No person, including pregnant women, is immune from the development of salmonellosis. The causative agent of the disease can wait anywhere; even eating a boiled egg is fraught with penetration of the pathogen into the body and the appearance of unpleasant symptoms. Salmonellosis is especially dangerous during pregnancy. At this time, a woman should try to protect herself and the baby as much as possible, since the disease often leads to complications.
Causes
The causative agent of salmonellosis is Salmonella bacillus, which is transmitted by the fecal-oral route. The most common type is S. Typhimurium. Typically affects the stomach and small intestine.
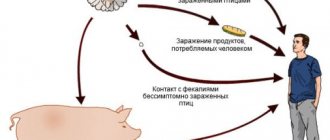
The main source of salmonella infection is pets and livestock. The infection can also be transmitted from person to person. Most often, salmonellosis is contracted through food - products of animal origin: meat, milk and dairy products, eggs. There is also a waterborne risk of infection through non-chlorinated tap water.
Salmonella can settle in food products if storage rules are not followed, due to insufficient heat treatment, and also if personal hygiene rules are ignored.
For pregnant women, salmonellosis poses a complex problem, since dehydration and intoxication can aggravate toxicosis and cause exacerbation of chronic diseases that the expectant mother had before and during pregnancy. Sometimes salmonella infection in pregnant women can be asymptomatic, but the woman herself is the source of infection.
Infection with Salmonella in the early stages of variability has pronounced symptoms. In the third trimester of pregnancy, the manifestation of symptoms of salmonellosis can cause the development of late toxicosis, which is very dangerous for the fetus and the expectant mother.
Scatological research
With this method, feces are looked at for the presence of:
- bile acids;
- occult blood;
- enterobiasis.
In the laboratory the analysis is carried out:
- chemical analysis;
- macroscopic and microscopic examinations.
With the macroscopic method, feces are examined for:
- quantity;
- consistency;
- smell;
- color;
- leftover unprocessed food.
Chemical analysis examines stool for occult blood. Its presence indicates blood loss as a result of damage to the gastrointestinal tract.
Microscopic examination determines the presence of muscle fibers, undigested plant fiber and other components. In combination with blood tests and other studies, a scatological examination helps the doctor understand the patient’s condition.
The RPHA method (RNGA) is a passive hemagglutination reaction. This is one type of serological test that is highly sensitive.
During the test, the patient's blood serum is taken and mixed with the reagent in a centrifuge for an hour.
If the red blood cells become heavy enough from the precipitate that has fallen on them in the form of antibodies to the pathogen, then they fall to the bottom of the test tube, and the reaction is considered positive.
However, the RPHA reaction may be false positive if:
- autoimmune diseases;
- acute viral infections such as influenza or acute respiratory infections;
- poisoning;
- pregnancy.
Symptoms
The first signs of salmonellosis in pregnant women:
- nausea and intense vomiting,
- headache,
- diarrhea,
- dizziness,
- temperature increase.
In some cases, the temperature may be elevated to subfebrile levels - 37° C.
People infected with salmonella often exhibit symptoms of pancreatitis, an inflammation of the pancreas. There is a decrease in blood pressure, and a change in pulse rate and strength is observed.
If treatment is not started in a timely manner, worsening the condition may pose a danger to the fetus and the expectant mother. Symptoms increase rapidly, so when the first signs of salmonellosis appear, you should consult a doctor.
From the second trimester of pregnancy, if salmonellosis is suspected, the patient is hospitalized in a maternity hospital that specializes in obstetric care for women with signs of infectious diseases.
Diagnosis of salmonellosis
To diagnose the disease, a number of examinations are carried out:
- anamnesis collection,
- tests of stool, blood, urine, vomit.
conclusions
Anyone can develop salmonellosis. This is a dangerous disease that is fraught with serious consequences. At the first symptoms of pathology, especially during pregnancy, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. Timely diagnosis and competent therapy can prevent dehydration and other complications.
Daria Shirochina
Practitioner. She graduated with honors from Vitebsk State Medical University in 2012 with a degree in general medicine. She was awarded a certificate of honor for her achievements in her work.
Complications
How dangerous is salmonellosis for a pregnant woman and fetus? Salmonella bacillus has the ability to penetrate the placental barrier. Therefore, there is a high risk of infection of the fetus, which poses a great danger to the unborn baby. Also, salmonellosis in pregnant women provokes an exacerbation of toxicosis and other pathological conditions. The process of dehydration of the body in expectant mothers with salmonellosis occurs more rapidly, which can also pose a danger to the normal development of the fetus.
Course of therapy
Doctors usually do not prescribe antibiotics to pregnant women. Treatment is limited to diet (see diet for salmonellosis), medications against diarrhea, and drinking enough water and nutrients that are essential for the full development of the fetus.
A prerequisite for successful recovery is constant monitoring by a doctor, who adjusts his prescriptions as necessary. This is due to the fact that a woman’s body can react unpredictably to an infection, and salmonellosis can change from a mild to a complex form at any time.
In emergency cases, antibiotics must be prescribed, most often Amoxicillin and Cephalosporin - they are recognized as relatively harmless for the treatment of infections in pregnant women. More modern and effective drugs of the group called fluoroquinolones, which are prescribed today for the treatment of salmonellosis for pregnant women, have many contraindications.
Treatment
What can you do?
At the first signs of intoxication in the body (vomiting, diarrhea, fever), you need to protect the body from dehydration. To prevent the condition from worsening and the development of metabolic complications, you should definitely consult a doctor.
If the disease occurs in a subclinical form, the pathogen can be detected in the body, but there are no symptoms.
To prevent dehydration of the body, fractional dehydration is necessary. Water should be given frequently, one teaspoon every 3 to 5 minutes.
Treatment of salmonellosis at home is unacceptable. If you are suspected of being infected with salmonella, you may be hospitalized in the infectious diseases department.
What will the doctor do?
In the hospital, you will receive intravenous drips of fluid. This will help eliminate signs of dehydration or overhydration. Both of these phenomena are very dangerous, both for the fetus and for you.
Salmonellosis during pregnancy is treated with antibiotic therapy. In this case, medications are prescribed that eliminate the damaging effect on the growing and developing fetus.
The doctor also prescribes the use of sorbent drugs, the action of which is aimed at absorbing and removing infections, toxins and other waste products of microorganisms from the intestines.
It is very important to follow a special diet if you have salmonellosis. At the initial stage of the disease, it is better to reduce the amount of food consumed.
If you have salmonellosis, you should limit the consumption of foods that provoke fermentation, hard-to-digest foods (brown bread, high-fat milk, raw vegetables), and pickles. Your diet should contain easily digestible food with the addition of lean boiled meat. It can be:
- hard cheese of mild varieties;
- low fat cottage cheese;
- fruit jelly;
- fish, steamed meat cutlets;
- rice or oatmeal porridge with water.
Salmonellosis during pregnancy
Salmonellosis is an infectious disease caused by various types of salmonella. The disease is characterized by a wide variety of manifestations from asymptomatic carriage to the development of severe forms. How does salmonellosis manifest itself during pregnancy and what is the danger of this condition for the fetus?
Causes
The causative agent of salmonellosis is bacteria of the genus Salmonella from the Enterobacteriaceae family. DNA-containing salmonella differ in their antigenic composition and ability to cause disease in humans.
Microorganisms are very stable in the external environment. Salmonella live in water for up to 5-6 months, in meat products - up to 4 months. Dangerous bacteria can exist in frozen meat for 6-12 months. Many Salmonella species remain viable in soil for 18 months.
The main source of infection for humans is food (meat, cheese, dairy products). Infection occurs when food contains a large amount of a dangerous infectious agent. In small quantities, salmonella is not dangerous. The disease can also be transmitted from person to person.
There is no pronounced seasonality. People of all ages are susceptible to salmonellosis. Pregnant women, due to a physiological decrease in immunity, are at high risk for developing this disease.
Salmonellosis is considered as a separate pathology caused by certain types of bacteria of this group. The disease should be distinguished from typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever, which are also caused by Salmonella. The mechanism of transmission of infection and the characteristics of the development of the disease are approximately the same in all cases.
Gastrointestinal variant
One of the most common forms of the disease. It is this variant that is most often registered in pregnant women who have consumed stale and poor-quality food. With the gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis, the following symptoms occur:
- nausea;
- repeated vomiting;
- pain in the epigastrium and umbilical region;
- loose, watery stools.
The disease usually occurs against the background of a significant increase in body temperature (up to 38.5 °C and above). Fever may be absent if the disease is mild. In this case, salmonellosis is often mistaken for signs of severe toxicosis in the early stages of pregnancy, which complicates diagnosis and delays the start of treatment.
Typhoid-like variant
The disease occurs suddenly with a sharp increase in body temperature, nausea and vomiting. After 24-48 hours, diarrhea and nausea resolve, but fever remains.
Symptoms of general intoxication occur: weakness, chills, headache, confusion. The pregnant woman's condition is progressively deteriorating. A skin rash may appear on days 5-7 of illness.
The duration of the disease is from 2 to 3 weeks.
Septic option
The most severe form of salmonellosis. During pregnancy, it is quite rare and is observed mainly in women with defects of the immune system (congenital immunodeficiencies, HIV infection).
In the first days, the disease progresses in a typhoid-like manner. A few days later, the woman’s condition noticeably worsens. Body temperature during the day ranges from almost normal to extremely high. Foci of secondary infection develop in organs and tissues that are difficult to treat. In the absence of qualified assistance, septicemia can lead to the death of a woman.
Bacterial carriage
A special form of salmonellosis in which no symptoms of the disease are observed. At the same time, the expectant mother is a source of infection for the people around her. The carriage of dangerous bacteria can last from 2 weeks to 3 months. Chronic bacterial carriage is said to occur if Salmonella is detected for more than 3 months in a row.
Consequences for the fetus
In the first trimester, salmonellosis, like any infectious disease, can lead to irreversible disruption of fetal development and spontaneous miscarriage. Termination of pregnancy may also be associated with severe intoxication of the body. It is known that an increase in body temperature over 37.7 °C significantly increases the risk of miscarriage and regression of pregnancy up to 12 weeks.
In the second and third trimesters of pregnancy, salmonellosis can cause the development of placental insufficiency.
Significant intoxication of the body and depletion of its reserves leads to the fact that the placenta ceases to cope with its function. The baby does not receive nutrients and oxygen in the required volume.
All this leads to delayed fetal development and can cause premature birth.
Dehydration of the mother's body also affects the condition of the baby.
Repeated vomiting and severe diarrhea deplete nutrients, including vitamins and important minerals. Lack of useful elements leads to fetal growth retardation.
Against this background, it is possible to terminate the pregnancy (up to 22 weeks) or give birth to a low-birth-weight baby ahead of schedule.
Treatment methods
When the first signs of illness appear, a pregnant woman should call a doctor at home. For mild forms of salmonellosis, treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Hospitalization to the infectious diseases department is indicated in case of a woman’s serious condition, severe dehydration and the appearance of various complications of pregnancy.
Drug therapy
The most important thing in treating salmonellosis is to prevent dehydration. For this purpose, oral administration of glucose-saline solutions (Regidron, Oralit and others) is prescribed. The powder is diluted with boiled water according to the instructions.
The prepared solution must be taken in small sips of up to 1.5 liters during the first 2-4 hours. In the future, as the condition improves, the amount of fluid consumed decreases.
The need to take saline solutions continues until all signs of dehydration disappear.
Oral rehydration solutions are approved for use at any stage of pregnancy. Expectant mothers suffering from heart and kidney diseases should use saline solutions with caution.
In such a situation, you should definitely consult a doctor and clarify the permissible amount of the drug.
For some chronic kidney and heart diseases, such treatment is carried out only in a hospital under the constant supervision of doctors.
To reduce intoxication of the body and remove toxins, enterosorbents (activated carbon, Smecta, Polysorb, etc.) are used. The drugs are prescribed in accordance with the instructions. Sorbents should be taken 2 hours before or after any other medications. During pregnancy, enterosorbents can be used at any stage.
Antibacterial therapy for the gastrointestinal form of salmonellosis is usually not prescribed. After correcting the water-electrolyte balance, the woman’s condition noticeably improves, and there is no need to use other drugs. Antibiotics are used in a hospital setting for severe forms of salmonellosis (including typhus-like and septic).
After recovery, the pregnant woman is prescribed probiotics - drugs that restore intestinal microflora (Acipol, Linex and others). The course of rehabilitation treatment lasts 2-3 weeks.
Non-drug therapy
On the first day after the onset of the disease, it is recommended to refrain from eating. You are allowed to drink water and sweet tea. After 1-2 days, the diet is expanded with easily digestible foods. You should refrain from eating meat, milk and heavy foods for 1-2 weeks.
Prevention
Following simple recommendations will help prevent the development of the disease:
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Buy food from trusted places.
- Do not consume suspicious products with an unpleasant odor or expired dates.
- Keep the room clean and do not forget about regular wet cleaning.
When the first signs of salmonellosis appear, you should consult a doctor (local therapist). If your condition worsens significantly, you should call an ambulance. Timely diagnosis and adequate treatment can avoid the development of dehydration and prevent possible complications of pregnancy.
obstetrician-gynecologist Ekaterina Sibileva
Source: https://spuzom.com/salmonellez-pri-beremennosti.html
Prevention
To protect yourself from salmonellosis infection, you must follow the following basic rules:
- be sure to wash your hands before eating,
- wash vegetables and fruits before eating,
- Never drink raw tap water,
- follow the rules of culinary food processing,
- exclude raw eggs from the diet,
- whole milk.
At the first signs of infection, you should definitely consult a doctor.
Salmonellosis during pregnancy is a dangerous infectious disease. The causative agent is Salmonella bacillus. The bacterium owes its name to the American scientist Salmon, who identified and described the first diseases in animals.
Microorganisms are very tenacious. They live in an aquatic environment for five to six months, in meat products for up to four months, in frozen meat for up to twelve months. They remain in the soil for up to one and a half years. They are able to survive even at temperatures of plus 80 degrees, and are resistant to salting, smoking and freezing.
Types of salmonellosis
There are several types of salmonellosis.
Gastrointestinal type.
It is this variant that is registered not only in pregnant women, but also in other categories of people. The disease occurs with high fever. Salmonellosis is sometimes mistaken for toxicosis in pregnant women in the early stages. Signs similar to toxicosis: nausea, vomiting.
Typhoid-like.
The disease begins abruptly with an increase in temperature. After the second day, the disgust and vomiting disappear, leaving fever and trembling in the body, powerlessness, and headache. A rash on the skin is possible on the fifth or seventh day. The duration of the disease is up to 21 days. Septic type.
The most severe form of the disease. It begins with signs of a typhoid-like disease. Sites of inflammation develop in other organs. Temperatures can range from stable to high.
Bacteria carrier
Signs of salmonellosis are not clearly visible, but a person can be a source of infection. Laboratory tests are being carried out. The material for analysis can be stool and blood.
Causes of the disease
The source of infection can be animals: cattle and sheep, pigs and horses. But the main carriers are poultry: chickens, ducks, geese, their meat and eggs. Patients with salmonellosis can also be a source of infectious disease.
The disease is transmitted:
- through meat and dairy foods, eggs, cheese,
- through contact with sick animals and people by shaking hands,
- drinking liquids with contaminated bacilli,
- when inhaling dust.
The greatest likelihood of illness is in the summer. At this time, the rules for storing and preparing food are often not followed.
A small number of bacilli is not dangerous. There is no age limit; both young children and the elderly can be affected by the disease. Salmonellosis is a separate type of disease and differs from typhoid fever and paratyphoid fever, the causative agents of which are also salmonella.
Signs of the disease
Salmonella bacteria enter the body through food, saliva and liquid. Once in the intestines, they multiply and release harmful substances, endotoxins. Here the bacilli are engulfed by macrophage cells that destroy the bacteria. But this is precisely what contributes to the release of endotoxin, which destroys the intestinal microflora and causes severe intoxication. There is a gradual introduction of salmonella into the lymphatic system and then into the blood. This gives rise to the development of second foci of the disease and this is very dangerous for a pregnant woman and her fetus.
Salmonellosis has three forms: mild, moderate and severe.
Mild is the appearance of weakness and loss of appetite, pain and cramps in the abdominal area, headache.
The average is characterized by a temperature of at least 39 degrees, brittleness throughout the body, convulsions, dizziness, disgust, vomiting, diarrhea, and loss of strength.
Signs of a severe form include: temperature 40 degrees, severe weakness, chills. Blood pressure decreases and blood circulation is impaired, frequent vomiting. The appearance of pregnant women is exhausted, dry skin. Diuretic properties decrease until they disappear.
Particularly dangerous signs:
- frequent vomiting with bloody discharge,
- diarrhea more than 10 times per day,
- temperature above 39 degrees,
- rash on the skin,
- pain in the joints, heart area, right and left hypochondrium.
Incubation time lasts from 6 to 24 hours . Symptoms of inflammation of the pancreas often appear, and the hepatic gland is involved in the inflammatory process. Salmonellosis during pregnancy is severe and can cause the loss of a child.
Why is salmonellosis dangerous during pregnancy?
Salmonellosis can occur in pregnant women. In this case, there are a lot of nuances in treating the disease, diagnosing it, etc. Thanks to this article you can learn all the most useful and important things on this topic.
With the help of the article, it will be possible to solve a lot of current problems related to the identification of this disease and the selection of optimal treatment methods. In general, the article will bring a lot of useful information to every reader.
What is salmonellosis?
Salmonellosis is an acute infection that can spread in the human intestine after the pathogen enters the body.
Special bacteria enter the body through carriers, which are usually food. Salmonella can be found in various foods, but the most dangerous among them is meat.
The vital activity of bacteria also persists in some other products, including milk, sourdough, butter, sausage, and eggs.
Bacteria are microscopic, which completely eliminates the possibility of seeing them. It is also impossible to feel them, because they have no taste and do not change the color of the food. Therefore, it is possible to find out whether they are present in food or not only through analysis. But you can completely stop their vital activity with the help of high temperatures.
For this reason, it is recommended to subject foods to severe heat treatment before consumption. But the bacterium can also enter the body through regular tap water. Many people drink it, but it is better for pregnant women to immediately give up this habit. Swimming in dirty water can lead to illness.
Pregnancy and salmonellosis
The routes of transmission of this disease are different. The danger of the disease for pregnant women is due to dehydration. A pregnant woman is not recommended to get sick at all.
Of course, no woman wants to put her unborn child in danger because of some kind of illness, but sometimes it still comes. You must take treatment seriously, because only a competent approach will allow you to get rid of the disease as soon as possible.
A pregnant woman should try to protect herself from potential sources of infection. Among them are sources such as domestic and farm animals, fish, cats, sick people, etc. Food must be processed before eating.
Symptoms
Bacteria establish themselves in the gastrointestinal tract after entering the body. This provokes intense diarrhea, vomiting, and headaches.
Chills and fever may also occur. If a pregnant woman experiences similar symptoms, she should seek qualified help from specialists.
A severe form of salmonellosis can lead to inflammation of the heart muscle , gall bladder, bleeding inside the intestines and other unpleasant problems. This can happen in the absence of timely treatment.
The incubation period of this disease is usually counted from the moment the pathogen enters the body of a pregnant woman. After a certain time, the first clinical symptoms appear.
The duration of the period can vary, ranging from six hours to six days. But usually the period averages from 12 to 24 hours from the moment of consumption of the product that was contaminated.
Salmonella penetrates the stomach and attaches to the mucous membrane there. Diarrhea can cause severe dehydration in a pregnant woman. We must try to minimize it.
Disturbances in water-salt metabolism can be very serious. Depending on the severity, other symptoms may occur, such as dizziness, low blood pressure, etc.
Complications
As a rule, this disease does not pose too significant a danger to the woman’s body, as well as to the unborn child. But still, sometimes pregnant women can experience some unpleasant complications.
Among the basic difficulties can be identified acute loss of fluid in the body, which is provoked by diarrhea and vomiting. It is possible to exclude dehydration and potential problems with the cessation of the supply of nutrients to the fetus. To do this, a woman must continuously replenish fluid reserves.
In case of a severe form of the disease, which lasts for several days, it is imperative to seek specialized help. Otherwise, there may be a poor supply of nutrients to the fetus, which in turn can provoke premature birth or even miscarriage.
Prevention
It is very important to try to protect your body from the penetration of such bacteria . This is important for both the pregnant woman and the fetus. There are several basic tips that will help minimize the risk of infection. You can highlight them in a small list:
- Bacteria cannot tolerate high temperatures. They begin to die at temperatures of +70 degrees. Therefore, you need to boil the food for ten minutes to get rid of bacteria.
- It is also extremely important to wash your hands thoroughly, especially before eating or preparing food.
- Bacteria can survive in frozen foods. For this reason, you need to be careful when defrosting them. The liquid that forms after this process must be drained, and the product itself must be washed. The dishes are then washed in hot water, and as thoroughly as possible.
- Bacteria actively multiply in warm conditions. Therefore, a pregnant woman or her family members are required to store food according to the rules. You need to do this in the refrigerator. Under no circumstances should the cooling process be interrupted for long.
Analysis for salmonellosis during pregnancy and its features
Such an analysis plays an important preventive role when carrying a child or planning it. It must be taken into account that a person is capable of carrying a pathogen for a long time, but at the same time has absolutely no idea.
Modern analysis allows you to correctly identify the presence of the disease. A smear is usually taken from a pregnant woman in the same way as from everyone else. The procedure is painless and quite productive in terms of detecting the disease.
Treatment
Treatment is usually based on symptomatic therapy, as well as the elimination of dehydration. It is best to contact professionals to prescribe the correct treatment. They will prescribe the necessary medications.
Typically, chloramphenicol, ampicillin, and ceftriaxone are used for these purposes . Such drugs are suitable for use by pregnant women. In some severe cases, a pregnant woman may be prescribed chloramphenicol. But it is prescribed infrequently and only when the bacteria are resistant to other drugs.
In case of illness, the first thing to do is gastric lavage. Thanks to it, you can avoid intoxication of the body. After this, the pregnant woman should be offered sweet and hot water.
In order to prevent dehydration, you need to take a saline solution. You can make it yourself or purchase it at a pharmacy.
Doctors may also prescribe certain antibiotics. You should not select medications on your own, because there is a risk of illiterate choice and incorrect treatment. But for a pregnant woman, such a risk is simply unacceptable.
It is advisable to follow a special diet. It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods that may be potentially dangerous. Also, a pregnant woman’s diet should not contain chemical products. It is important to strengthen the immune system, which will allow a pregnant woman’s body to quickly recover after an illness.
Source: https://moeditya.com/pregnancy/bolezni-pri-beremennosti/salmonellez-pri-beremennosti
Fetal infection
Infants have an increased risk of developing a generalized form with frequent deaths. It is not advisable for a baby to get sick.
Most salmonella (two common types are Salmonella Enteridis and Salmonella Typhimurium) are the cause of salmonellosis, expressed as mild gastroenteritis. Endotoxin causes symptoms including:
The incubation period lasts a few hours, sometimes a day, averaging 1-2 days. In a week, a strong body will improve. The baby's immunity has not yet developed. Antibiotics will be required in 2% of cases. With pregnant women, the problem comes down to a limited choice of medications. Example: fluoroquinolones provoke a risk of developing disorders in the fetus.
Sticks through the placenta cause undesirable consequences for the child and parents, even in the absence of pronounced symptoms. In 2004, Scandinavia magazine published a story about a girl who was hospitalized at 25 weeks of pregnancy. Gastroenteritis of salmonella origin was found. Due to the registration of strange deviations from the normal heart rate of the fetus, doctors performed a caesarean section.
Four hours later, the baby died, despite the efforts of doctors. The pathologist concluded that the cause was blood poisoning with salmonella. As a result, many fetal systems failed. A truly terrible case was brought to the attention of the public by the press in 2008. After suffering a simple infection (salmonella), the mother had a miscarriage at 16 weeks.
Serological method
This method is used to study immunochemical reactions of blood. Such diagnostics can significantly expand the doctor’s capabilities in making a diagnosis.
There are two main objectives of using this method:
- identification of antigens;
- determination of antibodies.
One of the most important chemical methods is enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). It is based on the interaction of antigens and antibodies.
An enzyme molecule is chemically attached to the antibody molecule. The enzyme is used as a marker to monitor one of the reaction components.
The main components of the reaction are:
- antigen;
- antibody;
- enzyme-labeled antibody;
- enzyme substrate;
- indicator dye.
The wells of a special plate are sensitized with antibodies specific to the desired antigen. Next, adding the test material and then antibodies to the same antigen, labeled with an enzyme.
After adding the substrate and chromogen, if the antigen is present in the material, the well turns yellow. The color intensity is proportional to the concentration of antigen to the pathogen.
Nutrition
Complications
In severe cases, salmonella leaves the lymphatic system adjacent to the intestines and enters the bloodstream. Bacteremia causes catastrophic consequences with a fatal outcome. Caused by complications - the infection affects arbitrary internal organs and tissues. Consequences:
- Heart valve defects.
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the heart (endocarditis).
- Pathogenic process in bones (osteomyelitis).
- Kidney damage (pyelonephritis).
- Brain defects.
- Reiter's syndrome.
Due to toxins, the bacterium provokes autoimmune reactions - the body fights its own cells. The affected area includes joints, eyes, and other parts of the body. Pregnant women have a higher risk of complications compared to other categories of citizens.
Protection rules
Salmonellosis is “afraid” of basic hygiene rules and good heat treatment of products - at high temperatures the bacterium does not survive, so the disease does not develop, even if salmonella has reached a person. Salmonellosis and pregnancy should not coincide in time, which is why pregnant women are simply obliged to increase vigilance during the entire period of waiting for a child.
What rules will help to avoid infection:
- Be sure to wash your hands with warm water after walking outside, visiting the toilet, or interacting with your pet.
- If you have prepared raw meat or dishes made from raw eggs, immediately wash your hands with warm water and soap, as well as knives, plates, and cutting boards that have come into contact with the food.
- Eat only boiled, fried and stewed meat. Steaks cooked medium-well, especially with blood, cannot be eaten. Soft-boiled eggs and fried eggs are high-risk dishes. Want to eat a soft-boiled egg? Wash the egg thoroughly with warm water and soap.
- Wash all fruits before eating, even bananas and oranges, from which we usually remove the skin.
- Give preference to products made from pasteurized milk, which already contains all living bacteria.
As you can see, it is quite easy to protect yourself from such a nuisance as salmonellosis if you follow simple hygiene rules and do not eat half-raw meat and eggs. Even the biggest fans of steaks and tartare are better off giving up gastronomic delights while expecting a baby. But the main advice is that if you suspect something is wrong, you have loose stools and vomiting, do not blame everything on the course of pregnancy. Get tested, get examined and continue to enjoy such a wonderful time as pregnancy.
Salmonellosis can occur in pregnant women. In this case, there are a lot of nuances in treating the disease, diagnosing it, etc. Thanks to this article you can learn all the most useful and important things on this topic.
With the help of the article, it will be possible to solve a lot of current problems related to the identification of this disease and the selection of optimal treatment methods. In general, the article will bring a lot of useful information to every reader.
Salmonellosis in infants
Salmonellosis and pregnancy are incompatible things. Complications await the baby. Infants often develop a generalized form, which is fraught with complications. It is not possible to predict the result in advance - the microbe infects new areas depending on the characteristics of the baby’s body. In 2006, the journal Obstetrics and Gynecology published information about a baby who was seriously retarded in development. The cause was either maternal salmonellosis during pregnancy or infection in the child after childbirth.
Diagnostic measures
After the expectant mother notices alarming symptoms, she should immediately contact a medical facility for consultation. To diagnose salmonellosis, specialists will first collect a history of the disease, after which they will prescribe a series of laboratory tests. The results of a smear and urine and blood tests will help differentiate salmonella from other helminthic infestations.
Learning to cook
Mom should learn to cook. A smart wife looks after herself, others tyrannize their soulmate. It will be difficult for lovers of homemade mayonnaise and confectionery. The yolk coagulates at 70 degrees Celsius. Heating it for half an hour (when pasteurizing) will not be easy.
Do not attempt to perform this operation in a microwave oven - this may damage the product. The chicken egg bursts and scatters throughout the chamber of the device. It’s easier for housewives with a multicooker with the Chef function. Following the instructions, set the temperature to 63 degrees for a long time:
- Pour enough water into the multicooker bowl.
- Turn on the program.
- While the water is heating, wash the eggs.
- Check the temperature with a thermometer (remote infrared milk thermometer).
- Once the desired level is reached, place the eggs for half an hour.
After the specified time, there will be fewer bacteria inside. To clear your conscience, wait longer - the yolk will not immediately reach the desired temperature. There are no difficulties with other products - they do not have components that coagulate when heated. Boil the milk, heat the cottage cheese. This destroys beneficial lactic acid bacteria, but the product becomes safe.
What you need to know
Salmonellosis, the causative agents of which were first discovered in 1880 by K. Ebert, is anthropozoonotic, i.e. an infectious, invasive disease that affects both people and animals.
Bacteria can survive for quite a long time in the external environment; some species are resistant to antibiotics and disinfectants.
The infection is characterized by damage to the intestinal tract and general intoxication of the body, while recovery (in the most common form of the disease) occurs after 7-10 days.
There are several forms of the disease, with varying degrees of severity:
Gastrointestinal. Characterized by water-salt imbalance and diarrhea.
Typhoid-like. Accompanied by fever, enlarged spleen and liver, and the appearance of a rash.
Septic. It is characterized by the appearance of purulent lesions on the body.
Meningeal. Affects the central nervous system, accompanied by convulsions, vomiting, stiff neck, swelling of the fontanelle in infants.
Erased. Involves a slight loosening of stools for two days.
- Subclinical. It has a hidden course and can only be detected in a laboratory way.
After suffering from salmonellosis, the person who has recovered from the disease develops immunity, which lasts no more than a year. After this time, re-infection becomes possible.
A healthy body is quite resistant to infection, and it requires ingesting quite a lot of pathogenic bacteria to become infected.
However, there are factors that can weaken the body and make it vulnerable to salmonellosis. This:
- Using heartburn medications. These medications reduce the acidity of gastric juice, which can destroy Salmonella bacilli.
Inflammatory phenomena in the intestines. Their presence makes the intestinal walls most vulnerable to the penetration of microbes.
Weakened immunity, HIV infection.
Staying in places with poor sanitation and lack of central sewerage. During pregnancy, you should refrain from traveling to countries with a low standard of living and a hot, humid climate.
Lack of purified drinking water for cooking and drinking.
Presence of pets, reptiles, birds.
The source of contamination is usually products obtained from farm animals that are infected with the infection. This:
Salmonella bacilli persist in these products if they are not cooked properly, and if food is stored at temperatures exceeding 4 °C, the bacteria begin to actively multiply.
In addition, the infection can enter the body through raw, unboiled water from contaminated bodies of water, used for making ice or drinking.
Infection with salmonellosis can occur through excrement or the oral route; transmission of infection through household contacts (through shared toys, towels, hygiene items) is possible, but the main route of infection is food.
Salmonella that enter the stomach with food are not exposed to gastric juice and, together with processed food, move into the intestines, where they are introduced into the intestinal walls.
From there, Salmonella enters the bloodstream, attaches to the membrane of blood cells, and then penetrates the red blood cells, causing their degeneration.
The penetration of microbes into the submucosal layer of the intestine is counteracted by phagocytes, which is accompanied by the occurrence of inflammatory reactions: the temperature rises, and general health worsens.
From the affected layer of tissue, fluids are released into the intestinal lumen, which increases the volume of the contents. This causes frequent loose stools, which leads to dehydration.
Diagnostics
At the slightest suspicion, consult your supervising physician. He will tell you how to get tested for salmonellosis during pregnancy. To detect bacteria, a spinal cord puncture is taken. The principle of collecting analysis depends on the capabilities of the laboratory. It is acceptable to donate stool and blood.
A smear for salmonellosis is taken from the anus before childbirth. The purpose of the event is to eliminate the influence of Salmonella bacteria on the fetus. In emergency cases, the doctor will think about antibiotics to destroy the pathogenic factor.
Feces on the disgroup
Feces are given to determine:
- quantitative and qualitative changes in fecal microorganisms;
- ratio of microorganisms;
- severity of the pathological process.
The required components of such a study are:
- quantitative techniques;
- multi-vector studies, i.e. determination of all microorganisms present in feces;
- comparison of the results obtained with the clinical data of the patient and his age indicators.
Microbiological studies of stool are based on inoculation of the delivered material on nutrient agar prepared in an analyzer. The crops are then tested by strains and enzymatic methods.
How to avoid getting infected and protect yourself from infection?
In order not to exclude salmonellosis during pregnancy, you need to:
- practice hand hygiene before eating food;
- eat only washed fruits and vegetables;
- do not drink unboiled tap water;
- subject products to proper heat treatment;
- remove raw eggs and whole milk from your diet;
- store food in the refrigerator;
- do not eat in public catering and canteens;
- do not visit places with unfavorable sanitary conditions.
To prevent salmonellosis during pregnancy, you should exclude raw eggs and soft-boiled eggs from your diet (sometimes the bacterium is in the egg itself), and also refrain from eating meat dishes that are medium-rare or with blood. If the meat of chicken and other animals is not properly cooked, it becomes a carrier of pathogenic bacteria.
Concept of infection
The bacterium easily tolerates low temperatures without losing its ability to reproduce. Salmonella can live in water for six months, and in soil for a year. It does not die in food for about 3 weeks.
You can become infected in several ways:
- when eating meat and eggs;
- upon contact with a patient;
- while swimming in a pond next to which cattle are grazing;
- upon contact with animal feces.
After infection, symptoms begin within 48 hours. Manifestations of the violation are as follows:
- hyperthermia;
- intoxication;
- diarrhea;
- nausea, vomiting;
- excessive formation of gases.
Stool with salmonellosis is watery, foamy, after a few days with an admixture of mucus.