Anyone knows that alcohol is a dangerous poison for the body, but few people really think about the fact that you can die from alcohol poisoning. Meanwhile, statistics for Russia for 2011 alone indicate that about 12 thousand residents died from poisoning with ethanol drinks, and this figure is gradually growing.
It is important to remember that alcohol intoxication is a dangerous, life-threatening condition.
If symptoms characteristic of this pathology develop, it is necessary not only to call an ambulance, but also to be able to alleviate the patient’s condition before specialists arrive.
Symptoms
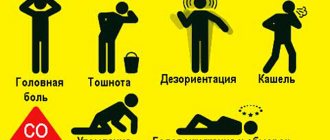
Symptoms of intoxication differ from the usual hangover associated with alcoholism:
- Profuse sweating.
- Coordination is impaired.
- Speech becomes slurred.
- Poisoning is accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Weakness and a sharp headache appear.
- The victim turns pale and the skin becomes blue.
- Possible loss of consciousness, convulsions, coma.
The symptoms of methyl alcohol poisoning are much more pronounced:
- Sharp pain in the abdomen, vomiting mixed with bile or blood.
- Vision is impaired - possible blurred vision, partial blindness.
- Respiratory paralysis.
- Possible death.
Such signs do not appear immediately after drinking, but arise within 24 hours. In case of methanol poisoning, you should urgently call emergency services.
Primary symptoms
Schematically, all alarming signs can be divided into primary and secondary. The last option is suitable for situations where the first manifestations were ignored or were not blocked properly.
The early stage of a sharp deterioration in the condition often goes unnoticed by others due to the fact that the influence of alcohol-containing components on the human body is taken for granted. It is difficult to detect even in those who are trying alcohol for the first time, not to mention drunkards with many years of experience who are capable of drinking lethal doses.
The first typical signal of approaching severe intoxication is a painful shine in the eyes, which is similar to the condition when the patient has become a victim of the flu or a cold. Often it is additionally accompanied by bursting of small vessels in the eye, which ends in the so-called “bull's eye”.
Next, the body begins to signal a gradually deteriorating state of health through increased activity of the sebaceous glands. Outwardly, this is expressed in profuse sweating and the “cold sweat” effect. Against this background, the victim develops fever, trembling of the limbs, accompanied by chills.
If at the beginning of the gatherings the victim showed excessive cheerfulness or aggressive behavior, then at the stage of poisoning it gives way to drowsiness, lethargy, general depression and fatigue.
A little later, the gastrointestinal system begins to protest, as evidenced by:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- pain in the abdominal area;
- stool destabilization.
Often vomit contains an admixture of bile, which indicates a much more serious situation than it might seem from the outside.
Other symptoms include:
- dizziness;
- loss of consciousness;
- respiratory dysfunction;
- increased salivation;
- tearfulness without obvious reasons;
- muscle weakness;
- restriction of physical activity.
Despite the stereotype that all of the above is a normal phenomenon, doctors recommend keeping your ears open. In severe cases of primary symptoms, the patient may develop paralysis of the respiratory center or complete shutdown of the motor center.
Often, alcoholics and those who overestimated their capabilities die due to cardiac arrest in an alcoholic coma simply because they were not provided with pre-medical assistance in time. People around simply considered dangerous signals a common occurrence.
But even with a relatively mild degree of poisoning, it is worth seeking help from specialists. More severe forms of damage will have to be treated in a hospital inpatient department. An ambulance team must deliver the victim there.
An identical scheme should be followed if there is poisoning with nicotine, products with a high content of nicotine, or simply suspected of intoxication. The first step is to call doctors, and then provide assistance at the scene of the incident.
First aid
The faster and better quality pre-medical care is provided to the patient, the higher the likelihood of safely waiting for the doctors.
First of all, it is necessary to monitor the respiratory ability of the poisoned person. Required:
- Provide fresh air flow.
- Remove any remaining vomit from the respiratory tract.
- Place the patient on his side.
- Secure your tongue so that it does not fall into your throat.
If a person is unconscious, it is necessary to revive him. Ammonia is suitable for this - its vapors are excellent for fainting.
To relieve acute intoxication, you need to carry out a stomach cleansing procedure: give the victim plenty of water and induce vomiting. This can be done using a mustard cocktail (2 tsp of powder per glass of liquid) or water with soda. If there is nothing at hand, you can simply press two fingers on the root of the tongue - the patient’s gag reflex will work.
As soon as the patient begins to get rid of intoxication products, you can move on to the next stage - adsorption. Activated carbon, absorbent gel (Enterosgel, Atoxil) or powder (Polysorb, Smecta, Enterodes) help cure the body of ethanol residues.
It is important not to leave the patient alone, even if he appears to feel better. An attack of intoxication may recur, and it will be difficult to cope with it without outside help.
Stages of alcohol intoxication
First, let’s find out what symptoms require help. Based on the amount of alcohol in the blood (in ppm, ‰), there are 3 stages of alcohol intoxication:
- Mild intoxication – up to 1.5 ‰
- Average intoxication – up to 2.7 ‰
- Alcohol poisoning – more than 2.7 ‰
It is the last stage that requires medical attention and it is this that we will consider in this article. Using an alcohol calculator, you can calculate your blood alcohol content based on your gender, weight, and amount of alcohol consumed.
What not to do
Here is a list of activities that absolutely cannot be done in case of alcohol poisoning, since they can worsen the patient’s condition or even lead to fatal consequences:
- After poisoning, you should not drink alcohol again, even if it seems that there has been an improvement. Intoxication is too heavy a load for the body; the liver may simply not be able to withstand repeated intoxication.
- The patient needs rest! Therefore, you should not lift the victim out of bed or disturb him in any way.
- If a person is drunk, you should not put him under a cold shower. At this moment, thermoregulatory processes are disrupted, the alcoholic may catch a cold or die from hypothermia.
- Do not leave the patient unattended. He may lose consciousness, choke on his own vomit, or injure himself.
- If there is no positive dynamics, you need to call a medical team. A person may suffer from chronic diseases, and heavy libations often cause exacerbation. In this case, medical intervention cannot be avoided.
What not to do
When you are near someone who has been poisoned, do not do the following under any circumstances:
- Do not leave a person unattended;
- Do not try to place the victim on his back or leave him lying on his back;
- Do not lift the person to his feet or force him to move;
- Do not pour cold water on the patient;
Complete treatment
After providing first aid (on your own or with the help of doctors), it is important to continue treatment correctly , because acute poisoning can greatly affect your well-being.
If a person is in the recovery stage and can move without assistance, then doctors recommend maintaining minimal activity. Light physical activity, even a walk around the house, speeds up metabolic processes and helps eliminate toxins. It is better to stay outside more or open the windows wider - the influx of fresh air improves your well-being and saturates the brain with oxygen.
It is important to monitor your diet. Complete fasting will deprive you of the strength to recover, and heavy food will increase the load on the affected digestive tract. The best option is a light diet. You can eat chicken broth or a boiled egg, liquid oatmeal. Crackers and sweet hot tea are acceptable. But you shouldn’t eat fatty, spicy, salty foods. Also, you should not eat too much at one time. For a person who has been poisoned, split meals are suitable: eat little by little 5-6 times a day.
And of course, the main rule is that you must completely abstain from alcoholic beverages (including low-alcohol drinks - beer, wine). Otherwise, the entire positive effect of the treatment will be nullified.
Impact of a surrogate on the body
Despite the fact that the mechanism for providing first aid for alcohol overdose and the use of surrogates remains almost the same, their symptoms may differ.
Some experts even believe that surrogate drinking causes more serious harm to the body than an overdose of high-quality alcohol-containing drinks. The reason for such a statement lies in the many accompanying components, each with its own spectrum of action on internal organs and tissues.
Not only low-quality vodka or underground crafts of elite alcohol are considered surrogates. Here you can include various medicinal tinctures and other pharmaceutical preparations that are not intended for heavy libations or, in general, for internal use.
Also dangerous are household chemicals such as glass cleaners, perfumes and even moonshine made at home. The latter contains too much fusel oil even when cleaned with activated carbon. They cause irreparable harm to almost every system of the body.
The main difference between a proven industrial product and a surrogate is the excess of the maximum permissible norm of methanol. Here, even with timely assistance, there remains a high risk of death due to the general serious condition. The patient has to deal with a number of typical complications caused by irreversible processes. Most often this is blindness and various abnormalities in the functioning of the cardiovascular system. It cannot be done without varying degrees of damage to the liver and kidneys.
To avoid becoming a victim of extensive intoxication, you need to know your limits and not drink any alcoholic beverages on an empty stomach. If a person knows exactly the time of the upcoming drinking feast, it is worth taking activated charcoal in advance. The weight is taken as a basis, which allows you to calculate the correct number of tablets based on the instructions for the medicine.
If you can’t do without drinking at a celebration, then it’s better to spend money on high-quality alcohol to avoid buying a surrogate. You should also avoid drinking carbonated drinks with alcohol-containing liquids. Due to carbon dioxide bubbles, the absorption of toxins and ethanol, methanol will be carried out much faster.
Another golden rule is to avoid reducing the strength and combining different types of alcohol in one go. All together, this will help maintain health, and also serve as a factor reducing the negative consequences of overdose and poisoning.
According to official data from Rosstat, in 2011, 11.7 thousand residents of the Russian Federation died as a result of acute alcohol poisoning. And according to estimates from the Center for Research on Federal and Regional Alcohol Markets, real mortality from alcohol poisoning is tens of percent higher than statistical indicators.
Almost every Russian may be faced with the need to provide emergency assistance to acquaintances or random people due to alcohol poisoning. This is confirmed by the following facts:
- Russia ranks fifth in the world in terms of alcohol consumption per capita according to WHO.
- According to official information from Rosstat, 12 million residents of the Russian Federation abused alcoholic beverages in 2011.
| 12 million Russians abuse alcohol |
In this article you will find information about acute ethyl alcohol poisoning and its consequences. You will also learn about the signs based on which you can suspect this condition. Finally, you will receive information about providing first aid to a patient injured as a result of excessive alcohol consumption.
Consequences
Inaction or improper treatment in case of poisoning with excess or low-quality alcohol can lead to dangerous consequences.
The patient's kidneys may fail, and a heart attack or stroke may occur. There is a high probability of brain damage. In extreme cases of poisoning, convulsions, breathing problems, and loss of vision are observed. An alcoholic can fall into a coma. Death occurs due to failure of vital organs or general intoxication.
If possible, it is better to place the patient in a hospital. There, a nurse will put him on an IV and provide professional care.
What kind of alcohol can cause poisoning?
Poisoning occurs as a result of drinking ethyl or methyl alcohol, low-quality vodka and moonshine. Cosmetics (cologne, lotion) and technical fluids (wood alcohol, brake fluid) lead to severe poisoning. An alternative to dietary liquids is tincture of hawthorn and red pepper. Ethanol partially neutralizes the body, and an overdose threatens a person with death. In case of severe poisoning, call an ambulance.
Only a doctor can correctly prescribe medications that treat alcohol poisoning.
Degrees and clinical picture
Alcohol poisoning is a condition in which the functional activity of most organs and systems is disrupted, disorganization occurs in their work, which causes the formation of symptoms such as clouding or complete impairment of consciousness, changes in the rheological properties of blood, hemodynamic disturbances, and dyspeptic symptoms in the gastrointestinal tract.
Alcoholic coma is a complication of alcohol poisoning in which severe disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system are formed, which leads to depression of consciousness and the respiratory center, and loss of a number of reflexes to external factors. The clinical picture of alcoholic coma in case of poisoning with alcohol surrogates is formed from the following stages and symptoms.
Toxicologists, psychiatrists, narcologists and neurologists in clinical practice distinguish several successive degrees of development of poisoning and alcoholic coma.
- Superficial coma of the first degree (resorption stage) lasts approximately 6-7 hours. At this time, ethyl alcohol penetrates the systemic bloodstream, reaching the liver it breaks down into active metabolites, the most toxic of which is acetoaldehyde. Symptoms such as constriction of the pupils, changes in facial expressions, and preserved reaction to light and painful stimuli are observed. After gastric lavage, the victim comes to his senses.
- Superficial coma of the second degree (elimination phase) lasts for 12 hours. Alcohol undergoes breakdown in the body. However, its concentration in the blood decreases, which leads to relaxation of muscle tissue, lack of reaction to ammonia and gastric lavage.
- Deep coma is characterized by a lack of response to external stimuli: constriction of the pupils and lack of reaction to light, does not respond to ammonia, tendon-muscle reflexes are not evoked, pain receptors are intact. Convulsive seizures and breathing problems may occur. Body temperature can drop to 35 degrees, blood pressure is low, and the pulse is thready. The victim requires emergency hospitalization in a detoxification department or intensive care unit.
It is important to note that the first stage of ethyl alcohol poisoning can be managed without the use of specialized medical care, while the second and third stages require a qualified treatment approach and special equipment.
How does the poisoning process occur?
Alcohol, entering the body through the bloodstream, reaches the blood-brain barrier, where it begins to break down or break down into toxic metabolites.
The most dangerous neurotoxic metabolite is acetaldehyde; it disrupts the water-salt balance, retaining water in the intercellular space. This causes the development of edema and dehydration, reduces the total blood volume, which leads to the development of weakness, lethargy and hypoxic phenomena in the tissues of the body.
Acetaldehyde also has a dyspeptic effect on the organs of the gastrointestinal tract - a person experiences a feeling of severe nausea and vomiting, and pain appears in the epigastric region. The first signs of poisoning and symptoms may develop within the first hours after drinking an alcoholic drink.