To protect against ionizing radiation, the following methods and means are used:
· reduction in the activity (quantity) of the radioisotope with which a person works;
· increasing the distance to the radiation source;
· radiation shielding using screens and biological shields;
· use of personal protective equipment.
To protect against alpha radiation, a 10 cm layer of air is sufficient. When located close to the alpha source, organic glass screens are used.
To protect against beta radiation, it is recommended to use materials with low atomic mass (aluminum, plexiglass, carbolite). For comprehensive protection against beta and bremsstrahlung gamma radiation, combined two- and multilayer screens are used, in which a screen made of a material with a low atomic mass is installed on the side of the radiation source, and behind it - with a high atomic mass (lead, steel, etc.) .).
To protect against gamma and X-ray radiation , which have a very high penetrating ability, materials with high atomic mass and density (lead, tungsten, etc.), as well as steel, iron, concrete, cast iron, and brick are used. However, the smaller the atomic mass of the screen substance and the lower the density of the protective material, the greater the thickness of the screen required for the required attenuation factor.
To protect against neutron radiation, hydrogen-containing substances are used: water, paraffin, polyethylene. In addition, neutron radiation is well absorbed by boron, beryllium, cadmium, and graphite. Since neutron radiation is accompanied by gamma radiation, it is necessary to use multilayer screens made of various materials: lead - polyethylene, steel - water and aqueous solutions of heavy metal hydroxides.
Premises intended for working with radioactive drugs must be separate, isolated from other premises and specially equipped. Walls, ceilings and doors are made smooth, without pores or cracks. All corners of the room are rounded to facilitate cleaning the room from radioactive dust. The walls are covered with oil paint to a height of 2 m, and when radioactive aerosols or vapors enter the air environment of the room, both the walls and ceilings are completely covered with oil paint. The premises are equipped with good supply and exhaust ventilation, and daily wet cleaning is carried out.
Individual protection means . To protect a person from internal radiation when radioisotopes enter the body with inhaled air, respirators (for protection from radioactive dust) and gas masks (for protection from radioactive gases) are used.
When working with radioactive isotopes, gowns, overalls, overalls made of undyed cotton fabric, as well as cotton hats are used. If there is a danger of significant contamination of the room with radioactive isotopes, a film (oversleeves, trousers, apron, robe, suit) is put on over cotton clothing, covering the entire body or areas of possible greatest contamination. Plastics, rubber and other materials that are easily cleaned of radioactive contamination are used as materials for film clothing. When using film clothing, its design provides for forced air supply under the suit and armbands.
Types of protection against ionizing radiation [edit | edit code ]
- physical: the use of various screens, weakening materials, etc.
- biological: is a complex of repair enzymes, etc.
The main methods of protection
from ionizing radiation are:
- protection by distance;
- shielding protection:
- from alpha radiation - a sheet of paper, rubber gloves, a respirator;
- from beta radiation - plexiglass, a thin layer of aluminum, glass, gas mask;
- from gamma radiation - heavy metals (tungsten, lead, steel, etc.); Gamma radiation is absorbed more efficiently the higher the average Z of the materials, so a ton of lead can be more effective than a ton of iron.
- from neutrons - water, polyethylene, other polymers, concrete; according to the law of conservation of energy, neutrons effectively dissipate energy on light nuclei, so a layer of water or polyethylene for protection against neutrons will be much more effective than armor steel of the same thickness;
- time protection;
- chemical protection.
Applications of beta radiation
Just like other types of radioactive radiation, beta radiation is widely used in medicine. These are beta therapy and radioisotope diagnostics.
- radiation therapy
For therapeutic purposes, applicators emitting beta rays are applied to the affected areas.
- For malignant tumors, interstitial and intracavitary beta therapy is used. The therapeutic effect is achieved due to the destructive effect of beta radiation on pathologically altered tissues.
- Radioisotope diagnostics uses beta particles as a radioactive tracer to detect tumor tissue.
Beta radiation sources are used in chemistry, to control various automatic processes, in car repairs, in archeology to determine the age of rocks, etc.
Physical protection (shielding) [edit | edit code ]
The thickness of a layer of a given material that reduces the radiation level by half is called a half-attenuation layer
. The ratio of radiation levels before and after protection is called the protection factor.
As the thickness of the radiation protection layer increases, the amount of transmitted radiation decreases exponentially. So, if the half-attenuation layer of compacted soil is 9.1 cm for gamma radiation from fission fragments, then a 91 cm thick embankment (a typical embankment over a radiation shelter) will reduce the amount of radiation by 2 10, or 1024 times.
The absorption rate (exponential) depends on the energy. For example, the half-attenuation layer for cesium-137 radiation is several times smaller than for cobalt-60 radiation.
The table below shows the characteristics of the half-attenuation layer of gamma radiation from fission fragments of some materials (in CGS units) [1]:
| Protection material | Half attenuation layer, cm | Density, g/cm³ | Weight of 1 cm² half-attenuation layer, g |
| Lead | 1,8 | 11,3 | 20 |
| Concrete | 6,1 | 3,33 | 20 |
| Steel | 2,5 | 7,86 | 20 |
| compacted soil | 9,1 | 1,99 | 18 |
| Water | 18 | 1,00 | 18 |
| Wood | 29 | 0,56 | 16 |
| Depleted uranium | 0,2 | 19,1 | 3,9 |
| Air | 15000 | 0,0012 | 18 |
Time will protect against radiation
This is more likely not protection, but an actual reduction in the time spent at the source of radiation. The less time a person is near a radiation source, the less harm it will cause to health. This method of protection was used, for example, during the liquidation of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant. Liquidators of the consequences of an explosion at a nuclear power plant had only a few minutes to do their work in the affected area and return to safe territory. Exceeding the time led to an increase in the level of radiation and could be the beginning of the development of radiation sickness and other consequences that radiation can cause.
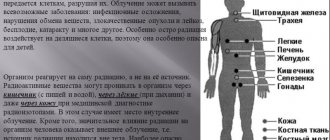
To weaken the effect of radiation on the body it is necessary. Effects of radiation on the body
Effective radiation treatment, unfortunately, harms healthy tissues and organs. And each new dose of radiation that a person receives during radiation therapy reduces the body’s protective functions and weakens the immune system.
Why is radiation dangerous and what happens after exposure:
- skin damage. It is accompanied by pain, swelling, redness, blisters form, pigmentation appears, and hair stops growing. Radiation ulcers are a complication. May cause skin cancer;
- disruption of the mucous membranes of the larynx, oral cavity and respiratory organs. The structure of the lung tissue becomes heterogeneous, a complication is acute radiation pneumonia, foci of infiltration. Hyperemia, erosion and necrosis of individual areas. Radiation therapy of the larynx provokes a cough with sputum, impaired salivation;
- changes in bowel function. Necrosis and ulcerative processes are observed on the walls, unstable stools, diarrhea, and there are frequent cases of bleeding from the intestines. Fistulas and scars form, the absorption of vitamin B 12, proteins and iron is disrupted;
- partial dysfunction of the urinary system. Kidney failure, nephritis, increased urea in the blood. From the bladder side, radiation cystitis, ulcers, necrosis and fistulas are possible;
- liver problems. Radiation hepatitis, fibrosis;
- consequences for the spinal cord are numbness of the extremities, irritability and weakness, pain in the sacrum, dizziness;
- complications for the brain. Memory impairment, emotional instability.
Radiation protection by distance
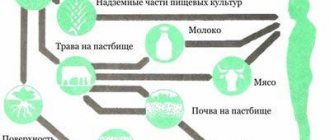
The most reliable way to protect yourself from radioactive radiation is to move away from the source of radiation as soon as possible. The distance depends on the radiation intensity, climatic conditions and terrain. For example, in the mountains the spread of radiation is noticeably less than on the plain, since mountains are a natural barrier to radiation and significantly reduce it. And when there is wind, you need to go against the wind, since most of the radioactive dust is spread with the help of the wind. And if possible, you can remove the radiation source to a safe area or for burial.
Radiation in the mountains. 1. Everything comes from space
Culture and Chernobyl have taught us to panic at the mere mention of the word “radiation.” But it's like being afraid of your skin or fluids, since radiation is all around us. She is among us, she is inseparable from us. Every day you come into contact with radioactive material, and it’s not at all about nuclear power plants, nuclear submarines and modern gadgets. We simply live in a radioactive environment. 85% of the annual radiation dose is so-called natural radiation. Part of it is formed due to cosmic radiation. But throughout history there have been no idiots walking around with lead umbrellas, but there are people who live more than a hundred years and do not get sick. For that matter, the largest release of radiation in history occurred in 2004, and neither Chernobyl nor Fukushima had anything to do with it. The culprit is a neutron star located 50 thousand light years from our planet. Why, in the next few thousand years the double star system WR 104 should turn into a supernova. This release of radiation may or may not cause a mass extinction on Earth. In any case, these are the doses you need to be afraid of.
Radiation protection with special means
In special cases, it is necessary to carry out protective activities in areas with increased background radiation. An example would be eliminating the consequences of an accident at nuclear power plants or working at industrial enterprises where there are sources of radioactive radiation. Being in such areas without using personal protective equipment is dangerous not only for health, but also for life. Personal radiation protection equipment has been developed especially for such cases. They are protective screens made of materials that block various types of radiation and special clothing.
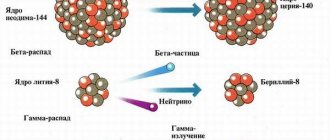
general description
Beta radiation is produced by the decay of atomic nuclei of radioactive substances.
Beta particles are either an electron or a proton (determined by polarity). Their flight speed can vary from 100,000 km/s to the speed of light. Therefore, in the surrounding space they can cover distances of up to 2 km.
However, they can penetrate into biological tissue only 2.4−2.6 cm. This is due to the dependence of the penetrating ability of the type of radiation under consideration on the density of the medium. Due to their insignificant mass, the emitted particles, deviating, describe chaotic trajectories inside the substance.
Alpha radiation protection
Alpha particles penetrate into the tissues of the human body only to a shallow depth, damaging only the surface of the skin. External α-irradiation is not particularly dangerous. But the entry of these fairly massive particles into the body (with food, water or through damaged skin) is fraught with serious poisoning due to their strong ionizing effect, the formation of oxidizing agents, free hydrogen and oxygen. Rubber gloves and a regular respirator help protect a person from alpha radiation. cotton clothing, polyethylene raincoat, paper, plexiglass.
Effect of β-particles on humans
As a result of β-irradiation, active radicals are formed in the cells of the body, which are highly reactive. Negative radicals enter into biochemical interaction with cell substances according to the type of oxidative reactions.
In cells, β-radiation provokes biochemical reactions that damage the DNA structure, disrupt the permeability of cytomembranes and the composition of intracellular substances. As a result, cell mutation or apoptosis occurs. All tissues have the ability to regenerate. When irradiation exceeds a threshold value, some cells are restored, while others lose their ability to regenerate.
Changes accumulate, leading to dysfunction of organs or the appearance of malignant neoplasms. When cells are irradiated, disruption of the DNA structure leads to mutations that are inherited. External exposure to β-rays on unprotected skin causes 1-2 degree radiation burns. β-particles penetrate the skin to a depth of 1-2 cm, which can cause damage to the basal layer of the skin in areas of the body unprotected by clothing.
In areas with delicate and thin skin, areas of necrosis may form; on coarser and thicker skin, trophic disorders are noted under the influence of β-particles. In this case, there is no damage to the bone marrow, and depression of hematopoiesis does not occur.
External skin injuries are called β-burns, although they are different in nature from thermal and chemical burns. The lesions occur gradually. There is redness and swelling, accompanied by itching.
When the skin is damaged, the initial period of damage is hidden. This phase can last from several hours to several weeks. The defeat leads to hair loss and desquamation of the upper layer of the epidermis. When mucous membranes are irradiated, redness and swelling are noted.
A dose of 500-100 rads causes severe swelling, redness, pain and erosion of the skin. Restoration of the skin structure occurs slowly. Painful sensations persist for a long time, and atrophy of the skin is noticeable. With moderate exposure, symptoms persist for 3-4 weeks.
Laser radiation and its effects on humans
When the skin is irradiated at a dose of 1000-3000 rads, changes appear several hours after irradiation. In this case, severe changes are observed, accompanied by the appearance of blisters on the skin, changes in blood composition, increased body temperature and dyspeptic disorders.
An extremely severe degree of skin damage (˃ 3000 rad) is accompanied by the formation of foci of necrosis, ulcers and the threat of sepsis. More dangerous for the body's condition is internal radiation caused by the penetration of radioactive particles through the respiratory system or digestive tract. At the same time, the threat to tissue health increases.
The degree of damage to biological tissue depends on the type of tissue, the time of contact with the radioactive substance, and the intensity of radiation. The most intense exposure is observed in the first few days after radioactive fallout (65%).
Gamma radiation protection
The most difficult thing is to protect yourself from gamma radiation. Uniforms that have a shielding effect from this type of radiation are made of lead, cast iron, steel, tungsten and other high-mass metals. It was lead clothing that was used during work at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant after the accident.
All kinds of barriers made of polymers, polyethylene and even water effectively protect against the harmful effects of neutron particles. For better efficiency, especially when it is not 100% known what kind of radiation you need to protect yourself from at the moment, it is better to use combined means of protection. For example, brick walls covered with polyethylene and heavy metal sheets will provide good protection against all types of radiation.
Required thickness of materials to reduce gamma radiation by 1000 times:
wood 2900 cm
radiation protection
How to understand the danger of EMP?
There are two ways to determine harm from EMR. In the first case, buy a dosimeter to measure radiation and check the devices at home and at work. Compare the results obtained with acceptable standards.
The second option is to check your health. The combination of negative symptoms that appears will indicate that there is a problem. Especially if such a picture emerges against the backdrop of a change of job or place of residence. Since the damage from radiation accumulates gradually, it will take some time for symptoms to appear.
The set of symptoms is something like this:
- the immune system can no longer cope with the simplest colds,
- the nervous system becomes more labile and receptive,
- libido decreases,
- endurance deteriorates,
- work activity is significantly reduced.
Definitely, the best option would be to resort to the measurement method. This way you can understand exactly what kind of device it is and what danger it poses, and take the necessary protective measures.