Most residents of the CIS have a gas stove at home.
It is both cheaper in price than an electric stove and more convenient in everyday life: you can quickly adjust the temperature, and cooking food on a gas stove takes less time. It is important that it does not depend on interruptions and power outages. At dachas, in villages and simply in houses where gas is not supplied, gas cylinders are often used. But there is a main disadvantage of gas stoves - household gas is dangerous. It contains methane and a few other substances - odorants. Methane has no odor and burns with a blue light. If, when you turn on the stove, you feel a characteristic smell of fuel, and an orange color is added to the blue flame (in a small percentage) - your gas is diluted with cheaper impurities. However, a small admixture of odorants is necessary for a person to notice a gas leak in time. Methane is toxic and explosive if accumulated indoors. Poisoning with this gas occurs when the air a person inhales consists of more than a quarter of it. Methane affects the central nervous system and respiratory organs. There are often cases when the victim simply fell asleep, having previously made a mistake in using the gas stove and leaving a leak. In a dream, you may not notice that you are breathing gas, especially if the aggravating circumstance is alcohol intoxication. Therefore, it is very important to follow safety precautions.
Characteristics of methane
Natural gas called methane does not have any color and also does not have a specific odor. The smell that is felt when the stove is lit is due to the addition of an additive in the form of methyl mercaptan gas to the methane. But there is little of this additive in the methane mixture itself.
It should also be noted that people with a poor sense of smell may not be able to smell. In the physiological process of combustion of this gas, a blue flame can be traced. If the ratio of methane to air goes beyond a certain norm, the mixture may explode.
The weight of methane is much lighter than air itself, which is why it is impossible to get poisoned by it in the open air; methane simply rises. But there is also the so-called “second side of the coin”. In a closed room, gas can accumulate over a certain period of time and create unfavorable conditions for human health. To be poisoned by this gas, its concentration in the air of about 25 percent will be sufficient.
Also, household gas (a mixture of propane and butane) can penetrate the body, and especially the brain, at a fairly high speed. In addition to the brain, methane affects the respiratory system. The central nervous system is very strongly affected. If the effect of the gas on the body is not eliminated as soon as possible, complete poisoning and ultimately death occurs.
Causes
You can become poisoned by household gas by inhaling it. This substance penetrates into the air in different ways:
- Leaky joints of gas pipes in the apartment.
- Poorly closed stove handles.
- Malfunction of gas equipment.
- Intentional organization of leakage for the purpose of suicide or murder.
- Damage to gas hoses and pipes.
Gas leaks are especially dangerous at night. In this case, hypoxia develops during sleep, which goes unnoticed by the person. This often causes death. Moreover, the victims die without regaining consciousness.
Signs and forms of household gas poisoning
In the medical field, there are four types of gas poisoning. The signs of gas poisoning in an apartment of each type are the same.
Light degree:
headache;- secretion of tears;
- general weakness;
- sharp pain in the heart area;
- dizziness;
- increased level of sleepiness.
Medium severity level:
- damage to the central nervous system (CNS);
- collapse;
- increased heart rate (HR);
- imbalance of body coordination.
Severe degree:
- the myocardium—the muscle of the heart—is damaged;
- a person loses consciousness;
- methane toxins damage the brain;
- the lungs swell.
And the last type is instant intoxication:
- complete loss of consciousness;
- heart stops (after five minutes);
- asphyxia is observed.
Read also: Mercury poisoning: symptoms of intoxication, diagnosis and treatment
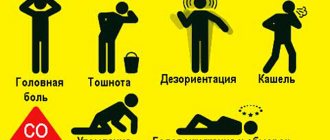
Symptoms of intoxication
Gas poisoning, the symptoms of which are numerous, is primarily accompanied by a headache that is aching or dull in nature. In addition, there is no localization of this pain. But in this case you need to be careful, because such a symptom does not always indicate poisoning, because it could be fatigue or a cold.
There is another rather serious symptom in the form of pain in the chest cavity. It is important to understand that you cannot ignore any sudden changes in your body.
Very often, with methane poisoning, one feels dizzy, loses orientation in space, and loses the ability to control one’s body. This symptom manifests itself in the form of the inability to hold anything in the hand, or simply the hand suspended, in this case the gait is of a staggering type. If the so-called intoxication increases, then consciousness becomes confused and speech disappears.
If there is too much methane in the air, then an attack of nausea is provoked, and then uncontrollable vomiting.
It is very important to realize that if you find the above symptoms of household gas poisoning, then this is a very serious reason to be wary, especially if several symptoms appear at once. You need to know that poisoning with a gas such as methane develops rapidly. From the onset of the toxin's effects on the body until the victim loses consciousness, a matter of minutes can pass. In this case, you need to leave the room and call an ambulance.
Providing first aid to the victim
Few people know that death can occur not only in the case of an immediate form, but also in other degrees of complexity of poisoning. In order to prevent this outcome, it is very important to provide correct and timely medical care to the victim.
The first thing to do in case of gas poisoning is to remember - you cannot provide assistance in the same room where the poisoning occurred. The victim must be taken to fresh air. Next you need to call an ambulance. It is necessary to eliminate the release of methane into the room and turn off all burners. If this room is an apartment, all windows and doors must be opened to allow fresh air to enter. Next you need to do the following:
- the upper half of the victim’s body must be freed from obstructive clothing;
- if the victim has lost consciousness, artificial respiration must be performed;
- place the victim on a soft surface;
- place a cold object on the forehead, preferably ice;
- In order for the blood to circulate better and remove toxins, it is necessary to place a pillow under the knees;
- let the victim smell cotton wool on which ammonia has been applied;
- the limbs, as well as the chest, must be rubbed, but not with strong movements;
- if the patient is nauseous, he must be turned on his side. This is required to ensure that the victim does not suffocate on vomit;
- in the event that a person’s breathing has not returned to normal (less than 8 breaths per minute), it is necessary to repeat the process of artificial respiration.
Read also Isopropyl alcohol: composition and applications
Only after you are sure that the sick person is recovering and there is no serious threat to his health, should you provide him with plenty of fluids. The water must be still; tea, kefir or milk will do. When the doctor examines the victim, depending on the individual characteristics of the body and the severity of the poisoning, he may prescribe certain medications that will restore the functioning of the following objects:
- organs of the body's respiratory system;
- hearts;
- all damaged vessels;
- central nervous system.
How can you get poisoned?
Violation of body functions due to the ingestion of exogenous toxins occurs when inhaling gas-containing air. Symptoms of acute intoxication develop gradually and imperceptibly, especially during physiological states characterized by a lack of response to stimuli (sleep, drug or alcohol intoxication). The risk group includes the following cases:
Domestic gas poisoning
Carbon dioxide intoxication
Malfunction of gas equipment (cylinders, pipes, valves, gas stove)
Failure to comply with safety precautions when using gas equipment (incomplete closing of the valve regulating the supply)
Staying in rooms with poor ventilation while the car engine is running (unventilated garages)
Taking intentional actions to cause a methane leak
Staying for a long time in places where there are a large number of cars with running engines (motorways, busy roads, tunnels)
Systematic inhalation of gaseous paraffin hydrocarbons (industrial premises, mines)
Untimely or incomplete closing of stove dampers (in rooms with stove heating)
Smoking a hookah with insufficient oxygen supply to the smoking device
Production workshops where carbon dioxide is used for the synthesis of organic substances
It is important to know
The process of methane poisoning is quite complex, as are the consequences. In the process of rescuing a person who has been poisoned by this gas, you must remember that lighting a fire in the same room is strictly prohibited. If you are not careful, this can lead to very negative consequences.
Under no circumstances should the victim be given drugs such as morphine or adrenaline.
You need to be careful when performing artificial respiration; you need to place a damp gauze cloth on the victim’s mouth. This is necessary in order not to get hurt yourself.
Only if all the rules are followed can all undesirable consequences be eliminated.
Treatment after methane poisoning
If gas poisoning is serious, the treatment process takes place in a hospital. To date, no drug has yet been developed, or a so-called antidote, to urgently remove toxic substances from the human body. Based on this, the medical industry has developed a therapy that consists of three stages.
First of all, the victim must undergo a full examination. Only after all the studies have been completed can one or another therapy be prescribed. It is necessary to know which organs have been subjected to greater intoxication and what needs to be treated more diligently.
When prescribing a type of treatment, it is necessary to be guided by the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. As a rule, in most cases, the prescriptions for the treatment of poisoning are as follows:
- drugs to normalize the functioning of the heart, as well as the entire cardiovascular system;
- painkillers. They are aimed at relieving pain in the chest area, as well as headaches;
- medications that are anti-inflammatory in nature. First of all, this medicine is aimed at improving the functioning of the respiratory system.
Read also Toxicity of chemicals, their classification by hazard
Next, the doctor must prescribe physiotherapy to his patient. In this case, breathing exercises of a therapeutic nature are implied. Gymnastics is aimed at improving the functioning of the respiratory tract. It also helps prevent inflammation in the body.
Therapeutic measures must be carried out if the patient is conscious. All treatment is carried out exclusively individually and taking into account all physiological characteristics.
If the patient is unconscious, then this is another form of poisoning - severe. In this case, medical specialists carry out resuscitation measures. Such events include:
- supplying oxygen to the lungs of a sick person. There are also cases when doctors use the so-called Ambu bag;
- Glycosides are also used;
- Antihypoxants are administered intravenously.
After the patient’s condition becomes better, the attending physician refers him to another department and prescribes therapeutic treatment.
Possible consequences
The most typical complications of household gas intoxication:
- respiratory diseases (laryngitis, bronchitis, bronchopneumonia, pneumonia);
- chronic heart failure;
- decreased cognitive function.
Since the development of long-term consequences cannot be ruled out, after the end of hospitalization the victim is recommended to undergo preventive medical examinations at least once every six months. Removal from observation occurs no earlier than after 3 years.
Main safety precautions
If you show the slightest signs of methane poisoning, you must leave the room. Those around the patient need to know what safety measures must be followed so as not to harm themselves or the patient. In this case, experts advise:
In a room where there is a high concentration of gas in the air, you cannot light a match or any other object that produces fire, you cannot turn on the light. This can all lead to an explosion;- When providing assistance, it is necessary to take the victim out into fresh air. If for some certain reason assistance had to be provided indoors, then you should have several assistants who will be in the fresh air and will come to the rescue if necessary. This is justified by the fact that you can also inhale gas vapors;
- If the victim has lost consciousness, then you need to bring him back to his senses with the help of cotton wool and ammonia;
- There are situations when the poisoning was mild, but a visit to the doctor had to be postponed for several days. In this case, you need to remember two things: you must visit the doctor, the patient must be given kefir. Kefir is a dairy product that eliminates the effects of toxins.
The condition of methane poisoning is considered to be the most dangerous to human life. Therefore, it is necessary to take such situations seriously.
Detoxification Options
In case of poisoning with natural or industrial gases, it is not necessary to carry out detoxification measures; it is enough to use methods designed to treat the consequences caused by a lack of oxygen.
Methane, when burned incompletely, forms carbon monoxide. Poisoning by its vapors is subject to mandatory detoxification.
To cleanse the blood, it is necessary to use efferent therapy. Actions help cleanse any biological fluid from the presence of toxic elements and foreign proteins.
The victim is undergoing hemosorption and plasmapheresis therapy. Such methods are only possible within a medical institution. The blood is purified outside the victim's body. It is filtered through a specialized apparatus and then returned to the circulatory system.
To prevent poisoning, an antidote is administered - Acizol.
It is possible to use sorbents that remove toxins through normal release.
In a home atmosphere, CO toxins are eliminated by taking activated carbon in combination with a decoction of rolled oats.