Signs of the disease
Rotavirus infection is called stomach or intestinal flu. The disease debuted with clinical symptoms reminiscent of an acute respiratory viral infection. The parents believe that the baby has a cold and begin treatment for respiratory tract infection. It is necessary to prevent the child from developing symptoms of damage to the digestive system.
Flow without temperature
Sometimes the disease occurs without high fever. The clinical variant is atypical for rotavirus infection and is misleading when making a diagnosis.
When an infection develops without fever
Rotavirus without fever can be:
- If the infection is atypical. The symptoms are erased and resemble another disease.
- In a child with a weakened immune system: in case of an intestinal infection, there is no pronounced protective reaction of the body.
- The disease occurs in adult patients without fever.
- If the child has previously had a rotavirus infection, it is easier to tolerate it again. Often the baby does not have a temperature.
Known Symptoms
Rotavirus infection enters the child’s body, reaches the intestinal lumen, begins to invade and multiply. The incubation period occurs without fever or other clinical symptoms.
- Diarrhea. Changes in stool character. At first, the stool has a mushy consistency, then becomes liquid. The changes are due to the localization of rotavirus in intestinal epithelial cells. Absorption processes in the intestines are disrupted, and a lot of fluid enters there. Pathogens are quickly washed out of the body. The frequency of diarrhea is from 5 to 15 times a day. In severe forms of the disease, diarrhea occurs up to 50 times a day. There are small mucous, foamy impurities. The appearance of blood in the stool indicates a secondary bacterial infection.
- Nausea, frequent vomiting. Against the background of nausea, children's appetite decreases until they completely refuse food. Nausea on an empty stomach, after eating. Vomiting is especially common in the first days. Repeated urges lead to the development of dehydration.
- Pain and rumbling in the abdomen are typical for young children. The amount of gases in the intestines increases, and intestinal epithelial cells are affected.
- Signs of dehydration. Repeated vomiting and diarrhea lead to symptoms of dehydration. The younger the child, the more rapidly the clinical picture develops. In newborns, symptoms of exicosis develop within 30-60 minutes. Clinically, dehydration manifests itself in dry lips, mucous membranes, sagging skin, sharpened facial features, and pale skin. The pulse is frequent, weak filling. The volume of urine excreted is significantly reduced. The child requires hospitalization and parenteral therapy. Treatment is with saline solutions.
Why does a child develop loose stools after rotavirus - duration and what is the danger
Rotavirus often occurs in children, but the course of the disease is especially difficult in children under 3 years of age.
This infectious pathology is serious not so much in terms of clinical signs as in possible complications (cardiac, renal failure, dehydration).
And in order for therapeutic actions to be correct and effective, you should understand why loose stools occur after rotavirus in a child and how to avoid adverse manifestations.
How does infection occur?
Rotavirus (intestinal flu) is a microbial provocateur from a group of viruses. It is invulnerable to external factors and is retained for a long time in water, on food, and various objects. The virus is not susceptible to low temperatures, so it is strongly observed in children in autumn and winter.
The cause of infectious rotavirus is a sick person. A significant amount of the virus is observed in patients with severe clinical manifestations of the disease, as well as in people who are already recovering. The spread of rotavirus can last 2-3 weeks, during which time the patient is dangerous to others.
Rotavirus infection occurs due to:
- direct contact with an infected person;
- eating poorly washed vegetables and fruits;
- drinking raw tap water;
- swimming in polluted lakes and reservoirs;
- failure of the patient to comply with hygiene rules;
- insufficient heat treatment of products.
It is almost impossible to avoid infection with rotavirus. The infection is widespread everywhere, children often get sick, and they have a hard time suffering from the disease. If a child is in a group, group outbreaks occur. After recovery, a person receives short-term immunity, and re-infection is acceptable after a couple of months.
Symptoms
Symptoms of rotavirus infection in young children are caused by impaired absorption in the gastrointestinal tract and excessive release of electrolytes and fluid into the intestinal space.
It is difficult to guess how long the incubation period of rotavirus lasts; it is individual for each person, the average number does not exceed 7 days. Symptoms of intestinal flu develop very quickly, appearing already on the second day of illness.
Rotavirus in a child manifests itself with the following symptoms:
- vomiting and diarrhea are the most important symptoms of the virus;
- intoxication of the body: malaise, loss of appetite;
- the temperature with rotavirus reaches subfebrile levels, very rarely it can be high;
- mild pain, bloating in the abdomen.
It is precisely diarrhea and change in the color of stool during rotavirus infection that become one of the important diagnostic indicators. Human feces have a copious liquid character, sometimes with an unpleasant aroma, and are orange or yellow in color. Frequent vomiting and watery stools lead to dehydration.
In children under 7 years of age, although rare, the following may appear due to rotavirus:
- redness of the throat mucosa, soreness;
- conjunctivitis;
- nasal congestion;
- decreased blood pressure;
- cardiopalmus;
- dry mucous membranes;
- decreased amount of urination.
Such signs require urgent hospitalization of the child and the necessary assistance. With rotavirus, diarrhea lasts from 1 day to a whole week.
Diagnostics
Basically, the diagnosis is determined by the doctor without conducting any kind of research. A rotavirus specialist can send a patient for testing:
- blood and urine tests;
- coprogram;
- bacteriological analysis of stool to study microbial changes;
- rapid test (for the presence of viruses);
- in case of severe dehydration, the electrolyte composition of the blood is produced.
Due to the implementation of these diagnostic methods, other infectious diseases with similar symptoms are excluded.
Treatment
Therapy for diarrhea in patients of different ages is practically no different, with the only exception being breastfed infants.
Therapeutic measures for rotavirus infection and diarrhea are complex, aimed at eliminating certain present symptoms. There are no special drugs to destroy the virus. Medicines, herbal medicine and dietary nutrition help get rid of the disease.
Drug treatment
The duration of diarrhea is affected by the treatment started. The doctor prescribes medications to help cope with the symptoms of rotavirus:
- Antimicrobials (Enterofuril, Metronidazole, Tsiprolet) - if a person has bloody stools, such medications are used. This manifestation indicates the addition of a bacterial infection, then antibiotics cannot be avoided.
- Enterosorbents (Polysorb, Polyphepan, Smecta) - remove toxic substances from the body, inhibit the attachment of the virus to the intestinal mucosa.
- Electrolytes (Regidron) - the product is diluted in liquid and should be taken in small sips. If rotavirus causes diarrhea that lasts for 5 days, the drug will help reduce water loss from the body.
- Enzymes (Festal, Mezim) - normalize the digestive system.
- Antiviral (Arbidol, Kagocel) - reduce the time of diarrhea.
- Prebiotics, probiotics (Bactistatin, Bifiform, Maxilak) – improve the microflora in the intestines.
A patient with rotavirus needs to drink a lot of fluid to avoid dehydration, at least 2.5 liters per day. You should also take chamomile infusions, loosely brewed tea, and compotes.
Diet
To restore the body after rotavirus in children and adults, you will need a special diet. For diarrhea and vomiting, products with a strengthening effect are used. You need to exclude milk and its products, which promote the growth of bacteria. Breastfed children should continue to be fed mother's milk.
A child's food for rotavirus should not contain:
- sweets (sweets, chocolate);
- Rye bread;
- legumes;
- soda;
- fresh fruits, vegetables;
- cheese, sausage;
- canned food, pasta.
It is good to eat rice porridge cooked in water, white bread crackers, various jelly, slimy soups, sweet tea. It is also recommended to use vitamin complexes.
If you have rotavirus, you should eat in small quantities, but often (5-6 times a day). I steam the food or give it to the child boiled or baked.
If the patient refuses to eat, you should not force him. As your condition recovers, your appetite will improve on its own.
Prevention
Preventing the formation of rotavirus with preventive measures is very important in order to prevent its development in the future. The infection is resistant to external conditions, can be found in feces, and does not die in cold and heat. It is destroyed only by boiling.
To avoid infection and prevent diarrhea after rotavirus, it is necessary to avoid direct contact with the patient.
For prevention you should:
- wash your hands thoroughly after visiting the toilet or going outside;
- do not take other people's dishes;
- Wash fruits and vegetables well, you can douse them with boiled water;
- Do not use objects of a sick person.
If a child is treated correctly and promptly for rotavirus, the prognosis will certainly be positive. Well, if you follow preventive measures, you can completely avoid the development of the disease.
The information on our website is provided by qualified doctors and is for informational purposes only. Don't self-medicate! Be sure to consult a specialist!
Rumyantsev V. G. Experience 34 years.
Gastroenterologist, professor, doctor of medical sciences. Prescribes diagnostics and carries out treatment. Expert of the group for the study of inflammatory diseases. Author of more than 300 scientific papers.
doctor
Source: https://gastrot.ru/kishechnik/zhidkij-stul-posle-rotavirusa-u-rebenka
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic rotavirus infection does not occur in childhood. The disease debuts with clinical signs of respiratory catarrhal phenomena. That is why rotavirus infection is called intestinal flu.
Rotavirus does not occur without diarrhea. In mild cases, the stool changes: it becomes mushy and grayish in color.
Adults with sufficiently strong immunity act as carriers of the virus and do not feel signs of developing the disease. Mild course - the disease is carried on the legs without diarrhea and vomiting, accompanied by minor abdominal pain and nausea. The course of the disease without vomiting and diarrhea leads to infection of relatives and colleagues.
Diarrhea after rotavirus in a child: causes, how long it lasts and treatment methods - Gastro Portal
Rotovirus diarrhea is a symptom of a viral disease, rotavirus gastroenteritis, most often found in children aged 6-24 months. The disease occurs in about 95% of children under 5 years of age.
The infection is highly contagious and usually recurs after treatment. Patients with rotavirus gastroenteritis have repeated vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. The length of time the disease lasts depends on the strength of the immune system.
Typically, problems last 2-7 days.
Rotavirus primarily affects the pediatric population. The younger the patient, the more dangerous the virus, which can cause serious health problems. In adults or older children, the dramatic course of rotavirus infection is rare.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rd6QwXLdOpo
An older person builds immunity against the virus over a long period of time. Severe infection in adulthood is typical only for a person with a weakened body.
According to experts, this is also due to the difference between the pH of stomach acid in adults and children.
Causes
Diarrhea is caused by rotovirus, a persistent virus that multiplies quickly. Pathogens settle on the intestinal wall, making the intestines unable to absorb water and minerals.
Rotovirus is a non-enveloped, round RNA virus. The name comes from its shape: lat. rota = wheel. There are 3 groups of rotaviruses: A, B and C. The most common infections are caused by group A.
The infection is seasonal. The most common incidence is recorded from November to March.
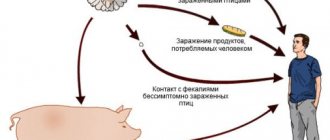
Young children become infected with the virus primarily through contaminated objects - toys and other things that “taste” and on which rotaviruses survive for a long time. The next route of infection is directly from an infected person. Therefore, the risk of rotavirus infection is very high.
Infection can occur on a changing table in a pediatrician's office, from a person who does not wash their hands after changing a diaper, etc. The virus, after passing through the gastrointestinal tract, is excreted from the body in feces.
Rotaviruses are a significant problem in hospital wards. According to experts, every fifth rotavirus diarrhea occurs during a child’s hospitalization for a completely different reason.
The risk of infection with rotavirus, the severity of the course, duration - how long it will last in adults and children, how many days of hospitalization will be required - it is impossible to predict. Rotavirus infections are difficult to avoid. However, severe dehydration due to diarrhea can be prevented.
Treatment with traditional methods
Traditional methods for the treatment of rotovirus diarrhea can be used and be effective only if the disease is not in acute form. Often the symptoms of the virus are so inexpressive that no one suspects the presence of the disease and considers the manifestations to be signs of a common stomach disorder.
Since the rotovirus affects the small intestine, causing irritation (enteritis), which is accompanied by nausea and vomiting, the following drinks will help:
- chamomile tea – 3-4 times a day, 1 glass (for children – 3-4 times a day, ½ glass);
- to maintain fluid balance - drink 1 liter of water per day, to which add the juice of ½ lemon, 1 tbsp. sugar and salt.
Nutrition
For effective treatment, adequate fluid intake and an appropriate diet are important. It is advisable to supplement dietary changes with the intake of lactobacilli to normalize the intestinal flora.
If a child becomes ill, do not force him or her to eat! Wait until his condition improves a little - he himself will ask for food.
If your baby is infected with rotovirus, do not stop breastfeeding. Breast milk is optimally absorbed in the body than other products, and also promotes recovery after illness.
What to feed a child with rotavirus and diarrhea? To speed up the recovery and recovery of a baby around one year of age, the following products are recommended:
- rice or buckwheat;
- fried eggs;
- fresh cottage cheese;
- yogurt.
2-3 days after eliminating the symptoms of the disease, you can carefully introduce meat, fish soups, and vegetable broths into the diet.
For at least 5-7 days after the disease is cured, it is recommended to exclude the following foods from the diet:
- fresh and dried fruits and vegetables;
- fatty fish and meat;
- cow's milk;
- bread, baked goods, confectionery;
- millet, wheat porridge;
- pasta;
- legumes;
- onion garlic;
- sausages, smoked meats;
- canned foods.
The introduction of these products into the diet of a child (and an adult) should be gradual, careful, taking into account changes in health.
Diarrhea due to rotavirus infection in children and adults
Rotavirus is an infectious disease that develops when pathogenic microbes enter the body. As a rule, the virus is transmitted through food and can enter through dirty hands. In common parlance, rotavirus is also called intestinal flu. It is characterized by pronounced symptoms, such as vomiting, nausea, general weakness, cough, and diarrhea due to rotavirus.
Due to the typical symptoms, the disease is often confused with poisoning and incorrect therapy is carried out, which only worsens the patient’s condition.
That is why, if you are faced with sudden changes in body temperature, diarrhea and vomiting, do not rush to do an enema or carry out other erroneous therapeutic measures, you have probably developed intestinal flu, and it should be eliminated in other ways.
Features of the course of the disease in adults
Signs of the disease are individual for each age group. In adults, symptoms are not as severe as in children. Their immune system is able to fight the pathogen.
Accordingly, among the signs of the disease, patients note only a sore throat, cough, temperature fluctuations and diarrhea due to rotavirus. In adults, diarrhea due to rotavirus infection takes on an atypical brownish-gray hue.
A person may experience abdominal cramps and nausea.
It is important to note that diarrhea with rotavirus does not appear immediately, but only on the 3rd day of infection. Until this time, a person can assume that he has a common cold and take antiviral drugs. Rotavirus diarrhea is very contagious, it can be transmitted through household contact. That is why it is so important to identify the disease in a timely manner and protect the sick person from healthy people.
Patients are interested in whether diarrhea is always present with rotavirus; the answer depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Doctors say that patients with strong immunity may have a blurred clinical picture of this disease. The carrier of the virus may not be aware of his infection, thereby exposing his environment to danger.
Such carriage poses a particular threat to people working in the food industry. The patient himself may not experience the severe symptoms that characterize this infection.
After contact with it, people with less stable protective properties will immediately fall ill with vomiting, nausea and severe diarrhea, which with rotavirus can occur up to 10 times a day.
Source: https://sevastopol3gb.ru/prochee/ponos-posle-rotavirus-u-rebenka-prichiny-skolko-dlitsya-i-metody-lecheniya.html
Features of infection without fever in adults
Adults rarely get sick with rotavirus infection. It was believed that the disease was a prerogative of childhood.
In adults, body temperature does not rise during infection, and general signs of intoxication are mild.
On palpation, patients experience pain in the epigastric region, around the navel. Rumbling and transfusion in the right iliac region are characteristic. The liver and spleen do not change in size during rotavirus infection and are painless on palpation. Abdominal pain is mild or absent.
During sigmoidoscopy, severe hyperemia and swelling of the mucous membrane of the rectum and sigmoid colon are observed.
In the acute period of rotavirus, changes in the urine are observed: blood and protein appear in the urine. The amount of residual nitrogen in the urine increases. On the first day, leukocytosis appears. Later it gives way to leukopenia. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is unchanged.
Diarrhea due to rotavirus in a child: how long does it last and what to feed – Without toxins
Rotavirus infection or “intestinal flu” is caused by a pathogen of the genus of viruses from the Rotavirus family and is characterized by signs of general intoxication. The patient experiences an increase in body temperature, diarrhea, episodes of vomiting, weakness, and fatigue. How long diarrhea due to rotavirus in a child can last depends on the state of the baby’s immune system and the strain of the pathogen.
Causes
The risk group includes persons of any gender and any age category. But most often, rotavirus infection, which causes diarrhea, affects young children under 2 years of age. In adult patients, the disorder occurs as a result of contact with a sick child. There are not very many possible causes of the disease, but they all lead to nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Factors that provoke infection include:
- Consuming dirty foods or raw/contaminated water.
- Eating food prepared in violation of heat treatment rules.
- Lack of hygiene.
- Contact with a sick person.
You can get infected anywhere. The main routes of transmission are fecal-oral. Rotavirus survives at low temperatures and retains the ability to be active and reproduce even after prolonged exposure to the refrigerator. It is also possible that the body may be damaged by airborne droplets. When you sneeze, droplets of mucus enter the air and people susceptible to the disease become infected.
Symptoms
You can tell that diarrhea is caused by rotavirus based on certain symptoms. For example, food poisoning, unlike this disease, develops rapidly, and similar signs of the disease appear in all people who have eaten the same food.
Symptoms of rotavirus infection are generally similar to the flu. There is a certain pattern of disease development:
- Incubation period . On average it ranges from 15 hours to 6 days.
- Initial . At this stage of the disease, the throat becomes inflamed, a wet cough, and conjunctivitis are possible.
- Spicy . Lasts about five days. The most striking sign of rotavirus infection in children is vomiting and diarrhea. The baby becomes lethargic, capricious, and loses his appetite. Loose stools after the onset of rotavirus are watery, foamy, and have a repulsive odor. There may be mucus in the stool. With a mild course of the disease, the stool takes on a mushy consistency. Often, diarrhea caused by rotavirus infection is accompanied by painful, pulling sensations in the stomach, and loud rumbling.
- Intoxication . It usually starts on the third to fifth day. In this case, impotence, weakness, drowsiness and other signs of poisoning are observed.
- Recovery . Lasts one or two days.
Rotavirus is a seasonal disease and, in addition to an eating disorder, is accompanied by respiratory symptoms. Stool and urine change color (urine becomes dark, sometimes with blood, and stool becomes grayish-yellow).
How long diarrhea that begins with an intestinal infection will last will depend on the age category of the patient and the general condition of the body.
If medical attention is not provided, diarrhea syndrome can last a month.
Important! Repeated loose stools can lead to dehydration (dehydration), which is very dangerous for children.
Therapeutic measures
It should be noted that there are no special drugs for the treatment of rotavirus. Therapy must be comprehensive. Diarrhea due to rotavirus is dangerous because it can cause dehydration, so it must be eliminated as soon as possible. The second unpleasant aspect of the disorder is general intoxication, which must be combated simultaneously with diarrhea syndrome.
Experts prescribe:
- Enterosorbents , absorbing toxic substances produced by rotavirus infection. They not only cleanse the body, but also restore damaged mucous membranes and prevent viral cells from attaching to the intestinal walls.
- Enzymes that restore the functioning of the digestive system.
- Antimicrobial agents in the presence of blood in the stool, which means the addition of bacteria, as the body becomes more vulnerable.
- Electrolytes that stabilize water-salt balance. To prevent dehydration, you need to drink constantly, especially when diarrhea, which is provoked by rotavirus, lasts for a long time. In the first days, the child should be given water or saline solutions, for example, Regidron. It is diluted in a liter of water and drunk in small sips so as not to vomit too much. Also, when treating diarrhea, you can use the following remedy: 2 tablespoons of granulated sugar, 1 tablespoon of baking soda, 1 teaspoon of table salt, grapefruit juice mixed and dissolved in a liter of water. Take 2-3 sips every half hour. Infants can be given water from a small spoon or from a syringe.
- Antipyretics . If a high temperature appears with diarrhea due to rotavirus infection, then in such cases give Ibuprofen, Nurofen.
- Antidiarrheal medications that stop diarrhea in a child after rotavirus, for example, Loperamide, Imodium.
The baby may be admitted to a hospital where medications are administered intravenously when diarrhea due to rotavirus does not go away for too long. The patient is prescribed:
- Symbiotics - they allow you to establish intestinal microflora in the shortest possible time.
- Antiviral drugs are drugs that shorten the duration of the disease.
Folk recipes
To make diarrhea go away faster after rotavirus infection, you can use traditional medicine. For this, healing decoctions and infusions are prepared:
- A drink made from chamomile flowers and mint leaves. The raw materials are steamed with boiling water and left for half an hour.
- The fruits of blackberries, bird cherry and blueberries are poured with boiling water, infused and given to the child to drink throughout the day.
- Pour a teaspoon of St. John's wort into a glass of boiling water and wait 1-2 hours. Give the patient 100 ml before meals.
If a child has rotavirus and diarrhea, the stomach should not be washed. During this manipulation, the beneficial intestinal microflora is washed away. Doctors recommend resorting to a cleansing procedure in case of persistent vomiting.
How long does diarrhea last in a child with rotavirus infection and how to stop it
page Diarrhea
Frequent loose stools can cause several groups of infectious diseases. Diarrhea due to rotavirus in a child begins with symptoms of acute respiratory viral infection, and then diarrhea occurs. This intestinal infection requires immediate treatment; the peak of the disease occurs in the off-season.
Symptoms of diarrhea due to rotavirus in a child
Rotavirus infection has several names: intestinal flu, stomach flu, rotavirus enteritis. Under powerful magnification, the causative virus looks like a wheel.
Rotavirus infection in children is expressed by the following symptoms:
- High body temperature, up to 38-39 degrees.
- Attacks of nausea.
- Diarrhea, characterized by loose green stools.
- Vomiting reflex.
Rotavirus enteritis is caused by an infection that enters the lumen of the small intestine. There the pathogen lives an incubation period, during which it does not manifest itself.
The duration of the interval from infection with an infectious pathology to the onset of symptoms depends on the human immune system and the number of pathogens that have penetrated the intestinal tract. It takes 3-5 days for rotavirus to reproduce and accumulate.
The release of viral particles begins when the disease shows its first signs. Until this moment, a person cannot transmit the infection by airborne droplets.
Symptoms of rotavirus begin with acute respiratory viral infection, followed by diarrhea after a while. Without proper treatment, the duration of the disease is prolonged several times. The child experiences discomfort in the abdominal area, becomes lethargic and weak.
How many days does diarrhea with rotavirus last?
The duration of the disease is 4-5 days. In severe cases, diarrhea goes away within 10-12 days.
When the disease is acute, with severe pain and vomiting, the patient must be taken to the hospital.
Typically, acute abdomen syndrome is diagnosed, which occurs as a complication of rotavirus infection. About 30% of cases of intestinal damage can be completely asymptomatic.
Diarrhea in the case of rotavirus in a child occurs almost immediately. The stool changes consistency, becomes liquid, sometimes foams, and has a characteristic sour odor. The volume of bowel movements is small and frequent, up to 10 times a day. It is difficult to feed the baby, he loses a large amount of fluid, and there is a risk of dehydration.
The child may feel nauseous, the intestines are irritated, and the urge occurs even after a sip of water. Diarrhea due to rotavirus in children can reach up to 15 bowel movements per day, which indicates a massive infection that can lead to dehydration. It is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner for qualified help.
What to feed your baby
If you have rotavirus, you need to feed your child properly. Diet and simplified nutrition is a necessary means of treating the disease.
During an exacerbation, the baby’s gastrointestinal tract is weakened and exhausted by constant painful bowel movements, so food should be easily digestible. Rice and some vegetables have strengthening properties.
Fermented milk products should be avoided; they promote the growth of bacteria.
If a child is breastfed, you cannot stop it! Pediatricians advise putting the baby to the breast more often. This does not contribute to increased urge; on the contrary, breast milk makes bowel movements easier.
In some cases, intestinal flu causes lactose intolerance; mother's milk is not digested in the baby's stomach. In such a situation, it is recommended to use dairy-free formulas and reduce breastfeeding to 2 times a day.
After recovery, the infant can again drink mother's milk.
The following products help stop diarrhea in children aged 1 year and older:
- The main diet should be porridge-like soups; food should be offered to the baby exclusively in pureed form. This allows food to be digested easier and faster. Light tea or blueberry juice will help restore water balance. All food should be provided to the baby at a comfortable warm temperature.
- Stale crackers - sweet pastries and fresh bread should be avoided.
- Boiled eggs, porridge with rice or semolina water.
- Fish rich in Omega-3 fatty acids is welcome, but not fried. The meat should be boiled and lightly salted.
Source: https://crrezonans.ru/diareya/diareya-pri-rotaviruse-u-rebenka-skolko-dlitsya-i-chem-kormit.html
How do intestinal infectious diseases usually manifest?
The main reason for the spread of infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract is non-compliance with hygiene standards. Unwashed hands, fruits, vegetables, eating expired food, insufficient heat treatment of dishes, an abundance of flies and cockroaches are the main factors that lead to pathogens entering the human body.
Manifestations and symptoms of intestinal infectious diseases directly depend on the pathogen. There is a pathognomonic clinical picture, on the basis of which you can easily make a correct diagnosis without waiting for test results.
The main symptoms that are common to most infectious intestinal diseases include:
- general weakness, malaise;
- loss of appetite;
- diarrhea;
- lack of thirst;
- aching pain in the abdomen, epigastrium;
- fever, sweating.
The most dangerous consequences of an intestinal infectious disease with diarrhea are intoxication and dehydration. The clinical picture is blurred, there are practically no symptoms, but the patient is a source of bacteria and actively releases them into the environment. Such a bacteria carrier is much more dangerous to its environment than a patient with severe symptoms.
Establishing diagnosis
If an intestinal infection is suspected, patients are hospitalized in the infectious diseases department.
The doctor examines the patient, collects anamnesis, asks him about the foods he has consumed over the past few days, and the catering places where he has eaten. In order to select the correct etiological medicine for an intestinal infection, you need to make an accurate diagnosis, identify the pathogen, and also assess the condition of the internal organs and the entire body as a whole. The following are the main methods of laboratory and instrumental examination if an intestinal infection is suspected:
- A complete blood count allows you to distinguish between bacterial and viral infections.
- A biochemical blood test is aimed at identifying disorders of internal organs and electrolyte imbalances in the body.
- Bacteriological examination of stool is carried out to identify the pathogen. It can be used to determine the type of intestinal infection. This is necessary to prescribe etiological treatment.
- An electrocardiogram is necessary for the timely detection of rhythm disturbances that may occur against the background of water-electrolyte shifts.
- A general urine test is needed to assess the condition of the kidneys, which are very sensitive to various intoxications and infections.
- An ultrasound examination of internal organs is carried out to identify possible disorders in the pancreas, liver, gall bladder and kidneys.
This list of examinations can be expanded or narrowed by the attending physician depending on the clinical picture and condition of the patient, and the results of tests already received.
Please note that diagnostics and diagnosis are carried out in parallel with providing the necessary assistance to the patient, combating intoxication and dehydration.
Can an infection occur without diarrhea?
An intestinal infection can occur without diarrhea and vomiting in rare cases. This directly depends on the nature, type of pathogen, general resistance of the body and localization of the pathogen in the gastrointestinal tract.
It is worth mentioning the intestinal flu caused by rotavirus infection. Its clinical picture is similar to a common cold - general malaise, weakness, chills, fever, sweating. Diarrhea, nausea, and even vomiting are often associated.
An intestinal infection without vomiting and diarrhea with a high fever is a casuistry. The increase in body temperature is explained by massive intoxication, without which the existence of bacteria and viruses in the body is simply impossible; they release toxins in the process of their “life activity.” Manifestations of body poisoning are present.
Children are susceptible to intestinal diseases and infections more often than adults for several reasons:
- unformed immunity;
- neglect of hygiene rules;
- immaturity of the gastrointestinal tract;
- weak stomach acidity.
In children, the incubation period of the disease is shorter, and the disease is more severe. An intestinal infection without fever and diarrhea in children, especially infants and infants, is impossible.
It is important to monitor the amount of fluid consumed, because it is dehydration caused by diarrhea that causes convulsions and disruption of the cardiovascular and excretory systems. It is not recommended to give your child antiemetic or antidiarrheal drugs on your own; this is to combat the symptoms, not the cause of the intestinal disease.
Liver diseases accompanied by vomiting
The liver is the largest and most mysterious internal organ. It is assigned a whole range of different functions. Despite the level of modern medicine, not all secrets about the work of the organ have been discovered. Interesting information includes the fact that the organ is capable of self-healing. If part of the liver was removed (for example, as a donor), then after 3-5 weeks the liver is restored to its previous size. Malfunctions of the liver greatly affect the functioning of the brain.
Important! Drug abuse or long-term treatment with strong drugs are the most common causes of liver cell destruction.
Most liver diseases are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and heartburn. Such diseases include:
- hepatitis A, B, C and chronic;
- hepatosis;
- cirrhosis;
- gallbladder and biliary tract disease;
- dyskinesia, etc.
The liver suffers the most from alcohol and chemicals. Liver diseases are often accompanied by a bitter taste, enlarged liver, and morning sickness. Even if the symptoms periodically disappear, the problem remains and gets worse. Many severe pathologies do not reveal themselves in the early stages or are manifested by minor discomfort, with which people usually live for a long time.
To treat the liver, drugs are prescribed that are called hepatoprotectors in medical circles. Their main purpose is to help the liver recover, protect against harmful influences or slow down the development of chronic diseases. They can be prescribed for both therapeutic and preventive purposes. They are not fast-acting drugs; they are prescribed in long courses and the results are observed after a while. Some effective liver treatment drugs are described in the table below.
Among the folk remedies that are especially useful for the liver: a decoction of corn silk and nettle, tincture of immortelle.
Important! The information in the article is provided to clearly demonstrate the importance of the correct course of treatment and the need to seek help from doctors. Especially when it comes to small children.
Work experience more than 7 years.
Professional skills: diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and biliary system.
It often happens that at the very beginning, when an intestinal infection is observed, there is no diarrhea, and sometimes constipation may even appear. The acute process begins with an increase in temperature, and diarrhea gradually develops. It happens that when infected, for example, with helminthic infestations, the infection immediately manifests itself as profuse diarrhea and all other unpleasant symptoms occur simultaneously.
Not a single infectious intestinal disease, of course, is complete without diarrhea, and then specific treatment and rehydration are required to avoid dehydration. Typically, 2-3 days after infection, the immune system begins to develop resistance to viral invasion. The main thing is to hold out for the first few days. Dehydration of the body, which can occur due to rapid loss of fluid due to frequent, profuse diarrhea and vomiting, should not be allowed. It is important for parents not to miss the moment when their children show primary signs of an intestinal infection.
What will the body temperature be with an infection in the intestines?
Temperature is a sign of intoxication of the body with infection; it is a protective mechanism aimed at reducing the activity of pathogenic microflora in the intestines. Hyperthermia sometimes reaches high levels, which is typical for severe poisoning. At a temperature of 38-39°C and against the background of severe dehydration with diarrhea, confusion and fainting may occur.
Other symptoms of severe intoxication include disturbances in heart rhythm and breathing. The disease is characterized by a sharp increase in body temperature against a background of moderate weakness. This condition is especially dangerous in young children. If an intestinal infection is not accompanied by diarrhea, but by fever and constipation, this greatly complicates a timely diagnosis.
Providing first aid for intestinal infection
Help with the development of an intestinal infection should be provided in the first minutes of symptoms. The development of this disease can be determined by a rapidly rising temperature and profuse stool, and a deterioration in the person’s condition. When the first clinical signs of this disease develop, you need to call an ambulance.
Remember that self-treatment of intestinal infections in adults at home is very dangerous and can lead to serious consequences. Only a doctor, after a detailed examination of the patient, can prescribe the correct etiological treatment.
While waiting for doctors to arrive, begin providing first aid to the poisoned person. Thanks to it, you can slightly alleviate the patient’s condition and reduce the severity of intoxication syndrome.
Below are the main steps you can take to help a sick person before the ambulance team arrives.
Why rinse it, you ask, if intestinal poisoning occurs after a certain incubation period, the dangerous food has long left the gastric cavity? In fact, this procedure will help remove some of the toxins and waste products of microorganisms and will significantly improve the patient’s well-being. It should also be taken into account that acute poisoning may manifest itself at first in similar symptoms, in which cleansing the stomach is the main emergency life-saving procedure.
To rinse your stomach, you will need plain water at room temperature. You need to drink 2-3 glasses of water in one gulp and induce a vomiting attack by pressing your finger on the root of the tongue.
Features of diagnosing the condition
If the clinical picture of an infection in the intestine is vague, it is important to find the cause of this condition. It is possible to accurately determine the causative agent of the disease only through bacteriological examination of stool during diarrhea or vomit. This is the only way to identify the etiological factor and prescribe adequate therapy.
It is important to differentiate the infection from non-bacterial food poisoning, an attack of appendicitis, myocardial infarction (the abdominal form of which is accompanied by pain not in the chest, but in the abdomen), and ectopic pregnancy. There are many other pathologies that are accompanied by abdominal pain, weakness, excessive sweating with no diarrhea.
It is important to examine family members as well; the patient is often a releaser of pathogenic flora into the environment. The severity of symptoms of intestinal disease in relatives depends on the length of the incubation period and the resistance of the organism itself. An infection in the intestines can occur without diarrhea and vomiting only if it has a clinical picture of acute gastritis. If the small or large intestine is affected, stool and digestive disorders will always be observed.
Dysbacteriosis: disease or not, but the body suffers
Nausea, occasional vomiting, metallic taste, bad breath – perhaps the intestinal microflora needs help. Dysbacteriosis is more often manifested by stool disturbances, but depending on the root cause and characteristics of the body, the first indicator may be attacks of vomiting.
Later, a whole bunch of troubles appear:
Important! The intestinal microflora of a child is formed during childbirth, and the process is completed by the age of 7-13 years. Not only the intestines have their own microflora, but also the throat, vagina, stomach, etc.
Dysbacteriosis in its consequences can be compared with impaired functioning of the kidneys or liver. Healthy microflora is necessary for many reasons:
- acids, antibacterial substances (lysozyme), alcohols, which secrete beneficial bacteria, inhibit the processes of decay and fermentation in the intestines, and do not allow the development of pathogenic microorganisms;
- take part in the metabolism of lipids, the decomposition of proteins and bile acids, ensure the absorption of substances, nullify the effect of toxins that are secreted by pathogenic microorganisms, and protect the intestinal walls;
- human immunity largely depends on a healthy intestine, where immunoglobulin A is synthesized;
- healthy microflora does not allow pathogenic microbes to poison the body with toxins and disrupt the functioning of organs, ensures the absorption of nutrients in full, so a person retains not only excellent health, but also youth for longer.
Dysbacteriosis is considered not only an increase in the proportion of harmful bacteria, but also a decrease in the number of beneficial microorganisms. Treatment is selected depending on the severity and causes.
| Bactisublin, Enterol, Biosporin | Biological products have an antibacterial effect. Accepted 7 days. |
| Bacteriophage | Viruses that infect bacterial cells, drugs based on them have been used relatively recently, usually containing a combination of several viruses aimed at certain types of bacteria. They have a targeted effect and do not harm the intestinal microflora. |
| Probiotics saturate the intestines with living beneficial bacteria, thereby helping the body return to normal faster. Taken from the first days of illness and another 1-2 weeks after recovery and withdrawal of all medications. |
| Creon or Mezim | Preparations that contain enzymes. Helps with digestion. Take up to 10 days. |
| Vitamins and immunomodulatory drugs | Prescribed during the recovery stage to strengthen the body and recover faster from illness. |
| Classification of the complexity of dysbiosis by stages | |
| Symptoms | Description |
| I | |
| It is practically asymptomatic. There may be causeless rumbling in the stomach. | The reason may be a change in diet or water. After eliminating the causes, the composition of the intestinal microflora returns to normal on its own. |
| II | |
| Some of the following reasons may occur: nausea, vomiting, problems with appetite, bowel dysfunction (constipation or diarrhea). | Such symptoms indicate significant structural changes in the microflora. A diet and a course of probiotics are required. |
| III | |
| Existing symptoms intensify, the patient feels pain in the intestinal area, and fragments of undigested food are released with feces. | Inflammatory processes can occur in the intestines, digestion is disrupted, and the body is practically defenseless against pathogenic intestinal infections. Diagnostics and a balanced course of medications are required. |
| IV | |
| A person suffers from painful manifestations of dysbiosis, and the body does not receive the necessary nutrients. I suffer from apathy, insomnia, depression and chronic fatigue. | The intestinal walls may become inflamed, minor bleeding is possible, vitamin deficiency and anemia occur. The processes of fermentation and decay intensify, creating a favorable environment for the development of infections; toxins can be absorbed into the blood through the intestinal walls and poison the entire body. Serious treatment is required. |
Reasons for unwanted changes include:
- primarily irregular, poor-quality or unbalanced nutrition, diets, water pollution and poor ecology in general;
- change in climate and composition of water consumed;
- abuse of bad habits, coffee and energy drinks;
- abuse of hygiene: the use of disinfectants in large quantities not only reduces the body's resistance, but can also provoke allergic reactions - this applies more to young children and overly caring mothers who are trying to create an almost sterile space, although standard rules of personal hygiene are quite sufficient;
- during intestinal cleansing, not only harmful, but also beneficial microorganisms are removed;
- a course of antibiotics or antiseptics in 90% of cases disrupts the intestinal microflora;
- hormonal imbalances or treatment with hormonal drugs;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- poisoning or severe food allergies;
- stress, neurological pathologies, lack of sleep, overwork, irregular days.
What is stomach flu
Intestinal or stomach flu is an infectious disease caused by rotaviruses. The disease manifests itself as intestinal and respiratory syndromes. Intestinal pathogens are viruses of the Reoviridae family, which are similar in antigenic structure. When viewed under a microscope, they resemble wheels, with a clear rim and short spokes. This viral pathology began to be studied in the early 70s of the last century, when they were discovered in the mucous membrane of the small intestine of sick children.
The source of infection is a sick person or carrier. In the younger age of the child, the source is the mother, and in the older age - the surrounding children, an epidemic in kindergartens, outbreaks of intestinal virus in schools, clubs, etc. In the first days, symptoms of intestinal flu appear, and the patient is dangerous to others, because during this period the content of virus colonies in feces reaches colossal numbers. Animals do not transmit this virus.
How is it transmitted?
The main mechanism of transmission of rotavirus infections is the fecal-oral route (the virus enters through the mouth). It is popularly called “the disease of dirty hands” (like any poisoning). The virus lives in food and any water, so it can be massively transmitted through it. The contact and household route of transmission occurred only sporadically. Infection with rotavirus infection occurs through dairy products: this is due to the life cycle of the virus and the peculiarities of processing milk products. The pathogen feels great in the cold and can remain this way for a long time.
Once in the body, the virus, as a rule, penetrates the intestinal mucosa (usually affecting the small intestine) and starts the process of destruction of intestinal villi. The digestive tract synthesizes enzymes that help break down food. As a result, incoming food cannot be digested normally, and disaccharides accumulate in the intestinal lumen, which attract water and salts. This entire mixture is excreted by the body through severe diarrhea, the body gradually becomes dehydrated and weakens.
Symptoms
Symptoms of intestinal infection are varied. In many children, the infection is severe and is accompanied by an increase in body temperature to 39°C or higher. If the disease in adults or children with strong immunity is mild, no severe fever is observed. Nuances:
- Patients complain of pain in the stomach, frequent nausea and severe vomiting. Sometimes, upon examination, slight redness of the throat and enlarged lymph nodes in the neck are detected.
- Characteristic is the appearance of copious loose stools with a pronounced, sharp, sour odor, without blood or mucus. If blood or mucus is added, this indicates the presence of a concomitant disease. Inflammation of the stomach and small intestine due to foodborne infections is called gastroenteritis.
- Children have frequent vomiting. In adults, frequent vomiting may not occur or may occur only once.
- There are signs of damage to the upper respiratory tract (nasal congestion, difficulty swallowing).
- Possible manifestations of ARVI with intestinal syndrome in adults.
Diarrhea
The stools are frequent, have a watery texture, a strong foul odor, and are green or cloudy white. The intestinal form of influenza is accompanied by loud rumbling in the stomach, the urge to defecate is frequent and productive. If there are bloody streaks in the stool or loss of mucous lumps, you should think about the addition of other respiratory infections, serious diseases, bacterial infections such as shigellosis, escherichiosis. Against the background of frequent diarrhea, dehydration of varying degrees develops. In adults, intestinal infection without diarrhea is not uncommon.
Clinical picture of intestinal infections
Signs of an intestinal infection do not appear immediately after infection. Typically, there is an incubation period between exposure to infection and the onset of symptoms. This is the time required for pathogenic microbes to penetrate the intestinal walls, reproduce and produce toxins.
The duration of the incubation period is individual for each pathogen. For example, with salmonellosis it can last from 6 hours to 3 days, and in the case of cholera - 1-5 days.
Below are the main symptoms of gastrointestinal infections:
- Hyperthermia is an increase in body temperature. Its numbers can reach 38-39 degrees. This is due to severe intoxication and acute inflammatory process developing in the intestinal walls.
- Nausea and vomiting. At first, the patient may vomit food debris, then the vomit consists of gastric juice, bile and liquid taken orally.
- Abdominal pain. It can be acute or aching, localized in different parts of the abdomen. Dysentery is characterized by tenesmus - acute pain during defecation.
- Diarrhea. The type and consistency of stool depends on the type of pathogen. So, with cholera, the stool is watery, reminiscent of rice water. Salmonellosis is characterized by loose, green, foul-smelling stools. With dysentery, streaks of blood and mucus can be seen in the stool.
- General weakness and malaise - develop due to intoxication and loss of large amounts of fluid.
- Increased gas formation, flatulence, bloating. These processes may be accompanied by severe intestinal colic.
- In the case of rotavirus, the patient develops catarrhal symptoms: nasal congestion, runny nose, sore throat, cough.
With an intestinal infection, dehydration may develop. With vomiting and diarrhea, the body loses a large amount of fluid and essential microelements. The patient's pulse quickens, blood pressure decreases, breathing quickens, and the skin turns pale. Against the background of this condition, convulsions, disturbances in heart rhythm and consciousness may develop.
Symptoms in children
In children, due to weak childhood immunity, the disease is more complex and more severe. The intoxication of the body is severe, vomiting is frequent and watery, diarrhea appears, which can reach 10 times a day, sometimes more. Flu with diarrhea and fever leads to dehydration, which develops in 75-85% of examined children, and often provokes the development of renal failure and hemodynamic disorders.
The amount of urine excreted by the child is significantly reduced, and albuminuria (albumin in the excreted urine) may be observed. Often the appearance of leukocytes and red blood cells in the urine, and residual nitrogen in the blood serum increases. The onset of the disease is accompanied by leukocytosis (an increase in white blood cells), after a period of height - leukopenia (a decrease in the number of blood white blood cells).
Causes
Often the disease occurs when eating unwashed fruits; they become infected with an intestinal virus through insufficient processing of meat and dairy products, through dirty hands and water. Bacterial causes of infection:
- caliciviruses;
- noroviruses;
- adenoviruses;
- astroviruses.
Parasitic causes are also known. Parasites are tiny microorganisms. They rarely cause influenza. More often, infection occurs with Giardia or Cryptosporidium. Similar symptoms can be caused by chemical toxins, heavy metals, and specific medications (aspirin, antibiotics, steroids, laxatives).
Diagnostics
The symptoms are similar to those of other gastrointestinal diseases (common flu, gastritis, viral gastroenteritis, enterocolitis, dysbiosis, etc.). Diagnosis is not easy. The final diagnosis can be made after detection of the virus using laboratory methods - polymerase chain reaction (PCR), passive hemagglutination test, complement fixation test (FFR), ELISA methods, etc. All changes in blood and urine are normalized after the patient recovers.
Available diagnostic methods:
- complete blood count (increased white blood cell count, increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate);
- general urinalysis (appearance of protein, leukocytes, erythrocytes, and sometimes hyaline casts).
Treatment of intestinal flu
All treatment comes down to symptomatic therapy (elimination of symptoms) and prevention of dehydration. Apply:
- antipyretics;
- enzymatic preparations;
- detoxification therapy.
It is recommended to take adsorbent or astringent medications (for intestinal disorders) if your stomach hurts badly - painkillers and antispasmodics help. Mild or one-time vomiting or diarrhea does not require treatment. It is recommended to take antibiotics when respiratory infections (cough), infectious diseases occur, in order to avoid the spread of infection, dangerous complications, the main one being intoxication, which is difficult to treat.
Drugs
For drinking, use an effective rehydron solution (capable of normalizing water-salt metabolism). Additional tools:
- The drug paracetamol can be prescribed as an antipyretic.
- Enzyme preparations: mezim, festal.
- Adsorbents and astringents: activated carbon, polysorb, smecta.
- Lactic-containing bacterial preparations: acylact, lactobacterin, linex (to restore intestinal microflora).
- Antispasmodics or painkillers: spasmolgon, no-shpa, citramon, analgin.
Features of care and treatment
Treatment for viral and bacterial diseases differs. The only common features are symptomatic therapy and nutrition.
The diet for poisoning and symptoms of acute gastritis involves fasting on the first day. The nutritional condition for rotavirus is the exclusion of dairy products from the diet. This is due to the development of lactase deficiency during a viral infection.
If you have an intestinal infection, eat small and often. Fatty and salty foods are excluded from the diet; fried and smoked foods are prohibited. The food requirement for intestinal infections is gentle.
Treatment for influenza of rotavirus etiology involves the appointment of antiviral therapy and measures for rehydration and detoxification. Whether a viral infection can be treated with antibiotics depends on the course of the disease. Prescription of antibiotics is necessary when a secondary bacterial infection occurs.
Treatment for dysentery and salmonellosis involves the prescription of antibiotics.
Pathogenetic therapy involves the administration of rehydration agents. Intestinal sorbents are used to remove toxins from the body. To restore normal intestinal microflora, probiotics are used. Improve the digestion process with the help of digestive enzymes.
Treatment in children
It is necessary to isolate the child from other children. Special saline solutions must be used to prevent dehydration of the body. Approved adsorbents for children and lactose-containing preparations are used to restore microflora. With prolonged diarrhea and persistent vomiting, signs of underlying complications may develop. It is recommended to call a doctor; hospitalization is possible.
It is not recommended to lower the body temperature below 38°C, because the virus dies at high temperatures. If the temperature reaches dangerous levels, you can use:
- physical methods: wiping with water;
- chemical: taking drugs by mouth or as rectal antipyretic suppositories (which is more acceptable in childhood).
How to treat a patient?
First of all, the patient should be soldered with special saline solutions. Regidron or its analogs are perfect. You can prepare the solution yourself. In the first day or two, if there is severe vomiting, you should not try to feed the patient. The solution should be taken a teaspoon after each urge or every 20-30 minutes. Soldering is the basis for treating rotavirus in the acute phase. If it is impossible to ensure sufficient fluid intake into the body at home, then special solutions are administered through the system (dropper).
Severe pain can be relieved with No-shpa. Smecta and Motilium will also ease the condition.
Important! You should not use Imodium or other medications for the disorder. Its principle of action is to relax the intestinal wall. If feces are not excreted, this can lead to the absorption of toxic substances into the blood, which will worsen the condition.
| What medications are needed for treatment | |
| Name | Action |
| Intestinal antiseptics: |
- very effective against most pathogens;
- do not provoke dysbacteriosis and do not suppress the immune system, which is their main difference from antibiotics;
- it is important to start taking medications as soon as possible;
- the course is 3-7 days.
Prevention of intestinal flu
In Europe and the USA, specific prevention is carried out using vaccines. We do not have such vaccines. There is a standard set of preventive procedures that are aimed at preventing viruses from entering the body:
- isolation of patients;
- hand hygiene, washing vegetables, fruits;
- eating only fresh dairy products and fermented milk products;
- sanitary control of public catering places, food products, markets and stores with dairy products.
Preventive measures
It is very important to prevent the occurrence of the disease by prevention in order to avoid it in the future. Since rotavirus is killed instantly by boiling, be sure to boil all water before use. The same should be said for milk and dairy products. Fruits and vegetables should also be washed thoroughly, especially before giving them to young children. It’s best to even pour boiling water over them. If someone in the family becomes ill with rotavirus infection, be sure to feed him from a separate bowl and wipe it thoroughly with a towel to avoid infecting other family members.