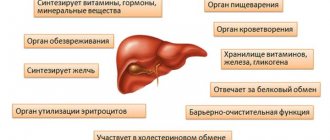
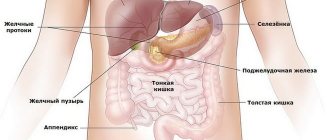
A feature of a chronic disease is a blurred clinical picture, which is caused by the regular intake of small amounts of poisons into the body over a long period of time. Symptoms develop slowly, but in the absence of medical care they gradually lead to complications in the form of decompensated liver failure, cirrhosis and malignant tissue transformation.
The risk group includes:
- children and elderly people;
- patients who prefer to take medications without first consulting a doctor;
- workers with chemical substances;
- people who abuse alcohol.
Causes and risk factors
Toxic hepatitis tends to develop in the human body due to the ingestion of harmful compounds.
This has already been noted above, but now it needs to be clarified that poison does not always penetrate accidentally; there are also cases of intentional poisoning and liver damage due to professional activities.
Doctors are accustomed to calling harmful substances the concept of liver poisons. Behind them lies the mission of damaging a vital organ.
Let's figure out what are the ways these negatively affecting substances enter the liver.
Ways of liver poisons entering the body
After conducting a special study taking into account different cases from the clinical pictures of patients, medical specialists came to the same conclusions.
They consist in the fact that today there are only 3 ways for toxic compounds to enter the liver. They all have one ultimate goal - organ intoxication!
Since a person cannot exist without a liver, it should be noted that when faced with pathology personally, you need to know that the prognosis is not comforting, and therefore it is important to follow all the instructions of the attending physician!
So, the ways in which harmful substances enter the human body are:
- through the digestive tract;
- through the respiratory system;
- through the epidermis.
Some poisons can instantly disrupt the basic functions of the liver as soon as they enter the blood.
It quickly travels through the vessels to the organ, and therefore toxic compounds have a direct effect on the cellular system of the liver, no matter how sad it is to realize this.
Hepatotropic poisons are exactly as stated above. Other types are not excluded. They also take on the main goal associated with the disruption of blood flow in the body.
The process of destroying the entire system begins with small vessels. But it is thanks to them that the liver receives nutrients.
In such cases, there will be a lack of oxygen in the cellular system. When complete anemia occurs, it will simply be impossible to talk about the functional functioning of the liver.
Mechanism of action
The formation of liver damage differs depending on the effects of medications.
It can be:
- Destructive effect on hepatocytes. The processes of biotransformation of a drug entering the liver cells, such a process involves several stages. First, enzyme systems interact with the components of medications, oxidative reactions occur, as a result of which, in some cases, the drug is converted into an active metabolite. In some cases, this component turns out to be a more toxic product than the drug that the patient used. The second phase is characterized by the interaction of active metabolites with various substances such as sulfate ion, glucuronides, with the help of which water-soluble compounds are created, which are then removed from the cell.
- The effect of the drug can occur on a cell in the liver or due to the disruption of the drug's binding with glucuronic acid, when glutathione stores are depleted, various processes can occur.
- After such biotransformation, oxidative reactions create a large number of reactive oxygen species, which can have destructive effects. This is mainly accompanied by necrosis in hepatocytes. Therefore, acute and chronic hepatitis often develop, and cytolytic syndrome prevails.
- In some cases, a kind of competition arises. When multiple medications are used, they can interfere with the interaction of bilirubin with glucuronic acid. Therefore, ordinary jaundice occurs. For the patient, this condition does not pose a danger if the level of direct bilirubin is not too high. Therefore, in this situation, no interventions are necessary for treatment.
Can be formed:
- Acute or chronic hepatitis.
- Fatty liver disease.
Damage can manifest itself in different ways.
Who can be affected by the pathology?
Chronic toxic hepatitis was most often recorded in the younger generation, the elderly and representatives of the weaker half of humanity.
Those people who prefer to self-medicate will also be at great risk. Employees of enterprises associated with chemicals and their production are at risk.
Another risk category consists of drunkards who cannot break the habit of drinking alcohol.
¼ of patients with liver pathology were affected by taking medications. This is data that was reported by research organizations in the United States of America.
In our country, cases of acute forms of toxic hepatitis are most often recorded, which were provoked by the desire of people to combine alcoholic drinks with taking pills aimed at pain relief.
Stages of developing pathology in the body
There are 4 stages of development of this pathology. Experts advise turning to them for help at the first stage, as an extreme case during the manifestation of symptoms of liver damage from poisons.
In such cases, treatment will be much more effective than later, when the situation becomes more complicated.
Let's list all the stages, briefly describing each of them.
Latent period
The poison enters the body.
Manifestation of acute symptoms
Body temperature begins to rise. Following the fever, yellowness of the epidermis appears. The patient has no appetite, and therefore the patient experiences a sharp weight loss.
In this state, a person will be tormented by weakness and will not have the strength to perform those tasks that in the recent past were inherent in everyday life.
This will be followed by manifestations of mental disorder. Hysterics and a craving for scandals, tears and a sharp rise in mood are not excluded. There may be a blurred consciousness, confusion of thoughts.
The liver is no longer able to resist toxins, and therefore sends signals to the brain about its failure.
Exit stage
It takes time from symptoms to complete recovery. But this stage is ambiguous.
After all, the time may end from the developed symptoms - the death of the patient.
Consequences
Negative and positive consequences are noted. Advanced cases provoke the development of liver organ dystrophy.
In this case, it is important to come to an appointment with a gastroenterologist on time. Of course, you should be especially careful when choosing a doctor so that the diagnosis can be made quickly and accurately.
Only in this case will the correct treatment be prescribed. Subsequently, chronic toxic hepatitis will end in recovery.
Diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to carefully collect an anamnesis of the disease. The patient's medical history should include a detailed description of the symptoms and the characteristics of their occurrence. The patient must be told about previous contact with poisons, taking hepatotoxic medications and his profession. If the cause of the pathology is alcohol, the patient may not admit to an addiction, which requires a conversation with relatives.
In diagnosis, it is important to take into account each symptom of the disease, which will allow you to get a complete picture of the pathology. For a more detailed examination, laboratory and instrumental methods are used.
Laboratory methods
Laboratory diagnostics include the following studies:
general clinical analysis, in which a decrease in the level of hemoglobin, platelets and leukocytes may be observed;- coagulogram – signs of blood clotting disorders are revealed;
- biochemistry – allows you to assess the severity of liver dysfunction. The analysis includes the study of transaminases (ALT, AST), alkaline phosphatase and protein. Note that these enzymes can be altered in people without liver disease, so it is important to determine how elevated they are relative to normal;
- Markers of viral hepatitis are a mandatory analysis, thanks to which it is possible to confirm or refute infectious liver damage.
Instrumental studies
To visualize the liver, assess its size, density and consistency, an ultrasound examination is prescribed. It is used for primary diagnosis, as well as for the purpose of monitoring the dynamics of treatment.
The doctor can also use computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging, which are necessary to study blood flow and target examination of internal organs. Diagnosis of blood vessels is carried out by Doppler ultrasound. Using elastography, it is possible to accurately determine the structure of the liver.
Differential diagnosis is carried out with other forms of hepatitis, malignant liver disease, developmental anomalies, and cholelithiasis.
Complications of the disease
The danger of the pathology lies in the fact that liver failure develops against the background of the death of hepatocytes.
Subsequently, they will be replaced by fat cells. All this leads to impaired liver functionality.
Swelling, weight loss, and the occurrence of neuromuscular and mental disorders are observed. It is no longer possible to do without the help of a specialist with a wide range of knowledge in the field of gastroenterology.
A more serious complication would be cirrhosis of the liver. This pathology is chronic. It involves the death of hepatocytes, as well as their gradual replacement by connective tissue cells.
Experts also include progressive pathology of the liver and central nervous system as complications of acute toxic hepatitis.
It was called hepatic coma. In this case, a person may experience convulsions and confusion of reflexes and consciousness. A fatal outcome cannot be ruled out.
Treatment
Before treating toxic hepatitis, stop contact with the substance that causes chronic or acute poisoning. Subsequently, detoxification therapy is carried out, and antidotes are prescribed according to indications. Treatment is aimed at restoring the functions of the gland and other organs that were damaged by the poison. A mandatory part of patient therapy is correction of the regimen and diet.
Can it be cured?
It is impossible to say that patients will fully recover in 100% of cases, since it is not always possible to cure toxic hepatitis. In some cases, the action of a toxic substance leads to irreversible consequences. For example, poisoning with toadstool alkaloids (amanitins and phalloidins) is fatal in most cases.
In case of acute intoxication, it is possible to cure the disease with less toxic substances. The shorter the effect of the poison on hepatocytes, the better the prognosis for the person. With timely consultation with a doctor and comprehensive adequate therapy, it is possible to cure a patient affected by toxins.
How to treat?
In case of poisoning, patients undergo the following measures:
- gastric lavage;
- cleansing enema;
- hemodialysis (according to indications);
- administration of enterosorbents.
Features of toxic hepatitis in children
In our country, the toxic form of hepatitis is diagnosed in childhood quite rarely. But this is not a reason to say that the younger generation will not be affected by this problem.
A risk factor is the penetration of toxic compounds into the liver organ completely by accident.
The fault will lie in the negligence of the parents, as well as in cases of using medications for other purposes, without following the doctor’s instructions. Children can experience poisoning from mushrooms and plants.
The pathology is quite difficult. If proper medical treatment is not observed, death cannot be ruled out.
Children most often suffer from the acute form of the disease. The symptoms are similar to the same clinical picture that appears in adults. The prognosis in this case will be unfavorable.
Diagnostic measures
In order to accurately identify the type of hepatitis, various methods are used.
1. Detailed information will be provided by a biochemical analysis with determination of bilirubin level indicators - direct and total.
2. Conduct general urine and blood tests, do a coagulogram with determination of PTI. Research is required to help rule out other types of hepatitis.
3. Analysis of biological fluid will answer the question of what caused the development of hepatitis in this case - a medicine, an industrial or plant poison.
4. An ultrasound of the abdominal organs is performed.
5. If the diagnosis is still difficult to make, then CT and MRI are performed.
6. The doctor may prescribe scintigraphy, needle biopsy or laparoscopy. These studies help to identify the cause of the disease and assess how much the inflammatory process has developed.
Medical therapy
First you need to stop complete contact with the toxic agent, as well as prompt elimination of them.
It is important to eliminate unpleasant symptoms, as well as the regeneration of hepatocides. The liver has the ability to repair itself. Damaged cells can recover up to 75%.
During the treatment of toxic hepatitis, it is customary to use special medications with a hepatoprotective effect.
During hepatitis, the course of treatment is 6-7 months. This is a really long time, but the pathology is also serious.
Description of drugs
As mentioned above, you need to include restorative drugs in your daily routine that will be beneficial for liver cells.
Essentiale forte
Essentiale Forte differs from other medications in that it contains soybeans, or rather fats derived from them.
Its advantages are that the liver begins to strengthen, because it is affected by special essential phospholipids, they penetrate into the organ, taking up positions in places that have been damaged.
The medicine is also prescribed by doctors because it helps reduce cholesterol and increase the secretion of bile.
Essentiale forte is the best enemy of liver cirrhosis, because it stops scarring of the surface tissues of the organ.
The drug is often prescribed in cases of a therapeutic course to eliminate alcoholic hepatitis.
It has also proven itself to be effective in treating congestions with mushrooms, antiepileptic compounds and pesticides.
Heptral
The main active ingredient is ademetionine, which stimulates the growth of liver cells. It takes part in the synthesis of serotonin, as well as the neutralization of toxins.
This component is produced by the organ, but if the liver has abnormalities, the concentration of the substance decreases.
Heptral replenishes ademetionine deficiency and also promotes natural synthesis.
The advantages of the drug include the possibility of expelling bile and the formation of phospholipids; strengthening the neutralizing ability of the liver, as well as the synthesis of specific amino acids.
The product also has antidepressant properties; Heptral is actively involved in the production of dopamine and serotonin, and helps increase the sensitivity of brain structures to these substances.
Prevention of toxic hepatitis
Preventive measures for toxic hepatitis include complete prevention of contact with toxic substances.
If the disease appears in a person who is an employee of hazardous production, it is necessary to change jobs or retire, if possible.
It is also not recommended to drink alcoholic beverages; it is important to avoid smoking. The patient should eat fractionally, the portions are not large.
It is better to do unloading once a week. It is desirable that it be on vegetables or fruits. Persons working in workplaces with exposure to hazardous substances should consume dairy products. Milk is better, but not very fatty.
Treatment consists of drawing up a specific course of medications. You also need to observe bed rest.
If a large dose of a toxic substance enters the body once, vomiting can be artificially induced. Gastric lavage is recommended. This will help cleanse the body.
Removing toxins is possible using activated carbon. Droppers with electrolyte solutions are also shown.
The procedure of plasmapheresis is not excluded. To reduce the effect of poison on the walls of the stomach, you should drink milk or a decoction based on flax seeds.
It will be useful to take vitamins B and C, hepatoprotectors, and choleretic drugs. As mentioned above, it is important to follow a protein-free diet; therapeutic nutrition makes a great contribution to human health.
If the first signs of the development of an acute form of toxic hepatitis are identified, you should consult a doctor. Subsequently, the specialist will prescribe urgent hospitalization.
Prevention of the disease consists of systematically undergoing treatment in specialized sanatoriums; it is important to attend examinations annually.
Forecast
As a rule, provided the exposure to toxic substances on the body is stopped in a timely manner, the prognosis is favorable. If a person continues to abuse alcohol, take hepatotoxic medications in high doses and come into contact with industrial chemicals, treatment success will be minimal.
Prevention of toxic liver damage involves following safety precautions when working with dangerous poisons. In addition, do not forget about regular medical examinations. They make it possible to diagnose the disease at the initial stage of development. This is especially important for workers whose profession requires them to constantly interact with chemicals.
Therapeutic nutrition course for a patient
Treatment of toxic type hepatitis will not be successful unless a therapeutic diet is established.
Only thanks to this measure will it be possible to launch regenerative processes, providing the body with nutrients of particular importance.
One of the main principles of the new way of eating will be frequent meals. You need to sit down to eat 6 times a day.
It is important not to overeat; portions should be small. A prerequisite is that the products must be at room temperature.
It is important to avoid any contact with all types of liver poisons.
Small meals will improve the flow of bile. Fried, spicy, fatty, salty foods should be excluded from the diet.
There is a taboo on both canned food and smoked meats. The main part of the diet will consist of products with fiber and pectin.
These are fresh fruits, vegetables, legumes. If you want to eat meat, it should not be fatty. It is better to pay attention to chicken or rabbit meat.
In fact, the menu can be quite varied, and therefore the patient will not worry about it.
Diet
A diet for toxic hepatitis is a diet that the patient will follow until complete recovery. These rules are reminiscent of a normal healthy diet with mandatory calorie counting and determining the ratio between proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Preference is given to food prepared at home without the addition of dyes and flavors.
Excluded:
- Broths.
- Refractory fats, spices, herbs, marinades and pickles, canned food.
- Coarse fiber (legumes, rutabaga, nuts, seeds, mushrooms, white cabbage), vegetables with essential oils (radishes, onions, garlic, green onions, radish).
- Fatty meats, offal and fatty fish.
- Confectionery with cream, black bread, muffins, millet.
- Coffee, ice cream, chocolate, cocoa.
- Egg yolks.
- Sour fruits and berries, vegetables and raw fruits.
- Alcohol and carbonated drinks.
Doctors include the following in the list of products that must be consumed for toxic hepatitis:
- dietary varieties of fish, poultry and meat;
- fruits and vegetables, with the exception of those that can irritate the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract and affect the acidity of the stomach;
- fruit and vegetable purees, as well as soft fruits (bananas);
- cereals in the form of porridges or soups;
- refined vegetable oils, with the exception of olive oil (it is too fatty and will not be beneficial for the liver, although it contains a large amount of vitamins);
- dried fruits prepared at home without sugar;
- green tea, vegetable and herbal infusions;
- low-fat fermented milk products, cottage cheese without restrictions;
- egg whites, eggs in limited quantities.
In general, timely diagnosis and proper therapy helps to completely cure the disease. Therefore, the prognosis is favorable. However, acute damage to the digestive organ by large doses of a toxic substance, coupled with the lack of qualified medical assistance, can lead to death.
Source: simptomy-i-lechenie.net