The liver performs a large number of functions in the body. One of them is protective. The digestive gland acts as a filter. It passes blood through itself, cleansing it of toxins. But what happens to the poisons in the organ?
Blood toxins, lingering in the liver, affect the liver itself. Iron neutralizes some substances, but with a large dose and strong or regular exposure, liver cells die. Toxins of various groups can have a detrimental effect. Symptoms of intoxication are very similar. Then how to distinguish what is poisoning the liver? And, most importantly, how to help a person in this situation?
The concept of the liver and its functions
The liver is a large gland of mixed secretion, located mainly in the right hypochondrium. It has a soft structure and a protective capsule and belongs to the parenchymal organs. In its lower part is the gallbladder. The weight of the organ in an adult is approximately 1/40 of the body weight.
Many chemical processes occur simultaneously in the liver parenchyma. However, the main one is the antitoxic function.
Main functions of the organ
Substances entering the blood from the intestines are converted under the influence of liver enzymes, turning into harmless and low-toxic substances. They are then excreted in feces and urine. In this way, the liver neutralizes toxins.
In addition to the antitoxic function, the organ takes part in the following processes:
- digestion;
- metabolism;
- excretion of metabolic products;
- immune defense of the body;
- maintaining hemodynamic parameters.
A healthy human liver is capable of neutralizing a significant amount of toxicants. All of them have a negative effect on the organ, but due to its anatomical features, it recovers quite quickly without intervention from doctors.
The exception is when an excessively large amount of a toxicant or substances that can affect hepatocytes even in small doses enter the body. The liver's response to toxins of this group may vary.
Drug poisoning
Intoxication of the liver with medications prescribed by a doctor has a slight toxic effect. But taking the drug more than prescribed by the doctor acts as a toxin. Among these drugs:
- sulfonamides, such as biseptol, and antiviral amantadine;
- drugs for the treatment of tuberculosis and cardiac drugs
- weight loss medications and antidepressants;
- hormones, steroids and estrogens;
- antifungal ketoconazole and fluconazole;
- antitumor, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Drug intoxication of the liver occurs as a critical toxicosis due to an increased one-time intake rate. Gradual accumulation over a long period of time can also cause drug toxicity. Differences only have consequences. Some lead to cell death, others affect the bile ducts, and others affect blood vessels.
Hepatotoxicity of chemical compounds
Hepatotoxic substances are chemical compounds that can negatively affect hepatocytes. Toxins in the liver cause many severe pathological processes.
Concept of hepatotoxicity
In the process of life, the body is constantly exposed to harmful substances
It is known that almost all substances entering the bloodstream have an effect on the liver. However, for the development of a noticeable toxic effect, their concentration must be high enough.
The organ neutralizes small amounts of poisons without serious consequences for the body. Signs of toxic liver damage occur when consuming chemical compounds to which the sensitivity of hepatocytes is increased.
Toxic damage to the liver tissue can have two mechanisms: direct impairment of hepatocyte function and a cholestatic effect. In the first case, disturbances occur associated with changes in the structure of the organ (steatosis, necrosis), in the second - with a violation of the outflow of bile (cholestasis).
Hepatotoxic substances
The list of substances that have hepatotoxic effects is quite wide. The most common ones are shown in the table below. The instructions for working with it usually tell you how strongly a particular compound affects the liver.
Table of groups of hepatotoxic compounds and their representatives:
| Group | Subgroup | Representatives | |
| Aliphates | Heptane | |
| Alcohols | Ethylene glycol | ||
| Aliphatic amines | Ethylenediamine | ||
| Cyanide | Acrylonitrile | ||
| Mycotoxins | Aflatoxin | |
| Bacterial toxins | Ethionines | ||
| Antibiotics | Rifampicin | |
| Anesthetics | Cyclopropane | ||
| Analgesics | Indomethacin | ||
| Anti-alcohol | Disulfiram | ||
Note: in the table, alcohols are included in the category of industrial toxicants. However, in reality, the hepatotoxic effect of ethyl alcohol most often develops not in production, but with long-term regular consumption of it in food. In such people, damage to hepatocytes leads to the diagnosis of “liver cirrhosis of alimentary-toxic origin.”
Types of hepatotoxic effects
Cirrhosis of liver tissue
Unsuccessful neutralization of toxic substances in the liver (we are talking about hepatotoxic substances) can lead to the formation of the following pathological processes:
Steatosis
– accumulation of excess lipids in hepatocytes.
Fibrosis
– replacement of healthy parenchyma with collagen strands.
Cholestasis
– violation of the synthesis or outflow of bile.
Hepatitis
– diffuse inflammation of the liver parenchyma.
Necrosis
- formation of areas of necrosis in the tissues of the organ.
Liver cirrhosis of toxic origin
– a structural and functional disorder characterized by the formation of fibrous septa and a high risk of malignancy.
Cancer
– degeneration of liver cells with the formation of a malignant tumor.
The exact pathological process that will develop in the patient often depends on the type of toxicant and its effect on the liver.
Table of the relationship between various types of xenobiotics and a particular pathological process:
| Toxicant | Initiated process |
| Focal necrosis | Acetaminophen, carbon tetrachloride |
| Toxic hepatitis | Aspirin, paracetamol |
| Cholestatic phenomena | Erythromycin, estrogens, anabolics |
| Steatosis | Ethanol, corticosteroid hormones |
| Cirrhosis of toxic etiology | Food alcohols, metatrexate |
| Cancer | Oral contraceptives, arsenic, androgens, anabolic steroids |
It is worth noting that all of the above processes, with the exception of toxic hepatitis, are the result of long-term regular use of small doses of a toxicant. This becomes possible with alcoholism (ethanol) or when working in production where safety precautions are not followed. The price of carelessness is the health and life of the employee.
With the simultaneous consumption of a large amount of poison, acute poisoning develops, where disruption of vital functions comes to the fore: breathing, blood circulation, cardiac activity. In this case, as a rule, irreversible liver damage does not develop. Existing functional impairments disappear as the patient recovers.
Hepatoprotectors
This group of drugs has a restorative effect on liver cells, normalizing its function, and improves tissue condition. These drugs are recommended for use not only for liver diseases - they are actively used by athletes who need to protect the mentioned organ during enormous physical exertion. After all, the liver cannot withstand such an active lifestyle on its own, so it needs help.
These drugs can also be used by older people who want to improve their liver function. In addition, these may be groups of people who work in hazardous industries.
When liver cells are intoxicated, Sibektan and Silimar are often used, which effectively help the detoxification process.
Symptoms
Pain in the right hypochondrium is a common symptom of liver damage
Symptoms of toxic liver damage can vary significantly depending on what kind of pathological process is taking place and how severe it is. Thus, with steatosis and fibrosis, the patient does not have an obvious clinical picture of the disease.
The patient may experience some heaviness in the right hypochondrium, nausea, and a feeling of bitterness in the mouth. This becomes especially noticeable when eating fatty, spicy or other irritating foods. Advanced steatosis is characterized by a slight increase in the size of the liver and a change in its color due to fatty infiltration of the parenchyma and outer membrane.
Liver necrosis is characterized by pronounced clinical manifestations. The patient complains of acute pain in the right side, nausea, and vomiting.
He has yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyes. Hyperthermia may occur, sometimes reaching quite high numbers, and signs of general intoxication: headache, muscle pain, changes in psycho-emotional status.
With a widespread process, hepatic encephalopathy occurs - a mental disorder accompanied by hallucinations, confusion, and inadequate assessment of the surrounding reality. Ultrasound shows areas of necrotic parenchyma, an increase in the level of liver enzymes and an increase in ESR are noted in the blood.
With toxic hepatitis, the doctor notes an increase in body temperature in the patient to 38-39˚C. Pinpoint hemorrhages appear on the skin, and increased bleeding is noted. The stool becomes discolored and the urine takes on the color of dark beer.
Jaundice develops as the inflammatory process spreads. Possible encephalopathy. Treatment of toxic liver damage accompanied by mental disorders often requires fixing the patient to a bed.
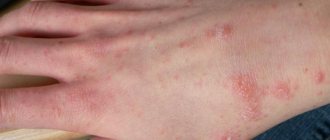
If toxins are not removed, steatosis and hepatitis can cause the development of cirrhosis. In this case, the patient retains the above-described symptoms, which are accompanied by palmar erythema, spider veins on the surface of the skin, and ascites. The liver is noticeably enlarged, and splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) is possible.
Palmar erythema (redness) in cirrhosis
Interesting to know: in some cases, cirrhosis is practically asymptomatic. The patient does not develop an increase in the size of the organ, and there are no characteristic signs of the disease. Unfortunately, as the liver removes toxins from the body, cirrhosis does not go away. Clinical manifestations appear later, when the organ receives significant damage.
With liver cancer, the patient has all the symptoms described above. The patient quickly loses weight, despite adequate nutrition, and there is a low level of sugar in the blood. Ascites may develop. Pain syndrome can occur in the early stages of the disease. However, more often this happens when the enlarged organ begins to compress the surrounding anatomical structures.
Diagnostics
Patients with liver intoxication will be assisted by a gastroenterologist or a more specialized specialist - a hepatologist. To make a diagnosis, the doctor will conduct a thorough examination of the patient:
- collect anamnesis, find out about the occurrence of symptoms, against what background they appeared;
- assess the patient’s living and working conditions;
- analyze the effect of medications taken by the patient;
- will conduct an external examination, assess the size of the liver in comparison with the norm;
- will prescribe the necessary laboratory and instrumental studies.
The doctor must confirm his assumptions with test results. The following studies will be indicative in this case:
- a general blood test, where the doctor will be interested in the level of leukocytes and eosinophils, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, coagulogram;
- a general urine test that will show the presence or absence of protein breakdown products;
- blood chemistry. As a result of this analysis, almost the main indicators will be determined - the level of AST and ALT, alkaline phosphatase;
- blood test for hepatovirus and protein fractions.
As a visual diagnosis, doctors prescribe an ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, a biopsy, and if necessary, elastography will be required. Fibergastroduodenoscopy, computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are performed as standard.
Treatment of pathology caused by toxic liver damage
Treatment for liver diseases caused by toxic exposure consists of two parts:
- pharmacological therapy;
- diet.
Moreover, the second point of the above list is almost more important than the first. Without dietary restrictions, drug therapy for liver diseases is ineffective in almost all cases.
Pharmacological therapy
Pharmacological therapy for toxic liver damage is carried out using the following drugs:
hepa-merz – 4 ampoules per day;
ursodeoxycholic acid – 500 mg/day;
Prednisolone 40-60 mg/day;
multivitamins.
The development of liver necrosis requires hospitalization of the patient in the intensive care unit, where he is given symptomatic, decongestant, infusion, and hemostatic therapy. Oncological processes, as well as treatment of cirrhosis, in most cases require surgical intervention followed by a course of chemotherapy (fluorouracil) and radiation therapy.
Diet
Usually the patient is assigned table No. 5
Diet for toxic liver damage is an important component of treatment. Patients are prescribed table No. 5, which includes products such as slightly dried bread, boiled lean meat, milk soups, fish, kefir, and dairy products.
The general principle of nutrition for liver diseases is to limit the amount of fat with a normal carbohydrate content and an increased amount of protein. The total caloric content of the diet should be about 3 thousand kcal/day. The ratio of proteins, fats and carbohydrates should be 4:3:20, respectively.
It is strictly forbidden to eat spicy, salty, fatty, fried and other irritating foods. Alcohol is contraindicated even in small quantities. You should eat 4-6 times a day, in fractions.
It is interesting to know: neither drug treatment nor diet will help if the toxicant continues to enter the body. You should completely prevent the toxic substance from entering the affected liver: change your place of work, stop drinking alcohol, etc. The body will remove toxins on its own, after which the process of its restoration will begin.
Help in the early stages of alcohol intoxication
If we are not talking about any complex forms of this disease, then something can still be corrected here. First of all, you should completely eliminate alcohol consumption.
The patient should enrich his diet with a sufficient amount of minerals and vitamins, be sure to follow a special diet and consume food rich in proteins.
Correction is also made with the help of medications. Here you can try therapy with a glucose solution or the use of phospholipids, which help restore cell membranes.
Forecasts
The prognosis for liver cancer and cirrhosis is unfavorable. The process is irreversible. About 70% of patients who receive the necessary treatment and follow a diet pass the five-year survival line.
Only a few are approaching the ten-year mark. Steatosis and fibrosis are not such aggressive pathologies, so the prognosis for them is favorable. With supportive care, patients have a normal life expectancy.
The prognosis for necrosis depends on how quickly and competently the assistance was provided. If the patient’s life was saved in the acute stage of the disease, further liver regeneration occurs independently.
Diet
Patients must follow a diet, since the affected liver can no longer fully perform the functions it previously performed.
To help the body recover and reduce the load on the liver, you need to follow the following nutritional rules:
- small portioned meals at least five times a day;
- complete abstinence from alcoholic beverages, fatty, smoked, fried, sour and seasoned foods;
- if intoxication was provoked by drugs, then they must be completely abandoned and other drugs must be selected;
- protein restriction per day - in its pure form no more than thirty grams;
- The basis of nutrition for a patient with liver intoxication is vegetables (except mushrooms) and fruits, legumes, moderate consumption of fermented milk products.
Liver intoxication is a serious illness. Often the patients themselves are to blame for it, consuming large quantities of alcohol and narcotic drugs. Intoxication can be stopped at an early stage if the pathology can be diagnosed in time. In advanced cases, the prognosis is disappointing.
Prevention
The basis of any detoxification is plenty of fluid intake.
The basis for the prevention of toxic liver damage is the avoidance of direct contact with hepatotoxic substances. If this is not possible, you should undergo preventive courses of hepatoprotective treatment and undergo regular examinations to determine the functional and anatomical state of the organ.
People living in remote regions and who do not have the opportunity for timely examination in a hospital need to think about how to remove toxins from the liver using folk remedies. As a rule, medicinal plants that have a choleretic effect (wormwood, tansy) are used for this purpose. For detoxification, it is also recommended to drink large amounts of fluid for several days after receiving a dose of the toxicant.
Risk factors
The following categories of people may be at risk:
- Having a genetic predisposition;
- People with underweight, obesity and paratrophy;
- Patients who have impaired lipid metabolism in the body;
- Patients with type II diabetes mellitus;
- Patients with liver damage (viral hepatitis);
- People over 40 years of age;
- Residents of environmentally polluted areas;
- People who abuse alcohol.
The influence of external and internal factors on the liver
Therapy methods
In case of critical toxicosis, you need to call an ambulance. Before arrival, the first thing you need to do is rinse your stomach with water with the addition of potassium permanganate, drink activated carbon in the ratio of 1 tablet per 10 kg of body weight. Use the choleretic medicine Essentiale or Holosas. The patient is required to undergo hospitalization, detoxification of the gland, individual nutrition, and the use of drugs that protect and regenerate the liver.
Drug therapy consists of the use of antidotes and hepatoprotective agents. They are considered the best medicines that restore the action of cells, normalize the activity of the gland and improve the condition of tissues.
Surgical treatment is used in extremely advanced stages. A part of a relative's organ is taken for transplantation.
For the liver, treatment must begin with a diet, and it should last more than one month. Alcoholic drinks and smoking are contraindicated.
Food should consist of low-fat meat and seafood, dried fruits and legumes, vegetables and fruits, low-fat kefir and cottage cheese, vegetable oils and nuts. Excluded from the menu: fatty and fried foods, smoked and pickled foods, spicy foods, mayonnaise and sauces.