Lactic acid products are among the most valuable and healthy in our diet. It is an important source of calcium necessary for healthy bones in adults and children. These products contain bacteria necessary for the normal state of intestinal microflora. Sour cream is especially versatile in our diet - as an independent product and as an additive to soups, main courses, and also as a base for sauces. But milk, unfortunately, is a nutrient medium not only for beneficial microorganisms. Dangerous microbes also successfully develop in it. Therefore, sour cream poisoning is a common occurrence.
Causes of poisoning
A person who has wondered whether it is possible to be poisoned by cheese should know: poisoning with this food product almost always occurs because it contains various infections. Bacteria, penetrating the human body, leave toxic substances in it, which provoke the appearance of a lot of unpleasant symptoms.
Harmful microorganisms can enter the product at various stages. This may be the process of manufacturing, packaging or even storing the product, which is why it is so important to responsibly choose a variety and a manufacturer who closely monitors production technology and is responsible for quality.
Milk used to make cheese must undergo heat treatment. If this does not happen, and the cow giving this milk was infected with the infection, it will be transmitted to the cheese product, which poses a great danger to humans and can provoke a lot of intestinal diseases.
Symptoms of poisoning can also appear after consuming cheese made from pasteurized milk - in this case, bacteria obtained during production and present on the equipment with insufficient compliance with sanitary standards penetrate into the cheese.
Note! Today, blue cheese is very popular, but few people know that it should be eaten in small portions with long breaks, since it contains a natural antibiotic. If you are poisoned by a product, be sure to provide first aid to the victim and contact a medical specialist.
Recovery period after cheese poisoning
After the symptoms of poisoning have subsided, doctors recommend refraining from eating for 24 hours, and then eating only light, diet foods .
On the first day, biscuits and crackers, baked apples, and ripe bananas are introduced. On the second day, you can give the patient viscous porridge in water, with a small addition of salt - buckwheat, rice, oatmeal. It is advisable to grind the cereal first and then cook it. From the third day, you can give low-fat broths with chopped meat, mashed potatoes and dairy products. Then the diet is gradually returned to the usual, but for another couple of weeks the consumption of greens, fried and canned foods is avoided. Whole milk is first diluted with water, and then porridges and soups are cooked in it. The diet must include bifidokefir , which tones the entire body and stabilizes the functioning of the digestive tract.
During the recovery period, it is recommended to take medications that contain bifidobacteria. They contribute to the population of the gastrointestinal tract with beneficial microflora.
Salmonellosis
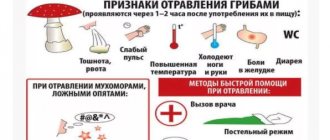
Six hours after a toxic substance enters the human body, the victim exhibits the first symptoms of the disease. They manifest themselves in the following unpleasant reactions for humans:
- There is severe pain in the abdomen.
- Diarrhea continues for quite a long time, causing discomfort.
- Severe nausea develops into constant vomiting.
- The heart begins to beat faster.
- Blood pressure gradually decreases.
- The general body temperature rises, the victim develops a state of chills.
- Muscles and joints noticeably weaken.
- The liver and spleen are significantly enlarged, which can only be detected by a specialist after examination.
Such a disease requires immediate intervention from a medical professional, since the consequences of such intoxication can become irreversible. A person's health deteriorates throughout the course of the disease, and without appropriate treatment there is a risk of developing jaundice.
What to do if you are poisoned by sour cream
Treatment for identified symptoms of sour cream poisoning should begin immediately:
- The first step is to get rid of the source of poisoning that has begun to adversely affect the body. To do this, you need to rinse your stomach to remove toxins. The patient is given several glasses of clean boiled water to drink. You can add a few manganese crystals to the water. But to avoid burns, it is better to first dissolve the crystals separately and add a few drops to drinking water until it turns pink. You can simply salt the water. After filling your stomach with water, you must induce vomiting in any way.
- Remains of a low-quality product are removed from the intestines using an enema.
- After removing the source of poisoning, the patient should be given any sorbents: 10-20 tablets of activated carbon (Enterosgel, Smecta, Polysorb are also suitable). They will take on the toxic substances remaining in the body.
Restoration of the gastrointestinal tract
How long to treat sour cream poisoning? If the listed methods do not improve the patient’s condition in one day, you should seek medical help. This is especially necessary if the temperature remains high, fever appears, severe pain continues and there is obvious dehydration. Treatment in a hospital will restore water-salt metabolism with the help of intravenous solutions, relieve spasmodic pain, the patient will be prescribed antiseptics and enzymes to improve the intestinal microflora.
Coli infection
This type of infection occurs if a product made from milk that has not undergone heat treatment has been consumed. In most cases, young children are affected by the disease, since their bodies are not able to resist infection, and the disease can manifest itself in a period of six hours to six days.
The disease manifests itself as follows:
- The victim's appetite decreases.
- In young children, body weight decreases significantly.
- At a certain period, the victim begins to develop a fever.
- The urge to vomit gradually intensifies.
- Diarrhea can recur up to ten times a day, which causes some discomfort.
In the absence of timely medical care, the victim develops dehydration, which puts all important systems at risk. Calling an ambulance is mandatory in all cases, especially if a small child, a pregnant woman or an elderly person has suffered from the bacteria.
First symptoms
Poisoning is possible due to the fault of four bacteria that produce dangerous toxins. Symptoms of cheese poisoning differ depending on the causative agent of the infection.
Salmonellosis
Salmonella
Salmonella does not ferment lactose and produces a dangerous toxin. After 6 hours the first symptoms appear:
- severe abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea;
- increased heart rate, decreased blood pressure;
- fever, complaints of chills;
- physical weakness;
- enlarged liver and spleen (diagnosed by a doctor).
If symptoms of intoxication are detected, immediately go to the hospital. Delay increases the risk of developing jaundice.
Coli infection
The disease is caused by pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli. The infection affects children and people with weakened bodies; it is especially dangerous for a pregnant woman to become infected. The incubation period is up to 6 days, after which symptoms appear sharply:
- temperature;
- dysbacteriosis, diarrhea, vomiting;
- decreased appetite and body weight;
- fever.
Delay in providing medical care will ruin the water-salt balance of the body.
Brucellosis
The causative agent is the microbacterium Brucella melitensis, which lives in goats, pigs and cows. Outbreaks of rod activity are observed in spring and winter. Bacteria are dangerous due to their long incubation period - from 1 to 3 weeks. The impact falls on the reproductive and nervous systems, the musculoskeletal system.
The acute form is characterized by lack of appetite and sleep, migraines, weakness of the body and irritability. Other symptoms:
- severe chills;
- temperature up to 40 degrees;
- muscle pain.
During a less serious form, the temperature fluctuates, and joints, muscles and bones hurt. No appetite, constant thirst, dry mouth, rashes. The subacute form affects the musculoskeletal system, the consequences are polyarthritis and bursitis.
Doctors describe the chronic form as periods of exacerbation and decreased activity of toxins. The disease parasitizes the nervous system, the sensory organs suffer, and hyperhidrosis begins. Consequences of the disease:
- periostitis;
- spinal deformity;
- disruption of the genitourinary system.
Important! The initial symptoms of infection (physical weakness, severe joint pain, fever and sweating) are similar to a cold. Self-medication for brucellosis will greatly worsen the patient’s well-being.
Listeriosis
The disease is caused by the bacteria Listeria monocutogenis. Microorganisms are heat-resistant and psychlorophilic - they survive heat treatment and continue to multiply in food products (bread, cheese). Causative agents of foodborne infections and perinatal pathologies in humans. Bacteria poison the body, penetrate the mucous membranes, then settle in the tonsils with blood and lymph.
Angina
In severe cases, a possible complication is sepsis. Signs of infection appear within a period of 3 days to 1.5 months:
- sore throat, cough and runny nose, enlarged tonsils with white coating;
- fever;
- intoxication;
- enlarged liver and spleen;
- skin rashes;
- conjunctivitis.
For newborns, pregnant women, and people with a weakened immune system, the disease is dangerous: infection is asymptomatic and causes serious abnormalities in the fetus. Newborns develop severe fever and diarrhea. Patients develop skin rashes. If the pus reaches the brain, the infection will end in death.
Brucellosis
This type of disease is considered extremely dangerous, since the first symptoms of poisoning do not appear immediately, but only several weeks after eating the toxin. Unpleasant sensations in the abdominal area may not occur at all, but other signs appear that become a real problem for the victim:
- general weakness and severe deterioration in health;
- discomfort in the joints;
- a significant increase in general body temperature;
- increased sweating.
The main problem is that the patient cannot independently determine the poisoning, since some symptoms are similar to a common cold. That is why the consequences can be extremely negative, and if the slightest ailment is detected, it is recommended to immediately consult a doctor.
When medical attention or treatment is required
When poisoned by expired products, many people neglect to see a doctor. However, there are situations when you cannot do without medical help:
- signs of poisoning are observed in children and pregnant women,
- dehydration progresses rapidly,
- intense abdominal pain occurs that does not disappear after defecation,
- the condition does not improve within 2 days,
- There are bloody impurities in the stool.
In such cases, you should immediately contact an infectious disease specialist who will select treatment tactics. Detoxification therapy is most often prescribed. Also, the attending physician will definitely prescribe antibacterial agents, taking into account the causative agent of the disease.
Listeriosis
This type of bacterium poses a serious danger to women expecting a child. The fact is that one of the effects of this microorganism is a negative impact on the fetus, as a result of which it develops a number of dangerous pathologies. The danger is that the risk of miscarriage or the birth of a child with various diseases increases significantly.
The manifestation of the disease occurs within a period of one day to one month from the moment of eating cheese, with the primary symptoms being diarrhea, severe nausea and vomiting. In the absence of the necessary treatment, the disease develops into meningitis, which poses a mortal danger to the health and life of the victim.
Possible consequences
Foodborne illnesses caused by cheese poisoning go away within a few days, leaving no negative consequences. Unfortunately, the same cannot be said about listeriosis and brucellosis.
Listeriosis is especially dangerous for children in the first year of life, as it is often complicated by the development of meningitis or infectious-toxic shock. This disease also poses a risk for pregnant women, since its pathogen is capable of penetrating the uteroplacental barrier and causing developmental disorders of the fetus.
Untimely initiation of treatment for brucellosis contributes to the transition of the disease to a chronic form, in which the musculoskeletal system is significantly affected.
Emergency help
The victim is unlikely to want to eat cheese after poisoning, but stopping eating this product will not help get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease. In order to eliminate the consequences and possible development of pathologies, it is recommended to pay close attention to first aid measures for the patient. The speed of the patient’s recovery and the chance of a quick return to a normal lifestyle depend on it.
Note! Some people have allergic reactions to the product, so if you suspect it, check with your doctor to see if cheese can be eaten.
First aid for intoxication with cheese products can be provided using the same methods as for any other food poisoning. It is important to adhere to a certain course of action, and then the victim will soon recover:
- Gastric lavage is required. To do this, use a large amount of warm water mixed with a solution of potassium permanganate. It is necessary to rinse the stomach until the remaining food is removed from it and the water at the outlet becomes clear.
- After the toxin is removed from the body, it is necessary to take sorbents that will help get rid of residual elements of the poison. Activated carbon or Smecta are perfect for this; they must be taken in strict accordance with the instructions.
- After the procedures, it is necessary to provide the victim with complete rest, plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration, and good ventilation in the room. If the symptoms do not disappear, you should immediately call a medical specialist who will assist the victim, establish an accurate diagnosis and provide treatment.
Video: food not for the faint of heart - wormy cheese banned in Italy.
The danger of poisoning from home-made cheese
Now some people are trying to eat healthy and prepare dairy products on their own.
You can find many starters on sale that help you make various cheeses at home. How healthy is this cheese and can you get poisoned by it? At home, you can prepare natural cheeses without additives or preservatives . These products are natural and very tasty, but the shelf life is an order of magnitude lower than that of industrially produced cheese products. To avoid getting poisoned by homemade cheese, it is enough to use clean dishes, wash your hands well before cooking and store the finished product in the refrigerator.
Prevention
Eliminating poisoning is a simpler process than treating it. Only a responsible approach to your diet will ensure you a normal life without serious consequences. You can avoid cheese poisoning by following simple rules:
- Be sure to check the expiration date of the product. If it comes out, do not eat it under any circumstances.
- Check the integrity and tightness of the packaging, this way you will save yourself from a lot of trouble.
- Inspect the appearance of the cheese; there should be no foreign inclusions in it.
- Store product as directed.
- Undergo a medical examination to determine if you have any allergic reactions to the product or if you are susceptible to them.
Taking care of your health is the task of every person. Despite the obvious benefits of cheese products, they often cause irreparable harm to health, so you need to carefully shape your diet, trust a specific manufacturer, and if there is the slightest disturbance in the body, you should immediately consult a doctor.
How to protect yourself from sour cream poisoning
To avoid severe food poisoning, you should choose dairy products carefully. Even if you buy homemade milk, cottage cheese and sour cream from private traders on the market, do not be lazy to check them first: buy a liter of milk and keep it warm at home. If during this time it has not turned into sour milk, it means that antibiotics were added to it to protect it from souring. Is it worth buying other products from such an owner?
Be even more careful when shopping at the store. Pay attention to the following indicators:
- Best before date. If the manufacturer claims that the product can be stored for more than four days, it definitely contains preservatives. Of course, avoid expired products.
- Read the composition of sour cream carefully. In a quality product it is short and includes cream and sourdough. But if preservatives, thickeners, and dyes are listed, this is not sour cream, but a surrogate of technical oil with the addition of chemical components.
- Check the integrity of the packaging. If it is broken, this is a direct route to any infection. Sour cream in swollen packaging, crumpled packs and glasses should also raise suspicion.
- If the external condition is normal, but when opening the package the sour cream turns out to be separated into liquid and sediment, has an unpleasant odor, a changed color, or an unusual consistency - it is better to stop using it.
Attention to the quality of dairy products cannot be excessive - this will preserve the health of you and your loved ones, and a high-quality product will bring the expected benefits from it. And remember: when the first symptoms of sour cream poisoning appear, treatment should be followed immediately.
When does a patient need to be hospitalized?
In some cases, the patient should be immediately taken to the emergency department. You can find out when you need to do this by the following signs:
- nausea and loose stools do not go away for several days (after two, you must definitely call a doctor!);
- worsening manifestations of dehydration, then you need to replenish fluid loss with the help of droppers ;
- persistent fever and/or persistent increase in temperature;
- the pain doesn't stop.
All this suggests that the intestines or other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are still not working correctly and the body cannot get rid of the infection.
You cannot bring the patient into a state of shock! If any of these symptoms persist for more than two days, call an ambulance.
Why is it so easy to get poisoned by dairy products?
You should be very careful with dairy products. In summer, ice cream poisoning is one of the most common among all types of poisoning . The main reasons for this are as follows:
- Poor hygienic conditions in areas where animals are kept. Dangerous bacteria often spread there and end up in dairy products.
- Illness of staff and animals themselves. Quite often you may encounter the fact that cows or goats are not checked for mastitis or other diseases. Farm workers may have skin diseases.
- Storing dairy products in inappropriate conditions. Usually, when storing milk, sour cream and other similar products, no one monitors the temperature, which leads to poisoning.
Very often, dairy products can be contaminated with staphylococcus and other microorganisms . And they damage the intestinal cells and cause all the above-described processes associated with poisoning.