Meeting a snake is a pleasant event for few people. In rare cases, reptiles bite a person in defense, however, not in all cases this poses a threat.
Most members of the snake family do not pose any danger, but there are some species with which you need to be extremely careful. Many people know that a snake bite will not cause harm, but whether this is true or not, the reader can find out by reading this article.
This type of snake is found everywhere, preferring to settle on river banks, marshy areas, forests and field plantings. It is a frequent visitor near villages and summer cottages, where it lives in little-used agricultural buildings or garbage heaps. It, like any other reptile, is attracted by the presence of food, so there are more snakes where small rodents, lizards, frogs and toads are found.
Snakes are diurnal animals; at night they mostly stay in shelters. Since they do not have poison and are quite weak, they are hunted by small mammals, for example, hedgehogs, cats, foxes, snakes and others. The size of reptiles depends on gender - females are slightly larger than males and can reach up to a meter in length.
The note. The longest snake seen in the forests of Russia reached almost three meters in size.
They reproduce in early summer, hiding the laid eggs in burrows. Animals love warmth; they can often be found basking in clearings, stumps, and various heaps.
On sunny days, the reptiles are quite active, hunt among grassy vegetation, avoid meeting people, and upon contact, as a rule, they flee. Snakes are good swimmers and can spend long periods of time under water; for example, water snakes are good at fishing.
In spring and autumn they are less active due to cold air. In winter, several individuals gather, forming clubs, trying to find shelter under stumps and in hollows, but they can also be under floor niches, in basements, if these rooms are rarely visited by people.
Difference between vipers (black - Nikolsky, gray - steppe) from snakes (water and common)
The color of the common grass snake can vary from light gray to tarry, so it is not surprising to confuse it with a viper, which often happens during an unexpected encounter. But distinguishing the first from the second is quite simple.
Just pay attention to the distinctive characteristics below:
- The presence of yellow or orange spots on the back of the head, but this only applies to the common grass snake (see photo in the table below).
- Snakes, unlike venomous snakes, do not have a triangular head shape because they do not have venom glands. The head is oval, does not stand out much and blends smoothly into the body.
- All grass snakes have round eye pupils. Among the representatives of vipers they are cat-like - narrow and vertical.
- Color. Snakes are distinguished by a shiny tint, while vipers are matte (with the exception of Nikolsky’s black viper).
Table. Types of snakes in Eurasia:
| Name and what it looks like | Main differences | Distribution area | Danger to humans |
| There are two yellow or orange spots on the head, the color ranges from gray to black | Temperate latitudes of Eurasia. Found everywhere except in big cities. | Can bite, not poisonous. | |
| Unlike the above, representatives of this species do not have yellow “ears”, instead there is one black V-shaped spot. Snakes are usually olive-colored with dark, large dots arranged in a checkerboard pattern. | Europe (south), Transcaucasia and Central Asia. Lives near bodies of water where it hunts. | Can bite, not poisonous. | |
| The front part of the body resembles the color of a tiger, the main part of the body is green with black stripes. Poisonousness depends on the food: if an animal eats a lot of toads that have toxin in their skin, then the snake is poisonous and can attack, otherwise it is less aggressive and tries to run away. | Primorye, Khabarovsk Territory, Korea and Eastern China. | There are toxins, but they are not lethal. If the bite is deep, the poison will enter the bloodstream, which will cause a reaction in the body similar to a viper bite. |
Danger to humans
Of the three species presented in the table, the tiger snake can be dangerous; the rest, although they can bite, do not contain poison. All these snakes can live close to a person, but they themselves never attack first.
The most common individual is one that has two yellow spots or “ears,” as people most often say. This is the most widespread species, representatives of which are found in significant numbers in forests and coastal areas.
The animal avoids humans, and when they meet, they try to hide. If he fails to do this, then most likely he will take a defensive position - he will curl up in a half ring, hiss and throw himself.
In this case, you are more likely to get a bite. If his actions are not successful, the animal will begin to pretend to be dead, turning its belly up, opening its mouth wide, and will lie motionless for some time, and then again try to run away.
The snake is easy to catch. To do this, you can lightly press it down with a stick or grab it by the tail. As soon as he calms down and stops behaving aggressively, you can pick him up.
Note. The common one has an unpleasant, persistent odor. When caught, it releases even more foul-smelling substances, and it is also possible for the snake to defecate on a person. All these are natural defense mechanisms developed by nature. Without soap, it will be difficult to get rid of the smell, which must be taken into account if you want to play with the animal.
In the water, until it is picked up, it will not be able to bite, since there is no support for this, but if it ends up on the shore or is squeezed in the palm of your hand, then the animal, depending on its disposition, can cause trouble, which does not happen often. In all cases, the snake bites a person through his fault. If you do not touch the reptile, then it will not attack.
Peculiarities of tiger snake behavior
The pattern of behavior of representatives of this species is similar to its relatives, but with the difference that its aggressiveness will depend on its nutrition. Toxic substances from poisonous frogs that an individual feeds on can accumulate in the glands, so the more such animals in the diet, the higher the degree of aggression.
When encountered, the tiger snake takes a defensive position, hisses, and a small hood is blown out in the chest part of the body, like a cobra. These snakes have small teeth, unlike vipers and other dangerous crawling reptiles, they do not have poisonous fangs.
When bitten, as a rule, the front teeth penetrate the skin, which does not cause significant harm, but if toxins from the back teeth enter the bloodstream, severe swelling, dizziness and nausea develop. In essence, the symptoms will be the same as with a viper bite, however, death is unlikely. In this case, the victim should move less (preferably lie down), drink as much fluid as possible to reduce the concentration of harmful substances and remove them from the body as quickly as possible.
Important. The administration of an antidote in the form of serum is recommended only in exceptional cases, for example, with bites in small children, weak old people, or if a person develops a severe allergic reaction. For a healthy person, this will not be necessary, because the medicine itself is a foreign protein, which can provoke an increase in the negative reaction.
If the clinic does not have serum against tiger snake bites, the patient will be prescribed symptomatic therapy:
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- analgesics;
- diuretics;
- medications to eliminate the negative effects of poison on internal organs, which the doctor prescribes according to indications.
As a rule, negative manifestations do not last more than three days; the affected person recovers completely within 4-5 days.
Species: Natrix natrix (Linnaeus) = Common grass snake
Common grass snakes begin mating at the end of April - May, immediately after the first spring molt.
In July - August, females lay in one portion from 6 to 30 soft, parchment-covered eggs, which are often glued to each other like a rosary. Since eggs can easily die from drying out, female snakes lay them in moist, but well-retaining shelters: under fallen leaves, in damp moss, heaps of manure and compost, abandoned rodent holes, rotten stumps. If there is a lack of suitable shelters, several females sometimes lay eggs in one place. An interesting case is described when over 1,200 snake eggs, arranged in several layers, were found under an old door lying in a forest clearing.
It has been established that the grass snake embryo goes through the initial stages of development in the mother’s body, therefore, in newly laid eggs, the pulsation of the embryo’s heart is noticeable even with the naked eye. Despite this, the incubation of eggs lasts about 5-8 weeks. Young snakes that have just emerged from eggs are about 15 cm in length. They immediately scatter in all directions and begin to lead an independent lifestyle. Young snakes lead a much more secretive lifestyle than adults, so they are relatively rarely seen by humans.
Common snakes go to winter relatively late, in October - November, when night frosts already begin. They take refuge in deep rodent burrows or cracks in the ground, under the roots of rotten trees and in other secluded places. Sometimes they overwinter alone. As a rule, common snakes overwinter in groups of several individuals together, without avoiding proximity to snakes of other species. Winter hibernation of snakes in Eastern and Northern Europe lasts up to 8-8.5 months, and in the south of the range it is slightly less.
Awakening from hibernation occurs in March - April, when on warm days snakes begin to crawl out of their winter shelters and bask in the sun for a long time. At this time, they sometimes gather into balls of many individuals together. As the temperature rises, snakes become more active and gradually creep away from their wintering places.
The diet of snakes is based on small frogs, toads and their tadpoles. Occasionally, lizards, small birds and their chicks, as well as small mammals and their newborn cubs become prey for snakes. Young snakes feed more on insects. Common snakes practically do not feed on fish, preferring tadpoles and juvenile frogs, and small fish are eaten rarely and in small quantities, even in waters rich in fish.
A large snake can swallow up to 8 frogs or large tadpoles of a lake frog in one hunt. At the same time, frogs that are pursued by snakes behave in a special way. Although they could easily escape from the snake with large jumps, which is what frogs do when escaping from other enemies, here for some reason they make short and rare jumps. At the same time, they emit a different sounding cry, completely different from their usual “croaking”. This cry is more reminiscent of the plaintive bleating of a sheep. The pursuit of such a doomed frog rarely lasts long, and very soon it overtakes its victim, grabs it and immediately begins to swallow it alive. Usually he tries to grab the frog right away by the head, but often he fails, and he grabs it by the hind legs or side and begins to slowly pull it into his mouth. At the same time, the frog beats hard and constantly makes croaking sounds. If he swallows small frogs easily and quickly, then he sometimes has to spend several hours eating large individuals.
When a snake that has recently eaten is in mortal danger, it usually belches, like other snakes, the swallowed prey, opening its mouth very wide if the swallowed animal was large. Cases have been described in which snakes regurgitated live frogs, and those frogs, despite having been in the snake’s throat, later turned out to be quite viable. Snakes, like other snakes, are able to go without food for a long time, and once went without harm for more than 300 days. But snakes drink a lot, especially on hot days.
Snakes have a lot of enemies, both among birds of prey (snake eagles, storks, kites) and among predatory mammals (raccoon dogs, foxes, minks, martens). Even gray rats are serious enemies of snakes, eating clutches of eggs and young snakes. Snakes always try to escape from humans, but not being able to crawl away, they sometimes take a threatening pose. Curled up in a ball, they throw their heads forward from time to time, accompanied by a loud hissing sound. Snakes bite only in extremely rare cases, only after being caught, causing light, quickly healing scratches with their teeth.
Almost the only and very effective means of protecting snakes should be considered the extremely smelly yellowish-white liquid that they release from the cloaca. The caught snake in many cases quickly stops resisting, regurgitates the recently eaten prey, if any, from the stomach, and then completely relaxes the body, opening its mouth wide and sticking out its tongue. This state of “imaginary death” quickly passes if left alone or thrown into water.
Many people are interested in whether it is poisonous or not. If so, which species are dangerous and where are they found? And also first aid for a snake bite. There are several types of snakes, but in our area only the most common snake, the Common Snake, is mainly found. These snakes are buttery green in color with dark stripes, have round eyes and reach approximately 100-130 cm in length. They usually live near water and wetlands. Snakes eat insects, small fish, frogs, and rodents.
Common snake
Eggs are laid in early summer, and the young emerge closer to autumn. People generally no longer attack people; this is done by vipers, which are very similar to them and therefore they are often confused. There were, of course, cases when it bit a person, but these bites are not dangerous even during the mating season. Most often, for the purpose of self-defense, these reptiles emit a foul odor or pretend to be dead. Thus, it is clear that ordinary snakes are in no way dangerous to people and they are not poisonous. But there is still a species whose bite can take your life.
Breeding snakes
The main mating season is spring, but sometimes autumn mating is also observed. In general, snakes appear quite early after wintering. There is still snow everywhere in the forest, and somewhere on the edge, in clearings, you can find a snake curled up in a tight ball, basking in the rays of the spring sun. In such warm, wind-protected areas in the spring, males and females meet to procreate. In the most favorable places in good weather you can meet several pairs at the same time. Sometimes a female attracts several males at once - up to 20 applicants have been observed courting a single female. In this case, a group of snakes is formed, which is sometimes called a “mating ball.” At the same time, the rivals do not fight each other, much less bite. They only seek to prevent each other from taking possession of the female.
Courtship behavior in common grass snakes is simple. The male, approaching the female, periodically nods his head, then usually crawls onto her or presses tightly to her side, wrapping his tail around her tail. The male snake does not hold his partner with his jaws, as some other snakes do. During mating, snakes lose their usual vigilance, and you can get very close to them.
Common snakes reproduce by laying eggs that have different shapes - either oblong, elongated, or more rounded, and sometimes pear-shaped. The length of the egg is from 2 to 4 centimeters, the diameter is 1-2 centimeters. The eggs are covered with a white, leathery film, which is moist and sticky immediately after laying. This shell consists of microscopic fibers of various structures, which are impregnated with sticky protein. Thanks to this, the eggs stick together and stick to surrounding objects. After drying, the shell becomes denser and it is quite difficult to separate the eggs or remove them from the clutch. Such strong, non-crumbling masonry ensures better preservation of eggs and protects them from moisture loss.
The clutch size depends primarily on the age of the female. Young snakes lay 8-15 eggs, older ones - about 30. The record clutch consisted of 105 eggs.
For successful incubation of eggs, the female chooses a moist, warm place protected from the sun, most often heaps of loose substrate - peat, leaves, sawdust, etc. There, easily pushing apart, for example, foliage with her body, she builds a chamber and lays eggs in it in a compact heap. If an object lying on the ground (for example, a rotten tree trunk) is selected for this purpose, the eggs are laid in an elongated layer. Places with the most favorable conditions for laying eggs attract many females, and then mass clutches occur, which are widely known specifically among common grass snakes. Up to three thousand eggs were found in them, laid by many females.
A “public” incubator can be located in one place for several years. Sometimes mass clutches are found near human habitation. Once such masonry was made in the cracks of the stone wall of an old house. And when hatching began, the residents were subjected to a real invasion of newborn snakes. Frightened people killed more than 1,200 people.
Depending on the environmental temperature, the incubation period lasts one to two months. When ready to hatch, the chick has developed a special egg tooth, with which it makes several cuts in the shell of the egg and opens the exit to the outside. When it first sees the light, the baby snake carefully pokes its head out and, at the slightest danger, hides back into the egg. Only after making sure that nothing threatens him does he slip out of the shell.
The length of newborns is 14-22 centimeters; in color they practically do not differ from adult individuals. In nature, they immediately begin to feed on baby frogs, as well as earthworms and insects. They become sexually mature in the third or fourth year of life. The life of each common snake is associated with a certain space - an individual area in which it spends the main part of its active season from year to year. Such an area has an area of several hectares, and there are shelters, hunting and resting places well known to the snake. The individual territories of individual individuals overlap widely, since the snakes do not defend their possessions in any way. They may leave their areas for wintering shelters, but return back in the spring. Female grass snakes also migrate to egg-laying sites.
Tiger Snake
Yes, it is Tiger Snakes that are poisonous. If their saliva enters the human blood, poisoning will occur, the symptoms of which are similar to those of a viper bite. This snake also reaches about a meter in length, its physique is similar to ordinary snakes. The only thing that distinguishes it is that under the skin of its back, behind its head, it has about 19 pairs of nuchodorsal glands; they are visible from the outside as small ridges on the skin. There are two teeth in the mouth, which are greatly enlarged, bent back and separated from the rest of the teeth by a gap.
Tiger snake
They are the ones who bite through the prey. The Tiger Snake lives in Korea, Eastern China and the islands of Japan. But several years ago he was spotted in Russia, in the Yaroslavl region. Then this news caused a lot of panic among local residents. They were afraid to go out into nature, walk in forests and parks, because in our country there is not even an antidote for this snake. There were also deaths. Scientists biologists said that this species crossed with ordinary snakes and therefore multiplied greatly. But it seems that in 2020 nothing was heard about Tiger Already. Most likely it became extinct in our climate, so there is nothing more to be afraid of.
Forecast and consequences
With proper first aid, the prognosis is favorable. But incorrect therapy can lead to serious consequences. When bitten by a tiger snake, death is possible. There is also a danger of wound infection. If the abscess is large, it may be necessary to amputate the affected limb.
If a few days after the bite the victim’s body temperature rises, the bite site becomes red and swollen, you should seek help from a doctor as soon as possible. There is a serious threat to life.
If a few days after the bite the wound begins to hurt and swelling appears, you should not hesitate to see a doctor.
How to protect yourself from a snake bite
Despite the fact that the bite of a common snake in most cases does not pose a serious threat to life, it is unpleasant to encounter a reptile. You can easily protect yourself from injury. He will never bite just like that. Even when meeting a person, the snake will prefer to crawl away as quickly as possible. Therefore, if you had to deal with a snake, you need to behave calmly and not make sudden movements.
You definitely shouldn't do this:
- trying to pick up a snake;
- catch it with a stick;
- run after a reptile;
- throw stones at the snake.
It will definitely bite if you step on it. Such snakes live near ponds in tall grass. Therefore, it is better to walk in such areas in high rubber boots.
The tiger snake, in terms of the structure of the skull and the location of the poisonous teeth, belongs to the posterior sulcatated snakes; it’s just that the large teeth are located in the depths of the oral cavity.
First aid for a bite
If, nevertheless, someone is unlucky and he meets a Tiger Snake on his way, which bites him, then he needs to immediately call a doctor, and until he arrives:
- Take a horizontal position and try not to move;
- Let someone take care of sucking the poison out of the wound. This can be done using a rubber bulb, syringe, pipette. But if they are not at hand, then you can do it by mouth, if there is no damage to the mucous membrane;
- Treat the wound with alcohol;
- Bandage it tightly;
- To drink a lot of water.
But even despite whether a person has been bitten by a poisonous person or not, it is still better to immediately contact a specialist to be absolutely sure that there will be no consequences.
Already is a fast and agile snake. There are signs by which you can distinguish a grass snake from a viper. Experts and terrarium owners talk about the intelligence of snakes, but advise remembering that not all snakes are harmless.
Common snake, photo by Marek Szczepanek
Symptoms
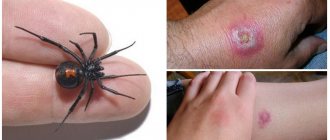
Dangerous consequences develop if a person develops an allergic reaction to the saliva of a reptile. Most people compare a snake bite to an injury from a cat's claws. Teeth marks appear on the body - red dots. Slight hyperemia and edema may be observed in this area. The first few minutes after the bite, blood will ooze. The discharge can be quickly stopped. The difference between a poisonous snake bite is that a person additionally experiences a strong burning sensation at the site of injury. Pain appears within 10–15 minutes.
If a person develops an allergic reaction after being bitten by a grass snake, the swelling will be more pronounced. In addition, itching will appear at the site of the bite. To avoid complications, the patient must receive medical assistance as quickly as possible. There is a high risk of developing angioedema.
I personally had to deal with a situation where, after being bitten by a snake, my brother’s leg became very swollen. The swelling subsided within 20 minutes after taking the antihistamine, even before the ambulance arrived.
At the site of the bite you can see puncture points from teeth
The bite of a tiger snake poses a great danger to health. These snakes have venom in their back teeth. There have even been recorded cases of death after a bite from such a reptile. The poison is especially dangerous for children and pregnant women. The patient exhibits signs of severe poisoning, such as:
- severe itching in the bite area;
- labored breathing;
- muscle spasms;
- limb spasms;
- significant increase in body temperature;
- general weakness and dizziness.
Symptoms will be more pronounced in weakened patients, as well as people prone to allergic reactions.
How to distinguish a grass snake from a viper?
Eyes.
The pupils of snakes are round, while those of vipers have the shape of a transverse “stick”. A characteristic feature of most snakes are well-developed eyes:
They have a round oval or vertical pupil, like a cat's, and often have a brightly colored iris, which usually harmonizes well with the overall coloring of the body. Snakes, which search for their prey mainly by sight, have greatly enlarged eyes, adapted to react to moving objects (Animal Life, Volume 5).
So: the pupils of snakes are round, and those of vipers are in the shape of a stick, which is located across the body.
Coloring.
The coloring of snakes is varied.
Among them there are snakes of dark olive, brown, brown and even almost black color. Some snakes have variegated skin with bright patterns. It is possible that this is the protective nature of the coloring, the desire to imitate poisonous snakes. The snake family is numerous. Therefore, in order not to confuse a snake with a poisonous snake, you need to know the characteristics of exactly those species that are found in a particular area. Let's look at three species of the genus Snakes
(
Natrix
) of
the
subfamily
Colubrinae .
Common snake
“It is well distinguished from all our other snakes by two large, clearly visible light spots (yellow, orange, off-white) located on the sides of the head. These spots have a crescent shape, and are bordered in front and behind with black stripes. There are individuals whose light spots are weakly expressed or absent. The color of the upper side of the body is from dark gray to black, the belly is white, with irregular black spots” (“Animal Life”, volume 5).
Perhaps this advice from a famous snake catcher will help someone:
It was quite simple to distinguish a snake from a viper: the snake has sharp yellow or red spots on its head, similar to ears, and its body is monochromatic - dark gray or black. Vipers do not have “ears” on the head, the body is gray or red, and a zigzag stripe stands out sharply on the back (A Nedyalkov. Naturalist in search).
Water snake
painted differently. This snake differs from the ordinary snake, although it often coexists with it.
The color of its back is olive, olive-gray, olive-greenish or brownish in color with dark spots located more or less in a checkerboard pattern or with narrow dark transverse stripes. There is often a dark spot on the back of the head, shaped like a Latin letter V, pointing towards the head. The belly is yellowish to reddish, mottled with more or less rectangular black spots. Occasionally there are specimens completely devoid of a dark pattern on the body or completely black (“Animal Life”, volume 5).
Zmeelov A. Nedyalkov warns that it is dangerous to rely only on the color of the snake’s skin. One day, a viper taught him a lesson that could end in tragedy:
I did not yet know that there were vipers painted solid black, and I almost paid a heavy price for my ignorance.
One day I was walking through the forest after rain and saw that the black body of a large snake stretched across the path. The snake's head was hidden in the grass. The black body means it's not a viper, but... I really needed a big one, so I bent down and, without any precautions, took the snake by the body with my bare hand. The snake hissed. Snakes usually do not hiss when picked up. My catcher’s reflex kicked in, and with my other hand I grabbed the snake by the neck so that it couldn’t reach me with its teeth. I look and her pupil is in the shape of a stick. Viper!
What saved me from being bitten was that the viper was very chilled after the rain, and chilled snakes are rather sluggish and clumsy (A Nedyalkov. Naturalist in search).
Tiger snake
, which is found in the Far East of Russia (as well as in Northern China, Korea, Japan), is brightly and elegantly colored:
The back is dark green or dark olive in color (occasionally blue specimens are also found), mottled with more or less clear black transverse stripes or spots, gradually decreasing in size as they approach the tail. In the anterior third of the body, the spaces between the black spots are painted a bright brick-red color. Under the eye there is an oblique black, wedge-shaped stripe, with its apex facing downwards, another black stripe runs from the supraorbital shield to the corner of the mouth. There is a wide black collar on the neck, or there is one triangular-shaped spot on each side of the neck. The upper lip is yellow, the eyes are large and black (“Animal Life”, volume 5).
Smell.
Snakes have one more difference from other snakes. Alarmed snakes smell disgusting:
The snake waved its tail and doused me with a stream of whitish, stinking liquid. The stench was terrible: a mixture of garlic fumes and some kind of chemical substance. I almost vomited, but I still threw the snake onto the shore. For an hour and a half I rubbed my skin with soap, sand, and alcohol, but I couldn’t remove the smell (A. Nedyalkov “Dangerous Paths of a Naturalist”).
It is believed that in those places where snakes are found there are no vipers. It's a delusion:
In addition to vipers, snakes were also found near the ditches. They say that snakes are at enmity with vipers and kill them. I have seen more than once how a grass snake and a viper lie side by side and calmly bask in the sun. And I never saw them fight (A. Nedyalkov “Naturalist in Search”).
Types of snakes
There are many different snakes, but the most common in our country are these three species.
(Natrix natrix
) is found in Europe (except for the Far North). It is a black or dark gray snake measuring up to 1.5 m (usually 1 m, females are noticeably larger than males) with two yellow or bright orange spots on the sides of the head. The snake can be found in overgrown bushes near water, in damp forests and swamps. The common snake sometimes settles near people’s homes: in heaps of garbage in the yard, in sheds, stables, cellars and poultry yards. It often hangs onto chickens and ducks or crawls into stables and barnyards. The snake even lays eggs here that resemble those of a pigeon. A dinner egg is filled with a yolk inside, surrounded by a thin layer of white. The eggs are covered with a leathery shell. The female lays eggs bound into “beads” by a gelatinous substance. Oviposition can be found in manure heaps, in a heap of dry leaves, damp moss or in loose soil. There can be 15 - 17 eggs (less often up to 30 pieces). About three weeks pass, and the cubs are born. The length of a snake that has just hatched from an egg is about 15 cm. It is capable of eating worms, snails and various insects.
The common snake spends the winter on land: it hides in old burrows made by mammals, climbs under the roots of trees, etc.
Water snake
(
Natris tesselata
) lives in the southern regions of Russia, as it is more thermophilic than the common one. There are many such snakes in the Volga region and on the Don. The water snake is often seen in Crimea (especially on the Kerch Peninsula). These snakes stay near water, not only fresh, but also salty. They swim well (even in big waves) and dive. They feed on frogs, tadpoles, small fish (gobies) and even shrimp. Less commonly, small mammals and birds. To make it easier for the snake to swallow the fish, the snake holds it in its mouth and swims to the shore. There it finds support for its body, sits comfortably near it, and then begins to swallow its prey. These snakes hide from the heat underwater. Snakes sleep in dry grass, in hay, climb into rodent holes, and under stones. In the morning, water snakes slowly crawl onto the banks of rivers and reservoirs. Snakes hibernate under rocks, in crevices and in dense bushes.
Already brindle
(
Rhabdophis tigrina
) in Russia is found in the south of the Far East (Primorsky Krai, near Khabarovsk) in wet areas near water, in forests and meadows. They are seen even in cities. The length of the snake is about 110 cm. It feeds on frogs, toads, small rodents and fish. This snake is considered conditionally venomous, as its poisonous teeth are located deep in the mouth (on the back of the maxillary bone).
For humans, tiger snake bites, usually inflicted by short front teeth, pass without a trace. However, in cases where the bite is inflicted by the enlarged posterior maxillary teeth lying deep in the mouth, and saliva and the secretion of the upper labial glands enter the wound in large quantities, severe poisoning can occur, not inferior in severity to that from the bite of real poisonous snakes (“Animal Life, Vol. 5).
Snake nutrition
Snakes are excellent swimmers and often get their food not only on land, but also in water. The diet of snakes mainly consists of small vertebrates: amphibians and reptiles. However, there are lovers of rodents, birds and fish. Frogs are a delicacy for snakes. He catches them in the water and on the shore. A hungry snake swallows several small frogs at once. In the water, it also hunts tadpoles and fish.
Watching him eat is unpleasant. He swallows frogs alive, just as some people swallow live oysters. The discrepancy between the sizes of the frog and the snake makes the process of eating a terrible sight - the snake’s large mouth with a small head, a thin body in which the swallowed frog sticks out like a terrible knot... As a child, I once came across a snake with such a knot on its neck. I poked it with a stick - a live and unharmed frog jumped out from inside, it was still crawling, but it was completely white: the stomach juice of the snake had discolored it (Hans Scherfig “The Pond”).
The snake is said to hypnotize its prey. Externally it looks exactly like this. A. Nedyalkov saw with his own eyes how the frog obediently approached the snake:
I have been told many times that snakes hypnotize frogs. But this time the “hypnosis” did not take place. To see everything better, I pulled away a branch of the bush. The frog noticed the movement of the branch and made a desperate leap, turning over its head in the air. He continued to lie motionless. Looking closely, I saw that from time to time he threw out a forked tongue from his closed lips. I didn’t bother the snake and returned to my place. About five minutes later, near the same bush, the frog purred again. I approached the bush again. He was already lying in the same place, and the frog was purring again and approaching him. She did not jump, but, carefully moving her paws, crawled the way soldiers crawl on their bellies. This time I did not move the branches, and soon the frog approached the snake at a distance of twenty centimeters. Suddenly it rushed towards the frog and grabbed it by the end of its muzzle with its mouth. The frog struggled, but could not escape. Moving his jaws, he grabbed her tighter and tighter. The frog no longer purred, but desperately scraped the snake’s head with its paws. The snake's jaws kept moving and moving. The frog's eyes were already at the very edge of its mouth. I felt sorry for the frog, and I pushed the snake with the end of the grabber. He didn’t immediately let go of his victim. Only after I squeezed his neck quite hard with my grip, did he open his mouth and the frog escaped. She immediately jumped into the grass, and then slid into the thick of the bush... I don’t think he hypnotized the frog. Most likely, she noticed his moving tongue, mistook this tongue for a worm, wanted to eat this worm and herself became the prey of the snake (A. Nedyalkov “Naturalist in Search”).
Handmade
Snakes have been kept in captivity since ancient Roman times. Then they caught mice. Nowadays, there are also hobbyists who keep snakes at home. They advise designing the terrarium as a “forest + pond”. It is advisable to feed snakes with frogs and live small fish. Snakes are considered intelligent snakes that can get used to humans. This is what Hans Scherfig recalls about something he already knew in his book “The Pond”:
He was so sweet and friendly. A real pet snake that was not afraid of people. He even got rid of his old bad habit of hissing and emitting an unpleasant odor when you touch him. Frightened snakes smell like garlic.
© Website, 2012-2019. Copying texts and photographs from the site podmoskоvje.com is prohibited. All rights reserved.
(function(w, d, n, s, t) { w[n] = w[n] || ; w[n].push(function() { Ya.Context.AdvManager.render({ blockId: "RA -143469-1", renderTo: "yandex_rtb_R-A-143469-1", async: true }); }); t = d.getElementsByTagName("script"); s = d.createElement("script"); s .type = "text/javascript"; s.src = "//an.yandex.ru/system/context.js"; s.async = true; t.parentNode.insertBefore(s, t); })(this , this.document, "yandexContextAsyncCallbacks");
Already
- a snake belonging to the class of mammals.
Many of us are terribly afraid of snakes, but should we be afraid of an ordinary snake
? Is it dangerous for humans and does it have poison? Today we will answer these questions, and also touch upon the snake’s habitat and find out what it eats in nature, and we will start with its characteristics.
Description of a common snake
Snake length
1 meter, but some individuals grow up to 1.5 meters.
Its main and characteristic feature
is bright spots on the back of the head.
They can be orange, yellow and whitish. Quite rarely, only black snakes or faint spots are found, so it is quite easy to recognize the snake. The skin
of the snake is dark gray, black or light gray.
Gray individuals may have dark spots. belly
is light with a dark stripe from the tail to the neck.
The body of the snake
is slender, and on some individuals you can see paired brushes, but not on all.
eyes
are round, but there are snakes with “cat eyes.”
The tail
is much shorter than the body, about 3-5 times, with a varied shape - sharp, steep, rounded.
Scales
are visible throughout the body , some individuals have smooth skin, others have visible ribs.
The snake has teeth on the top of its mouth, several teeth increase along the opening of the pharynx, some have teeth
, others have them bent, and also have a forked
tongue
.
The lifespan of an ordinary grass snake
in nature is about 20 years; at home, the figure remains the same.
Is the common snake poisonous and is it dangerous for humans?
Overall, snakes
safe for humans.
They do not know how to bite, but can scratch the skin, and if there is a bite, it is insignificant. And an ordinary snake
, when it sees a person, tries to hide as quickly as possible; it flees and does not attack.
But if they are caught by surprise, they hiss and turn their heads as if they want to bite, but they rarely get bitten, and the bite itself heals very quickly. snake
is a calm snake, but for the purpose of protection, it can shoot a white-yellow liquid from its teeth, which has an unpleasant odor, and if it does not scare away the observer, it opens its mouth and relaxes its body, feigning death.
At this moment, you can see drops of blood from the throat, or he will simply regurgitate food out of fear. But if you
don’t touch it, you won’t have to see all this.
WHAT DOES THE COMMON SNACK EAT, WHERE DOES IT LIVE AND KEEPING AT HOME?
What does the common grass snake eat in nature?
Snake's main diet
- amphibians and fish.
It feeds on frogs, tadpoles, and toads. In addition, snakes eat lizards, their eggs, mice, rats, moles, other rodents, insects, small birds, their eggs and chicks, bats, small squirrels, and even their own kind or other snakes. The grass snake
swallows its prey whole because it does not have teeth or other devices to tear its prey.
If the lunch is small, then he will quickly finish the meal, but if the prey is large, he will have to deal with it for several hours, and after such a meal he can go without eating anything for two days. It can go without food for a long time, but it cannot live without water, and in hot weather it is easy to find it near bodies of water. On
land it stalks its prey, in water it can sneak up on it for a long time, and then suddenly pounce.
Habitat of the common grass snake
Snakes can be found
near bodies of water, under a bridge, near a lake or pond.
In addition, they like to settle next to people, choosing quiet and secluded places such as a basement, haystack, cellar, barn, in the roots or hollows of trees, in the garden, in firewood, in a pile of stones, in a vegetable garden and even in a pile of garbage . Snakes
love warm bedding and live next to poultry, laying their eggs there, but they will never go to large animals.
Habitat of the common grass snake
– almost all of Russia, eastern Primorye, the borders of the Komi Republic, the border of Karelia.
Almost all of Europe, and some snakes also
found in Africa, Central, South and North America, Australia, Asia, Cuba, Indonesia, the Philippines, Japan, and Oceania.
VIDEO: ABOUT THE CONTENT OF THE COMMON SNACK
IN THIS VIDEO, YOU WILL SEE AND LEARN HOW TO CORRECTLY KEEP A COMMON SNACK AT HOME
A trip to the forest to pick mushrooms or just a walk in nature can give a person a lot of unpleasant moments (see). Often in forests and fields, people encounter snakes - ancient reptiles that have lived on earth for millions of years. There are quite a few varieties of snakes. Some are considered dangerous to humans (see), others cause a lot of unpleasant sensations (including pain), while others do not pose any threat to human life at all. It is very important to be able to distinguish dangerous snakes from harmless ones, so many people have a question: is the snake poisonous?
Snakes are often confused with vipers, and this ignorance of the variety of snakes becomes dangerous for humans (see). Much more muscular and larger than a viper, its skin is covered with scales. The snake has two yellow spots on its head, shaped like “ears.” It is very rare to find a reptile without these identifying marks. The body is mostly a single color, brown or gray-green. Vipers have a diamond-shaped pattern on their bodies. The pupil of the snake's eye is always round, while the pupil of a poisonous viper is vertical and constricted.
When can it bite?
The snake is a common species of snake living in the CIS countries, which does not belong to the poisonous group.
At the same time, a reptile bite can cause serious health problems. In some cases, a severe allergic reaction develops that is life-threatening. Therefore, it is important to know how to properly assist the victim. Snake bites can be especially dangerous for children, pregnant women, and people with weakened immune systems.
The common snake is a non-venomous species of snake
As a rule, snakes do not behave aggressively. They can exist peacefully next to humans. A snake bites only when it feels danger to itself or its offspring. Often the cause of a bite is the inappropriate behavior of the person harassing the snake. If you touch a snake with a stick or try to anger it, it will defend itself.
In the summer, you can suffer from a snake bite in a body of water, where the reptile lives. The man does not look at his feet and steps on the grass snake. The snake triggers a defensive reaction. In this regard, bites are most often detected on the legs. In preschool children, bites can occur on any part of the body. A child tries to pick up a snake and is injured as a result. In nature, it is necessary to supervise children with increased attention.
The tiger snake is a type of venomous snake. A reptile bite can be fatal. In Russia, such reptiles are rare. You can meet them in the Khabarovsk and Primorsky territories.
The bite of a tiger snake is fatal
Snakes become more aggressive during the mating season. This period lasts from April to May. Walking in the snake habitat at this time carries increased danger.
Many people confuse the snake with a viper, whose bites can lead to the development of dangerous symptoms. Death cannot be ruled out. If you are bitten by a snake, you must take the victim to a medical facility as quickly as possible.
Video: how not to confuse a snake with a viper
How do snakes live?
Snakes live everywhere; these snakes can be found in forests, fields, meadows, near ponds and reservoirs. The snake is about a meter long, females are larger than males, reaching a length of 1.5 meters, but large individuals have also been encountered. The largest one reached a length of about 3 meters. Reptiles feed mainly on small amphibians (frogs, lizards, newts). Juveniles hunt insects, tadpoles and small fish.
The snake tracks its prey, and then uses a throw to attack the prey. Sometimes snakes chase frogs. They grab their future food by the head or hind legs and then swallow it whole. The snake can attack small warm-blooded animals, such as rodents or chicks. They live in holes under rotten trees in a pile of leaves.
They breed from May to June. In winter, the snake hibernates. With the arrival of spring, it wakes up, sheds its old skin (molts) and begins to look for partners for mating. Shedding occurs in different ways: sometimes the snake’s skin comes off the body entirely (like a stocking). But it happens that the old stratum corneum falls off in pieces. In this case, the snakes rub their bodies against stones and trees, trying to free themselves from the old skin. A fertilized female lays eggs in a warm and damp place (a pile of rotten leaves, compost, rotten stumps). After 5-6 weeks, small snakes hatch from the eggs.
On warm sunny days, the snake loves to bask in the sun, so it can be found in the grass on lawns and fields. In nature, these snakes have quite a lot of enemies. Snakes often become prey for storks, snake eagles, and kites. Of the terrestrial predators, martens, raccoon dogs, minks and foxes are considered dangerous to snakes. In most cases, rats destroy snake nests by eating their eggs and newly hatched snakes.
Is it really dangerous for humans?
Despite the fact that it belongs to snakes, it is not poisonous. There have been many cases when these reptiles crawled into a person’s home without causing him any harm. Villagers said that snakes entered the cattle barn and sucked on the cow's udder to drink milk. The cow did not suffer from such a guest, since the snake did not bite through the skin of the animal.
Snakes love water very much. On hot summer days, snakes can be found near water bodies or ponds. The reptile feels great under water, swims quite quickly, leaving behind small ripples in the water. The snake can swim several tens of meters from the shore and stay calmly underwater for half an hour. It is quite easy to see a swimming reptile; it raises its head high from the water. If you encounter a snake in the water on a hot day, you should not be afraid of it. It is best not to touch the reptile, then it will try to stay away from the person. Snakes are very dexterous and agile, they crawl well through trees.
Do snakes have venom? The reptile has a pair of sharp teeth at the front, just like other snakes. However, these teeth do not contain any poisonous substance. The exception is the tiger snake, which has poisonous back teeth, but uses them only when swallowing caught prey. For humans, this does not pose any particular danger. The tiger snake lives in the Primorsky Territory, Khabarovsk, Korea and Japan. Since its poison is considered low-toxic, it does not cause harm to humans. In order to bite with its back teeth, the snake needs to deepthroat a person’s hand.
Attention! In Japan, there are known cases of severe intoxication of people after an encounter with a tiger snake. There were even deaths recorded! And for small children and people with allergies, tiger snake venom can be extremely dangerous. In such cases, the victim of a snake bite should be taken to a medical facility as quickly as possible.
Is a snake bite considered dangerous? The common snake, which is found in forests and fields, is harmless to people. The snake will never attack first. It takes a lot of effort to make her angry. Only to save its life can a reptile bite a person. It takes a stance, hisses loudly and lunges like all snakes. His teeth can only damage human skin, leaving small wounds in the form of scratches on it. There is nothing wrong with this; the injured person just needs to treat the snake bite site with any antiseptic. If this is not done, an infection may get into the wound and inflammation will develop.
conclusions
Is a snake bite dangerous for humans? No, if the person is completely healthy and has no allergic reactions to anything. It is worth remembering that this snake never attacks first. If a person notices a reptile of the snake family in the forest or in the water, then he just needs to let it go quietly.
The tiger snake is dangerous, but it lives mainly in the Primorsky Territory, Japan, and the Far East. Its bite can cause a serious condition for a child or an allergic person.
There is no need to be afraid of snakes. However, a person cannot always determine whether a snake is poisonous or not. Snakes are often confused with vipers. It is necessary to remember the reptile and report it to a medical professional. In a certain situation, this will help save a person's life.
The snake's bite will not cause any particular harm to the body, but is simply unpleasant. You should carefully watch your step when walking through a forest or swampy area and do not provoke the snake. Also, don't try to catch it yourself. If you want to have such a pet at home, it is better to contact a specialist who will tell you about caring for it in order to avoid negative consequences.
You go into nature and, therefore, you probably know that not only wasps, mosquitoes and ticks are waiting for you there. There are also snakes there. They are not as harmless as they seem at first glance. Your task is to know about those species that pose a real danger. Are you sure you know everything about snakes?
Don't know if snakes bite? Would you like to know more about them? Today we will tell you about these common reptiles. In our article you will learn everything about the snake, how to distinguish a snake from another snake and much more.
Where do their different species live?
In nature, near a lake or in a forest in summer or autumn, how can you recognize a snake? By yellow “ears”, but not all species of snakes have them. This melanistic species has no markings and is completely black. If you encounter a snake on the water, make sure it is not poisonous. Did you know that snakes feel free in water? They are especially fond of lakes, ponds and swamps. Here's where to find this reptile to show your kids.
Why are snakes dangerous?
Are they poisonous to humans? We answer: no, these snakes are not poisonous. Can it bite a person? Yes, and the wound after a bite can become inflamed. Even though snakes bite, basic caution will help you avoid unpleasant consequences. These reptiles are kept at home.
How to catch a snake safely? To avoid being bitten, protect your hands. This non-venomous snake can feign death. If he has already rolled over on his back, carefully pick him up. No special devices are needed.
How do snakes differ from vipers?
Most snakes belong to the family Colubridae. They are found on all continents. Among the colubrids there are snakes that live in water.
The viper is larger and longer. The color of a venomous snake is usually gray or black. The characteristic pattern on the skin is a zigzag all over the body, diamonds, and the belly is yellow. There are two teeth on the front edge of the jaw. In the viper they are poisonous.
This snake is not aggressive and rarely bites. You can safely pick it up. The yellow-eared one is also useful; it hunts small rodents. Poisonous snakes compete with non-venomous ones, so where these reptiles live, as a rule, there are no vipers. The only thing you should be wary of is the tiger snake - there is poison on its back teeth, which are located deep in the mouth.
Watch a video on Youtube about snakes and vipers, the differences are clearly visible. We'd love your advice on how to tell this harmless snake apart from the venomous snakes of your friends. So that when they relax in nature in the spring, they feel calm.
Or maybe some of you would like to get a snake at home? We promise to write articles on how to keep snakes at home. Expect it soon. It is very fashionable to have such exotic animals at home. Snakes are unpretentious, especially non-venomous ones. And they feed mainly on small rodents. If you find this advice useful, share it on social networks and write below in the comments if you have ever had unusual situations with snakes?
The snake is one of the types of snakes that do not belong to the poisonous group. However, the bite of a snake that attacks a person when its life is threatened causes the development of a complex symptomatic picture.
Most often, the reason for a snake attack is the inappropriate behavior of the person pestering the snake - touching the reptile with a stick, trying to anger it in every possible way.
Sometimes it happens that, being in the habitat of reptiles - a pond, in swamps, a person does not look at his feet, stepping on a snake. Children are often bitten when they try to grab the snake, and in defense of itself, the reptile bites its offenders.
The only species of snake that is poisonous is the tiger snake; its bite can cause death without timely assistance.
The habitat of the tiger species is Korea, Japan.
Snakes are fairly peaceful snakes. They calmly coexist with people, will never attack first, preferring to crawl away or pretend to be dead. The only thing a snake can do to scare you is its feces, which it releases when threatened, which is characterized by a foul odor. Often this reptile releases its feces onto humans.
Warning that it may attack, the snake begins to hiss loudly, sticking out its tongue. If you leave her alone at this moment, the matter will be limited to such threats.
The poisonous tiger snake behaves in the same way, with the only difference that when it bites, it releases a toxic substance, which is a rather dangerous toxin for the human body.
Many people often confuse a harmless snake with a viper, the bite of which provokes severe symptoms. If a snake has bitten and the victim is not sure what it was, it is recommended to take the victim to the hospital as quickly as possible and describe to the doctor exactly what the reptile that attacked the patient looked like.
Seeing a snake in their summer cottage or in the water, many begin to panic, thinking that they will now become a victim of a poisonous bite. There are a number of characteristics that can be used to distinguish snakes from other species of reptiles. These include the following:
- oval head shape;
- shiny scales;
- presence of yellow or orange spots on the head;
- round eye shape.
Despite the presence of teeth in the oral cavity, there are no sacs with poison there. The bite of this type of snake does not pose a danger to humans; the only thing that can happen is that if the wound after the attack is not properly treated, an infection can get into it, causing an extensive inflammatory process. Most often you can encounter a snake during the day, since the reptile sleeps at night.
The main source of food is frogs and small lizards.
This type of snake got its name due to its color similar to the fur of a tiger. Along its entire length, the reptile has muted orange stripes. Lives in China, Japan and Korea. At its core, it is not an aggressive type of snake, but if it feels threatened, it will attack. The degree of poisoning depends on which teeth the reptile used to bite the skin.
If the skin is pierced with short teeth of the front row, there will be no particular intoxication, since in this case the secretion, which contains toxic substances, does not appear. As in the case of a simple snake attack, the only thing that can happen is that the wound from the teeth gets infected.
If it is grabbed by the teeth located in the back jaw, the poison begins to rapidly enter the wound along the grooves from the teeth. Intoxication in this case will be very strong and without treatment will lead to death.
The symptomatic picture of a venomous bite from a tiger snake is the same as in most cases of attacks by venomous snakes.
First of all, the central nervous system and autonomic functions of the body suffer. Paralysis gradually appears, leading to disruption of the functioning of the heart muscle, causing heart failure, sudden cardiac arrest and death.
The only treatment method is the introduction of a special serum.
If she is not in the hospital, complex drug therapy is carried out to remove the toxin from the body. Anti-inflammatory and painkillers are prescribed, as well as drugs to relieve spasms and normalize the functioning of all internal organs and systems.
In order to avoid becoming a victim of a tiger snake attack, you must follow simple safety measures while in the habitat of these reptiles - look carefully around, do not touch the snake crawling past, do not put your hands in a pile of stones or holes.
Symptoms of a bite that are insignificant in intensity can only be observed if a person has a tendency to allergic reactions.
Clinical manifestations of a snake bite:
- teeth marks on the skin in the form of several reddish dots;
- slight bleeding from the wound site, which, in most cases, goes away on its own, without any assistance;
- itching on the skin, similar to a mosquito bite;
- minor swelling (optional symptom).
People who have been victims of snake attacks compare the feeling of a bite to the feeling of a cat digging into your skin.
A more serious clinical picture is observed when attacked by a tiger snake. A person shows signs of poisoning:
In most cases, complex symptoms after a tiger snake bite appear in children and people prone to allergic reactions.
In this case, the victim must be taken to a medical facility, since complications may develop; medicine knows cases of death.
If bitten, the victim, despite the fact that he was the victim of a non-venomous attack, needs first aid. First of all, you need to take the following actions:
- Wash the wound thoroughly under running water using soap, preferably laundry soap.
- Treat the wound with antiseptic drugs - hydrogen peroxide, Chlorhexidine.
- If swelling develops, you need to apply a cold object to the skin. This can be ice or a piece of frozen product, previously wrapped in a towel, so that there is no frostbite of the soft tissues, which provokes necrosis. If there is no ice, you can use a towel soaked in cold water, it must be constantly dipped again.
After this, the wound can be lubricated with iodine. In the future, if a person works in the garden and constantly gets his hands dirty, the wound can be covered with a bandage soaked in antiseptic and healing ointments or creams.
It is necessary to seek medical help if symptoms such as increased body temperature, severe fatigue and lethargy, extensive swelling at the site of the bite, and redness of the skin appear. These signs indicate that the wound has become infected and must be treated with antibiotics prescribed only by a doctor. In other cases, medical treatment is not required.
How not to behave when bitten by a snake? It is strictly forbidden to cauterize the wound site. Firstly, this is an absolutely useless procedure that will only cause harm by causing a painful burn on the body. Secondly, there is no longer any poison that would need to be pulled out of the wound.
The incision will cause severe swelling and redness.
How can one behave when meeting a person?
In most cases, when trying to catch a snake, a person may smell a very unpleasant odor. This is a peculiar substance secreted by the snake from its cloaca and necessary for protection from predators. The liquid has a yellow color and a strong, repellent odor, so catching a snake is not a pleasant experience.
The reptile can also depict imaginary death. Even if he recently swallowed prey, he regurgitates it, opens his mouth and turns upside down, pretending to be dead. As soon as you move a little away from the snake, it returns to its original body position and tries to crawl away. Snakes are useful reptiles, and there are no vipers in the forest where they live. These two species of snakes constantly compete in nature. It also hunts rodents, thereby exterminating their numbers.
Snakes can be kept as pets, as they are unpretentious. In captivity, the snake feels no less comfortable; it is important to bathe it on time and ensure that there is always clean, fresh water in the terrarium. Snakes very quickly get used to a person; a short time after catching a snake, it ceases to be afraid of a person and can even take food from his hands.
Natural enemies
This is a very shy species of snake. Snakes try to escape as soon as they hear strangers' footsteps. They try to escape from predators as quickly as possible.
The snake's main enemy is, first of all, man. But he also has other, natural enemies who kill the snake in order to eat it.
These include birds of prey such as gray herons and mammals such as cats, foxes and weasels. During winter fasting, even rats can eat them. Young animals are especially dangerous, since a defenseless animal is a real treat for them.
He's pretending to be dead
If a snake feels threatened in the water, it quickly moves to land. If a predator has driven her “into a corner,” she tries to change from the position of a victim to the position of an attacker. She begins to hiss and rush at the predator, thereby trying to scare away or disorient the potential threat.
When the snake does not see a way out of the situation and flight does not bring results, it pretends to be a corpse. At the same time, blood often appears from her mouth. This position allows you to disorient predators that react to movement.
If all else fails, then the snake secretes a liquid for protection. It is released through the gonads. Has a very unpleasant smell.
On very rare occasions she bites. But its bites are absolutely safe for people and pets.