Botulism is an acute infectious disease accompanied by severe damage to the nervous system. Without appropriate drug treatment, it leads to paralysis and paresis of all organs and systems. Possible consequences include respiratory arrest, cardiac arrest and death.
In this case, the causative agent of the disease is an anaerobic bacterium that can survive, multiply and release a deadly toxin in an environment without oxygen. It is resistant to high concentrations of organic acids, salt and prolonged boiling. This bacteria can only be destroyed by prolonged temperature exposure of at least 120 degrees in combination with pressure. Therefore, any home canned food - pickled cucumbers, meat stew, sweet jams carefully stored for the winter - can become a source of potential threat.
Botulism in canned food: how to distinguish normal from bad?
What foods cause botulism? You can suffer from botulinus toxin mainly through canned and pickled products. More than 85% of poisoning cases occur precisely from it.
Homemade canned food and twists most often become carriers of a dangerous fungus, because under production conditions everything is carefully sterilized, processed and tested in laboratories.
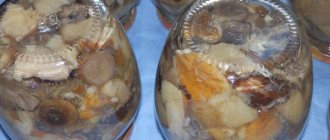
How to identify canned food that is unsuitable for food? The smell, color and even appearance of the marinade does not change; it is possible to determine whether there are toxic fungal spores in the jar only through clinical studies. In everyday life, it can be determined by two signs:
- swelling of the lid,
- surface of the can,
- cloudiness,
- pallor of the canned broth.
This product should be thrown away immediately.
What foods cause canned botulism:
- Tomato juice and tomato paste are least susceptible to the development of botulism due to their low acid content;
- Pickled mushrooms are more prone to botulism; dirt accumulated on their surface, improper heat treatment, and impaired preservation technology increase the risk of its development;
- Jam, pickled and canned vegetables can also become contaminated if they are not prepared or cured properly.
What to do to make the twisted product a joy:
- Clean and wash food before preserving;
- Sterilize jars for at least 20-30 minutes, do not shorten the time;
- Add unexpired acetic acid to the marinade, the acidity should be above 1.5%;
- Perform the process of preparing canned food only in a sterile place where there is no dust, crumbs and other debris;
- Can only fresh, unblemished food.
What can you do before the ambulance arrives?
Botulism develops very quickly and in order not to waste precious time before the ambulance arrives, you can take some measures. Gastric lavage is best done with a soda solution, since an alkaline environment is detrimental to botulinum toxin and the procedure must be performed in the first 2 days, when there is a risk that there are remnants of contaminated food in the stomach.
A siphon enema is also recommended with a soda solution. To perform the manipulation, you will need a clean 10 liter bucket, a probe, a funnel, and a container for rinsing water. Take enterosorbent (the most famous and effective medicines are Activated carbon, White carbon, Enterosgel and Polysorb.
If possible, put in an IV. Only a medical professional or a specially trained person can perform the procedure. Hemodez, Trisol, 5% glucose solution are considered simple and harmless drugs.
Botulism in mushrooms
You can be exposed to infectious-toxic poisoning not only from canned mushrooms, but also from fresh or otherwise prepared mushrooms.
Therefore, mushroom pickers should approach with caution not only the choice of mushrooms in a forest clearing, but also their preparation.
What to do to prevent mushrooms from causing harm to your health:
- Place only fresh, firm mushrooms in the basket. Avoid loose, soft and withered ones;
- Sort the collected mushrooms and put them in the refrigerator or at least in a dark, cool place, for example, a basement or pantry. Shelf life outside the refrigerator is 3-4 days;
- Do not cut the mushroom at the root; it is on the mycelium that a dangerous fungus can live;
- Before heat treatment, clean and wash.
How to reduce the risk of poisoning from canned mushrooms:
- Never close the jar with a metal lid; use paper or plastic to secure it with a thin rubber band at the neck. It has been proven that botulism develops only in closed containers;
- It will not be possible to kill botulism on mushrooms without special production equipment; a household stove cannot achieve the high temperatures at which the bacterium dies;
- Never buy mushrooms from sellers without a quality certificate, and avoid eating questionable pickled mushrooms from friends.
Botulism in mushrooms is a very dangerous disease. More information about mushroom poisoning can be found on our website.
Briefly about botulism
Botulism is an infectious disease that occurs when botulinum toxin, a powerful biological poison, enters the body.
The toxic substance is produced by Clostridium botulinum, microorganisms widespread in the environment.
Clostridia can be found in soil, decaying plants and animals. Microorganisms form stable spores, which up to a certain point are not dangerous to humans. For bacteria to produce a toxic substance, the following conditions must be met.
Conditions for toxin release:
- Lack of air.
- The ambient temperature is within 26-32 degrees.
- A certain level of acidity.
If one of the conditions is not met, the spores cannot turn into a vegetative form and begin to produce dangerous poison. Botulism spores are not killed by freezing, surface treatment with cleaning agents, boiling for less than 4 hours, or exposure to ultraviolet rays. Despite the widespread occurrence of Clostridium botulinum in nature, the disease botulism is diagnosed quite rarely.
Botulism in cucumbers
What foods cause botulism
Among home-canned products, pickled cucumbers are in first place.
Some housewives may deviate from conservation technology; such sealing is a potential threat to life.
How to prepare the right pickled cucumbers:
- Select only fresh, firm cucumbers. Old, soft, sticky ones should be discarded immediately;
- Before twisting, rinse 5-6 times under running water;
- Sterilize each jar according to regulations;
- Screw in a place that has been previously cleaned of contamination;
- Check the cucumbers for appearance - a swollen lid, cloudy brine with sediment is a sign of botulism;
- Store the opened jar in the refrigerator for no more than three days.
Foods most commonly associated with botulism
The source of botulism is, as a rule, various products prepared at home, when sanitary rules, preparation technology and storage conditions are violated. You can read about what causes the occurrence and development of botulism here.
Most often these are homemade canned goods. If they contain spores of the botulism bacillus (clostridium), it develops well with a lack of oxygen and at temperatures above 15°C.
According to statistics, mushrooms hold the lead among all canned foods ; they account for about 70% of cases of poisoning. The second “honorable” place is occupied by meat preparations, and then, in descending order of danger, cucumbers and other canned vegetables, fish preparations, sweet twists - compotes, preserves, jams, marmalades.
Mushrooms
Why are mushrooms the most dangerous? This is due to their special structure: the lamellar and tubular nature of the caps creates conditions for spores to get stuck in them, and it is very difficult to remove them from there. It is impossible to accurately determine by external signs whether there is botulism toxin in a jar of canned mushrooms.
There are several types of clostridia, some of which, when multiplying in the marinade , can release gas and cause the lid to swell. But in most cases, dangerous canned food retains its original appearance.
Another option is that the contents of the jar have become cloudy, the lid is swollen . The reason for this may be other pathogenic bacteria, including staphylococcus. Some housewives, to save money, wash the contents of such a jar, boil it, fry it, stew it, and then eat it.
Under no circumstances should this be done. For example, aerobic cocci trapped in canned food absorb oxygen. If clostridia spores are included with them, this creates excellent conditions for them to transform into a vegetative form and reproduce.
You cannot count on the fact that boiling and frying mushrooms will remove the toxin; even if boiled for 30-40 minutes, it may not be completely destroyed.
Such a “neighborhood” of bacteria cannot be excluded in any bomb canned food, so you need to throw it away without regret. And the presence of botulinum toxin or the bacteria itself can only be determined by laboratory testing.
Meat products
Spores can get into any meat preparation and develop there, thanks to the excellent nutrient medium. The danger of low-quality canned meat increases due to the decomposition of protein and the formation of toxic products, so such poisoning occurs in a more severe form.
The contaminated product may have no outward signs , but upon opening the can there is often an odor of old rancid fat. It depends on the type of botulism bacillus. However, its presence cannot in any way be excluded if the stew looks quite appetizing.
It is better to refuse home canning of meat products and not to buy them on the market, but to buy them in factory production, where the sterilization temperature is not lower than 120°C.
Cucumbers and other vegetables
Among vegetables, cucumbers rank 1st in terms of the risk of infection with botulism , especially those grown not in greenhouses, but growing on the ground. Spores can settle in the rough surface, cracks, in the bottom and nose areas of the cucumber. Even long washing with running water does not guarantee their complete removal. You can learn about the detection and prevention of botulism in salted and pickled cucumbers here.
You will be interested...
Determination and prevention of botulism in salted and pickled cucumbers.
Also dangerous are tomatoes, tomato juice and paste, peppers, zucchini, eggplants, especially those that are closed with the stalks not removed, as well as various stuffed vegetables. Lack of heat treatment, salt and vinegar and hermetic sealing create conditions for the development of spores trapped in the jar. Therefore, it is recommended to cover all canned vegetables with nylon lids and store them in a cellar or refrigerator, and store an open jar for no more than 2 days at a temperature not exceeding +8°.
There may be no external changes in contaminated canned food, it depends on the type of clostridia and the presence of other bacteria. Fermented, cloudy seams, as well as if there are air bubbles, should be thrown away without hesitation. Read about botulism in canned products here.
Fish (fried, salted, etc.)
Fish botulism is most widespread in Russia. The reason is long-term storage of fish without refrigeration before processing. The intestines of the fish are potentially contaminated with spores; the rod from them develops already by 48 hours of storage and begins to release a toxin.
Sturgeon are especially dangerous, as are herring, gobies, omul, and bream. If botulinum toxin has already formed in the fish, then there is no guarantee that it will all be destroyed during frying, much less salting and smoking, especially cold. All preparations should be made only from fresh or frozen fish.
Externally, it is almost impossible to determine the presence of infection. If clostridia have already developed, the smell of rancid fat may be felt, although it is not always possible to detect it when mixed with a fishy smell. In any case, if there is even the slightest doubt about the freshness or storage conditions of the fish, then you should refrain from such preparations.
Hermetically sealing canned fish and cold smoking fish at home is not recommended.
The optimal preparation is salting, provided that the salt concentration in the brine is at least 16% and the storage temperature is not higher than 8°C. You can eat it no earlier than after 3 days of keeping the fish in brine.
Botulism in fish: how to avoid infected fish?
What foods cause botulism
In Russia, botulism became common thanks to fish in the 20th century. It was fish products from sturgeon that discovered botulism for Russian medicine.
After a long study, it was revealed that a fish of the sturgeon family, salmon, is predisposed to the development of this toxic fungus.
Which fish products cause botulism? Potentially dangerous fish include river fish: bream, gobies, herring and omul. To avoid poisoning, you should follow simple and reliable recommendations:
- Never pickle fish that has been fresh without any processing or necessary storage conditions;
- Fish that is going to be eaten without additional processing, salted or smoked, should be kept in the freezer;
- If you suspect botulism, throw away the fish immediately; no heat treatment will save it from the toxin;
- The brining technology is simple - the salt content is more than 17%, the product must lie in a salt solution for at least 1-2 days;
- Buy fish only from trusted persons who have documents and a certificate confirming the quality of the product.
Symptoms and signs
The main symptom of botulism is a combination of a number of symptoms:
- nausea and vomiting,
- impaired visual function, expressed in loss of acuity, fog in the eyes, strabismus, double vision and dilated pupils,
- dysfunction of the speech apparatus,
- decreased ability to work,
- tachycardia and shortness of breath,
- increased blood pressure,
- paleness of the skin.
If a person has eaten potentially dangerous foods and experiences any of the above symptoms, they should immediately consult a doctor. He will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary treatment. In the case of illness, it is the only chance to survive. It is useless to treat botulism at home. The use of medications without the supervision of an experienced physician cannot promote recovery. Self-medication can cause serious health problems.
Botulism in honey: can a glass of milk and honey be dangerous?
Botulism in jam
Young mothers and others are interested in the question: “Is there botulism in dairy products? What about a spoonful of honey?”
Fresh, pasteurized and ultra-pasteurized milk cannot contain botulism. Condensed milk without additional filtration, dry milk powder and condensed milk may contain botulism spores. These are spores, not vegetative agents of the fungus. The main difference between them is that the spores cannot be killed by heat treatment - they are the germs of the fungus itself.
It is not yet possible to say for sure whether there is botulism in honey. There have been no recorded cases of spores or the fungus itself being found in the consistency of this bee product. But young mothers often complain about botulism caused by honey; there is an unconfirmed theory that it provokes childhood intoxication. Neither agreement nor denial of this conclusion has yet been made.
Rare forms of botulism
Wound botulism
Wound botulism develops when spores of botulism bacteria enter a wound.
Spores most often fall with the soil. Conditions close to oxygen-free are created in the wound; spores germinate into living bacteria, which begin to release botulinum toxin. The toxin is absorbed into the blood and causes characteristic symptoms of botulism (impaired vision, swallowing, respiratory function, muscle weakness, etc.). However, with wound botulism, symptoms of gastrointestinal disorders (abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea) and symptoms of general intoxication such as fever, headache, and dizziness do not occur. This is explained by the fact that the toxin enters the body in small portions. The onset of symptoms of the disease from the moment of infection is 4-14 days. One form of wound botulism is botulism in drug addicts. The disease occurs when "black heroin or black tar" is injected, the source material of which has been contaminated with soil and contaminated with spores. When suppuration occurs at the drug injection sites, favorable conditions are created for the life of bacteria and the release of toxin into the blood.
Infant botulism
Infant botulism most often develops in children during the first 6 months of life.
This is facilitated by the characteristics of the child’s gastrointestinal tract, which creates favorable conditions for the development of botulism bacteria. One of the reasons for the development of botulism in children is artificial feeding. When studying similar cases of the disease, bacterial spores were identified from honey, which was used to prepare nutritional mixtures. In addition, an important point is the sanitary and hygienic conditions in which the child grows up. Most cases of infant botulism have been reported in socially disadvantaged families. It is worth noting that botulism spores were found in the child’s environment, household dust, soil, and even on the skin of a nursing mother. When bacterial spores enter a child’s intestines, they find a favorable environment and transform into active forms that release a deadly toxin. Botulinum toxin is absorbed into the blood and spreads throughout the body, affecting the child’s nervous and muscular system. The first possible symptoms of botulism in children:
- Lethargy, weak sucking or complete refusal of it
- The appearance of visual disturbances (drooping of the upper eyelids, strabismus, limited movement of the eyeballs or their complete immobility), hoarse crying, and choking should be an alarm for parents. After which, you should immediately seek specialized medical help.
Botulism in infants with early damage to the respiratory muscles often causes sudden death in children in the first year of life.
source
Botulism in jam: unhealthy dessert.
If we talk about what products botulism is found in, we can safely say in jars of jam. Any type and variety falls under this category, be it apple, raspberry, peach or currant.
Botulism is formed and enters the jar under two circumstances:
- If the place where supplies were stored was not sterilely clean, there was dirt, dust, crumbs, dishes and jars that were not sterilized and washed;
- If the ingredients of the future jam themselves have not been carefully chosen and selected.
It’s easy to tell if jam is unsuitable for eating – a swollen lid, cloudy syrup.
Prevention measures:
- Before cooking, sort out fruits and berries. Soft, beaten, rotten ones are not even suitable for wine and liqueurs;
- Sterilize jars according to instructions;
- Wash the jam ingredients several times under running water;
- Cook jam only in clean bowls and pans, wash your hands before rolling.
By following simple tips and carefully selecting canned products, you can protect yourself and loved ones from acute botulism poisoning. The disease leads to death in 65% of cases.
Consequences and prevention of the disease
Lack of timely treatment for botulism can cause a number of complications:
- anaphylactic shock;
- purulent parotitis;
- serum sickness.
These complications are potentially fatal. To avoid them, you need to go to the hospital, where neutralization of the toxin, which is a waste product of Clostridium botulinum, is carried out using intramuscular injection of anti-botulinum serum. The course of treatment includes the use of a host of other medications. Their choice depends on the symptoms and existing complications.
Preventing botulism is quite simple. All you need to do is eat food and prepare food responsibly. By following simple rules, you can avoid serious health problems.
What fish can become infectious?
Bacteria can be found in river, lake, and sea fish. If we talk about any specific species of these vertebrates, then no one will give a definite answer, although more often the following were noticed in the carriage of clostridia:
- sturgeon breeds;
- red;
- burbot;
- herring;
- acne;
- zander;
- silver carp;
- bream;
- ide;
- perch;
- omul;
- bulls;
- nelma;
- loach.
But this list in no way suggests that other types of fish are less susceptible to infection.
Signs of botulism in humans
This disease is of infectious origin. The causative agent of the pathological process is clostridium, which produces botulinum toxin. Although cases of intoxication with the substance are now rare, botulism remains a deadly pathology.
The onset of the disease is acute. Symptoms can easily be confused with those of food poisoning.
Signs of botulinum toxin intoxication:
- colic in the stomach area,
- headache,
- intestinal upset – up to 10 times a day,
- vomiting, nausea,
- pyretic body temperatures,
- intoxication, weakness.
By the end of the first day, diarrhea stops and persistent constipation develops. Symptoms associated with damage to nerve fibers begin to appear.
Signs of damage by botulinum toxin on days 2–3:
- dry mouth,
- fog in the eyes,
- lack of contours of objects,
- increased heart rate,
- breathing rhythm disturbance,
- shortness of breath,
- dysphagia – the patient cannot swallow food, water,
- the tongue is motionless,
- strabismus,
- eyelid ptosis,
- difficulties with speech,
- nasality,
- unsteady gait
- urinary disturbance.