Radiation standards for humans
Are there safe doses of radiation? Even the most minimal doses of radiation can cause harm to health, which is often hidden. It is for this reason that we can only talk about permissible doses of radiation. These indicators are generally accepted, they are established by organizations such as WHO, UN, etc. They are used to control the absorbed dose of radionuclides in persons working under conditions of increased radiation exposure.
Background radiation up to 0.2 microsieverts per hour is considered completely safe (normal). The safety threshold is up to 0.5 microsieverts per hour. The volume of external and internal radiation received throughout the year, on average, reaches 3-4 millisieverts. All absorbed doses of radiation accumulate in the body and should not exceed 70-100 millisieverts over a lifetime.
What do single high doses of radiation lead to:
- 1 sievert – acute radiation sickness;
- 2.5 -4 sieverts - radiation sickness of moderate severity;
- 3-4 sieverts – severe radiation sickness, death is possible in 50% of those exposed;
- more than 7 sieverts – 100% mortality;
- over 10 sieverts is an absolute lethal dose, death within a few days.
Prevention
At the moment, there are no methods for absolute prevention of radiation sickness. The most effective methods are based on reducing the time of exposure to radiation, increasing the distance of a person from the radiation source and limiting radiant energy by shielding with heavy metals and concrete structures.
If you find yourself in an area of radiation contamination, then your first priority is to leave this area as quickly as possible. When it happens that moving is not possible, your maximum attention should be paid to personal hygiene.
- Firstly, do not leave the shelter (housing) unless absolutely necessary; the room must be wet cleaned 2-3 times a day.
- Secondly, if you suddenly have to go outside, wear clothes that are as light as possible, with long sleeves, a hood and a cap, and shower often if possible.
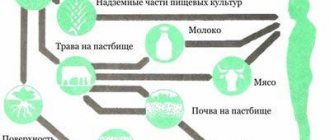
Particular attention should be paid to drinking water: it must be settled and filtered, at a minimum, with carbon filters. Food products also require careful preparation and processing: fish, liver, mushrooms and pork should be excluded from the diet; Peel fruits and vegetables completely, soak in water, and boil.
Studies on mice have shown that relatively small doses of ethyl alcohol can reduce the amount of radiation absorbed by the body. For this purpose, it is better to consume up to one glass of dry red wine.
There is information that domestic scientists have developed an anti-radiation vaccine, and it is undergoing preclinical trials.
Control sources
Life forced man to invent devices that measure the level of radiation and the dose received during irradiation. A test source is an object of ionizing radiation necessary to check the operation of instruments that measure radiation. They are:
- closed;
- open.
A closed control source is a device that prevents the radioactive substances it contains from entering the environment. An open source allows radiation to enter the outside when used. They have expiration dates and state standards.
Control source from the radiometer
Control sources are subject to strict accounting. Without restrictions, it is allowed to use sources that do not pose a danger depending on the radiation dose. Businesses and organizations using a reference source must be licensed. They are responsible for storage, use and disposal.
Their loss and uncontrolled use is unacceptable. All actions are controlled and documented. Instruments and the radioactive substance contained in them are accounted for separately. Any action performed on the control source, including its disposal, is documented.
The nature of ionizing radiation
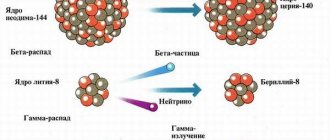
Any ionizing radiation can be attributed to one of two versions:
- electromagnetic,
- corpuscular.
The division is based on their nature. In the first case, the wave origin is as close as possible to visible light, and the range belongs to the ultra-short-wave category. Such radiation spreads at the speed of light and is characterized by particularly high penetrating power.
The most famous representatives of such exposure among ordinary people are:
- gamma rays,
- X-rays.
Corpuscular radiation includes three other representatives:
- alpha rays,
- beta particles,
- neutrons.
Alpha particles are the most powerful rays in terms of ionizing ability. This makes them the most dangerous for all life on our planet. But, despite the existential threat to humanity, these rays have little penetrating power. In practice, this means that the beam cannot harm a person if you move away from him at least half a meter or shield yourself with a cardboard shield.
Beta particles, on the contrary, have a more impressive penetrating ability at the expense of ionizing ability.
Neutron radiation has a strong penetrating ability. Researchers note that it threatens humans when exposed to external radiation.
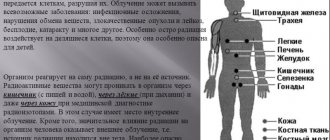
Any natural and artificial sources of ionizing radiation entail an impact on surrounding organisms. The severity will directly depend on the characteristics of the radiation itself, as well as the specific dosage.
Based on these principles, people have learned to protect themselves from possible defeats by being proactive.