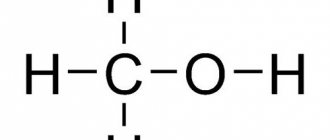Fulvic acid is one of two classes of humic acids, organic compounds found in soil, sediment and bodies of water.
As an active chemical compound, fulvic acid helps our body better absorb and utilize nutrients such as microbiota/probiotics, antioxidants, fatty acids and minerals.
This acid is considered a unique “nutrient enhancer.” We can get the benefits by taking it in supplement form or naturally through exposure to a lot of dirt/soil outdoors.
Thanks to its ability to improve our cells' absorption of substances such as antioxidants and electrolytes, fulvic acid has become a popular choice for slowing aging, improving gastrointestinal health, and protecting brain function. ()
The unique chemical structure allows fulvic acid to fight damage caused by free radicals, which contribute to aging and are associated with virtually every chronic disease.
Chemical properties
Orotic acid in appearance is a white powder with a crystalline structure without a specific odor or color. It dissolves poorly in water, and difficultly in boiling liquid. The substance is insoluble in methyl and ethyl alcohol , chloroform sodium hydroxide solution . The heterocyclic compound breaks down when exposed to bright light. Molecular mass of the product = 156.1 grams per mole.
This is a vitamin-like substance that affects metabolic processes and stimulates the growth of living organisms, but does not possess any vitamins. The acid was discovered in 1904, the substance was isolated from cow's milk. It was discovered in human milk and named vitamin B13 . Unfortunately, Orotic acid is not synthesized by human microflora (stomach) and therefore it is classified as a vitamin-like substance.
The product is found in food products and enters the body with minerals and compounds that are slightly soluble in water. It has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, heart muscle, protein metabolism, blood vessels and muscles. Orotic acid is actively used in cosmetology. It is believed that it simulates the metabolic processes occurring in the skin and activates the synthesis of nucleic acids and proteins.
The product is produced in the form of salts, in tablets of 100 and 500 mg and granules.
What to do if you are poisoned by acid vapors at home
In Russia, it is difficult to find highly concentrated hydrochloric acid for open sale. But even with a small concentration, poisoning by its vapors is possible. In everyday life, many people carelessly handle toxic substances and do not use respiratory and skin protection. Common causes of accidents include pouring acid, preparing solutions, or using gas equipment or batteries for washing without special care.
When the first aspiration symptoms of poisoning appear, it is urgent to ventilate the room and open windows and doors. If you smell chlorine, have a sore throat and coughing attacks, you must urgently climb to a height, the upper floors of buildings, stairs, the attic of a house or the roof. The acid vapor molecules are heavier than air, the gas spreads along the floor. You need to hold your breath, close your eyes, cover unprotected parts of your body, and move away from the scene of the accident as quickly as possible. In severe conditions, the victim is evacuated from the affected area.
If you lose consciousness as a result of concentrated hydrochloric acid poisoning, you need to turn a person on his side and monitor his condition so that he does not choke on vomit.
The mucous membranes of the nose, mouth and skin are washed with a 2% solution of baking soda. To prepare it, you need to take 1 glass or 200 ml of clean cool water and dissolve 1 teaspoon of soda powder in it. You can rinse your mouth and eye mucous membranes from the acid with running water until the symptoms of irritation disappear. Eye drops are used to relieve inflammation and pain with a solution of Novocaine 2%, 1-2 drops in each eye every 3-4 hours, Visine or analogues to reduce redness and burning, 3 drops in each eye every 2 hours. For inhalation, a similar solution of baking soda is used.
To reduce salt vapor poisoning of the entire body, drinking plenty of water is recommended, preferably with alkali (for example, Essentuki mineral water without gas).
In cases of intoxication, bandages with ointments should not be applied. You can only use neutralizing substances for this acid - water, sodium bicarbonate.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
The vitamin-like substance Orotic acid takes an active part in the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides, an integral part of nucleic acids, from which protein molecules are further formed. The substance affects the regeneration processes of liver cells, reduces the risk of fatty liver, lowers cholesterol levels in the blood, and has a beneficial effect on the functioning of the heart, reproductive system, muscles and blood vessels.
The drug, after ingestion, is absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract, but not completely; approximately a tenth of the dose taken enters the bloodstream. The drug is metabolized in the liver, forming the metabolite orotidine-5-phosphate . About 30% of the substance undergoes metabolic processes and is excreted through the kidneys.
Features of treatment
Highly concentrated hydrochloric acid is a caustic substance
, upon contact with skin causes severe chemical burns. Contact with eyes is especially dangerous. To neutralize burns, use a solution of a weak base, or a salt of a weak acid, usually baking soda.
When opening vessels with concentrated hydrochloric acid, hydrogen chloride vapors, attracting air moisture, form a fog that irritates the eyes and respiratory tract of humans.
Reacting with strong oxidizing agents (bleach, manganese dioxide, potassium permanganate) forms toxic chlorine gas.
In the Russian Federation, the circulation of hydrochloric acid with a concentration of 15% or more is limited.
Indications for use
The medicine is prescribed:
- as part of complex therapy for angina pectoris , myocardial infarction , arrhythmia (atrial fibrillation, due to magnesium deficiency), chronic heart failure ;
- as an additional remedy for hepatosis , hepatitis and other liver diseases;
- in the treatment of biliary tract diseases, acute and chronic intoxication;
- for the treatment of nutritional and nutritional-infectious dystrophy in childhood;
- for atherosclerosis , vasospasm , hyperlipidemia ;
- as part of complex treatment of myocardial dystrophy , dermatoses ;
- with progressive muscular dystrophy, anemia ;
- as a general strengthening agent during increased physical activity, during the period of convalescence .
Instructions
There are several forms of fulvic acid: ()
Liquid or "Water" Fulvic Acid: Fulvic acid has been reported to be more bioavailable when taken in liquid form, which the digestive system does not need to break down before using the essential nutrients. Apparently, in liquid form, fulvic acid enters cells more easily. Review dosage recommendations carefully as overdosing may alter mineral levels in a potentially harmful manner. Most liquid products are sold in the form of an extract, about 12 drops of which must be diluted in 500-600 ml of clean drinking water.
Solid Fulvic Acid Supplements: Fulvic acid itself is yellow in color and does not have an attractive taste. Therefore, many people prefer to add it in powder form to juices and smoothies, which allows them to mask the unpleasant taste. You can add fulvic acid to liquid or take it with supplements to enhance their effects and increase bioavailability. It is recommended to dilute fulvic acid only in filtered water (no tap water or chlorinated water). Liquid products may be less sterilized, retaining more benefits and nutrients, so avoid supplements containing “sterile humic acids.”
Organic Crops: Although this method is indirect, you can get fulvic acid by eating organic foods. That's because fulvic acid is used to naturally replenish minerals and other nutrients in the soil and is commonly found in natural fertilizers for organic crops. Choose organic products, which have much more benefits. Unfortunately, modern farming methods fail to enrich the soil, and instead farmers overplant fields and use pesticides, herbicides and fungicides to suppress the natural microbial strains we need.
Interaction
Drugs that coat the gastrointestinal tract and have astringent properties slow down the absorption of this substance.
The effectiveness of the drug decreases when taken in combination with oral contraceptives, diuretics, muscle relaxants, insulin , and glucocorticosteroids.
Potassium orotate (salt of orotic acid) reduces the toxic effects of cardiac glycosides.
Orotic acid when taken with iron supplements, tetracyclines , sodium fluoride (if the interval between doses is less than 3 hours) slows down the absorption of the drug. funds.
When should you consult a doctor?
If acid gets on the skin and causes a first-degree burn (redness of the upper layer of the epidermis), you can cure the lesion yourself at home. If after first aid is provided, a person becomes worse, the pulse and heartbeat have increased, the color of the skin and sclera has changed, vomiting occurs, the urine is colored reddish, then it is urgent to seek help from a medical institution to eliminate poisoning of the body with dangerous hydrochloric acids.
If the eyes are affected, you should contact an ophthalmologist if the symptoms do not subside after 6 hours and vision decreases.
People with severe skin burns and acid poisoning require resuscitation measures. It is worth immediately providing them with the necessary assistance to avoid shock and infection on the wound surface. A life-threatening condition involving damage to the body, accompanied by internal bleeding.
At the first signs of poisoning as a result of exposure to acid-salt substances, you should immediately carry out first aid measures and consult a doctor about further tactics.
What information is missing from the article?
- List of effective medications
- A detailed overview of traditional methods of treatment
- Professional opinion of a specialist
- Detailed review of antidotes
Reviews
Reviews of the use of Orotic acid are left mainly by athletes who use it in combination with other drugs and patients with heart disease (the substance is prescribed in combination with magnesium). Reviews are mostly positive. Of the adverse reactions, the most common complaints are indigestion and loose stools. Allergic reactions occur rarely and do not require the use of antihistamines. After stopping the medication, the allergy goes away on its own.
Inpatient treatment of intoxication
Referral to hospital treatment of a patient as a result of poisoning depends on the degree of burn and the presence of intoxication with salt substances.
Active acid detoxification methods:
- administration of intravenous anesthesia,
- gastric lavage using a tube with cold water, forced diuresis with blood alkalization,
- swallowing small and non-sharp pieces of ice,
- drink plenty of a solution of 4% baking soda up to 1500 ml if the urine becomes dark and metabolic acidosis develops after the salt substance,
- If massive bleeding occurs during poisoning, a blood transfusion is given.
Additionally, treatment includes antibiotics and hormones, diagnostics and studies to monitor the functioning of body systems.
Industrial use
It is widely used in the metallurgical, food and medical industries.
HCL is used in various industries, and its concentration can be quite high.
- Metallurgy. Application in soldering, tinning and stripping of metals.
- Food industry. Application in the production of food acidity regulators, for example, E507.
- Electrotype. Used for etching.
- Medicine. Finds its application in the production of artificial gastric juice.
Included in synthetic dyes. Used in the production of cleaning products and detergents. But in liquids intended for household use, the concentration of sulfuric acid is insignificant.
Hydrochloric acid intoxication: symptoms
Symptoms of hydrochloric acid poisoning vary depending on how it happened. There are three ways for poison to enter the body:
- swallowing,
- inhalation,
- through the skin.
Each of them has distinctive features that a person needs to know.
If swallowed
Hydrochloric acid poisoning through the oral cavity occurs when the poison is swallowed. As a rule, this most often happens in people who are prone to suicide and children who drank the substance as a result of parental inattention. In this case, the following symptoms are noted:
- pain and burning in the mouth,
- nausea, brownish-black vomiting, often mixed with blood,
- coughing,
- profuse salivation,
- painful sensations in the esophagus, stomach, behind the sternum,
- the tongue turns black
- the skin may become yellowish,
- Painful sensations appear in the right side due to liver dysfunction.
Through the respiratory tract
Poisoning by hydrochloric acid vapor is no less dangerous than ingesting this substance.
It is also quite destructive. Occurs, as a rule, in production associated with this poison. The following symptoms are observed:
- the voice becomes hoarse
- pain appears in the nasopharynx,
- severe cough occurs
- possible pain in the chest,
- in case of severe poisoning, swelling of the larynx occurs,
- the person begins to choke.
In the absence of the necessary assistance, a victim of vapor poisoning may develop pulmonary edema, which can subsequently cause death.
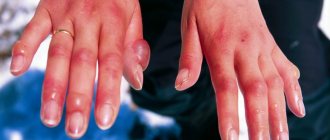
Skin contact
This cannot be called poisoning in the full sense of the word. However, getting acid on the skin brings a lot of suffering and trouble to a person. A burn occurs.
In this case, the following signs are observed:
- redness of the skin area,
- strong pain,
- blistering,
- change in skin color to lighter or, conversely, darker.
Without help, tissue death is possible.
In addition, we can note general signs of hydrochloric acid poisoning, regardless of the method:
- headache,
- pressure reduction,
- tachycardia,
- possible increase in temperature,
- loss of consciousness.
Of the internal organs, the liver is the first to suffer, as the organ responsible for cleansing the body of toxins. As a result, the functionality of the kidneys begins to deteriorate, up to renal failure.
A person may go into shock from an acid burn, causing death.
Etching in aqueous acid solutions
Among metals, in terms of the amount of scale that must be removed, especially before hot coating methods, iron and low-alloy steels occupy first place. The main etchants for removing scale from them are sulfuric and hydrochloric acids. Each of these acids has its own advantages and disadvantages, both technical and economic. In the proceedings of the IV International Conference of the Hot-Dip Galvanizing Association it is indicated that out of 22 English companies, only one carries out pickling in sulfuric acid, all the rest - in hydrochloric acid, and in the proceedings of the V conference of the same organization, which was held in 1958 in Belgium and Holland, Only hydrochloric acid was considered as an etchant. Thus, it can be considered that, at least in large enterprises, there is a tendency towards the predominant use of hydrochloric acid for descaling. The possibility of etching with hydrochloric acid in a closed cycle is also indicated, in which the consumption of acid is determined not so much by the reactions of dissolution of oxides, but by mechanical entrainment and the residue in the waste solution during regeneration.
When oxidized iron interacts with dilute acid solutions, oxides and metallic iron dissolve. The following reactions occur with solutions of hydrochloric acid: FeO + 2НCl → FeCl2 + H2O, Fe2O3 + 6НCl → 2FeCl3 + 3H20, Fe3O4 + 8НCl → 2FeCl3 + FeCl2 + 4H2O, Fe + 2HCl → FeCl2 + 2H, 2FeCl3 + 2H → 2FeCl2 + 2HCl, 2FeCl3 + Fe → 3FeCl2.
Reactions with sulfuric acid proceed similarly.
Of these reactions, the reaction of dissolution of metallic iron with the release of hydrogen and the reaction of dissolution of ferrous oxide proceed at the highest speed.
The processes of etching oxidized iron by directly exposing it to acid solutions without the use of electric current from an external source are usually called chemical etching, in contrast to electrochemical etching, which is carried out using electric current from an external network.
Meanwhile, there is reason to believe that the so-called chemical etching methods are essentially electrochemical. From this point of view, there is reason to assume that in sulfuric acid electrochemical processes are more clearly expressed than in hydrochloric acid. This can be judged by the relative rate of dissolution of iron and its oxides in hydrochloric (Table 5) and sulfuric acids of various concentrations. Table 5. Solubility of Fe, FeO and Fe2O3 in hydrochloric acid
| HCl concentration, % | Solubility, g/h per 100 g of substance | HCl concentration, % | Solubility g/h per 100 g of substance | ||||
| Fe | Fe2O3 | FeO | Fe | Fe2O3 | FeO | ||
| 1 | 20,8 | 0,112 | 0,48 | 10 | 72 | — | — |
| 2 | 22,7 | 0,17 | 0,63 | 14 | 109,6 | — | — |
| 3 | 31,6 | 0,31 | 0,76 | 18 | 191,0 | 38,6 | 79,7 |
| 5 | 40,7 | 0,71 | 0,88 | 21 | 356,0 | 43,8 | 99 |
| 7 | 50,1 | 1,6 | 1.8 | ||||
From the data in table. 5 it can be seen that the solubility of metallic iron in hydrochloric acid of any concentration is greater than the solubility of its oxides, the solubility of ferrous oxide is greater than the solubility of the oxide, and with increasing concentration of hydrochloric acid, the dissolution rate of its oxides increases to a greater extent than the dissolution rate of metallic iron.
In sulfuric acid, other relationships are observed between the rate of etching of metallic iron and its oxides. Thus, in 10% H2SO4 at 40 ° C, from 100 g of solvent substance 97.7 g Fe, 0.9 g Fe2O3 and 1.4 FeO, i.e. in 10% H2SO4 metallic iron dissolves in approximately 70 times more than FeO, and in 10% HCl - only 10 times. This ratio indicates a different electrochemical mechanism for the dissolution of scale in hydrochloric and sulfuric acids. It can be assumed that metallic iron, dissolving at a higher rate in sulfuric acid, releases such an amount of hydrogen that contributes to loosening the scale and mechanically separating it from the base. Fe3O4 is a semiconductor and in contact with metallic iron in dilute H2SO4, e.g. d.s. about 0.8-1.0 V at a current density of 2 mA/cm2. Hydrogen released at the magnetite cathode reduces Fe3O4 to FeO and Fe, which are much more easily dissolved in acids.
Fe2O3 is a poor conductor of electric current and cannot be treated like magnetite as a cathode in a short-circuited element. Moreover, this oxide forms a thin film that makes it difficult for the acid to reach the iron and, therefore, inhibits the operation of the galvanic cell.
The electrochemical mechanism for dissolving iron covered with scale is as follows. The oxidation of iron is accompanied by a change in volume, as a result of which cracks form in the scale, through which the etchant finds access to the most easily dissolved metallic iron. This is confirmed by the following data: Iron and its oxides Fe FeO Fe2O3 Fe3O4 Density, g/cm3. . . 7.8 5.9 5.1 5.2 Thus, we can conclude that the process of dissolving iron with scale is based on the operation of a short-circuited multielectrode element, in which metallic iron consists of anodic and cathodic sections, and its oxides are cathodes. The diagram of a three-electrode element can be represented as follows:
Fe (anode areas) (cathode areas) scale (cathode)
Peeling of scale occurs as a result of the reduction of iron oxides to ferrous oxide, which is easily soluble in acid, disruption of the adhesion of the oxides to the base metal after the dissolution of ferrous oxide, and also due to the mechanical action of hydrogen gas released on the surface of the steel. As a result of contact of the electrolyte with the metal located under the scale layer, hydrogen gas is released. Consequently, the discharge of hydrogen ions on the scale is impossible. It begins to be released only after the penetration of the electrolyte into the base metal, mainly as a result of the work of microcouples. The concentration and temperature of the acid have a significant effect on the etching rate, but they have different effects on sulfuric and hydrochloric acids. In sulfuric acid, increasing temperature has a stronger effect; in hydrochloric acid, the temperature has less of an effect, and due to the volatility of the acid it is impossible to increase it above 35-40 ° C. For example, the etching rate in a 3% solution of sulfuric acid at 80°C is 10 times higher than in an 8% solution at 20°C. With an increase in the H2SO4 concentration to 25%, the etching rate reaches a maximum, after why is it decreasing? At the same concentration, the etching rate in hydrochloric acid is greater than in sulfuric acid.
In addition, it is necessary to take into account the retarding effect of iron salts in the etching solution. Thus, with an increase in the FeSO4 content from 50 to 200 g/l, the duration of etching in 5% H2SO4 changes from 190 to 440 minutes.
- Etching in phosphoric acid
- Stainless steel pickling
What is the danger
Sulfuric acid is a substance classified as highly hazardous. Intoxication can occur not only when using the liquid itself, but also when inhaling its vapors, when sulfur dioxide is released.
The toxic effect of a substance in any form extends primarily to the respiratory system, mucous membranes and skin. Acid often contains arsenic, which can lead to worsening intoxication.
Poisoning by sulfuric acid vapor is no less dangerous than direct contact with liquid. The safe dose of the substance in the open air is only 0.3 mg per 1 square meter.
Upon contact with the skin or mucous membranes, the reagent leads to the formation of a burn, which is difficult to heal. With extensive damage, the patient develops a burn disease, which, without timely medical care, can lead to death.
The lethal dose of sulfuric acid for an adult is only 0.18 cm per 1 liter!
When you need medical help
In case of intoxication with vapors of the substance in question, you should contact a doctor in absolutely all cases. After all, such poisoning is very dangerous for human health, and sometimes even for human life.
After providing first aid to the victim, you need to call a medical team as quickly as possible.
Therapy in this case will be aimed at restoring the functioning of damaged organs, as well as maintaining vital functions.
Pesticide poisoning
Common causes of poisoning
It is quite problematic to encounter pure sulfuric acid in everyday life. In most cases, poisoning is a consequence of neglecting safety precautions when working with the solution in production.
Mass poisoning by vapors of a substance is possible if, due to technical failures or negligence, it is massively released into the atmosphere. To prevent such emissions, there are specialized services that monitor the operation of industries where sulfuric acid is used.