Both adults and children often suffer from intestinal infections, which are caused by various pathogens. These include norovirus, which provokes the development of the so-called intestinal flu . The symptoms and treatment of norovirus intestinal infection in children and adults are not much different from the treatment of rotavirus infection, but there are still certain differences.
General information
Norovirus infection (norovirus, "winter vomiting disease") is a disease that affects the gastrointestinal tract. It occurs equally in adults and children. A very contagious pathology that in most cases goes away on its own.
During the period of infection, it is important to prevent dehydration of the body. Therefore, it is better to consult a general practitioner or pediatrician, undergo a comprehensive examination and treatment selected by a specialist.
The following forms of the disease are distinguished:
| Name | Description |
| Light form | Diagnosed in 50-60% of cases. The pathological condition is characterized by high fever and minor pain in the abdominal area. Vomiting is always present and is rarely accompanied by diarrhea. Full recovery of a person occurs in 1-3 days. |
| Moderate form | A moderate form of norovirus infection is accompanied by high fever, symptoms of intoxication, repeated vomiting and upset stool, and stomach pain. The disease lasts 2-5 days. |
| Heavy | All clinical signs inherent in norovirus infection are present. Additionally, severe dehydration of the body occurs. |
| Erased | Pathological processes develop slowly and imperceptibly. The person's condition is satisfactory. In some situations, nausea occurs, sometimes stool is disrupted, body temperature is normal. |
Urgent hospitalization of the patient is required if a severe form of norovirus develops.
What is norovirus, general information
Let's find out what norovirus is and what disease it causes. Norovirus, also called Norfolk virus or Nora virus, causes acute intestinal pathologies, in particular acute gastroenteritis. Norovirus in Korea has fueled interest in this infection, but it has been known for a long time. It was first discovered in 1929 and called “winter vomiting disease.” In 1968 In the area of Norwalk in the USA, an outbreak of a massive intestinal infection was noted.
This disease was described in detail in 1972. Then it was called Norwalk virus. In 2002, it was given a new name - Norovirus.
The disease has different names - stomach flu, winter vomiting disease, norovirus infection, Norfolk agent. In Russia it is called intestinal flu. The disease is especially dangerous for children and the elderly, as well as for people with weakened immune systems.
How is norovirus different from rotovirus?
Laboratory diagnosis of norovirus has recently begun. Previously, it was classified as a rotavirus infection . It was only in 2002 that the virus received its name. Norovirus disease is similar to rotavirus in its mechanism of infection, symptoms and course. But still these are completely different pathologies:
The table shows how norovirus and rotovirus differ from each other. According to statistics, every fifth episode of acute gastroenteritis in the world is caused by norovirus. Of the 685 million cases, children under 5 years old account for up to 200 million. Of these, almost 50 thousand are fatal. And almost all are registered in developing countries. For comparison, on this site in the “Medicine” section, you can read about other pathogens of intestinal infections: rotavirus and enterovirus .
Difference from rotavirus
Norovirus infection (symptoms and treatment in severe situations require a comprehensive examination) is similar in course and clinical signs to rotavirus infection, but these pathological conditions have distinctive features:
| Norovirus | Rotavirus |
|
|
It is impossible to make a diagnosis on your own. A general practitioner or pediatrician will help determine the disease. It is important to go to the hospital in a timely manner, undergo a comprehensive examination and begin treatment. In some situations, it is enough to monitor the patient’s condition without undergoing therapy; the main thing is to prevent dehydration.
Epidemiology
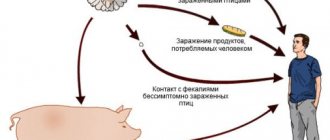
The source of infection is patients with latent or manifest forms of the disease, as well as virus carriers. Patients pose the greatest danger to others on the 3rd - 5th day of illness. The release of rotavirus decreases as stool normalizes and ranges from 10 to 14 days; with an erased form of the disease, it can last up to 20 days.
Children in the first year of life become infected from sick mothers. Organized children become infected in children's groups. The main mechanism of infection transmission is fecal-oral, which occurs in different ways (usually contact and household) with many factors of infection transmission (infected surrounding objects, food, water and drinks). Rotaviruses are released into the external environment not only with feces, but also with respiratory tract secretions. 10 viral particles are enough for infection.
Pathogens are the main cause of nosocomial enteric infections, especially among young children and premature newborns.
The optimal conditions for the life of rotaviruses are a temperature of 40C, humidity 90% and more or less 14%, so the peak incidence occurs in December - April. Sporadic cases of rotavirus infection occur throughout the year. In Russia, the incidence also increases in the fall.
Rice. 3. Severe rotvirus infection in children.
The causative agent of the disease is rotavirus - a microscopic particle covered with a three-layer shell and shaped like a wheel. Translated from Latin, “rota” means wheel. The virion consists of envelopes and a core containing double-stranded RNA and proteins.
Rotaviruses are resistant to environmental factors. Microbes do not die when exposed to low temperatures, ether, chlorine, formaldehyde, ultrasound. In hospital settings, the only disinfectant for them is ethanol. Viruses lose their pathogenic properties during prolonged boiling or treatment with alkalis and acids.
There are nine known types of rotaviruses that are dangerous to humans. Sick people release pathogens into the external environment with feces and saliva. Healthy carriers of the virus also often become a source of infection. The main mechanism of transmission of rotavirus infection is fecal-oral, which is realized through alimentary, water and contact-household routes through dirty hands, contaminated food, water, toys, and household items. In more rare cases, infection occurs through airborne droplets; the pathogen is transmitted by sneezing, kissing or coughing.
Rotavirus is characterized by an autumn-winter increase in incidence. There are both sporadic cases of the disease and epidemic outbreaks, which often coincide in time with influenza epidemics. Rotaviruses are widespread, but most cases of disease are recorded in countries with poorly developed medicine and low sanitary culture of the population. Young children infected with rotavirus die in these countries.
Rotaviruses often cause nosocomial infections, especially in children's hospitals, neonatal pathology departments and neonatal centers.
Transmission routes and incubation period
Norovirus infection (symptoms and treatment require medical consultation and examination) begins to develop as soon as it enters the human body.
Infection occurs in the following ways:
| Name | Description |
| Food | Infection of the human body occurs when consuming unwashed food (vegetables, fruits). |
| Water | Pathogenic bacteria enter the body with dirty water, where pathogens of pathological processes are present. |
| Contact and household | The source of infection is dishes, household items, and unwashed hands. |
| Airborne | The infection is transmitted from a sick person to a healthy person during coughing or sneezing. |
| Transplacental | The transmission of pathogens occurs from mother to child during fetal development. A pregnant woman does not have to be sick; it is enough to be a carrier of infection. Congenital pathology provokes the death of the child. |
A sick person is dangerous to others during the period of exacerbation of the infectious disease and over the next 48 hours. The incubation period lasts 24-48 hours after infection of the body.
People who have been diagnosed with immunodeficiency are sick for 120-180 days. In the case of chronic diarrhea, this time is extended to 2 years. Carriers of norovirus infection are dangerous to others for 3 weeks from the moment the body is infected with pathogenic bacteria.
Causes
The causative agent of the disease is an RNA-containing human norovirus belonging to the Calicivirus family. More than 7 genetic groups of the virus are known, only three are considered pathogenic for humans. The sources of the infectious agent are sick or asymptomatic carriers; cases of the virus being isolated from the body within two weeks after recovery are described. The predominant route of transmission is contact when sharing household items and utensils contaminated with pathogens.
Food infection is associated with the consumption of thermally unprocessed food (ice cream, fresh vegetables, herbs, shellfish) prepared with unwashed hands, water infection - when using unboiled tap water, less often from poorly treated coolers. The virus is most easily transmitted at low temperatures and high humidity. The pathogen is stable in the environment and remains viable for more than 28 days. Inactivation of norovirus is only possible when using chlorine-containing disinfectants.
Symptoms of norovirus infection
The first sign of norovirus infection is a disorder in the functioning of the digestive system.
Norovirus infection. Symptoms
The following clinical symptoms are associated:
- severe nausea and vomiting, after which there is no relief;
- diarrhea with mucous impurities;
- severe pain in the abdominal area of a cutting nature;
- increased drowsiness, headache, body weakness;
- worsening appetite, sometimes with loss of taste;
- slight increase in body temperature;
- painful urge to bowel movement;
- sore throat, runny nose, increased lacrimation.
In most cases, pathological symptoms disappear on their own. In rare situations, the patient needs hospitalization and therapy if severe dehydration is observed.
First aid for a child
As soon as the first signs of the disease appear, treatment must begin immediately. First aid for a sick child is as follows:
- The room where the sick child is located should be ventilated and provide a flow of fresh air.
- If a small child is sick, he is placed on his side so that during vomiting the substances do not enter the respiratory tract.
- It is advisable to rinse the stomach to get rid of pathogenic microflora. To do this, the child is asked to drink more water and then vomited;
- To cleanse the intestines, an enema is done with a weak saline solution. To do this, take a tablespoon of salt per 1 liter of warm boiled water.
- Then the patient is given a drug with an adsorbing effect, this can be activated carbon or white carbon.
- To avoid dehydration, the patient should drink frequently and in small sips.
Danger of disease
Complications and consequences that arise from norovirus infection depend on the degree of damage to the human body. The state of the immune system is also important, how capable it is of resisting pathogens.
In most cases, complications after norovirus infection occur as a result of damage to the central nervous system:
- brain tissue swells;
- encephalitis develops;
- convulsive syndrome occurs;
- hearing and visual functions deteriorate;
- epileptic seizures appear;
- the risk of paralysis of one half of the body increases.
Dislocation syndrome can appear in a person after norovirus. The pathological condition is characterized by herniation of the brain, when there is a high probability of stopping the functioning of the cardiovascular or respiratory system.
Purpose of analysis
To confirm that a patient has an enterovirus infection, various diagnostic methods are used. They are quite specific virological techniques.
The lesion is caused by an enterovirus that contains RNA. It enters the body through the stomach, where it multiplies, and then spreads throughout the body through the blood. The virus penetrates epithelial cells, and then into muscles and quite often affects the nervous system. Therefore, stool, swabs from the organs of vision and a swab from the throat for enterovirus are taken for research. To confirm that a patient has an infection, it is often necessary to use various techniques.
If you suspect the presence of enterovirus in the body, it is necessary to undergo diagnostics as quickly as possible.
We have selected useful articles on the topic
Methods for treating Staphylococcus aureus and restoring the intestines
01.05.2019
What can a nursing mother eat if her newborn has colic?
20.06.2019
How to eat for patients with intestinal diverticulosis
10.05.2019
It is at the initial stage of development of pathology that the concentration of viruses is greatest. Enteroviruses are found in feces for 14 days after infection, in the nasopharynx - no more than seven. After an illness, viruses remain in a person’s body for up to 15 months.
Read also: what rules must be followed when infected with enterovirus infection.
If enterovirus is suspected, it is very important to perform tests
When performing tests for enterovirus infection, various research methods are used, each of which is focused on achieving one goal:
- The focus of serological methods is to identify antibodies to infection produced by the body in response to infection. Early markers are IgA, IgM.
- Virological techniques are aimed at isolating enterovirus from taken material by growing samples on sensitive cultures. Immunohistochemical methods include available studies such as immunoperoxidase and immunofluorescence analyses.
- When performing molecular biological studies, the genetic material of the enterovirus itself is determined.
Dehydration due to norovirus infection
Norovirus infection (symptoms and treatment require the attention of a pediatrician or therapist) without timely treatment entails serious complications and consequences.
We are talking about dehydration of the body. Severe vomiting and diarrhea lead to the removal of large amounts of fluid, which is difficult to replenish.
Dehydration is a pathological condition in which there is less fluid in the human body compared to physiological norms.
The patient experiences the following accompanying symptoms:
- a sharp decrease in the level of urine excreted;
- urine becomes dark yellow;
- a person complains of general weakness in the body;
- the patient is thirsty;
- blood pressure decreases;
- heart pulse weakens;
- the person loses consciousness.
For the patient's body, fluid loss of 20-25% is a fatal norm. A therapist will help restore the water-salt balance. The therapist will prescribe special solutions (Oralit, Gastrolit), which are infused through an intravenous drip.
At home, folk recipes will help restore fluid levels in a person’s body. It is necessary to add 2 tbsp to 500 ml of boiled warm water. l. sugar, salt and ¼ tsp. soda
It is also recommended to drink unsweetened compote made from dried fruits, tea without added sugar, rosehip or blueberry decoction. If you experience severe vomiting, you need to replenish your fluid supply in small portions.
How else can you help a patient?
With norovirus, it is important to maintain electrolyte balance in the body and restore the patient’s strength. A strong decoction of rice with raisins is suitable for this. Pour two tablespoons of pure rice into a liter of water and bring to a boil. Add a tablespoon of washed raisins and simmer over low heat for about half an hour.
The broth is cooled and given to the patient half a glass every 20-30 minutes. This healing drink contains many minerals and vitamins; in addition, the rice broth has enveloping properties and gently relieves irritation from the stomach.
Diagnostics
A comprehensive examination for norovirus infection is necessary for everyone, adults and children. When the first clinical signs appear, it is important to consult a physician or pediatrician. If necessary, you will need to consult other specialized doctors (nephrologist, ophthalmologist, cardiologist, otolaryngologist).
To diagnose norovirus infection, patients are prescribed the following test measures:
| Name | Description |
| General blood and urine analysis | Results will show neutrophilia, lymphocytosis, and in some situations an accelerated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). |
| Serological studies | Tests will help determine the pathogen, type and stage of development of the infectious disease. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Research will help determine the type of pathogens causing pathological processes. |
| Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) | The most informative research method that allows you to confirm the development of norovirus infection. |
| Instrumental diagnostic methods |
|
The danger of norovirus infection is that differential diagnosis is necessary. Many diseases cause similar clinical signs and disorders in the human body. We are talking about fungal infections of the throat, meningitis, rubella, measles, scarlet fever, enteritis, pancreatitis.
Pathogenesis
The pathogenesis of norovirus infection has not been sufficiently studied, partly due to the difficulty of animal modeling. When norovirus enters the digestive system, it disrupts gastric motility and shows its affinity for the cells of the small intestine, especially the duodenum and jejunum. Viral particles can also be found in the spleen, ileum, mesenteric lymph nodes, and large intestine.
Replication of noroviruses leads to destruction of the intestinal epithelium, atrophy of intestinal villi, hypertrophic changes in glands, and impaired absorption of carbohydrates. Local inflammatory reactions depend on the preservation of mucosal immunity; the systemic immune response and the production of specific antibodies occur no earlier than 96 hours from the moment the pathogen enters the body.
Principles of disease treatment
Norovirus infection (symptoms and treatment are determined by the general practitioner, taking into account the patient’s condition) is eliminated using complex methods. Patients are prescribed symptomatic therapy using medications.
Additionally, it is recommended to adhere to a strict diet. If there is no individual sensitivity or medical contraindications, you can use recipes from witch doctors and healers.
Medicines are selected by a general practitioner or pediatrician. The specialist takes into account the patient’s condition and selects the most effective means based on the results of comprehensive diagnostics:
| Group of drugs | Name | Application |
| Antiemetics | Metoclopramide, Ondansetron | The medicine is taken orally 30 minutes before meals with a small amount of water. The adult dosage is 10-30 mg per day. Children are prescribed, taking into account body weight, 0.1-0.15 mg/kg 1 time per day. The course of treatment lasts a maximum of 5 days. |
| Medicines to restore water-salt balance | Regidron, Trisol | The medicine is taken orally, the powder is first diluted in cold boiled water. The average daily dosage for children and adults depends on weight; the doctor prescribes 80-100 mg/kg per day until the water and electrolyte balance is completely restored. |
| Sorbents | Atoxil, Smecta | The daily dosage for adults is 12-24 g. It is recommended that children be given the medicine from the age of 1 year. The dosage is 150-200 mg/kg. The daily dosage is divided into 3-4 doses. The course of treatment depends on the severity of the disease, in most cases it lasts 7-10 days. |
| Enzymes | Mezim, Festal | The medicine is taken orally, without chewing, with a sufficient amount of water. The adult dosage is 1-2 tablets before meals. Children are prescribed the medicine from the age of 3 on an individual basis. |
| Antispasmodics | No-Shpa, Spazmalgon | The adult dosage is 1-2 tablets 3 times a day. It is recommended to give children 20-40 mg 2 times a day, taking into account the child’s age and body condition. |
| Antipyretic medications | Ibuprofen, Paracetamol | The recommended dosage for adults is 400-600 mg 2-3 times a day. Children are prescribed 20 mg/kg of medication per day; the dose must be divided into several doses. |
| Immunomodulators | Viferon, Arbidol | The medicine is administered rectally. Adults and children are recommended to use 1 suppository 2 times a day every 12 hours. The course of treatment lasts 5 days. |
| Antihistamines | Suprastin, Tavegil | For adults, the drug is prescribed 1 tablet 3-4 times a day. The children's dosage is ½ tablet 2-3 times a day. It is recommended to take the medicine orally after meals. |
| Vasoconstrictor drops | Nazivin, Nazol | Children and adults are recommended to drop 1-2 drops into each nasal passage 2-3 times a day. The treatment regimen depends on the person's age. The course of therapy lasts 3-5 days. |
In severe situations, dehydration therapy is carried out, saline solution is infused intravenously through a dropper.
In the complex therapy of norovirus infection, the use of folk remedies is allowed if there are no serious contraindications or individual sensitivity to herbs. It is important to discuss treatment with your doctor to prevent an allergic reaction or possible complications.
Effective recipes from healers and healers for norovirus infection:
| Name | Recipe | Application |
| Rice congee | Boil the rice in clean water, strain and cool the remaining water. | Rice water effectively and quickly copes with intestinal disorders. It is recommended to consume it warm, fresh 3-4 times a day, 0.5 tbsp. The folk remedy helps restore fluid levels in the human body, binds and removes toxic substances. |
| Mint and calendula | Dried plant leaves are mixed 1 tbsp. l. Pour in hot water (1 tbsp) and leave for 30 minutes. The cooled broth is filtered and consumed internally. | Patients with norovirus infection are recommended to drink a decoction of mint and calendula 3 times a day, 1 tbsp. Herbs help reduce inflammation. |
| Compote based on viburnum | Pour 250 g of berries with hot water (1 l). Place the resulting mixture on the fire and cook for another 10 minutes. Cool the finished broth, strain and add 3 tbsp. l. natural honey. | It is recommended to drink compote 3 times a day, 0.5 tbsp. Viburnum increases the body's defenses, its resistance to pathogenic bacteria, and also reduces high body temperature. |
| Pharmaceutical chamomile | Brew 1 tbsp. dry raw materials 1 tbsp. hot water. Leave for 30 minutes, strain and take orally. | Adults are recommended to take 5 tbsp of chamomile decoction. l. 2-3 times a day. The children's dosage is 2 tbsp. l. 3 times a day. |
To rinse the mouth, it is recommended to use a decoction of oak bark, chamomile or sage. They have bactericidal and anti-inflammatory effects.
Specifics of PCR research
PCR analysis of feces identifies pathogens of infectious diseases and differentiates their types at the genetic and molecular level. The study evaluates DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) macromolecules from bacteria, protozoan parasites, worms, or RNA (ribonucleic acid) viruses. A small fragment of the pathogen found in excrement is sufficient for identification.
The tasks of molecular diagnostics include:
- detection of infectious agent;
- identification of the type of microorganism (virus, bacterium, protozoa, etc.);
- differentiation of type, genus, family, etc.;
- determination of treatment tactics in accordance with the diagnosed disease.
A sample of biomaterial is placed in a reactor (amplifier), and the reaction mixture is added. With a successive change in temperature, the hydrogen chains of deoxyribonucleic acid are broken, and complexes of the matrix with primers - short genetic fragments - are formed.
The reagents complete the template chain and, during the amplification reaction, form multiple copies of the pathogen. With a sufficient number of copies, the amplifier gives a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the detected pathogen.
RNA and DNA macromolecules are carriers of unique information characteristic of a particular species, therefore the accuracy of PCR diagnostic results is as close to 100% as possible.
What drugs should not be taken for enteroviral infections
If you have a norovirus infection, you should absolutely not take antibacterial drugs. With viruses, the active components of drugs are completely useless. But antibacterial agents have a detrimental effect on beneficial microflora. The patient's condition will worsen, leading to serious complications.
Medicines should be selected strictly by a pediatrician or therapist. It will take into account the human condition, the development of norovirus infection and the individual characteristics of the human body.
Preventive measures
There is still no vaccine against norovirus, so the only effective way to protect yourself from infection is prevention. Of course, any preventive measures will be less time-consuming and costly than therapy. Prevention of Norovir will be reduced to compliance with the following measures:
- consumption of boiled water;
- heat treatment of products;
- compliance with personal hygiene rules;
- daily ventilation of residential premises;
- maintaining the necessary sanitary conditions in the home;
- washing vegetables and fruits with soap and then treating them with boiling water;
- air disinfection using a bactericidal irradiator in crowded places;
- daily wet cleaning and disinfection in places where there are sick people;
- treatment of all surfaces with which the patient might come into contact;
- boiling dishes and disinfecting personal belongings of the sick person.
It is important not to forget that any interaction with sick people can lead to infection of healthy citizens. To avoid this, you should protect yourself from contact with sick people, and also treat those areas of the body and clothing that could come into contact with contaminated biomaterial.
Andrey Yurievich
Diet
Treatment of norovirus infection requires the patient to follow a strict diet. Proper nutrition will not only eliminate negative symptoms, but also reduce the burden on the gastrointestinal tract.
| Recommended Products | Prohibited Products |
|
|
In case of inflammation of the mucous membrane of the gastrointestinal tract, dietary nutrition should be as gentle as possible in order to prevent possible irritation. It is also important to prevent dehydration of the body; you must drink at least 2 liters of clean warm water in small portions every day (boiled or still mineral water, green or herbal tea).
In most cases, norovirus infection occurs without complications. Symptoms disappear on their own after 2-3 days. A person or child will need inpatient treatment if the signs of infection progress and severe dehydration occurs.
You cannot risk your health; you should immediately call a general practitioner or pediatrician. Otherwise, there is a high probability of serious complications.
How long to wait for answers and decryption
Patients are interested in the speed of analysis, waiting for an answer, and the longevity of laboratory interpretation. Children's clinics with infectious diseases departments are often not equipped with materials for testing. But you can identify the problem in a day. It is recommended to buy a test to recognize viral pathogens.
Depending on the workload, the medical staff will find out the reasons and the explanation of tests for infectious agents. Virologists use a table with a set of codes and ciphers. Treatment is prescribed.
Characteristics of the virus
Nora virus is a representative of RNA viruses from the Caliciviridae family. According to various sources, from 5 to 7 genogroups are distinguished. Of which, only G1 and norovirus G II, sometimes G IV, are the culprits of outbreaks of intestinal infections and are prone to widespread distribution, accounting for up to 90% of cases. The genogroups of viruses are very variable and are divided into genotypes.
Representatives of genogroups III and V are found only in animals. Norovirus type 2 is the most common group and is the main causative agent of outbreaks of intestinal infections worldwide. A distinctive feature of the Norfolk virus is its high contagiousness (infectiousness). Since the early nineties of the last century, norovirus 2 genogroups have been causing planetary epidemics of gastroenteritis.
Norfolk viruses are very viable in the environment - up to 30 days. Not sensitive to freezing, heating , UV radiation, and some disinfectants - ethanol and ether. Therefore, cleaning with detergents and alcohol-containing products will not clear the room of the pest. They die when heated above 60 C˚ and under the influence of chlorine-containing substances, such as chlorhexidine.
Susceptibility to norovirus enteritis is high. Virologists have proven that people with blood group I are more susceptible to infection. But people with groups III–IV are luckier; they get sick much less often.