Salmonellosis in children is often diagnosed. The peak incidence occurs in the summer-autumn period, especially if the seasons are hot. This disease is very serious, so it is advisable to start treating it immediately after the first symptoms appear.
What is salmonellosis
Salmonellosis is an intestinal infection caused by Salmonella bacteria. During its life, the pathogen releases toxic substances, poisoning the body and causing severe dehydration. In children, the disease progresses rapidly and in severe form.
Salmonella is not susceptible to some types of antibiotics and easily tolerates temperature changes. Survives even when frozen. The bacteria can be destroyed by thorough disinfection and boiling.
How dangerous is the disease in childhood?
Salmonellosis, as already mentioned, is a quite serious disease and often leads to dangerous complications:
- the baby may experience purulent complications;
- swelling of the lungs and brain often occurs;
- the child develops kidney failure;
- manifestation of convulsive syndrome;
- leads to reactive arthritis;
- infectious-toxic shock.
In this case, the probability of death is quite high.
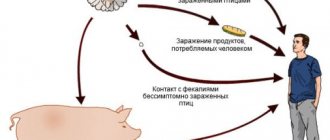
Routes of infection
Salmonella can live and multiply in humans and animals. It also survives outside the host’s body for more than a year.
Therefore, infection can occur in several ways:
- From improper processing of products. Unwashed chicken eggs, uncooked meat. The bacterium can also live in raw water. Eating it or washing fruits in it can provoke the development of the disease.
- Salmonella can enter the body through contact with a sick person (person or animal), through a handshake, an object, or by air. Adults who have been in contact with infected people can also be carriers. Basically, this could be medical staff in a kindergarten or school, if hygiene measures are not observed.
- The infection is also transmitted in utero from mother to child or through breast milk during feeding.
Salmonella infection most often occurs before the age of 5 years. When children do not yet constantly observe the rules of hygiene, they communicate closely with each other and take dirty objects and fingers into their mouths.
Preventive actions
To prevent salmonella infection, certain rules must be followed.
. In addition, you need to avoid places where poultry or wild birds gather. Meat products are prepared with careful adherence to cooking technology and do not eat raw chicken eggs.
The latent period of the disease does not last long, and then salmonellosis manifests itself in full. The disease must be treated only under the supervision of an infectious disease specialist, otherwise you can develop serious illnesses that will have to be treated for more than one month. If there is a person with salmonellosis in the house, then hygiene rules must be observed especially strictly.
General symptoms of salmonellosis in children
Salmonellosis in children, the symptoms of which differ from the type of disease and will be discussed below, has characteristic clinical features that can be used to distinguish the virus from an upset stomach. Depending on the method of infection, the disease may appear after 3 hours (the bacteria came from food) and after 4 days (with contact infection).
Common symptoms of salmonella:
- symptoms appear immediately in an acute form, without increasing;
- if there is a temperature, it reaches up to 39 degrees and stays at this level for at least 5 days. Symptoms are not always accompanied by fever;
- Loose stools occur immediately after eating or drinking liquid. It has a green tint, a strong unpleasant odor and foams;
- constant nausea accompanied by vomiting;
- severe pain in the abdomen and rumbling, regardless of the intake of water or food;
- bloating and increased passage of gases;
- Appetite decreases sharply and disappears over time. Infants experience frequent regurgitation of milk/formula;
- lethargy, drowsiness, apathy;
- severe dehydration, accompanied by dry skin. There is virtually no lacrimation. Urine output may disappear. In children under one year of age, the fontanelle sinks.
When infected, powerful poisoning of the entire body immediately occurs through the intestines with waste products of bacteria. The toxin produced by the pathogen is very strong.
It can kill other salmonella. Thus, they have a struggle for survival. Due to severe dehydration, you should immediately call a pediatrician and begin treatment. Children under 5 years of age are treated as inpatients.
Medicines
The main list of medications prescribed for salmonellosis. Table
| Name | Dosage | Contraindications | Indications |
| Loperamide is an antidiarrheal agent | Allowed for children from 4 years of age in tablets From 6 years – in capsules Take 1 capsule or tablet after each trip to the toilet. Take until diarrhea stops. | Lactase deficiency Individual intolerance to the components of the drug Children under 4 years old | Treatment of diarrhea of various origins: infectious, allergic, drug-induced. |
| Ibuprofen | To reduce the temperature in children, a suspension is used. 6-12 months – 50 mg 3-4 times a day 1–3 years – 100 mg 3 times a day 4-6 years – 150 mg 3 times a day 7-9 years – 200 mg 3 times a day 10-12 years – 300 mg 3 times a day | Peptic ulcer Diseases of the liver, kidneys, heart | Antipyretic and analgesic. High body temperature Headache, toothache |
| Enterosgel | Children under one year old – 6 times a day before each feeding ½ teaspoon 3-5 years – ½ teaspoon 3 times a day 40 minutes before meals. This pause must be observed until the next meal. 5-14 years – 1 dessert spoon 3 times a day | Acute intestinal obstruction Sweet enterosgel is contraindicated: Children under one year old. Appointments are only possible with a doctor’s prescription under the strict supervision of medical personnel. | Diarrhea of any nature Intestinal disorders, including those caused by intestinal infections Allergy |
| Smecta | Children over 4 weeks old Children under one year old - 1 sachet diluted with 100 ml of liquid. For infants, the drug is dissolved in 50 ml of expressed breast milk or in a mixture Children from 1 year to 2 years – 2 sachets of 200 ml per day. The drug dissolves in any liquid whose temperature is slightly above room temperature Children over 2 years old – 3 packets per 300 ml of liquid | Intestinal obstruction Individual intolerance to the components of the drug Impaired intestinal absorption function Chronic constipation | Diarrhea of drug or allergic origin Infectious diarrhea Discomfort in the intestines Irritable bowel syndrome |
| Festal (as an option, you can take Mezim or Creon) | Not for use in children under 3 years of age. The dose is prescribed individually by the attending physician. The drug can be pre-diluted in liquid Mezim can be used from one year onwards. | Hepatitis Increased bilirubin | It is an enzymatic preparation for any digestive problems. Congestion in the intestines. |
| Linex (analogs of the drug Oactobacterin, Acipol) | Children from 0 to 2 years – 1 capsule 3 times a day. The contents of the capsule are diluted in any liquid. Children from 2 to 12 years old - 2 capsules 3 times a day. | Individual intolerance to components Dairy intolerance Children should only be prescribed by a doctor | Dysbacteriosis Restoration of the gastrointestinal tract after taking antibiotics |
| Regidron (as an option it is possible to use Oralit) | For infants and children under 6-7 years of age, the solution is given 5-10 ml every 7-10 minutes. It is better to give the solution chilled | Unconscious children Kidney failure | Nausea combined with vomiting and diarrhea Prevention of dehydration |
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Amosin POWDER FOR PREPARATION OF SUSPENSION FOR ORAL ADMINISTRATION: instructions, description PharmPrice
Antibiotics are not the main weapon against tenacious salmonella. There are cases when taking antibiotics only aggravates the situation, since due to certain processes the removal of harmful parasites from the child’s body is delayed.
Antibiotics are usually prescribed for the treatment of children in the first two to three months of life, or if the Salmonella bacteria has spread beyond the intestines.
Gastrointestinal toxic infection
Gastrointestinal salmonellosis affects the digestive tract. When the symptoms are not pronounced, the disease can be confused with gastritis. The disease can occur in 3 forms.
| Symptoms | Gastric | Gastroenteric | Gastroenterocolitic |
| Temperature | Maintains 38 degrees and is not easily knocked down | On the 2nd day from the moment of the first symptoms it rises to 39 degrees | Absent or reaches 37.5 degrees |
| Pain | Strong and sharp. Localized in the navel or stomach area | Mainly in the supra-umbilical region | Localized in the colon area |
| Nausea, vomiting | Nausea and vomiting occur periodically | Constant nausea accompanied by profuse vomiting | Periodic attacks of nausea with vomiting |
| Chair | Liquid or gruel, green in color, contains undigested food. There may be mucus present. Characterized by a sour odor | On the 3rd day, stool becomes less frequent, mucus appears in it, and blood may be present. Sometimes there is a false urge to go to the toilet. It has a yellow-brown or dark green tint. The consistency of the stool is close to rice water | The stool is watery and green with food particles. Frequent false urges |
| Dehydration | Observed, but not in an acute form | In acute form | Not strong |
| Acuteness of the course | Symptoms appear 2-3 hours after infection | Symptoms intensify on the 3rd day, initially similar to the gastric form | Symptoms are pronounced from the onset |
| Abdominal condition | There is bloating and rumbling | The colon is painful on palpation | It is impossible to touch the rectal area |
| General state | Severe weakness | Weakness and malaise | Satisfactory |
| Language | — | Covered with a thick coating and dry, because of this there is an unpleasant odor from the mouth | — |
| Flatulence | — | Present, but not clearly expressed | — |
| Intoxication | Pronounced | Moderately expressed | Weakly expressed |
Depending on the severity of the disease, symptoms may increase or decrease. It is important not to confuse this form of the disease with gastritis and dysentery, since the treatment of the diseases is completely different. The difference is especially noticeable in the use of antibiotics.
Incubation period
The disease does not make itself felt at first and is asymptomatic. The incubation period can last up to 7 days. It all depends on the state of the immune system, the method of infection and age.
In adults, the duration of the latent period ranges from 2 hours to 6–7 days. In people with poor health due to radiation or severe pathology, the first symptoms appear within a couple of hours.
In case of mass infection (alimentary route of infection), the incubation period lasts a day, and in case of contact-household infection - 5 days. Most pathogenic microorganisms die before reaching the intestines due to the action of enzymes and gastric juice. But this does not mean that the disease will not develop. The occurrence of unpleasant symptoms (fever, vomiting, epigastric discomfort) after the death of Salmonella is provoked by toxins that have managed to enter the bloodstream.
The duration of the incubation period is determined by the concentration of the pathogen in the body.
In children, the disease does not last as long as it does in adults. The first symptoms appear one and a half to two hours after penetration of the pathogen. Sometimes the incubation period is 4 days. Salmonellosis in young patients, due to physiological characteristics and low acidity in the stomach, is difficult. A larger number of microorganisms remain viable in the baby’s digestive system.
Stages
The incubation period for salmonellosis is divided into 3 conventional stages:
- Hidden course of pathology or adaptive phase. After entering the body, the bacterium penetrates into target cells. This stage is accompanied by the death of some pathogens and a decrease in the concentration of the pathogen.
- Reproduction phase. When salmonella enters a favorable environment, it increases its population.
- Dissemination. The last stage of the incubation period. It begins after reaching a certain concentration of the pathogen. Salmonella spreads throughout all tissues and systems.
What happens in the human body
The pathogen, after entering an environment favorable for life, actively multiplies throughout the day. The first manifestations of the disease occur after the end of the incubation period. It is different for everyone (from several hours to 7 days). Bacteria that do not die in an acidic environment penetrate the intestines and release toxins. There is indigestion, damage to the nervous system and weakening of vascular tone.
As salmonellosis progresses, the pathogen, along with the bloodstream, enters the urinary system, lymph nodes, and spleen. A strong immune system destroys the bacterium, and if it is weakened, new foci of inflammation form and a typhus-like or septic form of the disease occurs.
Typhoid-like type
Salmonellosis in children (symptoms for the typhus-like type are clearly and acutely expressed only at the beginning of the period) in this form are often confused with typhus. Children under 3 years of age are most often susceptible to this disease. If the diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, the disease can be fatal. Symptoms during the course of the disease occur in waves, with an increase and attenuation.
Characteristic features:
- loose, watery stools. May bother you from 4 to 7 times per day;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating with flatulence;
- poisoning of the body with toxins is not clearly expressed;
- general weakness is accompanied by headaches;
- constant dryness in the oral cavity, which provokes an increase in the size of the tongue;
- blood vessels burst on the surface of the skin, causing pinpoint red rashes;
- the temperature jumps from 37 degrees to 39;
- the liver and spleen increase in size.
Nausea and vomiting are present only for the first 3 days, then they stop. When the temperature is high, the patient develops a fever. You cannot start treatment on your own; you must urgently call an ambulance, since even an experienced infectious disease specialist cannot always immediately recognize the disease.
In newborns and infants
For this category of patients, there are both general symptoms and features that are most pronounced in young children due to general intoxication of the body. In this case, there may not be an increase in body temperature. In infants, malnutrition can be observed; such babies lag behind in development and do not gain weight well. In the vast majority of cases, they behave restlessly. This can be expressed both in frequent manifestations of regurgitation and poor sleep. In this case, bloating is observed. Cold hands and feet may also be one of the symptoms. The presence of dehydration in a child’s body can be judged by such characteristic signs as dry skin, mucous membranes, tongue and other signs.
Septic form
The septic type is the most dangerous, as it occurs in the most severe form and in children under 1 year of age. The body is not able to fight the disease on its own, since there is no immunity yet.
Parents should start sounding the alarm if the following symptoms appear:
- the temperature immediately rises to 40 degrees and can drop or drop by only 1-1.5 degrees;
- constant nausea with vomiting;
- loose stools with mucus and streaks of blood;
- the child is in a feverish state with increased sweating;
- the liver and spleen increase in size, jaundice may appear;
- blood pressure decreases and heart rate increases;
- the child is not calm, there is no normal sleep.
Due to the severity of the disease, brain damage occurs. For this reason, it is urgent to begin to stop the disease before it causes serious side effects or death. After recovery, the bacteria is present in the baby’s stool for 30 days. If the infection is observed in the stool in the future, then the disease has become chronic.
The causative agent of the disease
Russian scientists have worked hard - they have compiled a list of names of bacteria that are more often found in the Russian Federation and cause salmonellosis in a child. The bacilli belong to the genus Salmonella, from which the specific name of the disease comes. Based on the structural characteristics of DNA, doctors distinguish 2 types.
Pathogens are limited to a small number of serovars that are rarely encountered in practice. The number of serotypes is large - more than 2500. 10-15 are of practical importance for doctors. These species account for 90% of cases. The optimal environment for reproduction is moderately alkaline (pH from 7.2 to 7.4), observed in the duodenum, at a temperature of 37 degrees Celsius.
What complications can there be?
Salmonellosis in children most often occurs with pronounced symptoms.
If you do not go to the hospital in a timely manner or with improper treatment, the disease can leave behind serious complications:
- high temperature and toxins cause swelling of the brain and lungs;
- the functioning of the kidneys and liver is impaired;
- suppuration of the gastrointestinal tract;
- reactive arthritis;
- chronic dysbacteriosis;
- transition to a chronic form;
- death.
When the disease enters the chronic stage, the child may remain a spreader of the infection, so he is prohibited from attending kindergarten and then school. Infectious diseases after salmonellosis occur in severe forms and are difficult to treat.
Salmonellosis - consequences and complications
Even after the main symptoms of the disease disappear, it is impossible to stop treatment until the entire course is completed. Salmonella in a child can cause complications. In the first place are disorders in the functioning of the digestive system. Infants may suffer from bloating and colic. If the baby was treated with antibiotics, dysbiosis may develop while taking them, which sometimes manifests itself as constipation, followed by diarrhea.
Some children are left with a food allergy – skin or respiratory – as a “memento” after salmonellosis. This complication manifests itself as dry skin, redness, and severe itching. Allergy symptoms usually appear after consuming a product that irritates the immune system. The most “popular” allergens:
- citrus;
- chocolate;
- fish;
- eggs;
- chicken.
Diagnostic features
It is impossible to determine 100% the presence of bacteria in the body through examination. If salmonellosis is suspected, the baby is immediately placed in a separate room in the infectious diseases department. After this, diagnostics begin.
Types of examinations for salmonellosis:
- Tank culture of feces and vomit to identify the presence of the pathogen. The process can take up to 10 days. When salmonella is detected, its type is determined and which antibiotics kill the bacteria.
- Analysis of stool for the presence of dysbacteriosis, coprogram. It checks how active the enzymes in the digestive tract are.
- General blood analysis. It is taken several times throughout the illness. To determine the effectiveness of treatment.
- Express analysis. This is done to quickly determine the presence of salmonella, since treatment must be provided urgently and there is no way to wait 10 days. Before receiving the culture tank analysis, standard therapy is carried out to improve the patient’s condition.
If infection of several organs is suspected, additional tests (urine, bile, intestinal and stomach lavage) may be prescribed. Stool cultures are taken after recovery until the pathogen has completely disappeared from it.
The big picture
Children's salmonellosis is severe and long-lasting. Due to the weakness of the immune system, intoxication is pronounced, and epithelial lesions are deep. From time to time, bacteremia develops (bacillus in the blood), reaching toxic-dystrophic, septic forms. In newborns and infants it goes away when the child reaches three years of age. A relatively mild course dominates here, up to the development of carriage (without symptoms).
There is no incubation period. The first signs of salmonellosis in children are observed within a few hours after contact with the infection. The gastrointestinal form manifests itself more often in children - up to 98% of cases. Other – falls on a more dangerous generalized course with general poisoning of the body. In 80% of cases there will be signs of acute intestinal poisoning. In the subacute version, 1-2 signs are recorded (colic and intoxication), and after a couple of days symptoms of dyspepsia appear. Intoxication provokes the manifestation of a number of nonspecific symptoms:
- Fever.
- Sweat.
- Chills.
- Prostration.
- Physical inactivity.
- Decreased appetite.
Dyspepsia covers a spectrum of symptoms related to the gastrointestinal tract. In two thirds of cases the liver becomes enlarged. The disease is often accompanied by mucosal inflammation syndromes - gastritis, enteritis, enterocolitis, hemocolitis. The disease lasts from several days to weeks. Clinical signs are not used for classification and diagnosis.
Individuals with a deficient immune system suffer greatly for obvious reasons.
Descriptive picture by severity
There is no classification based on clinical signs. Doctors have long noticed the key points. The severity is determined by changes in the blood and signs present in the stool.
Light
This share of cases in epidemics accounts for up to 40% of those registered. The disease begins with a fever with a temperature of up to 38 degrees Celsius. Intoxication is mild, there is mild pain in the absence of palpation. The stool is loose and infrequent (up to 5 times a day).
Treatment
At the first symptoms of salmonellosis, you should go to the hospital and get tested to clarify the disease. Depending on the type and form of the disease, treatment is prescribed. For children under one year old and in severe forms of the disease, the infected baby is admitted to the hospital.
When treating salmonellosis, the following therapy is mandatory:
- medications for dehydration and drinking plenty of fluids (sweet water, fruit drinks, compotes);
- dietary menu;
- means that restore the functioning of the digestive tract;
- At high temperatures, antipyretics are given. If vomiting and diarrhea are severe, the drugs are administered intramuscularly;
- Bed rest is required from the 1st week.
Antibiotics are prescribed for severe forms of the disease, for children under 3 months of age, and for the presence of blood clots in the stool. In other cases, reception is undesirable. Since the medicine slows down the recovery process, and many types of antibiotics are powerless against salmonella.
Treatment of children over 1 year of age
Why is salmonellosis dangerous in children? This is the first question that arises for parents whose baby is faced with this disease. As a rule, if you consult a doctor in a timely manner, the disease does not cause any complications. However, if a baby whose immunity is not strong enough (for example, an infant) encounters it, or the treatment was not prompt enough, the consequences can be serious.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Mice in the apartment: where to come from and what to do
Treatment of salmonellosis. We have already mentioned that the course of the disease is accompanied by vomiting, diarrhea and other unpleasant symptoms. However, even after recovery, the child faces a number of complications:
- prolonged dehydration leads to interruptions in the functioning of the renal channels (renal failure) and contributes to the accumulation of nitrogenous waste in the patient’s blood;
- bacterial discharge lasting more than 3 months after recovery is a clear sign that the disease has had too strong an effect on the body, and the child now requires treatment for chronic salmonellosis;
- prolonged intoxication negatively affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system. In particularly advanced cases, it causes cerebral edema;
- the consequences of salmonellosis can also be expressed in inflammation of various internal organs, since salmonella spreads throughout the body through the bloodstream;
- In young patients suffering from chronic diseases, relapses caused by immunodeficiency are common.
However, we should not forget that in addition to these, the disease also has social consequences. For example, if there is a suspicion that a child is a bacteria carrier, entry into public places is closed to him. And if in the case of an amusement park or swimming pool this does not cause any particular harm, then a ban on visiting a school or kindergarten may cause a lag in the program and a prejudiced attitude.
Salmonellosis in children is treated in an infectious diseases hospital. Treatment includes bed rest, diet and measures aimed at eliminating the pathogen, as well as the changes that it causes.
Self-medication with antibiotics at home is unacceptable. Antibacterial drugs are indicated only for severe forms of salmonellosis in children (levomecitin or analogues are prescribed to children over 3 years of age under the strict supervision of a doctor).
Sorbents are used - natural or synthetic substances that are capable of absorbing and removing microorganisms, toxins, and other waste products from the intestines.
Diet is of great importance in the treatment of salmonellosis in children. It is advisable to limit the amount of food for the first 3–5 days. Breast milk is used to feed children of the first year. Children over one year old need easily digestible pureed food (soups, boiled rice, pureed vegetables) with the addition of steamed meat, fish (from 3-4 days) and limiting fatty foods.
For the entire duration of the illness, foods that increase fermentation and intestinal motility (rye bread, whole milk, raw vegetables, sour berries and fruits), as well as pickles and spices are excluded from the diet.
Treatment of salmonellosis. What can a child eat with salmonellosis? This issue is no less important than the others discussed in this article. Proper nutritional correction contributes not only to a speedy recovery, but also to the restoration of weakened immunity.
If the toddler’s age has already exceeded 4 months, and he himself is fed by artificial feeding, then for the first 1-2 weeks his menu includes: 10% rice and/or buckwheat porridge brewed in water; vegetable puree.
Subsequently, the doctor analyzes the combined results of treatment and diet, after which he makes a verdict on how effective the diet is and adjusts the course (as usual, towards expanding the range of foods allowed for consumption).
The diet of older children who fell ill just the other day consists of thoroughly pureed, easily digestible food that has undergone mandatory heat treatment. These can be soups, various vegetable dishes, boiled rice, etc. Meat and fish are allowed to be included in the menu, but only on the condition that they were steamed.
The following are prohibited: fermented milk products that enhance peristalsis (wave-like contraction of the walls) of the intestines; flour products made from rye; any sweets and pickles; vegetables and fruits served raw; berries and various spices.
- Hospitalization in case of severe disease. A pediatrician home call is required. Self-medication in this situation is unacceptable.
- Bed rest. In mild cases - 1 week, in moderate and severe cases - bed rest can last several weeks.
- Gastric lavage with glucose-saline solution.
- Droppers with sorbents after restoration of water-salt balance.
- Therapeutic diet - portions will be reduced by almost half, and it will last longer than in children under one year old.
- Enzymatic treatment.
- Prescription of drugs with immunorestorative action.
- In difficult cases, antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
- If the disease is accompanied by prolonged diarrhea, antidiarrheal drugs are prescribed.
- As accompanying remedies, children over 3 years of age are allowed to use herbal decoctions (mint, St. John's wort). They are designed to improve intestinal function after the acute phase of the disease.
- Bacteriophages and probiotics.
The pediatrician claims that the disease goes away on its own when the body begins to produce antibodies to the toxin that caused the unpleasant illness. To help your child’s body as much as possible, you need to:
- Avoid dehydration. For this purpose, special means are used that will maintain the water-salt balance. If you refuse to drink, an IV will be placed in the hospital.
- Monitor your baby's body temperature and take antipyretic medications at high temperatures.
- Follow a diet.
- Take lactobacilli.
Dietary recommendations
Salmonellosis in children (symptoms, even mild ones, mean adherence to a special diet) in the first days is treated by fasting. It is enough for the child to drink liquids. Gradually, you can begin to introduce dietary foods. This diet is maintained for at least 1 month.
Allowed menu:
- porridge cooked in water;
- soups only with vegetable broth;
- boiled lean meat and fish;
- cottage cheese and low fat cheese;
- jelly, compotes;
- boiled vegetables and fruits.
In the first week, food should be in crushed form. Use in small portions, every 3 hours, warm. If the child does not eat enough, supplement with jelly or compote.
During the diet it is prohibited:
- overeat;
- fatty and fried foods;
- use of spices;
- fatty dairy products;
- dishes prepared by smoking or pickling;
- roughage foods high in fiber;
- carbonated drinks and chocolate.
After complete recovery, regular food is introduced gradually. It is advisable to exclude semi-finished products from the diet for up to 4 months. Fried foods and sweets are introduced last, no earlier than after 2 months.
How to correct dehydration
First of all, the child needs to restore the water-salt balance. For this purpose, children are given solutions from Rehydron or Oralite. You need to give from 2.5 to 10 ml every 7-10 minutes. Until the daily dose prescribed by the infectious disease specialist is drunk.
If salmonellosis is suspected in children, you can prepare a rehydration solution from salt, soda and sugar!
When the medicine comes back out due to vomiting, glucose and saline solution are prescribed intravenously. The procedure is performed in a hospital. Water balance is restored on the 4th day.
The main causes of salmonellosis infection
Treatment of salmonellosis. The causative agents of the disease reproduce well in foods (milk, meat, eggs). They are practically not affected by heat treatment of products. For example, after smoking and salting, bacteria will not experience any discomfort, but freezing, on the contrary, will increase their lifespan in products.
There are an incredible number of causes of salmonellosis and, unfortunately, this disease often occurs in young children, because their body is still poorly adapted to life, and the immune system simply cannot fully resist the bacteria that have already gotten inside. It is also quite dangerous, so all parents should be aware of the existing threat and know how to eliminate the disease with minimal harm to the child. The most common causes of salmonellosis in children:
- unwashed hands, berries, fruits and vegetables, and other food products;
- pets, they themselves may not be sick, but they can be sources or carriers of bacteria (chinchillas, rats, hamsters, turtles);
- dust, earth, sand, bird droppings, often found on sites;
- street animals that arouse interest among the little ones;
- contaminated water.
Having learned how salmonellosis is transmitted, you can move directly to its symptoms. The disease can occur in different ways, so it is customary to distinguish three forms of its manifestation.
Drug treatment
Salmonellosis in children (symptoms are the first thing a doctor pays attention to when prescribing medications) is subject to complex treatment.
Depending on the severity of the disease, medications are selected:
1. If the patient has severe intoxication and it cannot be treated, then antibiotics are prescribed.
But since not all drugs kill salmonella, the most often prescribed are:
- penicillin drugs (amoxicillin, flemoxin);
- cephalosporins (ceftriaxone);
- aminoglycoside (netilmicin);
- carbapenems (meropenem).
An antibiotic may be ineffective for this type of salmonella, so strict monitoring of the patient’s condition is necessary. Replacement will be made if necessary.
2. If the temperature is high, means are prescribed to lower it. If the medicine is not absorbed, it is administered intramuscularly.
3. To restore the functioning of the digestive tract, it is necessary to take medications containing enzymes (festal or enzistal). As well as drugs that normalize intestinal function (Linex, Bificol).
4. If recovery is delayed, it is recommended to take antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs (Viferon or Immunal).
All of the listed drugs, except antibiotics (since they can be administered intramuscularly), are prescribed when the stool is restored and vomiting stops. Self-selection of medications is prohibited. Proper treatment is necessary from the first hours of the disease. Delaying therapy can be fatal.
Prevalence
Salmonella can be found everywhere. The pathogens are characterized by an increased social danger, since they easily infect young and elderly people, children, and pregnant women. Sometimes they cause epidemics.
Now the danger of infection with these gram-negative microorganisms lies in the formation of cell resistance to modern, popular antibiotic drugs. This phenomenon is explained by uncontrolled sales and the lack of creation of fundamentally new medicines with a different composition and mechanism of action. Treatment of salmonellosis with antibiotics sometimes occurs without medical supervision, which complicates the selection of medications in the future.
The most aggressive strains of salmonella are considered to be nosocomial infections. Disinfectants, antiseptics and similar compounds are most often used inside medical institutions.
Further observation
After recovery, the child is monitored for up to 3 months. During this time, you need to take a stool culture test every 30 days. If the result is negative, the baby can attend kindergarten and is removed from the doctor’s observation.
Contacted relatives and the kindergarten staff are checked for the presence of salmonella within 1 week. And a stool sample is taken for culture. If the result is negative, the person is considered healthy.
The apartment must be disinfected. Personal items are boiling. It is advisable to identify in advance what was the source of salmonella infection. It could be a pet or contaminated produce.
Prevention
Preventive measures that should be followed to prevent a child from contracting salmonellosis should mainly be aimed at eliminating foci of infection. This is the prerogative of medical and veterinary services that monitor the condition of pets. At factories producing meat, dairy, and egg products, a sanitary regime must be strictly observed, which will not allow infection to enter raw materials and food products.
Particular attention should be paid to measures to prevent the spread of bacteria in various preschools, schools and other children's institutions. These measures are almost the same as for other acute intestinal infections. It is required, if necessary, to take emergency measures to ensure that the identified source is isolated as quickly as possible in order to prevent an outbreak of the epidemic. You should also conduct a one-time bacteriological examination of the analyzes of all patients with intestinal dysfunction, as well as children who are admitted to children's institutions, and expectant mothers when admitted to maternity wards.
When the child has a complete clinical recovery, confirmed by bacteriological tests, you can stop isolating the little patient. However, children who are in junior kindergarten groups must be under medical supervision for three months. They need to be tested monthly for bacteriological studies to determine whether they are carriers of bacteria.
If group outbreaks of the disease occur, then not only all children are tested, but also the establishment’s service staff. In addition, products and their remains that were eaten in the last few days are subject to analysis; food storage areas, compliance with food preparation technology and other important points are examined.
How to treat at home
Traditional medicine for salmonellosis is not recommended, but if the disease is mild, you can improve the condition using proven remedies:
- You can give your child chamomile tea (sold in pharmacies, it is a good bactericidal agent). To improve the taste, you can add 10 ml of flower honey. Give 10 ml every 20 minutes in the first days.
- An infusion made from dried plantain leaves. Take 12 g of plant per 200 ml of boiling water. After cooling, drink in small portions.
- Massage using peppermint oil relieves pain in the abdominal area and improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Apply in the navel area, using circular movements in a clockwise direction. Sold in a pharmacy.
- A drink made from oak bark helps strengthen the stool. To prepare, take 12 g of dried and crushed bark and steam it in 200 ml of boiling water. You need to watch your stool, as the infusion has a strong fixative effect.
- Tansy infusion will help relieve colic. The ingredients are taken in a ratio of 1:20. Infuse and drink in small doses.
- Warm compresses will help relieve abdominal pain.
In case of salmonellosis, before using infusions, you need to clarify their use with your pediatrician. Since in children, the body, weakened by illness, may respond inadequately to folk remedies. After assessing the patient’s symptoms, the doctor will prescribe a dosage and course of medications. Inpatient treatment may also be prescribed.
Author: Kotlyachkova Svetlana
Article design: Vladimir the Great
Individual prevention
Needless to say, this is a very serious disease - Salmonellosis; treatment in children requires a lot of effort and time. To prevent such undesirable consequences, parents should make sure that the food is always of high quality; products should always be well heat treated before consumption. These recommendations apply to both meat and dairy products, eggs.
When a child is at home during treatment, he must be provided with individual hygiene items and cutlery.
When carrying out wet cleaning, you must also remember to wash the toys that the sick child comes into contact with. Prohibit your baby from putting various objects that are on the floor into his mouth. Make sure that he does not swim in unknown and, especially, bodies of water prohibited for swimming. If possible, create conditions that would prevent the baby from coming into contact with birds, such as pigeons and chickens, as well as other domestic animals.
You should not engage in self-medication and treatment with folk remedies for this disease, as this is considered unacceptable for salmonellosis. For preventive purposes, the child's parents and other family members are prescribed Salmonella bacteriophage on the recommendation of a doctor. The transferred disease forms a year's immunity in the child. Parents must follow the rules of feeding the child and remember that food for consumption should not be stored; if this is difficult to do for one reason or another, “boil” it again to 70 degrees.