for patients with severe viral infections. They are prescribed antiviral drugs, which often include immunoglobulins and other drugs.
For patients with bacterial infections, antibiotics are prescribed, along with which they are given hyperimmune components. Among them are antitoxic serums, different types of plasma, and immunoglobulins. What kind of disinfection therapy will be for each individual patient depends on the clinical indicators of the course of his illness.
Indications for detoxification therapy
- The need for emergency sobering up after a single episode of alcohol abuse.
- Preparing for coding. After a long period of heavy drinking, the break between detoxification and medication coding should be at least 4–5 days. In some cases (in particular, after a relatively short binge, the person is in satisfactory health and there are no contraindications), coding is possible immediately after detoxification of the body.
- Symptoms of severe alcohol poisoning. In the absence of addiction or in the initial stages of the disease, when the concentration of ethanol in the blood approaches the limit values, a kind of protective reaction “turns on”: severe vomiting, drowsiness, etc. But in the later stages of alcoholism, there is a real danger of severe intoxication, especially since in a state of abstinence a person is not particularly picky about the quality of the alcohol consumed.
- Binge drinking. The only option to safely “get out” of this state is comprehensive detoxification. Independent attempts to suddenly stop drinking are fraught with complications from the psyche (psychosis, delirium), cardiovascular system (severe hypertension, risk of heart attack, stroke), liver, kidneys.
- The initial stage of the fight against drug addiction.
- Severe withdrawal symptoms.
Pathogenetic treatment
It includes the following measures:
- hemodilution (blood dilution),
- elimination of hypoxia,
- restoration of blood circulation,
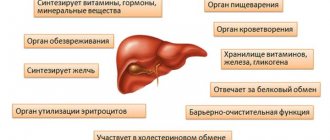
- supporting the work and restoration of detoxification organs.
Hemodilution reduces the concentration of poison in the blood, as well as in the intercellular space. Blood circulation is restored by introducing plasma substitutes and electrolytes. All types of hypoxia are eliminated through oxygenation, or oxygen therapy, which is carried out in special rooms. First of all, it is necessary to restore detoxification organs such as the kidneys and liver. To do this, the patient’s body is provided with plenty of water. The effectiveness of such therapy is determined by the hourly or daily volume of diuresis (urination).
Possible options for detoxifying the body
Detoxification can be carried out at home (exclusively for alcoholism) or in a drug treatment hospital. The first option is often preferred, since in this case there is no need to solve the problem of transporting a person who is intoxicated to the clinic. The procedure takes about 2–3 hours, and the doctor is nearby all the time and monitors the patient’s condition.
But detoxing at home also has a number of disadvantages. At home, comprehensive cleansing and complete restorative treatment is impossible. Of course, our doctor administers basic medications, but they are more likely intended to relieve an acute condition. The specialist also describes in detail the further therapeutic course, but responsibility for compliance with the medication regimen and their dosage “falls on the shoulders” of the patient.
The Alkoklinik inpatient department is equipped with rooms of various comfort levels, including single VIP rooms. If necessary, we can arrange transportation of the patient accompanied by a qualified narcologist. There are a number of benefits to inpatient detoxification. These include:
- 24-hour doctor supervision;
- supplementation of medicinal cleansing with hardware;
- the ability to quickly begin psychotherapy after symptoms of withdrawal have eased;
- coding using prolonged forms of drugs (they are sewn subcutaneously under local anesthesia);
- more effective detoxification of the body - doctors provide intensive infusion treatment almost around the clock for several days.
Diagnosis
The problem with poisoning is that the doctor needs to know exactly the cause of the pathology. Simply put, professional diagnosis becomes vital. You will need to provide the doctor with all the information about your cat, including any exposure to hazardous substances (if possible, of course). After recording the history, the veterinarian will perform a complete physical examination. Laboratory tests in this case include a blood test, including biochemistry, and a urine test. The results of these measures provide valuable information for making an initial diagnosis.
Products for detoxification therapy
According to experts, the best results are obtained by combining medications with hardware methods for purifying the blood from ethanol, narcotic substances and their breakdown products. This “tandem” is supported by means to restore the functions of the liver, kidneys, cardiovascular, nervous system, and digestive tract.
Use of medications
- Plasma substitutes, saline solutions. On average, the volume of administered infusions is up to 50 ml/kg. To exclude unwanted reactions, monitor blood pressure and diuresis. In the hospital, the parameters of acid-base, water-electrolyte balance, and the average volume of red blood cells are additionally checked. If necessary, the amount of injected solutions and the infusion rate are adjusted.
- Diuretics. Typically, an increase in the volume of circulating fluid leads to reflex stimulation of the kidneys. Accordingly, organs are “freed” from toxic compounds much faster. Sometimes this process is accelerated with the help of diuretics. In this case, it is necessary to control the level of basic electrolytes.
- Medications for detoxification. Medicines of this pharmacological group have the ability to “bind” elements of compounds toxic to tissues. As a result, relatively safe substances are formed that are excreted in the urine. Usually, for this purpose, Hemodez is used, which additionally enhances blood flow in the kidneys and glomerular filtration. This way you can avoid the use of diuretics.
- Vitamin therapy. The patient is required to be given B vitamins, ascorbic acid, and nicotinic acid. They participate in the synthesis of many coenzymes, contribute to the normalization of redox processes, and have a positive effect on tissue respiration and metabolism.
- Opioid receptor blockers. They are used only for detoxification against the background of regular use of opioid drugs. Typically, the procedure is performed under sedation.
In parallel with medications, drugs are used to detoxify the body to protect tissues from toxic substances and minimize the risk of complications from alcohol or drug poisoning. Therefore, hepatoprotectors and adrenergic blockers must be administered to prevent a hypertensive crisis. To ease withdrawal, sedatives are also indicated (they are used with caution if there is a risk of alcoholic coma), painkillers, antispasmodics, and sometimes corticosteroids, insulin, glucose (in the absence of contraindications).
Hardware detoxification therapy
- Plasmapheresis (membrane, cascade, discrete). The essence of the procedure is to separate the blood into formed elements and plasma. The latter contains the bulk of the toxins. The plasma is filtered and reintroduced to the patient.
- ILBI. A catheter with an emitter is inserted into the vein, which generates waves with strictly specified parameters (length, intensity, etc.).
- Intestinal lavage. The intestines are washed with a salt raster, which stimulates intense metabolic processes, motility of the digestive tract, and bowel movements.
In addition to detoxifying the body, hardware techniques generally improve a person’s well-being. Metabolism and rheological properties of blood are normalized, immune functions are restored. Their only drawback is that they cannot be performed at home.
Water
An excellent means of detoxification is ordinary drinking water. When drinking two or more liters of fluid per day, a person's diuresis increases and the elimination of toxins accelerates.
The method is a “home” version of forced diuresis. You can speed up the elimination of fluid with the help of mild diuretics.
The water load must be adequate to the amount of urine excreted. Detoxification is not the replenishment of blood volume. Therefore, the same amount of urine should be excreted as the amount of liquid that was drunk. The difference should not exceed 10%.
Note: if poisoning is accompanied by diarrhea, the volume of fluid released should be calculated along with feces. To replenish the loss of electrolytes, table salt or special rehydrating substances (rehydron) are added to drinking water.
Is it possible to detoxify on your own?
Without professional help, you can cope with the consequences of minor alcohol poisoning. The following measures are completely safe and quite effective:
- taking adsorbents, paracetamol in the dosage recommended in the instructions;
- artificial stimulation of vomiting (press your finger on the root of the tongue, drink a weak solution of potassium permanganate);
- drinking large amounts of liquid, and it is better to restore electrolyte balance with brine or alkaline mineral water;
- following a diet with a minimum content of animal fats, fast food, flour and confectionery products.
But in case of severe intoxication, and especially binge drinking, drug euphoria, you should definitely consult a specialist. Call us at +7 (495) 744-85-28 at any time of the day. We will conduct comprehensive detoxification therapy with mandatory confidentiality, and recommend tactics for further combating addiction.
Authorship and editing of the text:
Head of the Department of Psychiatry and Narcology of the Alkoklinik MC, psychiatrist-narcologist Popov A.G., psychiatrist-narcologist Serova L.A.
CAN'T FIND THE ANSWER?
Consult a specialist
Or call: +7 (495) 744-85-28
Call! We work around the clock!
Additional drugs
In patients with alcoholism, detoxification therapy necessarily includes symptomatic treatment and the use of drugs to relieve mental disorders (delirium):
- Magnesium sulfate, which has sedative, anticonvulsant, antispasmodic and diuretic effects.
- Tranquilizers to prevent psychosis (Diazepam, Rudotel, Phenazepam, Grandaxin and others).
- Psychotropic drugs with a sedative effect (Levomepromazine, Alimerazine, Meterazine, Haloperidol (for anxiety-paranoid syndrome), behavior-correcting drugs - Neuleptil, Sonapax and others.
- Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine (Finlepsin, Tegretol), sodium valproate (Konvulex, Depakin), Lamictal.
- Antioxidants: Mexidol, Cytoflavin. The drugs stimulate breathing and energy processes in cells, improve cerebral blood flow, help restore clear consciousness and improve the intellectual functions of the brain.
- When the activity of the respiratory center in the brain is suppressed: analeptics (solutions of sulfocamphocaine, cordiamine, caffeine).
- For psychomotor agitation, which is characteristic of atypical forms of alcohol intoxication, use a 0.5% solution of Relanium or Flormidal, sodium thiopental. Since these drugs cause depression of the respiratory center, they are used strictly under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary preparation for artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Chronic alcohol intoxication leads to the development of cardiomyopathy – damage to the heart muscle. If signs of heart failure appear (low blood pressure, increased heart rate), cardiotropic drugs are prescribed in the form of solutions:
- Korglykon;
- Strophanthin;
- Mildronate;
- Caffeine and other drugs.
When blood pressure rises to more than 180/105 mmHg. solutions of the following drugs are used:
- magnesium sulfate (magnesium sulfate);
- Papaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Eufillin.
Additional drugs
In patients with alcoholism, detoxification therapy necessarily includes symptomatic treatment and the use of drugs to relieve mental disorders (delirium):
- Magnesium sulfate, which has sedative, anticonvulsant, antispasmodic and diuretic effects.
- Tranquilizers to prevent psychosis (Diazepam, Rudotel, Phenazepam, Grandaxin and others).
- Psychotropic drugs with a sedative effect (Levomepromazine, Alimerazine, Meterazine, Haloperidol (for anxiety-paranoid syndrome), behavior-correcting drugs - Neuleptil, Sonapax and others.
- Anticonvulsants: Carbamazepine (Finlepsin, Tegretol), sodium valproate (Konvulex, Depakin), Lamictal.
- Antioxidants: Mexidol, Cytoflavin. The drugs stimulate breathing and energy processes in cells, improve cerebral blood flow, help restore clear consciousness and improve the intellectual functions of the brain.
- When the activity of the respiratory center in the brain is suppressed: analeptics (solutions of sulfocamphocaine, cordiamine, caffeine).
- For psychomotor agitation, which is characteristic of atypical forms of alcohol intoxication, use a 0.5% solution of Relanium or Flormidal, sodium thiopental. Since these drugs cause depression of the respiratory center, they are used strictly under the supervision of a doctor, with preliminary preparation for artificial ventilation of the lungs.
Chronic alcohol intoxication leads to the development of cardiomyopathy – damage to the heart muscle. If signs of heart failure appear (low blood pressure, increased heart rate), cardiotropic drugs are prescribed in the form of solutions:
- Korglykon;
- Strophanthin;
- Mildronate;
- Caffeine and other drugs.
When blood pressure rises to more than 180/105 mmHg. solutions of the following drugs are used:
- magnesium sulfate (magnesium sulfate);
- Papaverine;
- No-shpa;
- Eufillin.