Each disease is both dangerous and insidious in its own way. Unpleasant symptoms and poor health make us think that the disease has already arrived. A disease such as radiation sickness is a prominent representative of such ailments. Many people have heard about the existence of radiation sickness and the seriousness of its consequences for humans. Chernobyl, which made a lot of noise throughout the world, conveyed to people the necessary information about the serious danger from radioactive radiation in the shortest possible time. What this kind of danger is, we will discuss later in the article.
Radiation sickness is the body’s reaction to exposure to life-threatening radioactive radiation.
Types of radiation
The most dangerous for people are alpha, beta and gamma radiation, which can lead to serious illnesses, including genetic disorders, as well as death. The level of exposure to radiation on people's well-being is completely dependent on the type of radiation, its duration, and frequency. It follows from this that the consequences of radiation can occur both with a one-time interaction with the source, and with multiple interactions.
So, for example, if you store weakly radioactive items in your home, in particular antiques, radiation-treated precious stones or items made of radioactive plastic, then exposure cannot be avoided.
Classification
The classification is based on the criteria of time of injury and radiation dose. The main classifying features are: the nature of exposure, phases of the disease, severity, form of the disease. A detailed classification with comments is presented in the table.
| Classification sign | Form of the disease | Comments |
| Nature of exposure | acute | develops during a single massive attack of a high dose of radiation |
| chronic | occurs with prolonged, repeated exposure to low doses of radiation | |
| Shape (depending on radiation dose) | radiation injury | short-term single irradiation with a dose of less than 1 Gy |
| bone marrow | damage with a dose of 1 to 10 Gy, survival rate is 50% | |
| gastrointestinal | irradiation with a dose of 10 to 20 Gy, accompanied by gastrointestinal symptoms, is extremely difficult | |
| vascular (toxemic) | develops when exposed to a dose of 20 to 80 Gy, characterized by severe poisoning and circulatory disorders | |
| cerebral | the radiation dose is over 80 Gy, death occurs from cerebral edema in the first three days after the injury | |
| Phases of the bone marrow (typical) form | I – phase of primary general reactivity | develops immediately (in the first hours) after the lesion, accompanied by malaise, decreased blood pressure, nausea, and sometimes vomiting |
| II – latent phase | begins 3-4 days after irradiation, lasts about a month, is characterized by an imaginary improvement in condition | |
| III – phase of developed symptoms | occurs a month after irradiation, accompanied by disruption of various organs and systems (increased bleeding, gastrointestinal symptoms, general intoxication) | |
| IV – recovery phase | the duration of the recovery period depends on the radiation dose and the general condition of the body | |
| Period (for chronic radiation sickness) | formation | lasts from one to three years |
| recovery | begins three years after cessation of radiation exposure | |
| consequences | the outcome of radiation sickness may be recovery or partial recovery |
Units of measurement of radioactivity
Radioactivity is measured in Becquerels (BC), which corresponds to one decay per second. The level of radioactivity in substances is also often assessed in units of weight - Bq/kg, or volume - Bq/cubic. m³. Sometimes you can meet such a unit - Curie (Ci). It is an expression of enormous magnitude, equal to 37 billion Bq. During the decay of substances, sources emit ionizing radiation, the measure of which is exposure doses. They are measured by Roentgens (R). One Roentgen is quite a significant value, which is why in practice the millionth (μR) or thousandth (mR) fraction of a Roentgen is usually used.
I use household dosimeters to measure ionization processes over a certain time. This does not mean the exposure dose itself, but only the level of its power. The unit of measurement is microroentgen/hour. Actually, this indicator is considered the most important for people; thanks to it, it is possible to assess the danger of certain radiation sources.
Is radiation created by man?
Since all cases of radiation contamination of nature and death of people are associated with human activity, it is generally accepted that radiation is, in principle, the creation of human hands, but this is not so.
Radiation is completely natural. It was before us and will be, even if we ourselves or something destroys us on our planet. For example, the sun's rays are also radiation, it is just highly filtered by our atmosphere. Although, in hot countries where rays pass through the atmosphere in a straight line, the natural background radiation is quite high. It is unlikely that you will die from this, but it is still safer at the poles.
Tanning is great, but you need to tan wisely. don't forget about the cream.
There is radiation everywhere in space. This is because it is nothing more than high-energy particles that ionize atoms. As a result, they can lead to structural changes and even destroy molecules of the human body. The nuclei of some atoms are unstable and they can, by emitting particles, transition to a stable state. The result is alpha, beta or gamma radiation.
These particles are everywhere. That is why the concept of “natural background radiation” exists. It does not harm humans, since we have adapted to it, but with excess doses, such as sunny places and areas of radiation testing or disasters, it is better to be careful.
The influence of radiation on people's health
The effect of radiation on the human body is called exposure. During this exposure, radioactive energy is introduced into cells, destroying them in the process. Radiation exposure can cause a wide variety of diseases, such as infectious complications, metabolic disorders, malignant tumors and leukemia, infertility, cataracts and much more. In particular, radiation can have an unusually acute effect on the process of cell division, which is why it poses an extreme danger to the child’s body.
The human body can react not so much to the radiation itself as to its sources. Radioactive substances can enter the body in different ways. For example, its appearance in the intestines can occur when eating food or water, in the lungs during breathing, and on or through the skin during medical diagnostics using radioisotopes. This will be the so-called internal exposure.
How to remove radiation from the body? This question is undoubtedly asked by many people. For example, it is known that by consuming certain foods, as well as vitamins, you can help the body cleanse it of minor radioactive doses. Although during the Chernobyl disaster there were rumors that KGB representatives knew how to remove radiation while in the zone and came out of it without harm to the body. Speculation was based on the fact that they allegedly ingested some special top secret activated carbon or some analogue.
How does radiation sickness develop?
Radiation sickness can be called the body’s reaction to exposure to life-threatening radioactive radiation. Under the influence of such an unfavorable factor, processes that are unnatural for normal functioning are launched in a living organism, leading to failures in many vital systems. This disease is very dangerous for human life, as it is an irreversible process, the destructive development of which can only be stopped.
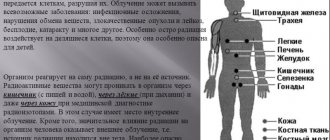
Radioactive radiation affects the human body as an aggressive factor that causes associated diseases. Its impact depends on the time and area of radiation, the method of radiation entering the body, as well as the immune resistance of the body itself. Considering the degree of radiation damage, we can identify the main areas that most often undergo pathological changes due to radiation sickness: • gastrointestinal tract; • central nervous system; • circulatory system; • spinal cord.
The consequences of radiation sickness in these areas lead to serious dysfunctions, which can manifest as a single complication or be combined with several. This combination is usually observed in cases of radiation damage of the 3rd degree, the consequences of which can take on very serious forms of disease, including death.
Are computers also sources of radiation?
Such questions worry many people in the era of computer technology and technology. The only elements in computers that, in theory, can be radioactive are monitors, especially electro-beam monitors. In modern displays, liquid crystal and plasma, radioactive properties are not observed.
In CRT monitors, as in televisions, weak sources of radiation are observed, but these are X-ray types of radiation. They appear on the inner surfaces of glass screens. Due to the significant thickness of these same glasses, most of them are absorbed. At present, it has not been possible to detect any negative impact of CRT monitors on health, and in the case of widespread use of LCD monitors, such issues will completely lose their relevance.
Can patients exposed to radiation expose others to radiation?
How carefully should patients behave after a radioisotope scan procedure or after a course of radiation therapy for cancer? How long do radioactive isotopes stay in the body? And how long does it take for radiation to be detected and affect others?
A report from Johns Hopkins University said patients exposed to radiation should be aware of the possibility of exposing others to radiation. After all, the main problem is that radioisotope scanning is not replaced by other examination methods. Unless we develop new diagnostic methods, radioactive research methods will only become more popular and accessible over time.
During examinations to diagnose thyroid dysfunction, coronary blood flow disorders or cancer, radioactive drugs are administered intravenously, swallowed or inhaled by the patient. After this, gamma radiation detectors or positron emission tomography (PET) scanners detect the radiation emanating from the particles and, after computer analysis, display data on the condition of a particular organ on the monitor screen.
Given these features, after the procedure, doctors advise patients to wash their hands thoroughly after using the toilet. It is also important to flush the toilet twice to ensure that any source of radiation is removed.
Different methods of radiation exposure result in different degrees of exposure. For example, radiation therapy produces much more radioactivity than radioisotope scans. However, in patients who have received external beam radiation therapy, the site of radiation is limited to the local area of tumor growth. In this case, there will be no harmful effects on other people.
It's a different story when the radiation source is internal, especially in cases where prostate cancer patients are treated with brachytherapy. During this procedure, small radioactive beads are placed into the prostate tissue. These tiny particles, about the size of a grain of rice, are placed in the tumor itself and the area around it.
A report from Johns Hopkins University states that when low-dose temporary implants are used, patients should remain in the hospital and limit contact with family members. Visitors can only stay close for 10 to 30 minutes, and pregnant women should not be near such a patient at all.
But it’s a completely different story when brachytherapy is performed with the introduction of permanent implants. The radiation intensity in this case weakens gradually over a long period of time, so the patient is required to take certain precautions. Radiologists do not advise such patients to hug family members or those who came to visit them for several days after the implantation procedure. And for the next six months, they must keep a distance of 2 meters from children and pregnant women.
Currently, radioactive iodine preparations are used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism (hyperfunction of the thyroid gland) and malignant neoplasms of the thyroid gland. In this case, during the first week after treatment, the patient should sleep alone, use separate towels and dishes, and wash clothes separately.
Patients should also be aware, but are sometimes not told, of one important fact: during their contact with other people, residual radiation in their body can affect the sensory systems of the other person's body.
After a bone or thyroid scan, the body emits radiation for three days. The heart scan results in follow-up radiation for 51 days, and after radioactive iodine therapy, radiation is recorded for three months.
But how often are patients told that they are radiation sources? The Journal of Nuclear Medicine recently reported findings from an audit of 66 health care facilities that found patients were often unaware of their own radiation exposure.
In addition, patients usually do not know what radiation dose diagnostic procedures produce. In fact, even the doctors who prescribe these methods have no idea about the radiation exposure their patients are exposed to, or significantly underestimate the intensity of exposure.
For example, the audit found that 94% of pediatricians who ordered computed tomography (CT) scans were unaware of the radiation dose the children would receive. They did not know that due to the higher sensitivity of children's organs, each CT scan of the stomach is equivalent to a dose of more than 4,000 roentgens. In fact, children are often exposed to levels of radiation that are believed to cause cancer.
Patients should remember that radiation is like an elephant: it cannot be ignored. Radiation accumulates and each subsequent radiation exposure is added to the previous one.
I advocated for us all to have radiation dose cards to keep track of throughout our lives. But so far no one has listened to me.
Dr. W. Gifford-Jones. is a medical journalist in private practice in Toronto. His website is https://mydoctor.ca/gifford-jones
English version
Can people be sources of radiation?
When human bodies are exposed to radiation, radioactive substances are not formed in the latter, that is, people themselves do not turn into sources of radiation. By the way, the production of X-rays, contrary to popular belief, is also safe for people. Therefore, unlike diseases, radiation injuries cannot be transmitted from one person to another, however, the presence of radioactive objects carrying charges can pose a danger.
Traditional methods of treating radiation sickness
Folk remedies for the treatment of radiation sickness are also often used as complex therapy with basic drug treatment. The main alternative treatment is also aimed at removing radionuclides from the body and stimulating the immune system. For these purposes, traditional medicine has a whole arsenal of excellent remedies that have a mild effect on the human body and allow them to be used for a long time. This treatment is quite effective and is an excellent method for prevention. In fact, there are a lot of recipes, but we will look at a few of the most proven and effective ones.
Infusion of pine needles. With the help of such an infusion, you can neutralize radioactive effects, that is, remove radionuclides from the body. We prepare an infusion based on half a liter of boiled water and five tbsp. l. crushed pine needles. Do not bring the infusion to a boil and leave for 24 hours. This medicine should be drunk in full during the day, the procedure should be repeated every other day for a month.
Healing sea buckthorn oil. This method is perfect for both prevention and treatment, because it has a pronounced anti-radiation effect. The essence of the method is as follows: you need to take 1 tsp. sea buckthorn oil 3 times a day for one month.
How are radiation levels measured?
Radiation levels are mainly measured using dosimeters. The presence of such household appliances is indispensable for those who intend to be extremely safe from harmful, and indeed sometimes fatal, radioactive effects. The main purpose of household dosimeters is to measure radiation doses in places where people are, as well as to examine any objects or items. This can be cargo, building materials, money, food, children's toys, etc. Instruments that measure radiation levels are purchased mainly by people who often visit areas with radioactive contamination, in particular caused by the Chernobyl accident. It should be noted that such outbreaks exist in almost most regions of the European part of Russia.
Dosimeters also help those who travel to unfamiliar territories far from civilizations, for example, while hiking, picking mushrooms and berries, and also while hunting. An indispensable condition, especially in recent times, is considered to be an inspection for radiation safety of places proposed for the construction or acquisition of houses, dachas, vegetable gardens or land plots, otherwise such acquisitions can only bring mortal danger or serious illness.
Cleaning food, soil or objects from radiation is almost impossible, as modern scientists claim. Although there is, of course, unconfirmed evidence that installations for such cleaning have existed for a long time, at least since the time of Chernobyl, they are classified for some unknown reasons. Thus, the only available way to protect yourself and your family is to stay as far away from all this as possible. With the help of household dosimeters, you can identify potentially dangerous sources.
Treatment of the disease
Unfortunately, no one is immune from radiation sickness; in the practice of doctors, this disease is often diagnosed in both adults and children. The causes are always different: from banal food products from the “Chernobyl zone” to radiation exposure in industrial conditions. Timely diagnosis of the disease often saves the lives of many people, while delaying treatment can result in death.
The main treatment of radiation sickness should be aimed at: • Determining the complete picture of damage to internal organs. It is on the basis of such an examination that complex therapy should be prescribed, which will be aimed at restoring, for example, the organs of the digestive tract, the hematopoietic system or the central nervous system, depending on where the pathological changes are recorded.
• Carrying out treatment. Treatment of radiation sickness must be carried out under the supervision of a doctor and should be aimed at removing radioactive substances from the victim’s body. All prescribed medications and tablets must be taken on time and as prescribed, because this disease tends to get worse without proper treatment. That is, the longer you do not treat radiation sickness, the greater the likelihood of serious health consequences.
• Stimulation of immunity. Regardless of the degree of radiation exposure, a person’s recovery time directly depends on how quickly his immune system is able to restore its former health. Therefore, “stimulating” the immune system is an important stage of treatment, which is aimed at a quick recovery of the patient. For these purposes, immunostimulants are used in medical practice, and a vitamin diet is also used to strengthen the immune system.
• Disease prevention implies further exclusion from the patient’s life of factors that can have a radioactive effect on his body. Preventive actions include changing jobs, observing the timing of X-ray examinations (once every six months), as well as completely eliminating the latter in cases of pregnancy.
Folk remedies for the treatment of radiation sickness are often used as complex therapy with basic drug treatment
In fact, there are a lot of ways to treat radiation sickness, but listing modern treatment methods and naming a specific medicine is inappropriate, since only a doctor must prescribe rehabilitation therapy.
Radiation was “created” by people
Lie
The radiation itself is of natural origin. In particular, as a result of solar radiation, background radiation is also generated. In the south, where, as is known, there is a very bright and hot sun, the natural background radiation is quite high. Of course, it is not destructive for people, but it is higher than in the countries of the northern hemisphere. In addition, there is cosmic radiation, which reaches our planet from outer space and encounters the atmosphere.
Pathogenesis
The damaging factors are alpha and beta particles, gamma rays, neutrons, and x-rays. At the same time, the first two types of radiation cause radiation sickness when it enters the body through inhalation of affected air and contact with it of the skin and mucous membranes, through food and water, and the rest can affect even with external influence.
As a result of radiation damage, radiation toxemia develops, when pathological changes occur at the cellular and molecular levels. Damaging substances affect cells of the bone marrow, lymphatic system and skin, endocrine glands, and intestinal epithelium. This leads to the development of bone marrow, intestinal, hemorrhagic and other syndromes that make up the clinical picture of radiation sickness.
The presence of lead walls will protect against radiation
Partial truth
In explaining this point of view, it is advisable to understand some points. First, there are several types of radiation, which in turn are associated with a wide variety of types of propagating particles. For example, existing alpha radiation very effectively ionizes everything around. However, they can be delayed by ordinary outerwear. Thus, if there are sources of alpha radiation in front of people, and they are dressed, and even wearing glasses, then nothing terrible threatens them.
Beta radiation has a lower ionizing susceptibility, but it is already more deeply penetrating radiation. But it can also be stopped, for example, with a small layer of aluminum foil.
Well, gamma radiation, which, when compared with the same intensity, has the lowest ionizing ability. At the same time, they have the best penetrating characteristics, and as a result are considered the most dangerous. Thus, no matter what protective suits people wear in front of gamma sources, they are still powerless and in any case will receive their dose of radiation.
In fact, protection from gamma radiation is mostly associated among people with the presence of lead cellars, bunkers and other similar attributes. Of course, the same thickness of a lead layer will be much more effective than the same layers, for example, of concrete or wooden shelters. Lead is not a magical material, although it has the most important parameter - high density. Actually, due to their high density, lead materials were actually often used in protective structures in the mid-20th century, at the height of the nuclear arms race. With all this, lead has a certain toxicity, which is why today people prefer to use, for example, thicker layers of concrete for the same purposes.
Why kill domestic animals?
Two weeks after the Chernobyl disaster, soldiers in protective suits arrived in Pripyat. They shot dogs and cats, which during this time had become quite thin without human care. The bodies of the animals were buried at a special site. No exceptions were made: the soldiers destroyed all the pets they encountered. Such measures were not taken to stop the suffering of animals. People were afraid that radioactive dust would “escape” from the zone along with cats and dogs.
During the evacuation, people were ordered to take only the essentials with them. Pets, no matter how beloved, were not included in this package. Residents of Pripyat were forced to reluctantly leave their dogs running after the buses until the last minute. But this measure saved the lives of thousands of people, since cats, dogs, rabbits, birds, livestock - any animal - could easily carry toxic dust on their fur and spread it in a safe area.
Some animals were lucky and were not found by soldiers with guns. But luck is conditional: due to numerous genetic damages, cats and dogs have developed mutations that are incompatible with life. In general, the exclusion zone has seen a decline in bird and mammal populations, but in unequal proportions. This is due to the fact that DNA repair occurs at different rates in different animals. Birds and mammals that remain in the exclusion zone suffer from cataracts and reduced brain size due to constant exposure to radiation through food, water and air. About 40 percent of birds in the affected area are sterile. Some species of animals and birds were able to adapt. For example, one 2020 report listed species such as wild boar and elk as thriving.
Taking iodine may protect against radiation poisoning
Lie
The use of iodine or any of its compounds does not at all counteract the negative effects of radiation. So why do doctors recommend taking iodine when man-made disasters occur in which radionuclides are released into the atmosphere? And all because when the presence of radioactive iodine-131 is detected in the atmosphere or water, it very quickly penetrates into people’s bodies. After which it accumulates in the thyroid glands, with a sharp increase in the risk of developing cancer and other diseases associated with these “delicate” organs. By “filling to the maximum” the iodine depots in the thyroid glands in advance, it is possible to reduce the uptake of radioactive iodine and, therefore, protect the tissues from further accumulation of radiation.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of radiation sickness is made based on medical history (there was a strong one-time exposure to radiation, or constant exposure to small doses) and the clinical picture.
Laboratory diagnostics help confirm the diagnosis:
- in a general blood test, a decrease in the number of red and white blood cells and an increase in ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate) are observed;
- a biochemical blood test shows a disturbance in the electrolyte balance of the blood, a critical decrease in the level of protein in the blood plasma;
- a myelogram (analysis of bone marrow puncture - extraction of a small amount of fluid from the sternum by puncture) reveals signs of severe inhibition of hematopoietic function.
Additional examination methods include analysis of scrapings from skin and mucous ulcers, blood cultures for sterility, electrocardiography, and ultrasound examination of internal organs.
Note! The lower the level of lymphocytes in the blood after 48 hours of exposure to radiation, the lower the chance of survival.
All radioactive substances necessarily glow
Partial truth
Experts call everything that is in one way or another connected with radioactive glow radioluminescence, and this is not considered an extremely common phenomenon. Moreover, as usual, it is not caused by the glow of the radioactive materials themselves, but occurs when the emitted radiation interacts with surrounding materials.
Back in the 1920s and 1930s, at the height of public interest in radioactive materials, a little radium was added to various household appliances, medicines and much more, including paint for watch hands and dial colors. This paint was basically a zinc sulfide base mixed with copper. Radium impurities emitted radioactive radiation and glowed green when interacting with paint.
Can radiation be washed off with water?
Radioactive particles cannot be destroyed, nor can their decay time be accelerated. Therefore, the only way to reduce radiation is to remove particles by mechanical, chemical or physicochemical methods. Decontamination with water is included in the first group, along with removing particles with a brush or vacuum cleaner. To increase effectiveness, soap or surfactants are added to the water. And this method really works. Moreover, it is suitable for everything: asphalt, household appliances, house walls, human skin. This method was used to save a frail antique violin that was very close to the epicenter of the Chernobyl disaster. Adding complexing agents, ion exchange resins, zeolites and sorbents to water increases the efficiency of decontamination, since the compositions remove radionuclides from the surface.
But if radionuclides are well bound to the surface or seep into small defects and cracks, they can no longer be reached by a stream of water. Then, for decontamination, they resort to more stringent methods: the top layer is dissolved with alkalis and acids. Strong oxidizing agents “rip off” organic dirt on which radioactive dust has adhered.
Radiation exposure will definitely lead to mutations
Is it true
Indeed, the process of radioactive radiation can lead to a wide variety of damage in DNA helices. To restore the entire gene system, during the repair process, damaged areas are filled in with random nucleotides. This is one of the options for the emergence of a new type of mutation.
With all this, it is advisable not to forget that people are quite well protected from background radioactive radiation. The presence of background radiation may not necessarily cause damage to the DNA helix. Sometimes, if one of the two circuits is damaged, it can always be restored using the backup second circuit.
Safe dose of radiation
Where does a person receive doses of radiation? Don't forget about natural radiation. In different parts of the planet, background radiation can differ significantly. So, on mountain peaks the radiation is higher, because there the atmosphere has lower protective properties. Increased radiation can also occur in places where there is a lot of dust and sand with thorium and uranium in the air.
What dose of radiation can be safe, maximum permissible, and the body will not suffer? It should not exceed 0.3-0.5 μSv per hour. But if you stay in this room for a short time, then the human body can tolerate radiation with a power of 10 µS per hour without harm to health, this is the maximum permissible level of radiation.