Viral intestinal infections are a whole group of different viral diseases that are characterized by symptoms of general intoxication of the body. Most often, the infection affects the stomach, small intestine, or a combination of both, causing enteritis and gastroenteritis. In addition, the human respiratory system may suffer.
Typically, disruption of the gastrointestinal tract is observed in diseases that are provoked by rotaviruses; in second place in the frequency of development of problems with the digestive tract are diseases caused by adenoviruses. Slightly less commonly, enteroviruses and rhinoviruses cause intestinal disorders.
Rotaviruses are usually divided into 5 groups (virus A, B, C, D, E); humans, as a rule, suffer from group A viruses, which multiply in the upper part of the small intestine (intestinal flu). Rotaviruses are very similar in structure to rhinoviruses:
- they multiply in the cells of the mucous membranes of the small intestine;
- affect people and animals.
The vast majority of adenoviruses provoke respiratory diseases, and only two types cause diarrhea. Among the enteroviruses that cause diarrhea, the most important is the Coxsackie virus group A.
Absolutely all viruses that cause intestinal infections are resistant to the external environment and physicochemical influences.
Acute intestinal infections in children
It is important for people with dysentery to undergo a course of therapy of up to a week.
Ideally, patients adhere to bed rest and engage in physical therapy. Eat right and your body will recover. Eat light meals - soup, porridge, boiled chicken. Don’t forget about recovery pills; take Fthalazol 4-5 times a day before meals (up to a week). With Escherichiosis, it is not permissible to indulge in self-medication at home. You need to go to the hospital. If you decide to treat yourself, choose a course lasting up to a week. If you are being treated with antibiotics, use Levomycetin. Use 0.5 grams 4 times a day half an hour before meals. In severe cases, the dose is increased to 1 gram at a time.
Infection is in 2nd place after the respiratory type. Causes:
- Failure of a child to comply with personal hygiene rules.
- Eating dirty, unwashed foods.
- Products produced by cattle.
- Inadequate sanitary conditions.
- Stopping breastfeeding at an early age.
- Bacteria that are pathogens.
Medicine for abdominal pain for children should definitely be in the first aid kit of parents. Treatment of colic and bloating involves the baby taking light medications. Their use must be agreed with your doctor. What helps with stomach pain:
- Disflatil;
- Espumisan;
- Festal;
- Enterosgel;
- Mezim;
- Lactovit;
- Linux;
- Activated carbon;
- No-shpa;
- Furazolidone.
Intestinal infections in children can be caused by various types of viruses and bacteria. All these pathogenic microorganisms are resistant to negative environmental factors; they can remain active for a long time at low temperatures outside the human body.
They live on food, household items and dirty skin of the body. It is very easy to introduce an infectious pathogen into the gastrointestinal tract; infection occurs through the mouth. The process of treating intestinal infections in children will take a lot of nerves from parents and will cause even more suffering to the child.
Intestinal infections are divided into the following diseases:
- Bacterial intestinal infections: salmonellosis, dysentery, escherichiosis, yersiniosis, campylobacteriosis, cholera, botulism, typhoid fever, acute intestinal infection caused by Klebsiella, clostridia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, staphylococcus and others.
- Viral intestinal infections caused by rotaviruses, enteroviruses, adenoviruses and others.
- Fungal intestinal infections caused by Candida fungi.
- Protozoal intestinal infections: amebiasis, giardiasis.
Treatment of intestinal infections in children is complicated by the fact that specialists need about 3 days to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease. During this period of time, pathogenic microflora begins to show activity in the biological material collected from the patient. While the analysis is being carried out, the child receives treatment with drugs that are effective against the vast majority of pathogens.
The disease is much more complicated in children under one year of age. Dehydration occurs quite quickly. But the main problem is that kids refuse to drink water and solutions. That is why they are hospitalized in a hospital, where drugs are administered intravenously.
Dangerous symptoms in children under one year of age are considered:
- lack of sweat;
- urinary disturbance. The child may not write for more than three hours;
- dryness of the mucous membrane of the tongue and mouth;
- manifestation of crying without tears.
If parents suspect an infection, they should urgently call an ambulance. You should not refuse hospitalization, since it is not always possible to overcome diseases at home.
The disease has several names: rotavirus gastroenteritis, stomach or intestinal flu, rotavirus infection. It is bacterial in nature.
A child’s stomach ache after rotavirus is precisely because of bacteria. The incubation period lasts up to 5 days.
An adult or child who has become infected with this disease is considered a carrier of the infection throughout the entire period from the moment of infection until complete recovery. The duration of the disease depends on the age and capabilities of the body.
Adults tolerate it more easily; with proper therapy, they begin to recover on the seventh day.
How does the disease progress?
The consequences of rotavirus infection can occur during the disease itself or some time after recovery.
Rotavirus infection is similar to the flu. Everyone knows that the flu is dangerous due to its complications, so people who have rotavirus infection are often concerned about the consequences of this disease.
Complications of rotavirus infection
Rotavirus infection has several names: stomach flu, rotavirus. The disease is caused by a virus that affects people of all ages, including very young children.
Rotavirus is a common infectious disease, especially dangerous for young children. In the United States, it affects one million children under the age of four every year.
Rotavirus infection is one of the most common acute intestinal infections that cause high childhood morbidity and even mortality. According to WHO, approximately 138 million cases of rotavirus infection are registered worldwide every year. Thus, a significant proportion of all intestinal diseases on the planet are caused by rotavirus infection.
Rotavirus infection is one of the most common intestinal diseases in the world
Causes of infection
— antibiotics (antibiotics do not affect viruses!!!!)
— pro- and eubiotics (Linex, Bactisubtil, Eubicor, Hilak, etc.)
- enterofuril and furazolidone
- enzymes
— immunomodulators
- weed ants
- imodium.
What threatens us in the end after lack of washing and thoughtlessness?
Pediatricians divide acute intestinal infections (acute intestinal infections) into two main groups:
1. OCI of bacterial nature:
- caused by obviously pathogenic enterobacteria (dysentery, salmonellosis, cholera, yersiniosis, etc.);
- caused by opportunistic microorganisms (Klebsiella, Proteus, Clostridia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc.).
2. Viral diarrhea (caused by ECHO, Coxsackie viruses, rotaviruses, adenoviruses, etc.).
I ate two spoons too much, and the mouse’s stomach hurt...
So, unwashed berries or microorganisms picked up in public places turned into bombs and started a war in the intestines. First of all, you need to assess the situation and understand WHAT could happen. We remember what the child ate and in what quantity. Where you were, where you swam and with whom you talked, do any of your relatives feel similar symptoms, do your friends get sick. This is the first thing you must understand. Second: assess the child’s current condition. This will help you decide on further actions. Is the child lethargic or active, does he have frequent loose stools or rare stools, his skin color is pale or normal, his eyes are clear or dull... Sometimes a confused mother goes to the forum and asks: what should I give my child for diarrhea? Advice pours in, one better than the other: Linex, Bifilin, coal, Smecta, Mezim-Forte... Mom grabs her head and realizes how bad and inattentive she is to her child. And he urgently purchases a list of beneficial bacteria and enzymes that are useless - and even very harmful for diarrhea. And then it turns out that there is nothing to treat, and loose stools do not cause much harm to the child: the toxins are washed away, the process continues, everything is fine.
In many cases, intestinal “breakdowns” that are not accompanied by high fever and extreme dehydration can be cured by two methods: soldering and diet. Some situations require medication intervention and should be under medical supervision. Therefore, we will not analyze them, but will consider only non-drug treatment. If your child’s condition causes you concern: he lies flat and vomits frequently – call a doctor! If the child is less than a year old, call an ambulance!
Consulting is Dr. Alexander Gorelov, professor of the Department of Childhood Diseases of the Moscow Medical Academy. THEM. Sechenova, Head of the Clinical Department of Children, Central Research Institute of Epidemiology, Doctor of Medical Sciences. :
Children, unlike adults, are more likely to experience severe forms of intestinal infections, since they become dehydrated more quickly as a result of water loss through vomiting and loose stools, and children’s cells, as is known, are 90% water and salts.
It should be noted that when any infectious pathology occurs, including intestinal infections, not only the number and pathogenicity of microbes that enter the baby’s gastrointestinal tract, but also the initial state of health of the child matters.
Signs of intestinal infection in a child
The disease can be recognized by intoxication of the body, temperature, headaches, mucous discharge with pus and blood. There are types of intestinal infections:
- Viral – mild symptoms. Characterized by headache, fever, weakness, mild diarrhea (without blood, mucus, pus).
- Intestinal – the infection is more complicated. Characterized by vomiting, pain in the center of the abdomen, diarrhea (with mucus, pus, blood), poor health, and loss of fluid. If there is an infection, the child will be weak and lethargic.
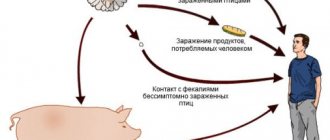
More often, a baby becomes infected through water, food, unwashed hands, dirty toys, and contact with children. A child with a weak immune system is susceptible to infection. The disease manifests itself in summer and autumn, when there are many factors for infection. Parents should protect the child, carefully monitor his actions so that he does not put dirty hands in his mouth, and before eating, wash his hands and the food he is going to eat.
Causes of infection
Early signs: no urine for 8-12 hours, dark urine with a strong ammonia odor, thick, sticky saliva.
Late signs: all of the above plus a sunken fontanel in an infant, sunken eyes, the child is inactive, drowsy, difficult to wake up.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of intestinal infection in children are divided into local and general.
General signs of the disease:
- intoxication: increased body temperature, headache, general weakness;
- dehydration: rare urination, dark urine, dry mucous membranes and skin, impaired skin turgor.
Local symptoms of intestinal infections in children:
- by type of gastritis: stomach pain, nausea, vomiting, loose stools;
- by type of gastroenteritis: pain in the stomach and umbilical area, vomiting, watery stool with mucus;
- according to the type of gastroenterocolitis: constant diffuse abdominal pain, vomiting, loose stool mixed with blood, which does not bring relief;
- by type of colitis: pain in the lower abdomen, pain during bowel movements, loose stools mixed with mucus and blood, false urge to go to the toilet.
The average incubation period ranges from one to five days. Rotavirus infection has an acute onset. With timely treatment, everything ends well.
The first symptoms are as follows:
- acute and cramping pain in the abdomen;
- repeated vomiting up to three to five times a day;
- lack of appetite;
- deterioration of general condition, weakness;
- increase in temperature values to 38-39 degrees.
The first and main symptom of infection is considered to be a stomach ache due to rotavirus. After some time, the patient begins to experience severe diarrhea. Feces are watery in nature with a yellowish tint. There are no impurities of blood or greenery. The smell is sour. Due to repeated diarrhea, the patient develops dehydration.
Critical dehydration is said to be:
- confusion and loss of consciousness;
- convulsive state;
- redness of the eyes;
- swelling of the palatine arches and pharynx.
On the second day after illness, drowsiness appears. The patient can sleep all day. This is due to the weakening of the body. The acute course lasts about 4-5 days, after which the symptoms begin to subside. These symptoms are more common in children.
Adults may have one-time diarrhea and a slight increase in temperature. In this case, rotavirus does not pose a danger to the patient himself, but he becomes its carrier.
Causes of infection
Recovery duration
After first aid has been provided and appropriate treatment has been carried out, the rehabilitation period begins, which includes the following measures:
- compliance with a therapeutic diet;
- ensuring rest, bed rest if necessary;
- taking a drug from the sorbent group.
The duration of rehabilitation varies depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the clinical case. Abdominal pain after an infectious disease is considered normal and is residual.
Dietary food excludes fried and fatty foods, spices, marinades and pickles, confectionery and flour products, mushrooms. If the therapeutic diet is violated, pain will occur very quickly, will be intense and can lead to complications.
Treatment of intestinal infection
Categories of patients for hospitalization:
- Children with acute intestinal infection.
- Infants.
- Children with digestive problems.
- Children with typhus.
- Children with cholera.
The child must have a diet. Infants are given non-calorie formulas. For older children, puree, vegetables (pumpkin, carrots), crackers, vegetable soup, porridge, boiled meat, yogurt, cottage cheese, kefir, fruits (apples, bananas, pears, lemon) and drink plenty of water.
Drink more fluids - it helps remove unnecessary substances from the body. If you feel unwell, it is advisable to use potassium permanganate. If there is increased fluid loss, it is recommended to drink 2 liters of water per day. If water does not help cleanse the body, use an enema. If it doesn't help, go to the hospital immediately.
How to treat an intestinal infection:
- Rehydration therapy. Used for acute dehydration. If there are no signs, do not delay prevention. Children under 2 years old can drink 100 ml. water, over 2 – 200 ml.
- Antibacterial therapy. Designed for infants. They treat with folk remedies, rub with herbs, and give tinctures.
- Assistive therapy. Normalizes the microflora of bacteria. It is recommended to use Bifidumbacterin.
- Diet therapy is the child’s compliance with nutrition.
It is recommended to take the drug Hilak forte.
Treatment of intestinal infections in children should be carried out comprehensively, involving the organization of oral rehydration, symptomatic, etiotropic and pathogenetic treatment, and diet therapy.
The diet for children in the treatment of intestinal infection is based on reducing the volume of food and increasing the frequency of feedings, using foods in easily digestible form or artificial mixtures for infants that have protective factors.
The basis for treating symptoms of intestinal infection in children is oral rehydration of the body with special solutions of salts and glucose (preparations Regidron, Citroglucosolan). You should also pay attention to drinking plenty of fluids. If drinking a sufficient amount of fluid is impossible, the child is prescribed infusion treatment with intravenous administration of a solution of albumin, glucose and others.
Pathogenetic treatment is carried out for intestinal infections in children, the symptoms of which require the use of enzyme preparations (for example, Festal) and antiallergic drugs (for example, Suprastin, Loratadine).
Symptomatic treatment of intestinal infection in children includes taking antispasmodic (for example, Drotaverine, No-shpa) and antipyretic drugs (for example, Paracetamol, Panadol).
Rotavirus infection is a disease associated with damage to the gastrointestinal tract. Every person has encountered this disease.
The course of the disease is severe in children under three years of age. Several weeks after the acute symptoms have subsided, parents ask each other and experts on social networks why their child has a stomach ache after rotavirus and how long the digestive system disorders last.
Features of rotavirus infection
Causes of infection
- Drink plenty of fluids! If there is vomiting, then you need to take a teaspoon every 5-10 minutes. The volume of drink should be equal to the volume of fluid lost through vomiting and diarrhea.
— Antipyretic at high temperatures.
If it is impossible to get the child drunk or there is uncontrollable vomiting, hospitalization for infusion therapy is indicated.
Historical information
Gastrointestinal infections have always accompanied humans.
For a long time, they were the cause of mass child mortality: the child’s body quickly becomes dehydrated. Other infectious diseases played a lesser role in the mortality of children under one year of age, although in the population their role as a population regulator was significant. Among the intestinal infections were quarantine ones, which regularly spread in epidemics. At this time, the mortality rate of the population of all ages went off scale. Unsanitary conditions and overcrowding of people in cities led to the spread of epidemics. It was noticed that the incidence of quarantine intestinal infections decreased sharply after the construction of sewer networks.
Educational work has played a major role in the fight against intestinal diseases, especially in children's institutions. It would seem that very simple procedures: washing hands before eating, heat treatment of food, boiling water - have proven effective in combating the spread of infectious diseases.
Stage two: diet therapy
So, the doctor came and reassured you: hospitalization is not needed, you can survive the intestinal sore at home. The child feels better, which means you can think about nourishing the tired body.
Infants, as usual, are the luckiest of all - they have breast milk. If a child is sick or has had rotavirus or another intestinal disease, the best diet for him is to abolish all complementary foods and “hang” on the chest.
If the child is already receiving complementary foods, they are added on the second or third day of illness: gluten-free porridge with water (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal is allowed), steamed (canned) vegetables, meat is returned last, a week after the illness we introduce baked (or canned) apples and pears, and only then – fermented milk products.
For an older child (after one year), give food more often and in small portions. If he does not vomit after eating, there is no need to go on a strict diet - eat porridge.
Do not insist that the child eat the entire portion; a couple of spoons is already good. Remember the golden rule of recovery: strength for it comes not only from food.
The body spends its resources to fight the disease, and food only distracts it, especially the wrong food. There is no need to give your child bread, crackers, crackers, or cookies during illness.
Do not force feed your child, do not overload his liver, believe me, he will catch up when he gets better.
During the acute period of infection, older children (after three years) must completely exclude whole milk and porridges made with whole milk, fermented baked milk, and cream from their diet; black bread; meat, chicken and fish broths; dishes made from beans, peas, beets, cabbage; grapes and citrus fruits; as well as everything fatty, fried, canned (except for canned baby food).
So: in the first days of illness, a child (excluding small children who are still receiving full breastfeeding or formula) may go hungry. Rice water and oatmeal are allowed. On the third day, he can be given porridge and fresh vegetables. If the child feels better, gradually expand the diet.
Infants, as usual, are the luckiest of all - they have breast milk. If a child is sick or has had rotavirus or another intestinal disease, the best diet for him is to abolish all complementary foods and “hang” on the chest.
If the child is already receiving complementary foods, they are added on the second or third day of illness: gluten-free porridge with water (rice, buckwheat, oatmeal is allowed), steamed (canned) vegetables, meat is returned last, a week after the illness we introduce baked (or canned) apples and pears, and only then – fermented milk products.
For an older child (after one year), give food more often and in small portions. If he does not vomit after eating, there is no need to go on a strict diet - eat porridge.
Do not insist that the child eat the entire portion; a couple of spoons is already good. Remember the golden rule of recovery: strength for it comes not only from food.
The body spends its resources to fight the disease, and food only distracts it, especially the wrong food. There is no need to give your child bread, crackers, crackers, or cookies during illness.
Do not force feed your child, do not overload his liver, believe me, he will catch up when he gets better.
During the acute period of infection, older children (after three years) must completely exclude whole milk and porridges made with whole milk, fermented baked milk, and cream from their diet; black bread; meat, chicken and fish broths; dishes made from beans, peas, beets, cabbage; grapes and citrus fruits; as well as everything fatty, fried, canned (except for canned baby food).
Treatment of intestinal infection should involve an integrated approach. In addition to stopping harmful microbes, the patient needs to neutralize toxins and restore water balance.
Peculiarities of nutrition of adolescents and fellow adults during exacerbations of diseases
Advised by nutritionist at Moscow City Clinical Hospital No. 20 Lyubov Evgenievna Nefedeva.
Chronic enteritis and chronic colitis with constipation
DON'T : Bread made from premium flour, puff pastry and butter dough; fatty meats, poultry, fish; canned food, smoked meats, marinades, spicy foods; hard-boiled and fried eggs; rice, semolina, vermicelli; legumes, radishes, radishes, garlic, onions, turnips, mushrooms; jelly, blueberries, quince, dogwood, chocolate, products with cream; horseradish, mustard, pepper; cocoa, natural coffee, strong tea.
YOU CAN : Gray, bran bread, crispbread; low-fat soups with meat, chicken, fish broth, borscht, cabbage soup, beetroot soup, okroshka; beets, carrots, tomatoes, lettuce, cucumbers, zucchini, pumpkin, cauliflower, white cabbage and green peas - as tolerated; crumbly porridges and casseroles; soft ripe sweet fruits and berries, soaked dried fruits - prunes, figs, dried apricots, apricots; fruit and vegetable juices; lactic acid drinks, fresh cottage cheese and cottage cheese casseroles, cheesecakes, mild cheeses.
It is better to cook food in water or steam, or bake. Fried foods and dishes have a bad effect on the condition of the intestines and other digestive organs. Eat vegetables and fruits boiled and raw. They improve intestinal function. In the morning, drink cold water with honey or juices of fruits and vegetables. At night - kefir, fresh or dried fruit compotes, fresh fruits and prunes.
Peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum, chronic gastritis with high acidity
NOT ALLOWED : Rye and any fresh bread, products made from butter and puff pastry ; strong broths, cabbage soup, borscht, okroshka; fatty meats, poultry and fish; fried and spicy foods, smoked meats, marinades, pickles, canned food, spices, gravies; hard-boiled and fried eggs; white cabbage, rutabaga, cucumbers, radishes, radishes, sorrel, spinach, onions, beans, mushrooms.
YOU CAN : Dried wheat bread made from premium and first grade flour, dry biscuit, dry cookies; pureed soups from vegetables and well-cooked cereals; boiled lean meat and fish without skin; milk, cream, non-acidic kefir and cottage cheese, sour cream - limited; 2-3 soft-boiled eggs or steam omelet per day; semi-viscous and mashed porridge with milk or water; potatoes, carrots, beets; sweet berries and fruits in pureed, boiled and baked form.
Avoid eating raw and unprocessed fruits and vegetables. Be sure to clean the fruits from seeds, grains and skins. Food should be pureed, boiled or steamed. Just not fried. With a mild exacerbation, you can afford baked dishes without a crust. Don't overuse salt. Avoid very cold and very hot foods. In case of a sharp exacerbation, consult a doctor immediately.
Chronic enteritis and chronic colitis with diarrhea
DON'T : Rye and bran bread, pancakes, butter dough; soups with cereals, vegetables, pasta, dairy, strong and fatty broths; fatty meat and fish, sausage; marinades, canned food, caviar; whole milk, sour cream, cream, cheese; millet, pearl barley, legumes; snacks; dried fruits, jam, honey, fruits and berries in their natural form; compotes, carbonated and cold drinks, coffee and cocoa with milk.
YOU CAN : White bread crackers, thinly sliced, untoasted; slimy soups made from rice, semolina and oatmeal in water or secondary broth; lean meat and fish in the form of meatballs, soufflés, cutlets, cooked in water or steamed; mashed porridge; soft-boiled eggs 1-2 per day, in a bag, steam omelettes; jelly from dogwood, blueberries, bird cherry, freshly brewed tea, rosehip decoction, dried blueberries, black currants, bird cherry, quince; freshly prepared pureed cottage cheese, butter - up to 5 g in the finished dish.
Try to eat liquid and semi-liquid pureed foods. You can add boiled and pureed meat, egg flakes, steamed meatballs and vegetable broths to soups. It is better to avoid vegetables in other forms. Berries and fruits are allowed only in the form of jelly and jelly. The exception is pureed raw apples. If tolerated, you can drink diluted fresh juices from various fruits, except grapes, plums, and apricots.
Chronic gastritis with low acidity
NOT : Rye and any fresh bread, flour products made from butter and puff pastry; milk, millet, pea, bean soups, okroshka; fatty and stringy meat, fatty fish; hard boiled eggs; onions, radishes, radishes, sweet peppers, cucumbers, rutabaga, garlic, mushrooms; smoked meats, pickles, marinades, canned food, spicy and fatty foods; mustard, horseradish, pepper; fruits and berries with coarse grains or rough skin.
YOU CAN : Dried wheat bread made from premium and first grade flour, savory buns and cookies; soups with vegetable broth, low-fat meat, fish, and mushroom broths; porridge from various cereals, except millet; boiled pasta and noodles made from premium flour; potatoes, zucchini, carrots, beets, cauliflower, parsley, dill, celery; kefir, yogurt and other fermented milk products, fresh cottage cheese and dishes made from it, cheese, sour cream - up to 15 g per dish.
This diet is good for mild exacerbation of the disease. You can eat not only pureed and boiled dishes, but also stewed, baked and even fried. However, you should fry without breading and avoid the appearance of a rough crust. Vegetables for soup should be finely chopped or pureed. If you are preparing rassolnik, it is better to replace pickles with brine.
All recommendations from this article are suitable not only for children, but also for adults!!!
Be healthy!
The materials published in this article are food for thought. For a diagnosis, nutritional advice, and treatment, please contact your healthcare provider.
Popular
Nighttime fun for two-year-old twins =)
How to involve dad in child care process
18 wise thoughts from Mother Teresa about peace, life and love that we all need to re-read more often
How wedding photos are actually taken
Are antibiotics needed?
The first option - the child found a beautiful box, ate the contents and got a stomach ache - this is a very dangerous situation that requires immediate medical attention and urgent gastric lavage. Anything is possible here - up to death.
The second option: the child was prescribed medication and while taking it, the child developed a stomach ache.
This is possible as a side effect of some medications; in children, these are most often antibiotics. If this happens, you cannot stop the medicine yourself, you need to consult a doctor; perhaps the child needs a special diet for the period of treatment, or the doctor will prescribe another medicine to reduce the side effects of the first.
First aid for poisoning
If a child has a tummy ache due to impaired digestion, parents need to carefully monitor their child’s diet: exclude all gas-forming foods from the menu (milk, pickles, beans, bread, kvass, mushrooms), supplement it with fiber.
What to do if an acute abdomen occurs? First aid for stomach pain is to call an ambulance. Only a doctor can determine the cause of acute pain and select the appropriate treatment.
Before the ambulance arrives, you are only allowed to apply an ice pack to the baby’s stomach to alleviate his condition.
Prevention measures
In order not to think about how to treat intestinal infection in children, you need to pay attention to the prevention of this disease. General recommendations boil down to maintaining personal hygiene, mandatory hand washing after using the toilet and outside, careful handling of food products, especially washing fresh vegetables and fruits.
If one of the family members or a child has symptoms of an intestinal infection, treatment should be carried out in a separate room, where disinfection must be carried out. The sick person is provided with separate bedding, towels, dishes and cutlery. After each visit to the toilet, you need to treat the toilet or children's potty with any disinfectant if the child uses it.
Detecting signs of an intestinal infection in a child is an urgent reason to consult a doctor. There can be no talk of any self-medication in this case. It is necessary to consult a pediatrician, undergo a proper examination and receive adequate medical care.
Rotavirus infection is an insidious disease. Even with good hygiene, there is a risk of contracting the virus. Most often, this disease affects children in preschool age.
But doctors highlight several preventive measures.
- Vaccinate babies up to 8 months. It shows 100% effectiveness if it was given to an infant. But thanks to this phenomenon, the mortality rate has dropped sharply.
- Observe hygiene rules. Wash your hands and face regularly. Rinse the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat.
- Avoid contact with sick people.
- If a person is a carrier himself, then he needs to stay at home for two weeks.
- After recovery, strengthen the child’s body. Give vitamin complexes, walk in the fresh air more often.
- Follow the diet and drinking regime.
- Don't drink raw tap water. Always boil it.
Do not treat yourself. Such symptoms can also appear in other pathologies. To make an accurate diagnosis, it is necessary to carry out differential diagnosis. To do this, the patient's stool is taken for analysis. Based on the test results, doctors determine whether the body has an antigen for the infection. When a person is completely healthy, the test result will be negative.
Rotavirus infection is not such a dangerous disease, unlike giardiasis, dysentery or cholera. The disease can be cured quickly, but only if the treatment is chosen correctly.
Can your baby get sick again?
A previous infection does not make the body resistant to it in the future . Type-specific immunity develops, and since there are several serological types of rotavirus, the likelihood of re-infection is very high.
The immune system is very weak, so the same type of virus can cause re-infection after a short period of time . Nevertheless, each time the disease is tolerated more easily, so repeated rotavirus passes with less pronounced symptoms.
Relapse of rotavirus usually occurs in infants 3-4 months after the disease. The main thing in preventing the recurrence of the disease is identifying the source of the disease and isolating it.