In life, people encounter all kinds of poisoning. Most believe that they can help themselves on their own. Patients do not consider it necessary to undergo research. This opinion is incorrect; in extremely rare situations, a person is able to cope with the ailment on his own. Diseases investigated in a timely manner will help to obtain the correct diagnostic result and eliminate subsequent complications in the body due to poisoning.
What is chemical poisoning and its features
There are acute and chronic poisoning by chemicals. The following can act as poison:
- Medications.
- Pesticides.
- Household and auto chemical goods.
- Solvents.
- Reagents used in laboratories.
- Chemical elements used in production.
Toxins can enter the body through the respiratory tract or digestive tract. Cases of penetration of poisons through the skin or mucous membranes have been observed. Poisoning can be caused by an anthropogenic factor.
Adults are exposed to poisoning due to non-compliance with safety rules or in the event of industrial accidents. Children become victims of exposure to chemicals due to the negligence of adults.
ICD 10 code – X40-X49 (accidental poisoning with toxic substances), T36-T50 (poisoning with drugs and biological substances).
Antidotes
In case of toxic poisoning, an important factor is the introduction of an adequate antidote - an antidote. Drugs that are used as antidotes, when they react with toxins, lead to the neutralization of the latter. Depending on the mechanism of action, antivenoms are divided into several groups.
There are antidotes whose work is based on physical processes. This is a group of medications called absorbents. The simplest and most accessible representative of this group is activated carbon.
Substances that form a combination similar to a toxic substance are also used, for example, methylene blue.
Another group of antidotes neutralizes toxins through chemical reactions. In particular, Unithiol.
Antidotes that compete with poisons are used.
There is a group of antidotes of an immunological nature. These are serums.
Conclusion
To neutralize toxic substances that have entered the body as much as possible - this is the main task of all measures taken in case of poisoning. Timely assistance plays a vital role in this regard.
Further symptomatic treatment is aimed at restoring the normal functioning of the body and is no less important for the victim.
Features of intoxication at home and at work
Damage to the body from toxic chemicals can occur in the workplace and at home.
Occupational intoxication is observed among workers of manufacturing enterprises whose activities are associated with chemical compounds and decomposition products during biochemical reactions. Unless we are talking about an industrial accident, poisoning is chronic and manifests itself in a characteristic clinical picture when the toxin accumulates and reaches a critical concentration in the body.
Poisoning by pesticides occurs in people whose profession is associated with the production, packaging, and transportation of substances used to control pests and weeds. Pesticide intoxication is a common occurrence among agricultural workers.
In manufacturing plants, toxins can accumulate in human blood and tissues for decades and manifest themselves as mild symptoms. Chronic poisoning can become fully known in the last stages of the disease.
READ ALSO: On what day are sutures removed after removal of a wen?
The peculiarity of some toxic substances is their negative impact on several body systems. Toxic substances include:
- neurotropic chemical elements and their compounds (affect the nervous system: compounds of manganese and carbon disulfide, carbon monoxide, mercury, phosphate, lead, benzene, arsenic);
- hepatotropes (cause negative effects on the liver);
- nephrotoxins (affect the function of the excretory system and cause pathologies of the kidneys, bladder and urinary system);
- hematotoxins (cause serious blood diseases. Benzene vapors pose a great danger. With chronic poisoning, leukopenia, lymphocytosis, and thrombocytopenia develop).
Occupational intoxication, characterized by the accumulation of poisons, is dangerous due to the gradual damage to organs and systems and depression of the central nervous system. Often people who have been working with chemicals for years have irreversible negative processes in their body when the toxin level reaches a critical level.
You can get poisoned at home by uncontrollably taking medications or using a gas stove ineptly. In case of a malfunction of the chimney or hood, spraying of plants with pesticides, or ingestion of cosmetics or household chemicals. Symptoms of intoxication can be caused by vapors of solvents, paints and varnishes, or mercury if a medical thermometer is damaged.
In most cases, poisoning at home is acute and exhibits obvious characteristic signs. If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, you can avoid damage to organs, restore their function, and eliminate the negative effects of poison on the body.
How toxins enter the body
It can happen in all possible ways. The most dangerous is inhalation. Due to the large surface area of the lungs, poison enters the blood quickly. This is accompanied by a growing clinic. More often found in industrial settings. Other ways of penetration to a person:
- Orally or by mouth. The gastrointestinal tract suffers. Toxins are absorbed into the blood. Some can cause burns of the mucous membranes with the development of massive bleeding.
- Percutaneously. Through intact skin. First they cause local changes, then systemic ones. These also include bites from poisonous snakes or insects.
- Injection. The rapid development of poisoning is characteristic. Most often medications, drugs.
- Through cavities. We are talking about entering the rectum, vagina in women or the ear canal.
In domestic conditions, food poisoning often occurs. More often this is due to an overdose of medications or alcohol intake.
In factories, toxins can be deposited on clothing. Therefore, in hazardous working conditions, workers should follow safety rules. Items from this area should not be taken into your home.
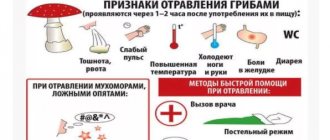
Signs and symptoms of toxic chemical poisoning
The main signs of mild intoxication are:
- weakness, apathy;
- pale skin;
- stomach ache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- chills;
- dizziness;
- cough (if chemicals enter the respiratory tract).
In case of severe intoxication, note:
- Redness, bluishness of the skin.
- Vomit.
- Increased salivation.
- Fainting.
- Problems with consciousness.
- Anemia.
- Cramps.
- Heartbeat disorders.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Change in color of the mucous membrane.
- Headache.
- Aches in the joints.
- Oliguria.
- Hyperthermic syndrome (increase in temperature is observed with toxic damage to the brain).
- Coma.
Upon contact of the reagent with skin, the following may occur:
- focal redness of the skin;
- rashes;
- the appearance of burn blisters;
- pain and burning at the point of contact;
- tachycardia;
- dyspnea.
READ ALSO: After a massage, a rash on the back, face and legs: what to do if acne appears? |
The leading cause of death is carbon monoxide poisoning. The peculiarity of the substance is that it is odorless and colorless and has a rapid effect on humans.
First aid rules
Competent provision of emergency first aid is an important stage in saving a victim from the influence of chemicals, fumes of toxic substances, and gas.
- If poison enters the digestive tract, the stomach should be rinsed immediately, allowing the victim to drink a lot of warm water and induce vomiting. It is recommended to carry out the procedure several times. If intoxication is caused by ingestion of an alkali or acid, gastric lavage cannot be done to avoid intensifying the reaction. They give you lime water, milk, sunflower oil, and egg whites to drink.
- In case of poisoning through inhalation of vapors or gas, it is necessary to remove or remove the person to fresh air. To avoid poisoning yourself, you need to cover your nose and mouth with clothing. The victim needs to unbutton his collar, free his neck from his tie, scarf, handkerchief and give him a drink of water. An unconscious person should be laid down and their head turned to the side in case they vomit.
- In case of food poisoning or ingestion of poison, cleansing enemas are given. For them, boiled warm water is used, with a temperature not exceeding 37 C. These actions reduce the absorption of toxins in the intestinal walls.
- Taking sorbents is necessary to absorb toxic substances. But sorbents are not antidotes - they eliminate those toxins that have not had time to be absorbed into the blood. They should be taken immediately after the first symptoms appear and call an ambulance. It is important to follow the dosage: 1 tablet of activated carbon is designed for 10 kg of human weight. It will not be possible to cleanse the body with a smaller dose.
- If the reagent comes into contact with the skin, the damaged area must be thoroughly rinsed with water.
Intoxication with pesticides occurs due to violation of instructions for the use and storage of chemicals. First aid for exposure to organophosphorus compounds:
- if the poison penetrates the respiratory tract, the patient should be given 2 tablets of belladonna (extract of the belladonna herb) or 8 drops of atropine 0.1%;
- if poison enters the gastrointestinal tract, the victim needs to drink 1 liter of water with 7-10 tablets of activated carbon dissolved in it and induce vomiting;
- if breathing stops, perform artificial respiration;
- give a laxative (solution of magnesium sulfate or Carlsbad salt);
- transport the poisoned person to the hospital.
READ ALSO: Meningococcal infection; Diseases
Treatment methods
Carried out in a hospital. Next direction:
- Removal of unabsorbed poison. Repeated gastric lavage is performed.
- Reducing the activity of the toxin entering the blood. Forced diuresis and hemodialysis are prescribed.
- Symptomatic therapy.
The victim is treated for several weeks. Carry out:
- Respiratory support: oxygen therapy, intubation, mechanical ventilation.
- Restoration of heart function: solutions of sodium, plasma, crystalloids.
- For liver and kidney damage: extracorporeal detoxification.
Additionally, they give vitamins B, E, A, ascorbic acid, and folic acid.
What medications to take for chemical poisoning
After first aid, treatment of chemical poisoning is carried out in a hospital. To carry out therapeutic measures, the patient's condition is assessed. If the chemical agent is known, the doctor may prescribe an antidote. In case of an overdose of narcotic opium alkaloids, Naloxone is prescribed. But not all poisons have antidotes; therapy is aimed at:
- Stopping the absorption of toxins into the body.
- Removing toxic substances absorbed by sorbents from the body.
- Elimination of symptoms of poisoning (restoration of the function of affected systems or organs).
If there is no vomiting to empty the stomach, the patient is given Ipecac syrup. The medicine can be given to a child and an adult to drink (15-30 ml), but simultaneous use with sorbents should be avoided. If there is no vomiting, a repeat dose of the drug should be taken after 20-30 minutes.
In a hospital setting, an intramuscular injection of Apomorphine may be prescribed, which induces vomiting within 5 minutes.
For the adsorption of poisons, the following are prescribed: Activated carbon: black and white, Carbolong, Smecta, Enterosgel, Polysorb MP, Polyphepan, Filtrum-STI. To remove adsorbed toxins from the body, laxatives are used: Magnesia, Sodium Sulfate. If there are seizures, the patient is administered intravenously Phenytoin, Diazepam, Phenobarbital.
In case of intoxication after chemotherapy, which is accompanied by vomiting, drugs are used to relieve unpleasant urges. The above sorbents are used.
Special studies
They also conduct special studies that are actively used in modern medical practice. They are considered complementary and have a narrow focus. A lumbar puncture is performed to check the cerebrospinal fluid. The procedure is carried out if dangerous damage to the cells of the central nervous system is suspected.
When an enzyme immunoassay is performed, the cause of intoxication is determined even in the most advanced cases, if it is impossible to study the composition of stool or rinse the stomach with water.
The interpretation of the studied tests should be carried out by a doctor who is directly involved in the treatment of a patient with poisoning. He understands such ailments and will select the most rational approach to treating the patient.
The right attending physician will help stop the development of intoxication in a timely manner, as he will offer to take the necessary health tests.
Possible complications
The consequences of exposure to toxins can be complications:
- Edema of the lungs, brain, larynx.
- Decreased central nervous system functions.
- Hypotension (severe decrease in blood pressure).
- Cardiac arrhythmia.
- Tissue hypoxia.
- Acute form of renal or liver failure.
- Violation of the water-electrolyte balance of the blood.
Poisoning with chemical substances is characterized as a dangerous condition for the victim and ignored symptoms can lead to disability. It is necessary to provide first aid in time, call a doctor and begin to treat intoxication.
News MirTesen
Possible consequences
Complications in half of the cases are fatal. In case of poisoning, paralysis of the respiratory center, pulmonary edema, and shock may occur. All this leads to irreversible processes in various organs. Consequences:
- severe neurological disorders due to brain hypoxia;
- personality change, complete maladjustment;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, lungs.
Afterwards, infectious complications may occur, in the form of pneumonia (usually from staphylococcus). Blood clots form.