Iron poisoning is an acute pathological situation that occurs as a result of an overdose of iron-containing drugs in adults and children. Medications in the prescribed concentration help to level the level of hemoglobin in the blood. When drugs are abused, there is a high risk of developing dangerous health consequences.
Symptoms of Iron Poisoning
There are 5 stages in the development of the clinical picture, but the symptoms themselves and their development vary. The severity of the first stage symptoms usually reflects the severity of the poisoning as a whole; subsequent stages of symptom development occur only if the symptoms in the first stage were moderate or severe.
Stages of iron poisoning
Time elapsed since poisoning
Vomiting blood, profuse diarrhea, irritability, abdominal pain, drowsiness. In case of severe intoxication - tachypnea, tachycardia, arterial hypotension, coma and metabolic acidosis
Up to 24 hours apparent improvement (latent period)
Shock, convulsions, fever, coagulopathy and metabolic acidosis
Liver failure, jaundice, coagulopathy and hypoglycemia
Obstruction of the gastric or duodenal outlet due to scarring
Iron poisoning may be suspected after taking multiple medications (because iron is found in almost all medications) and in young children with access to iron with unexplained metabolic acidosis or severe hemorrhagic gastroenteritis. Children often share with each other, so it is also necessary to examine relatives and friends of young children who have ingested iron-containing substances.
Abdominal radiography is usually performed to confirm foreign body ingestion; this helps detect undissolved iron tablets or iron deposits. However, chewed and dissolved tablets, liquid iron-based preparations and iron in multivitamins cannot be detected by radiography. Serum iron, electrolytes and pH are determined 3-4 hours after ingestion. Symptoms that support the suspicion of iron toxicity include vomiting and abdominal pain, a serum iron concentration >350 mcg/dL (63 μmol/L), iron deposits visible on x-ray, or unexplained metabolic acidosis. Knowing the indicators of iron content, one can only assume poisoning, but one cannot accurately judge its presence. Total serum iron binding capacity (TSIBC) is in many cases an imprecise indicator and cannot be used to make a diagnosis of serious poisoning. The most accurate method involves sequential measurement of serum iron concentration, HC03 and pH, then jointly assessing the results and comparing them with the clinical status of the patient. For example, poisoning is suspected when there is an increased concentration of iron in the blood, metabolic acidosis, worsening symptoms, or, most often, some combination of these symptoms.
We have strict sourcing guidelines and only link to reputable sites, academic research institutions and, where possible, proven medical studies. Please note that the numbers in parentheses ([1], [2], etc.) are clickable links to such studies.
If you believe that any of our content is inaccurate, out of date, or otherwise questionable, please select it and press Ctrl + Enter.
Iron poisoning is the leading cause of death from poisoning in children. Symptoms begin with acute gastroenteritis, progressing to a latent period, then shock and liver failure. Diagnosis is based on measurement of serum iron, detection of radiopaque iron tablets in the gastrointestinal tract, or unexplained metabolic acidosis in patients with other symptoms suggestive of iron toxicity. If large quantities of iron are swallowed, the intestines are completely washed out and poisoning is treated with intravenous deferoxamine.
Many over-the-counter medications contain iron. Among these and prescription medications containing iron, the most common are ferrous sulfate (20% pure iron), ferric gluconate (12% pure iron), and ferric fumarate (33% pure iron). Children may mistake iron tablets for candy. Multivitamins for pregnant women contain iron and very often cause fatal poisoning in children. Children's chewable multivitamins contain little iron, and poisoning is rare.
We recommend reading: Is it possible to take Sinekod during pregnancy in the 1st, 2nd, 3rd trimester? Sinekod during pregnancy: instructions for use
Prognosis and treatment of iron poisoning
If there are no symptoms within the first 6 hours after ingestion, the risk of serious poisoning is minimal. If shock and coma develop within the first 6 hours, the risk of death is approximately 10%.
If radiopaque tablets are visible on an abdominal x-ray, intestinal lavage is performed with polyethylene glycol, 1-2 l/hour for adults or 24-40 ml/kg per hour for children until the visible iron accumulation disappears on a repeat x-ray. Gastric lavage is usually useless; deliberately induced vomiting empties the stomach more effectively. Activated carbon does not adsorb iron and is used only if other toxins have been ingested.
All patients with symptoms more severe than moderate gastroenteritis should be hospitalized. For severe poisoning (metabolic acidosis, shock, severe gastroenteritis, or serum iron concentration >500 mcg/dL), deferoxamine is administered intravenously to chelate free ions in the blood plasma. Deferoxamine infusion is carried out at a rate of up to 15 mg/kg per hour, titrating the dose according to blood pressure. Because both deferoxamine and iron toxicity can lower blood pressure, patients receiving intravenous deferoxamine also need intravenous hydration.
Stages of iron poisoning
How to help?
If dietary supplement tablets, vitamin capsules or any other iron preparations entered the body no earlier than three hours before symptoms of an iron overdose were noticed, that is, poisoning began, the first thing to do is to rinse the stomach.
If iron supplements have been taken previously, then rinsing does not make sense, but you can give a saline laxative or do an enema in order to remove unabsorbed iron from the body.
Emergency first aid for this type of poisoning involves calling an ambulance and administering antidotes to the victim. However, any medications that neutralize the effect of iron oxide should be given to a poisoned person only when there is complete confidence that iron poisoning has occurred.
It is not recommended to take any medications on your own if you have an iron overdose during pregnancy.
Which antidote will be safest, and which medication can quickly remove “excess” iron from a woman’s body in case of an overdose, can only be determined by a doctor after taking the appropriate tests, since there is no “universal pill” for expectant mothers. Pregnant drugs. which remove excess iron are selected individually.
Without resorting to taking medications, you can reduce the toxic effect with the help of warm milk; it is a natural remedy that neutralizes the activity of iron in the body.
The same should be done if poisoning with thyroid hormones occurs.
Diagnosis
To determine the causes of intoxication, the doctor interviews the patient. This helps to find out how much of a particular medicine was taken. It is more difficult to diagnose in young children who cannot explain what they have ingested.
To identify the causes of poisoning, a number of studies should be carried out.
Blood analysis
To determine the volume of the drug, a laboratory blood test is performed. With its help, it is possible to assess the severity of the patient’s condition. The maximum content of the drug in the blood is reached approximately 2 hours after its penetration into the body. The number of administered antidotes depends on the results of the analysis.
Examination of vomit
If you provoke vomiting immediately after the medicine enters the body, you can see undigested pills in the masses. Their quantity and level of decomposition influences subsequent doctor’s prescriptions.
Radiography
This technique is used in case of severe overdose of iron preparations. This microelement does not transmit x-rays. Therefore, the resulting images will help determine the amount of undigested medicine.
Distinctive signs of excess iron
The characteristic symptoms of poisoning with preparations containing iron differ depending on the type of intoxication, that is, with a constant intake of this component in the body and, as a consequence, its chronic overabundance, the manifestations of deterioration in well-being will differ from the symptoms accompanying the acute development of the process of intoxication with this substance.
Chronic, persistent iron poisoning is characterized by symptoms that are often left without proper attention:
- Frequent and painful inflammatory processes in the urinary tract, bladder and kidneys, mistakenly mistaken for the consequences of drafts or infectious agents.
- Various types of pain in the heart, the development of coronary artery disease and aneurysm without the presence of objective prerequisites for these processes.
- The occurrence of neoplasms and hernias, mainly small tumors occur in the stomach and intestines, but can form in any other place.
- Frequent headaches.
- Almost constant grumpy and dissatisfied mood.
- Periodically occurring painful spasms in the kidneys and liver, accompanied by nausea.
Poisoning or an overdose of iron is just as difficult for the body to tolerate as a lack of this element; the symptoms of this condition are almost impossible to confuse with anything else, and help with an excess of iron should be provided immediately to avoid the development of complications.
Therefore, an excess of this element in the body is no less common than its deficiency, and taking into account. That iron, like many trace elements, tends to accumulate in cells, and when its amount reaches a critical threshold, a pathological condition develops with a number of symptoms, that is, poisoning.
Long-term use of incorrect doses
With the constant use of iron-containing drugs, the dose of which is incorrect, chronic poisoning may occur. However, the symptoms are not so acute and vivid, so making a diagnosis can be quite difficult. The most dangerous consequences occur if high doses of iron are taken by children for a long time. Such a systemic effect on the body can influence the occurrence of irreversible consequences.
High doses of iron are most dangerous for children
First of all, with constant exposure to iron on the human body, the excretory system suffers. As a rule, the kidneys are affected. The work of the liver is hampered due to disturbances in the hematopoietic system. The heart and blood vessels are also very sensitive to excess ferum in the blood. Oxygen metabolism is disrupted and coronary heart disease, loss of vascular elasticity, and hematopoietic processes may occur. Systematic long-term use of incorrect doses of ferum or iron-containing complexes is directly related to the occurrence of malignant neoplasms in the near future.
What kind of poisoning can there be?
Iron is not a harmless component; you can consume foods and supplements with it in any amount. Poisoning with iron preparations begins at the moment when its amount in the body reaches 30-32 micrograms per kilogram of weight, and at 220-250 micrograms per kilogram a coma occurs, followed by death.
Poisoning with drugs containing iron can be chronic or acute. Chronic intoxication is characterized by the constant presence in the body of a higher level of iron than is acceptable. At the same time, the person constantly replenishes his “stock” and feels periodic ailments that do not particularly bother him.
We recommend reading: Bad breath in a child, why sour and unpleasant odor occurs in children
That is, in fact, toxic components are released from the pancreas and the person’s condition sharply, literally before our eyes, worsens.
Separately, doctors consider poisoning with poisons and chemicals containing iron and its compounds as a base, for example, from spring to autumn, gardeners often seek medical help due to poisoning with iron sulfate, which is used to control insect pests.
Without resorting to taking medications, you can reduce the toxic effect with the help of warm milk; it is a natural remedy that neutralizes the activity of iron in the body.
It is important to know!
According to doctors, most often they have to deal with drug intoxication - this is the so-called drug poisoning caused by improper use of medications.
Iron poisoning poses a serious threat to health and performance. Iron is an essential element in the human body, so an excess or decrease in the amount of metal ions has a negative impact on it. Iron levels are regulated by special iron-containing medications. There are four grams of metal in the body. Exceeding the norm by 30-40 milligrams is considered a deviation from the standard.
Diagnosis of excess iron
Urine blood tests are used to assess the level of iron in the body.
The average level of iron in urine is 10-25 µg/l, in blood plasma - 0.8-1.4 µg/l.
To diagnose iron levels, a combination of tests is used, which includes: determination of serum iron, free erythrocyte porphyrin, and total iron-binding capacity of serum.
In addition, the level of iron in bone marrow aspirates is assessed.
With excess iron in the body, the following are observed: a decrease in the level of serum iron (1.5-3 times) and an increased saturation of transferrin with iron.
What can give off a metallic taste - video
Read further:
How long does alcohol intoxication and hangover last for the body ❶ ❷ ❸
Soda poisoning - how to treat, proper preparation of soda solution for children and adults
Analysis and diagnosis of salmonellosis - methods for children and adults
Ways to eliminate swelling after mosquito bites
How to use sodium thiosulfate to cleanse the body?
Article rating:
( 1 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
Share with friends:
You may also be interested in:
Ice cream poisoning
What to do in case of sausage poisoning: treatment methods
Sweet food poisoning - cakes, candies for children and adults
What to do if a child or adult is poisoned by tangerines - symptoms
Symptoms of excess iron
Symptoms of excess iron are:
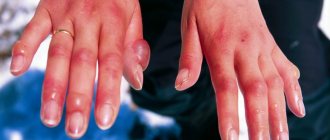
- icteric staining of the sclera, skin, tongue, palate;
- pigmentation on the palms, in the armpits, in places of old scars;
- itching;
- liver enlargement;
- headaches, increased fatigue, dizziness;
- heart rhythm disturbance;
- pale skin;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- weakness.
- iron deposition in organs and tissues, siderosis;
- heartburn, nausea, stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, ulceration of the intestinal mucosa.
- liver failure, fibrosis.
- suppression of cellular and humoral immunity.
If the excess is associated with hemochromatosis (a hereditary disease of iron metabolism), then at the onset of the disease for several years, patients may only complain of severe weakness, weight loss, fatigue, and decreased sexual function (men). Quite often there is pain in the joints, right hypochondrium, and atrophic changes in the skin. In the advanced stage of the disease, there is a classic triad of symptoms of iron excess: pigmentation of the skin and mucous membranes, diabetes and cirrhosis of the liver. Hemochromatosis can be combined with chondrocalcinosis, arthropathy, osteoporosis, tuberculosis, neuropsychiatric disorders, and porphyria cutanea tarda.
Damage to the intestinal mucosa, development of liver failure, nausea and vomiting are characteristic of cases of severe iron poisoning. Iron poisoning is the most common type of accidental poisoning in young children. Taking 3 g of iron sulfate or more can cause death to a child.
Symptoms of excess iron are:
Recently, drinking iron on a regular basis has become fashionable. Bloggers and “beauty experts” indiscriminately advise everyone to use it as an additive to a regular diet, but is this the case when it is permissible to engage in “self-medication” and prescribe such drugs to oneself? Maria Kirillova , Ph.D., general practitioner and medical cardiologist, to answer this question
How to determine your norm
Consultation with a doctor and tests are necessary to determine the individual norm per day. Uncontrolled use of iron supplements can cause side effects in the form of gastrointestinal disorders; liquid forms of the drug can damage teeth. In addition, only a doctor can take into account the interaction of iron with other supplements and medications, if any.
We recommend reading: Treatment of hemorrhoids during exacerbation: drugs and folk remedies
Excessive iron consumption leads to systemic poisoning with damage to the liver, heart, lungs and hematopoietic system. After long-term use of the drug at a dosage of 20 mg/kg, signs of gastrointestinal poisoning may appear, and a dose exceeding 40 mg/kg leads to acute intoxication. But this rarely happens. In general, it is not recommended for healthy people to take iron supplements.
To drink or not to drink
Iron deficiency is more common in women than in men. The following groups of people are most susceptible to this condition:
- pregnant women
- women with irregular menstrual cycles, heavy menstruation, women with diseases of the genital organs (for example, leiomyoma)
- Small children
- teenagers
- people with impaired functioning of the stomach, intestines, hemorrhoids
- patients receiving chemotherapy or taking drugs that affect blood clotting.
Iron in food
The main dietary source of iron is animal products; they contain heme iron. The greatest amount of iron is found in beef, lamb, liver, and to a lesser extent in fish, chicken, and cottage cheese. What is important is not the level of iron in the product, but its bioavailability. Compared to animal products, non-heme iron contained in plant foods (vegetables, fruits, grains) has reduced bioavailability, and therefore lower absorption. This process requires certain conditions: for example, vitamin C enhances the absorption of iron, and substances such as tannic acid, which is part of tea, or phytates, found in some products, on the contrary, inhibit the absorption of iron.
Recently, drinking iron on a regular basis has become fashionable. Bloggers and “beauty experts” indiscriminately advise everyone to use it as an additive to a regular diet, but is this the case when it is permissible to engage in “self-medication” and prescribe such drugs to oneself? Maria Kirillova , Ph.D., general practitioner and medical cardiologist, to answer this question
You read a lot and we appreciate it!
Leave your email to always receive important information and services to maintain your health
Harm to health from overdose
The body uses microelements in its work processes. Iron is especially in demand in some metabolic processes associated with myoglobin. Iron is distributed throughout the body, but the overwhelming majority is hemoglobin , about 20% is allocated to ferritin and a small percentage to the already mentioned myoglobin. Iron is absorbed from medications through the mucous membrane of the stomach and intestines, and enters the bloodstream in the form of ferrous iron. The body either sends the resulting microelement to reserve or directly to the bone marrow. Every day the body naturally excretes about 1 mg of iron.
Harm in case of overdose is caused by free iron, which certainly occurs when taking too large doses of drugs. Due to overoxidation, cells become damaged and mitochondrial damage follows. An overdose can result in death , which is caused by many pathological changes, the most typical of which are damage to cardiac muscle cells and hepatocytes, as well as necrosis of the gastrointestinal tract. Iron deposits accumulate in the liver, spleen and intestines.