The name of the medicinal herb celandine eloquently demonstrates its ability to treat skin and many other diseases. It has long been used in folk medicine, but the plant is poisonous, and the symptoms of celandine poisoning should be known to anyone who uses the roots, flowers or leaves to prepare homemade medicines. Pharmacies sell ready-made forms for topical use, for example, dry herbs or rhizomes, and at home, infusions and decoctions are prepared from the roots and flowers of this plant. Tinctures are often taken by dripping into milk, without realizing that they can be poisoned.
Characteristic features of celandine
Several species of celandine are described in the botanical literature, but the most famous and recognizable is the greater celandine, or Chelidonium majus. The plant with golden flowers and dark green petiolate leaves can grow up to a meter tall. Initially, celandine grew only in Europe and the Mediterranean countries, regions with a temperate climate. And during the era of the conquistadors, the herb was brought to America to treat skin diseases.
Some plant fruits contain a succulent structure (elaisoma), which ants feed their larvae. Celandine seeds resemble elaisoma in appearance, which forces insects to deliver them to anthills. In a moist, warm environment, the seeds germinate safely.
When a straight stem of celandine is broken, a thick juice is released, which turns orange in the open air .
The Latinized name of the plant means “swallow”. In ancient times, it was believed that birds treated their blinded chicks with grass juice by dropping it into their eyes.
Beneficial effects of the plant
Poisoning with various parts of celandine can occur both internally and externally. But if the recommended dosages are observed, the plant brings tangible benefits to the body:
- The bactericidal properties of celandine are used in the treatment of skin diseases. Warts or benign tumors are burned with diluted juice. Ointments based on celandine are used in the treatment of rashes of allergic etiology . When mixed with any fatty cream, the juice becomes an excellent remedy for removing dry calluses.
- The choleretic and analgesic effect of the plant has found application in the treatment of certain pathologies of the liver and gall bladder. Typically, a 5% aqueous infusion of celandine is used for this, which is taken drop by drop in strict accordance with medical recommendations.
The diuretic properties of the poisonous herb are not used in folk and official medicine due to the high toxicity of the herb. For the same reason, it was no longer used in the treatment of eye pathologies after increasing cases of ulceration of the mucous membrane.
Based on celandine, a drug was synthesized for the prevention and treatment of malignant tumors. Taking a pharmacological agent does not replace basic treatment and chemotherapy.
A fatty oil is produced from the seeds of the plant, which has an anti-corrosion effect . The bright orange juice from the stem is used to make dyes, including biological objects. The antimicrobial property of the plant is used to disinfect and regenerate burnt skin.
Poisonous properties of celandine
The composition of the herb is varied. The highest concentration of toxic compounds accumulates in the stem and roots . Toxic substances dangerous to human life include the alkaloids listed below:
- Sparteine. The properties of the poison are similar to that contained in hemlock. The alkaloid depresses breathing and reduces blood pressure to dangerous levels.
- Chelidonin. Papaverine and morphine have a similar effect to this compound: they disrupt the functioning of the central nervous system, reduce tactile reflexes, and provoke arterial hypotension. Taking a significant dose of an alkaloid inhibits blood supply in the human body.
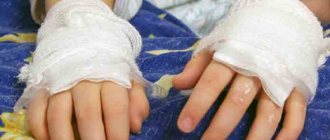
- Chelerythrine. The toxic substance can cause extensive burns of the mucous membranes and upper layers of the epidermis. Large blisters with liquid contents appear on the skin, which are unbearably itchy and painful.
- Sanguinarine. After entering the body, the alkaloid provokes a short-term euphoric state. It develops against the background of increased salivation and stimulation of the smooth muscle muscles of the intestines. After some time, the victim is diagnosed with tremors of the limbs, followed by convulsions.
- Protopin. Reduces a person's ability to quickly respond to external stimuli. The alkaloid causes a decrease in the functional activity of the central nervous system.
- Homochelylidonin. The substance has anticonvulsant and anesthetic properties. Reduces the sensitivity of the skin and mucous membranes to external irritants.
Human poisoning can occur under the influence of any component of the chemical composition of celandine. And with the combination of toxic properties, intoxication will lead to severe complications and death.
On agricultural pastures, animals avoid areas where celandine grows. When making hay, farmers try to prevent even individual specimens of the plant, which retains its toxic properties in dried form, from getting into the feed.
Treatment with celandine is contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding .
It is strictly forbidden to use products based on plant juice in the treatment of children and adolescents with increased permeability of blood vessels. The poisonous herb can provoke relapses of chronic diseases of the human liver and urinary system. People with systemic pathologies should consult an endocrinologist and dermatologist before using celandine infusions or tinctures.
Reproduction at home
Reproduction of Guzmania mix is carried out after flowering, through lateral shoots called children. The flowering process causes the gradual death of the mother rosette and the formation of children, which, as they develop, build up their own root system. After the roots reach a length of one and a half centimeters, the shoot is separated from the parent plant using a sharp, sterile garden tool.
Guzmania can also be propagated by seed. In this case, it is necessary to prepare planting soil based on peat chips and medium-grained sand. The seeds of the decorative crop must first be washed in a solution of potassium permanganate and dried slightly. Sowing is carried out superficially, and then the planting container is covered with a transparent film. The temperature for seed germination should be maintained at 22-24ºC.
The type of reproduction of Guzmania mix is reproduction by division. This process is carried out due to the shoots that a mature plant forms during the flowering season. With careful and attentive care in the future, it is these shoots that can transform into new plants capable of further development.
In order to begin separating the shoot from the parent bush, it is necessary to wait until the young shoots reach the minimum permitted length - 15 centimeters.
When you see that the young shoot is fully formed, you can carry out the procedure of separation and transplantation. The transplant process involves several simple steps.
- First you need to prepare a container with soil. It is believed that the ideal soil mixture for guzmania is a combination of peat, turf soil, coarse sand and sphagnum.
- Place a drainage layer at the bottom of the flower pot into which you will transplant the shoot, and then lay out the above soil mixture (up to about half of the pot).
- Place a young shoot on top and fill the pot with the missing amount of soil.
- At the end of the procedure, water the plant and use a damp cloth to remove accumulated dust and dirt from the surface of the flower.
Thus, we are convinced that, despite the widespread myth about the impossibility of growing Guzmania mix at home, this plant can actively grow and develop in indoor conditions. In order to maintain the vital activity of the plant at the proper level, it is necessary to follow all the care recommendations given by experienced flower growers, as well as botanists.
For information on the developmental features, transplantation, varieties and diseases of Guzmania, see the video below.
How can you get poisoned with celandine?
Patients are often admitted to intensive care wards with a diagnosis of acute poisoning by poisonous celandine alkaloids. In the vast majority of cases, the victims were treated on their own using prescriptions from dubious brochures or on the advice of a neighbor. Intoxication can develop due to improper preparation of plants and their further processing .
You cannot collect medicinal herbs growing along highways, big roads, in the courtyards of multi-story buildings, or near industrial enterprises. Celandine is able to actively absorb toxins from the surrounding atmosphere.
The main mistake people make when treating with poisonous herbs is gradually or quickly increasing the dose in order to quickly recover. Celandine alkaloids can accumulate in cells and tissues, so every extra drop of the drug taken will provoke fatal poisoning. The presence of pathologies of the urinary system in humans limits the use of the plant due to impaired blood filtration and (or) urine excretion.
Some patients in intensive care units approached therapy comprehensively, wanting to get rid of all diseases at once. They burned papillomas with celandine juice and at the same time drank celandine tincture to treat the gallbladder. Even a healthy liver will quickly fail if it cannot bear the excess load. Hepacites are not able to neutralize and process such a quantity of toxic compounds. Liver cells are destroyed and tissue necrosis of the biological filter occurs. Continuation of “therapy” ends in a large abscess.
Poisoning can occur if the rules for storing highly concentrated alcohol or water tinctures are not followed . Young children are extremely curious and can be attracted to mysterious bottles and bottles. There are many known cases of fatal poisoning of citizens suffering from alcoholism. Relatives did a great job of hiding alcohol from them, not taking into account the medicinal tinctures of celandine in alcohol. Alcoholics only need to take a small amount of this drug for the arriving doctors to pronounce the person’s death.
Consequences
If a person does not have severe disorders of the heart, kidneys, or breathing, then he is usually discharged after 12 hours. Recovery will occur much faster if you give the victim plenty of fluids. Meals should be light and dietary.
In case of severe renal dysfunction, the patient’s heart is transferred to the artificial therapy department. Eating celandine is especially dangerous for the liver. The dangerous consequences of intoxication with this plant are the development of cholestatic hepatitis.
In rare cases, a person cannot be saved.
Video: celandine.
Symptoms of poisoning by a poisonous plant
The severity of the clinical picture of poisoning is directly dependent on the dose of the toxic substance, the route of penetration into the bloodstream, and the victim’s body’s resistance to the action of endotoxins. Chronic poisoning is more often diagnosed among self-medicators who have been taking celandine solutions for years . The following symptoms are characteristic of this form of intoxication:
- Neurological disorders: apathy, sleep disorder, anxiety, irritability.
- Skin rashes, dry mucous membranes and dermis.
- Digestive disorders: nausea, heartburn, belching with an unpleasant odor, flatulence, bloating.
- Peristalsis disorder: chronic diarrhea or constipation.
- Decreased visual acuity, swelling and redness of the eyelids.
- Urinary problems, dark color and unpleasant odor of urine.
- Paleness of the skin.
The danger of such intoxication lies in the possibility of an even greater overdose. People are starting to take celandine in increased quantities to alleviate their condition.
In case of chronic poisoning, victims are not able to understand the problem or draw the correct conclusion about the cause of their poor health. Intoxication is detected at the stage of significant damage to the liver, kidneys, heart, and blood vessels.
An acute form of poisoning develops with accidental or intentional oral ingestion of a large dose of celandine alkaloids. The victim develops the following signs of intoxication:
- dilated pupils, lack of reaction to bright light;
- involuntary urination and defecation;
- tremor of the upper and lower extremities;
- breathing problems, convulsive wheezing when trying to take a breath;
- increased sweating, cold sweat, chills, fever;
- rapid heartbeat, arrhythmia;
- low pressure.
As celandine alkaloids are absorbed into the blood, a person experiences convulsions and develops pulmonary and cerebral edema . In the absence of medical intervention, the victim's death occurs within a few minutes.
Home care rules
Growing guzmania mix is not too difficult, which makes it possible for novice gardeners to cultivate this indoor plant. Attention should be paid to temperature, humidity, watering and fertilizing.
At the resting stage, indoor guzmania mix needs a temperature of 18-21°C. During the active growing season, including the flowering period, it is recommended to maintain the temperature within 22-24°C, which will allow the plant to bloom for three months. Tropical ornamental crops require a fairly high level of humidity, so the plant must be provided with regular moisture.
Watering and fertilizing
To irrigate the soil in a flower pot, only settled water at room temperature is used. A characteristic feature of epiphytic guzmania is the superficial location of rather tender roots, which are prone to rotting as a result of stagnation of water in the soil. In autumn and winter, watering should be very moderate, as the top layer of soil dries out. In the spring-summer period, irrigation activities are carried out once a day.
First aid and treatment of celandine intoxication
People around the victim cannot assess his condition due to ignorance of the dose taken. Therefore, you should immediately call a doctor who will conduct detoxification therapy. While the doctor is on the way, you need to provide first aid to the person. If he is unconscious, he must be turned on his side and covered . In case of cardiac arrest, resuscitation procedures are performed:
- indirect cardiac massage;
- mouth to mouth breathing.
If celandine juice gets on the skin or mucous membranes, it is necessary to wash off the toxic substance with a stream of water and treat with disinfectant solutions. If a toxic substance has entered the gastrointestinal tract, you need to induce vomiting:
- Dissolve several crystals of potassium permanganate in a liter of warm water and give the victim a drink.
- Cleanse the stomach until clear liquid free of food particles leaves the stomach.
In case of poisoning with plant alkaloids, you can give a person any laxative. Poison that is not adsorbed by the walls of the digestive system organs will quickly be eliminated from the body.
There is no complex antidote for celandine intoxication . The doctor hospitalizes the patient for treatment with drugs that neutralize the effect of alkaloids. Further therapy is based on eliminating the symptoms of poisoning with saline solutions with glucose and diuretics.