Radiation and ionizing radiation The word “radiation” comes from the Latin word “radiatio”, which means “radiance”, “radiation”.
The main meaning of the word “radiation” (in accordance with Ozhegov’s dictionary, published in 1953): radiation coming from some body. However, over time it was replaced by one of its narrower meanings - radioactive or ionizing radiation.
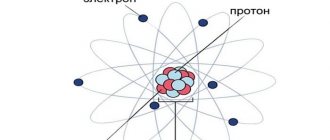
Ionizing radiation - in the most general sense - various types of microparticles and physical fields that can ionize matter.
Not all chemical elements have nuclei as stable as carbon. Many nuclei can unexpectedly decay, throwing out their parts with enormous energy and undergoing significant transformations. This phenomenon is called radioactivity. Radioactivity is divided into natural and artificial. There are five types of ionizing radiation (radiation):
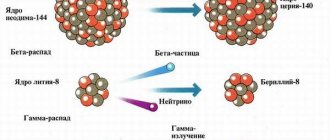
1. Alpha radiation - is a stream of nuclei of helium atoms, radiation has low penetrating ability (with external irradiation it is not able to penetrate the stratum corneum of the skin). The range in air is 2 cm. Thus, alpha radiation is absolutely safe during external irradiation and extremely dangerous during internal irradiation. The most effective protection is distance (more than 2-3 cm from the source); you can protect yourself from alpha radiation with a sheet of paper.
Source: chemlight.ucoz.ru Gamma radiation has a corpuscular nature
2. Beta radiation - is a stream of electrons, has a relatively low penetrating ability (2-3 cm with external irradiation). The range in air is about 15 cm. Thus, beta radiation can be dangerous with external irradiation (subject to contact with the skin), but it is more dangerous with internal irradiation, although less dangerous than alpha radiation. Protection - time and distance, as well as a screen (sufficiently thick clothing).
3. Gamma rays and x-rays are electromagnetic radiation. Both types have high penetrating power (on the order of a meter, i.e., with external irradiation, it penetrates the human body through and through). Thus, this radiation is most dangerous during external irradiation; you can protect yourself from it by distance, time and a screen (using petroleum products).
4. Neutron radiation - is a flow of neutrons. Characterized by high penetrating ability (even greater than that of gamma radiation), i.e. also permeates the human body during external irradiation. The ionizing ability is relatively low, but despite this, neutron radiation is very dangerous when exposed to external radiation. Protection from it by time, distance, screen (use lead plates).
Sources of radiation entering the human body
Radiation is found everywhere. The only question is in what quantities? In general, all sources of radiation on the planet can be divided into natural (cosmic radiation, gases, radioisotopes) and artificial (caused by humans). There are many ways that radiation, both artificial and natural, can enter the human body. Therefore, it is very important to know how radiation-safe an environment you live in.
There are many approaches to calculating radiation doses depending on the radiation source and the irradiated object. You and I are interested in radiation that affects humans: directly (external exposure) and indirectly (through food, air, water - internal exposure).
The absorbed dose is the energy of ionizing radiation transferred to a unit mass of a substance.
When applied to the human body, this is the energy of ionizing radiation transferred to a unit of mass of the human body. Taking into account the conversion of all types of radiation to gamma radiation and the different perception of different human organs, a unit of measurement called the Sievert is introduced for the absorbed dose (effective equivalent dose). 1 Sievert (Sv) = 100 Roentgen (R).
Dose rate is the radiation dose received per unit time, for example R/hour (roentgens per hour).
What kind of radiation is there?
Radiation is divided into subtypes based on the composition of the ionizing flux.
Particles come in different charges and sizes. Their penetrating ability and level of impact depend on these indicators:
- Alpha particles are positively charged nuclei of the chemical element helium (this does not mean that the helium in the balloons is radioactive!), they are heavier than the others, due to the fact that they have a charge, they are easy to stop even with a piece of paper;
- Beta particles are electrons that are always negatively charged and can be stopped with a thin sheet of aluminum foil;
- A gamma particle (photon) has no charge, but has a large amount of energy and the highest penetrating power; to protect against such radiation you need a lead coating;
- Neutrons are formed during the decay of a nucleus and the separation of electrons from it; they have no charge and are not dangerous.
X-ray radiation is also classified as ionizing radiation. Its particles penetrate well through soft tissue, which has found application in medicine in the form of an X-ray machine, but they are not as dangerous as gamma particles. We are exposed to x-ray radiation every day (in acceptable doses), the main source of which is the Sun. But even such radiation in high doses is dangerous.
How to measure radiation levels
Radiation levels can be measured using a dosimeter both in industrial and domestic conditions. For those who live near nuclear power plants, or people who are simply concerned about their safety, this device will be simply irreplaceable. The main purpose of such a device as a radiation dosimeter is to measure the radiation dose rate. This indicator can be checked not only in relation to a person and a room. Sometimes you have to pay attention to certain objects that may pose a danger to humans. Children's toys, food and building materials - each item can be endowed with a certain dose of radiation. For those residents who live near the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, where a terrible disaster occurred in 1986, it is simply necessary to buy a dosimeter in order to always be on alert and know what dose of radiation is present in the environment at a particular moment. Fans of extreme entertainment and trips to places remote from civilization should provide themselves with items for their own safety in advance. It is impossible to cleanse soil, building materials or food from radiation. Therefore, it is better to avoid adverse effects on your body.
What is alpha radiation and what are its dangers?
Streams of alpha particles are formed during the decay of radioactive chemical elements. They do not penetrate human skin, but are very dangerous if they enter the body (with food, water, air or through wounds). Here, when alpha particles come into contact with molecules within the cell, they ionize them. This starts a chain of chemical reactions, the end result of which is the destruction of tissue structures or DNA. But for this to happen, the radioactive isotope must enter directly into the body.
The affected area by alpha radiation is small (up to 10 cm from the source), since heavy particles quickly settle. Dosimeters do not detect alpha radiation and it is difficult to detect. But it is easy to protect yourself from it; you need thick clothing, gloves and a respirator - it is enough to cover the entire surface of the body and the respiratory tract.
External and internal irradiators
As mentioned above, the main background radiation is created by space objects , and there is not a single corner on planet Earth where the rays do not penetrate. The North and South Poles are most affected.
A very important factor is what altitude a person is from the sea, because the higher he is, the greater the radiation exposure. People living in mountainous areas are most susceptible to radiation. What can we say about pilots and aircraft crews, on whom the impact is maximum.
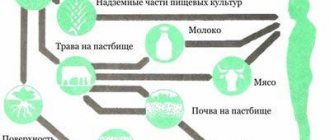
From the inside, radiation affects a person after contaminated food, water and air enter his body. It should be noted that people who prefer seafood receive a very high dose. The same can be said about deer meat, because these animals eat plants that can concentrate radioactive isotopes of the elements of the periodic table.
Just recently, scientists discovered that the previously beloved radon is actually very dangerous. It is independently capable of freeing itself from the Earth's crust. The gas has no organoleptic characteristics and is capable of penetrating into premises. The maximum concentration of this substance is achieved in basements and on the first floors.
Recently, scientists have been paying a lot of attention to nuclear physics.
Where can a person receive radiation from?
- Radionuclides have been created that are used in medicine, instrument making, geology and other branches of science. A variety of medical interventions involve the use of harmful rays. For example, this occurs during an X-ray examination.
- We must not forget about nuclear explosions, which have made a significant contribution to the current level of radiation on Earth. It is clear that the further a potential object is from a nuclear reactor, the lower the exposure dose to it. Almost all emissions from such reactors decay in the layers of the atmosphere, but there are also those that can spread throughout the Earth and harm the surrounding world endlessly.
- It is worth mentioning the mines and processing plants. Their production produces a lot of waste that remains radioactive for millions of years. This is the main source of impact on the population.
- Various technical means such as phosphors used on construction sites are very dangerous in terms of harmful radiation. What can we say about miners and gold miners who directly receive a dose of harmful radiation.
- In everyday life, a clock with luminous numbers can become an irradiator.
- It’s unfortunate, but even a color TV is capable of producing X-rays.
Thus, in the current world, every resident certainly receives a certain dose of radiation every day.
What is beta radiation and what are its effects?
Beta radiation is a stream of negatively charged particles that are more penetrable than alpha. But their ionizing ability is tens of times lower.
Beta particles travel up to 20 meters from the radioisotope, so they are more dangerous than alpha particles. They easily penetrate clothing and skin, affecting the cells of a living organism. It is this radiation that is called one of the causes of cancer.
For reliable protection against this type of radiation, a metal coating of a few millimeters, a gas mask and timely intake of radioprotective drugs are sufficient.
Gas discharge meters
Radiation can be detected and measured using a variety of sensors. The simplest of them are ionization chambers, proportional counters and gas-discharge Geiger-Muller counters. They are a thin-walled metal tube filled with gas (or air), along the axis of which a wire, an electrode, is stretched. A voltage is applied between the housing and the wire and the current flow is measured. The fundamental difference between the sensors is only in the magnitude of the applied voltage: at low voltages we have an ionization chamber, at high voltages we have a gas-discharge counter, somewhere in the middle we have a proportional counter.
The plutonium-238 sphere glows in the dark, like a one-watt light bulb. Plutonium is toxic, radioactive and incredibly heavy: one kilogram of this substance fits in a cube with a side of 4 cm.
Ionization chambers and proportional counters make it possible to determine the energy that each particle transferred to the gas. The Geiger-Muller counter only counts particles, but readings from it are very easy to obtain and process: the power of each pulse is sufficient to directly output it to a small speaker! An important problem of gas-discharge counters is the dependence of the counting rate on the radiation energy at the same radiation level. To level it out, special filters are used that absorb part of the soft gamma and all beta radiation. To measure the flux density of beta and alpha particles, such filters are made removable. In addition, to increase sensitivity to beta and alpha radiation, “end counters” are used: this is a disk with a bottom as one electrode and a second spiral wire electrode. The cover of the end counters is made of a very thin (10−20 microns) mica plate, through which soft beta radiation and even alpha particles easily pass.
What does gamma radiation bring and what are the consequences?
Gamma rays contain particles that have no charge, but carry a large amount of energy, so this radiation is the most dangerous. It spreads hundreds of kilometers from the source. This type of radiation has a mutagenic effect - it provokes changes in DNA. And a teratogenic effect - it causes pathologies in the development of the fetus, often incompatible with life.
Interestingly, gamma radiation simultaneously causes the appearance of cancer cells and also kills them with dosed targeted irradiation. It is used in medicine to treat cancer patients (radiation therapy).
Gamma particles easily penetrate metal. To stop them, you need a high-density material (lead, tungsten, steel, etc.) or a thick layer of concrete.
What negative effects can occur with radiotherapy?
Sometimes side effects occur with radiotherapy. These include:
- skin damage near the irradiated area;
- irritation;
- itching;
- dryness;
- blisters;
- increased fatigue.
When the head is irradiated, a sore throat often occurs and hair falls out. In addition, radiation can cause genetic changes in human cells.
Today, there are certain techniques that make it possible to accurately calculate possible permissible doses of radiation exposure. All questions related to side effects should be discussed with your doctor. Treatment is prescribed aimed at reducing intoxication of the body and restoring the functioning of organs.
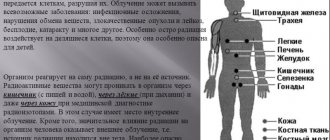
Impact of radiation on humans
Radioactive radiation affecting living tissues ionizes water molecules, resulting in the formation of free radicals - atoms that can damage cellular structures. With intense irradiation, this causes radiation burns; with prolonged irradiation with a low dose, mutations in cellular DNA occur. Mutations, in turn, can lead to cancer or be hereditary, which will affect the health of the heirs.
The most sensitive and vulnerable to radiation are children, pregnant women and the elderly. Their body does not have enough resources to neutralize free radicals.
The experience of observing the consequences of the bomb explosions in Hiroshima and Nagasaki, as well as the accidents in Chernobyl and Fukushima, shows that radiation leaves its mark on many generations. Thus, the incidence of childhood cancer (especially blood cancer) increased sharply in the years after the explosions and has not decreased to this day. Also in the first years after these disasters, there were mass births of babies with malformations and stillbirths in people exposed to high levels of radiation.
The most dangerous consequence of an encounter with radiation is radiation sickness, the symptoms of which appear after a single exposure to a dose of more than 100 roentgens. With such a lesion, nausea, vomiting and weakness are noted. As the dose increases, the severity of the manifestations also increases: hair loss, bone marrow destruction, burns, hemorrhages in the tissue, and their death.
Proper diet in case of danger of radiation exposure
It is well known that in the process of discussions on the topic of what radiation is, the question arises of how to protect yourself from it, what you should eat and what vitamins you should take. There is a certain list of products that are most dangerous for consumption. The largest amount of radionuclides accumulates in fish, mushrooms and meat. Therefore, you should limit yourself in consuming these foods. Vegetables must be thoroughly washed, boiled and the outer skin cut off. The best products for consumption during the period of radioactive radiation can be considered sunflower seeds, offal - kidneys, heart, and eggs. You need to eat as much iodine-containing products as possible. Therefore, every person should buy iodized salt and seafood.
Some people believe that red wine will protect against radionuclides. There is some truth in this. When drinking 200 ml per day of this drink, the body becomes less vulnerable to radiation. But you can’t remove the accumulated radionuclides with wine, so the total radiation still remains. However, some substances contained in wine drink help block the harmful effects of radiation elements. However, to avoid problems, it is necessary to remove harmful substances from the body with the help of medications.
Radiation protection
The best way to protect yourself from the harmful effects of radiation is to be as far as possible from the source of radiation, where there is a favorable background radiation (up to 50 microroentgens per hour). But it is impossible to predict all possible situations, so each of us should know how to protect ourselves from ionizing radiation.
Personal protective equipment is clothing - rubber, lead, as well as gas masks and respirators. Such elements should be provided to everyone who has a potential risk of exposure to radiation (workers of some factories, radiologists, etc.).
There are radioprotective drugs that neutralize the effects of low doses of radiation (Mexamine, Indralin, Cystamine, etc.). They are prescribed to people working in areas with unfavorable background radiation. The dosage regimen is determined by the doctor. In the event of a global catastrophe (bomb or reactor explosion), only an anti-radiation bunker can help people nearby. But there are very few such shelters, and it’s unlikely that you can get there in time. But, just in case, find out where there are some nearby.
There is a misconception that the use of iodine preparations helps cope with the effects of radiation. This is not entirely true. It is advisable to consume iodine before exposure to radiation. This is done in order to saturate the thyroid gland with this element and prevent it from absorbing radioactive iodine, which is often used in reactors. And consuming iodine after irradiation can only worsen the situation. Therefore, large doses of iodine should be taken only according to emergency recommendations of the Ministry of Emergency Situations.