One of the most common types of food intoxication is staphylococcal poisoning. The causative factor is the entry into the body of the toxic pathogenic agent Staphylococcus aureus.
This toxic substance provokes many different pathologies, affecting organs and systems of the whole body. The clinical picture of staphylococcal toxicosis, prevention and treatment methods will be described in our article.
When actively multiplying, staphylococci produce a substance called enterotoxin that is dangerous to the body.
About staphylococci
In appearance, staphylococci resemble balls (cocci) up to 1.5 microns. in diameter.
Clusters of bacteria resemble a bunch of grapes (Staphylе - bunch of grapes).
It causes purulent inflammation of various locations. The lesion may be local or widespread. Penetrating into the blood, bacteria can cause sepsis and toxic shock. Penetrating into the digestive tract they cause food toxicosis.
Staphylococci are extremely resistant in the external environment. At a temperature of 150° C, bacteria die only after 10 minutes. Microbes are extremely resistant to direct sunlight, drying, 100% ethyl alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, phenol solution and a number of antibiotics. Microbes persist for a long time in food, dust and household items.
The rapid development of resistance to antibacterial drugs makes Staphylococcus aureus the most dangerous microbial agent for adults and children.
Rice. 2. The photo shows Staphylococcus aureus in the nose.
Treatment
Staphylococcal poisoning requires emergency care and hospital treatment with a complex clinical picture. Hospitalization is carried out in the infectious diseases department, and the patient is temporarily isolated until the end of characteristic symptoms.
Standard instructions for medical therapy involve several activities:
- Gastric lavage. The procedure is carried out with plenty of water with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or a 5% soda solution.
- Reception of adsorbents. Activated carbon, known to all of us, is used to remove toxins from the blood; its price differs in its availability from other drugs. Gastric lavage and activated charcoal can be done before the ambulance arrives.
- Taking antidiarrheals.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Use an aqueous solution prepared according to the recipe: soda, salt, sugar, in a 1:1 ratio.
- Injections. Caffeine and camphor are used.
- Intravenous administration of 5% glucose solution or Sodium chloride.
- Prescription of rehydration measures.
- Taking medications that normalize intestinal function.
- Immunity restoration therapy.
Foodborne illnesses can usually be treated without antimicrobials
As a rule, staphylococci and food toxicosis do not require antibiotics. The main attention is paid to the patient's nutrition. You should avoid eating fatty, fried, spicy, salty foods. The diet must be followed both during the period of treatment and during the period of recovery of the body, gradually adding regular dishes to the diet.
The video presented in this article will tell our readers what methods are used to prevent staphylococcal toxicosis:
Properties of Staphylococcus aureus
Pathogenic staphylococcus synthesizes and secretes many substances that allow this type of microbe to survive in the human body and damage its organs and tissues.
Enterotoxins
Staphylococci, contaminating food products (meat, milk), release enterotoxins, which, when entering the human body, cause food poisoning. Enterotoxins are resistant to high temperatures and human digestive juices.
Exotoxins
Staphylococci produce a number of exotoxins. Exotoxins have the following properties:
- damage the membrane of red blood cells, causing their hemolysis;
- damage leukocytes;
- damage the skin of newborns (Ritter's disease), the skin of children and adults (bullous impetigo);
- cause toxic shock syndrome.
Enzymes
Staphylococci secrete a number of enzymes with multidirectional effects:
- facilitate the adhesion of microbes to human tissues and the penetration of the pathogen deep into the tissues, damaging them;
— destroy the sebaceous plugs of hair follicles, which contributes to the penetration of infection deep into the tissues;
READ ALSO: 27 remedies for acne on the face: effective and inexpensive ointment, cream, pharmaceutical preparations and tablets for the treatment of acne and post-acne
- cause the coagulation of areas of blood plasma around microbes, which, like a cocoon, envelops staphylococcus, protecting it;
- protect the microbial population from the action of antibiotics.
Allergenic components
Toxins and microbial cell components have strong allergenic properties, which contributes to even greater skin damage.
Breeding factor
Staphylococci contain substances that promote the proliferation of microbes in phagocytes - cells that protect humans from microbes.
Rice. 3. The photo shows a cluster of Staphylococcus aureus.
Epidemiology
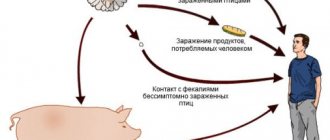
The infection is spread by patients and carriers of pathogenic strains of staphylococcus. Open purulent wounds, purulent inflammation of the eyes, mouth and pharynx, pneumonia and intestinal disorders are the source of staphylococcal infection. Food, contact and airborne droplets are the main ways of spreading infection. Surgical interventions, intramuscular and intravenous injections, various implants are also sources of infection. The infection can be transmitted to the fetus in utero, during childbirth and after the birth of the child.
Healthy carriers working in medical institutions, maternity hospitals and catering units are the most dangerous spreaders of infection.
Diagnostic measures
Diagnosis of pathology is based on the study of the symptoms of the disease, laboratory test results and epidemiological data. It is quite difficult to differentiate staphylococcal toxicosis from food toxic infections and acute intestinal pathologies. Laboratory data play an important role here.
Stool and vomit are taken for examination. Cultures can also be taken from the nose, rectum and throat. When staphylococcal toxicosis is diagnosed, food products are also examined for the presence of the infectious agent. The diagnosis is confirmed by the identification of the same type of staphylococcus in affected individuals.
Risk factors for developing staphylococcal infection
- The use of catheters in hospital conditions, the use of ventilation, during surgical manipulations through surgical instruments.
- Immune suppression before transplantation or implantation.
- Carrying out hemodialysis.
- Intravenous nutrition of premature infants.
- Diseases accompanied by decreased immunity (AIDS, diabetes, cancer, some lung diseases, skin and heart diseases).
- Intravenous drug administration.
- Piercing, tattooing.
Symptoms of staph infection
Manifestations of staphylococcal infection depend on the location of introduction of the pathogenic staphylococcus, the degree of its aggressiveness and the state of the human immune system.
Staphylococcal infection affects almost all human organs and tissues. Staphylococcal infection affects almost all human organs and tissues. There are more than 100 diseases caused by these microbes. The culprit of most of them is Staphylococcus aureus.
Staphylococcal infection and forms of its manifestation
- localized, mild forms of diseases such as rhinitis, nasopharyngitis, pyoderma;
- generalized forms, occurring in the form of septicemia (rapid proliferation of microbes in the blood) and septicopyemia (the occurrence of bacterial embolism and the formation of abscesses in organs and tissues);
- erased asymptomatic forms of the disease, which are difficult to diagnose. Often during an acute respiratory viral infection, staphylococcal infection worsens and can threaten severe complications.
The incubation period for staphylococcal infection ranges from several hours (with the gastroenterocolitic form) to 3-4 days.
Damage to the skin, its appendages and subcutaneous tissue
Staphylococci live mainly in the mouths of hair follicles. With the development of the inflammatory process (folliculitis) in adults, conical pustules form. In newborns, due to the underdeveloped follicular apparatus, staphylococcal infection causes blisters (bulls) with purulent contents.
Folliculitis is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. When the infection spreads to the walls of the follicle and surrounding tissues, a boil develops. When several follicles are involved in the inflammatory process, a carbuncle develops. Inflammation of the hair follicles in the area of the mustache, beard, and less commonly the pubis in men is called sycosis vulgar. With Hoffmann's folliculitis, deep inflammatory infiltrates (nodes) are formed, which merge to form abscesses. Abscesses form fistula tracts that undermine the skin.
Staphylococci are the cause of abscesses and cellulitis, hidradenitis and mastitis. When Staphylococcus aureus penetrates the mucous membranes, sore throat, stomatitis, and peritonsillar abscess develop.
Rice. 4. In the photo, Staphylococcus aureus in newborns is epidemic pemphigus of the newborn. A highly contagious disease that develops in newborns on the 3rd - 5th day of life and is characterized by the rapid formation of multiple blisters.
Rice. 5. The photo shows Ritter’s exfoliative (leaf-shaped) dermatitis of newborns. The cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. The disease is characterized by the appearance of large blisters that quickly burst, leaving weeping erosions.
READ ALSO: Blackheads on the face
Rice. 6. The photo shows pyoderma in children. When infected with Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus, red spots first appear on the skin. Then, in their place, bubbles with purulent contents appear, which quickly burst. In place of the bubbles, scabs appear, resembling “honey crusts” in appearance.
Rice. 7. In the photo on the left there is ostiofolliculitis (staphylococcal impetigo) and folliculitis (on the right).
Rice. 8. In the photo there is sycosis. The disease affects the follicles of the beard, mustache, and less commonly the pubic area. Foci of inflammation often have a confluent nature. After healing, scars do not form.
Rice. 9. In the photo on the left, a boil is one of the symptoms of a staphylococcal infection. With boils, the hair follicle is affected and a massive infiltrate develops. In the photo on the right there are multiple boils on the skin of the back.
Rice. 10. Barley on the eye is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the roots of the eyelashes or sebaceous glands. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common cause of the disease.
Rice. 11. The photo shows a carbuncle on the skin. A carbuncle consists of several boils located nearby. Making a diagnosis is not difficult. The cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus.
Rice. 12. In the photo, carbuncles on the neck are a symptom of a staphylococcal infection.
Rice. 13. In the photo, a carbuncle on the skin of the torso and thigh is one of the symptoms of the disease caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Rice. 14. In the photo, hidradenitis is a symptom of staphylococcal infection. Hidradenitis affects the apocrine sweat glands. Most often, hidradenitis is localized in the axillary region.
Rice. 15. The photo shows hidradenitis (a rarer localization).
Rice. 16. In the photo, an abscess (an accumulation of pus in soft tissues) is a symptom of an infection caused by Staphylococcus aureus.
Rice. 17. Mastitis in the photo. A common cause of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus.
Rice. 18. The photo shows phlegmon of the neck (left) and face (right). Staphylococcus aureus is the main cause of the disease. The disease develops as a result of the spread of microbes from affected areas into fiber and connective tissue.
Staphylococci in the nose and mouth
Rice. 19. Staphylococcus aureus in the nose is often the cause of inflammation of the paranasal sinuses.
Rice. 20. Staphylococcus aureus in the mouth affects the mucous membrane of a child. Aphthous stomatitis is one of its manifestations.
Rice. 21. Staphylococcus aureus in the mouth often causes pharyngitis, inflammation of the tonsils (picture on the left) and the development of peritonsillar abscesses (picture on the right).
Rice. 22. Staphylococcus aureus in the mouth often causes abscesses and odontogenic periostitis. The entry point for infection is diseased teeth.
Staphylococcus aureus in the ears
Rice. 23. Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus are damage to the outer (photo on the left), middle and inner ears and the development of an abscess of the outer ear (photo on the right).
Staphylococcus aureus in the respiratory tract
Rice. 24. Symptoms of Staphylococcus aureus - staphylococcal pneumonia (picture on the left) and abscess of the right lung (picture on the right). Often the bronchi are involved in the process, in which purulent-necrotic inflammation develops.
Staphylococcal toxicosis
Food poisoning caused by microbial toxins is one of the most common. Staphylococcal toxins do not change the smell, taste or appearance of food products.
Pathogenic bacteria are spread by sick and healthy bacteria carriers. Persons suffering from pustular skin diseases, cuts, festering wounds and sore throats are especially dangerous in terms of the spread of infection. Mastitis in animals and diseases of internal organs accompanied by suppuration can become a source of contamination of milk and meat.
READ ALSO: Newborn acne: photo of blooms on the face, how to distinguish it from allergies | Komarovsky
Staphylococcal lesions of the colon
Most often, staphylococcal damage to the colon accompanies dysbiosis and is observed with exhaustion and other conditions and diseases associated with a sharp suppression of the immune system. Manifestations of staphylococcal lesions of the colon are similar to those of dysentery, amebiasis and chronic ulcerative colitis.
Staphylococcal lesions of the genitourinary system
Most often, the infection penetrates the organs of the genitourinary system through injured areas that occur during operations, certain types of examinations and manipulations. Damaged epithelial cover is the entrance gate of staphylococcal infection.
Spread of infection through the bloodstream
Staphylococci, spreading through the bloodstream, can cause staphylococcal sepsis and toxic shock. There are lesions of the endocardium and pericardium, lungs, liver, spleen, kidneys, bone marrow, joints, brain and other organs.
Rice. 25. In 90% of cases, osteomyelitis is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. In the photo, the symptoms of infection are osteomyelitis of the upper jaw (photo on the left) and contact osteomyelitis of the finger (photo on the right).
Diagnosis of staphylococcal infection
- Diagnosis of an infectious disease is based on the detection of the pathogen or its toxins. To confirm the diagnosis of a disease of staphylococcal nature, bacteriological research methods are used - bacterioscopy and culture of biological material. The material for crops can be scrapings from affected areas of the skin, blood, urine, exudate, and feces. In case of food poisoning, the pathogen is isolated from the suspected products of poisoning.
- An increase in antibody titer during RA with an autostrain and a museum strain of staphylococcus undoubtedly indicates the staphylococcal nature of the disease.
- An increase in the titer of antistaphylolysin and antitoxin during the toxin neutralization reaction with antitoxin also indicates the staphylococcal nature of the disease.
- Currently, methods such as PCR, ELISA and RLA are widely used.
Rice. 26. The photo shows Staphylococcus aureus under a microscope.
Rice. 27. The photo shows a view of staphylococcal colonies isolated during breast milk culture.
Basic treatment methods
Depending on which organs are involved in the infectious process, the disease is treated by surgeons, therapists, pediatricians, ENT doctors, gynecologists, and ophthalmologists.
- Use of antibiotics to suppress the growth of microbial populations.
- Administration of staphylococcal toxoid, antistaphylococcal immunoglobulin and staphylococcal bacteriophage.
- Surgical methods of treatment (drainage of foci of purulent inflammation, removal of affected nectotic tissues).
- Local treatment for staphylococcal lesions of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Use of pathogenetic therapy methods.
- Use of immunoiodulators.
- Carrying out sanitation (improvement) of foci of infection.
Read more about the treatment of staphylococcal infections in the article “Treatment of staphylococcal infections.”
Disease prognosis
The prognosis of the disease is influenced by two factors - the state of the macroorganism and the severity of the disease itself.
Disease prevention
Carriage can be temporary (transient) or permanent. Permanent carriage is registered in 20% of adults, transient carriage – in 30%. The carrier state is especially dangerous among medical workers and catering workers. Their timely detection and adequate treatment can prevent the nosocomial spread of infection.
- Timely treatment of carious teeth, chronic sore throats and other foci of chronic infection.
- Adequate cleansing and treatment of skin lesions (scratches, wounds, cuts), which are the entry point for staphylococcal infection.
- Detection and treatment of carriage in expectant mothers and fathers.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules.
- A set of measures aimed at increasing immunity.
Staphylococcal infection has many manifestations. It occupies a leading place among purulent-septic complications in exhausted, weakened patients and young children, in operated patients. The greatest danger to humans is Staphylococcus aureus. Good immunity and adequate treatment are the key to a quick recovery.
News MirTesen
Prevention
In the fight against staphylococcus, it is very important to follow a number of preventive measures that every person should know about.
Table No. 2. Preventive measures in the fight against staphylococcus:
|
|
| A healthy and nutritious diet using only high-quality products will help avoid the risk of infection. Much attention is paid to physical activity, because regular exercise strengthens the immune system. |
| Antibiotics should be taken strictly in the indicated doses prescribed by the doctor after the examination. |
| While staying in medical institutions, you should observe the sanitary and anti-epidemic regime. Since there may be patients near you diagnosed with staphylococcal toxicosis. |
| As we have noted more than once, staphylococcal bacillus often lives on food. Therefore, when consuming them, it is worth thinking about this factor, especially in the summer. |
| This point especially applies to people employed in production, sales and storage of food products. First of all, they check for skin changes in the form of ulcers, boils, and open wounds. |
| When preparing dishes and processing food products, the thermal regime established by the standards must be strictly observed. |
| In areas where food is processed, stored and prepared, it is necessary to ensure the necessary sanitary conditions. |
| This responsibility falls on the workers of the farms where milk is obtained and sold for further processing. |
The general prognosis for staphylococcal toxicosis is favorable, but like any other disease, this pathology requires emergency care.
Interesting fact. Enterotoxin is a substance that, when accumulated in food, causes great harm to our health. A dangerous dose of the substance in minced meat reaches after 12 hours of improper storage; in cooked minced meat cutlets this period is 4 hours. The custard becomes inedible after only 3 hours.