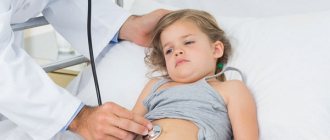
A sports pool, where preschoolers are taught to swim and older athletes train, is rather a sign of the school year. In the summer, we are attracted to swimming pools on vacation - in hotels, sanatoriums and even guest houses. A swimming pool is great fun for children and provides much-needed coolness in the heat. But swimming pools also pose dangers. Which? Specialists from the Institute of Child and Adult Neurology and Epilepsy named after. St. Luke's - pediatrician Lyudmila Nikolaevna Mukhina and neurologist, epileptologist Olga Anatolyevna Pylaeva.
Are you sure that chlorinated pool water kills all germs? Alas: if this were so, there would be no mass illnesses of children in hotels with swimming pools. Chlorine does kill many infectious pathogens, but some bacteria die a slow death that lasts several days.
The child drank too much water in the pool, and a couple of days later almost died
Whether your child is playing in the pool or on the beach, you are undoubtedly keeping a close eye on him.
After all, playing near the water is fraught with many dangers. However, there may be times when your awareness will go a long way in preventing a tragic turn of events. After a horrific incident that could have claimed the life of her 4-year-old girl, a mum is warning parents about the dangers of dry drowning.
A little girl was playing in a pool with a foam swimming tube. She blew in one end and blew out water from the other. By chance, Elianna opened her mouth wide while someone was blowing on the other end and water went straight down her throat. She immediately vomited, but had no other alarming symptoms. 30 minutes after the incident she was completely fine - playing normally, eating, etc.
The next day, Elianna developed a fever. “When a child has a fever, it’s not scary,” the mother thought. The next day, she slept most of the day but "appeared generally fine."
A day later, she went to the kindergarten, but her mother received a call and was informed that her daughter had a high fever.
“I remembered that pool incident and a story I read last year about a dad whose son died because he didn’t get timely treatment after the boy inhaled a bunch of pool water,” she wrote. “We walked from the garden to the emergency room, hoping the doctor would say, 'Her lungs are great, it's just a virus.' We were there for about 10 minutes when the doctor said that our daughter needed to be taken to the nearest hospital. Her heart rate was crazy, her oxygen was low, and her skin was purple, indicating an infection.”
At the emergency room, doctors discovered that Elianna had fluid in her lungs and pneumonia caused by inhaled water. She was given oxygen and antibiotics, but there was no improvement the next day. Doctors changed her antibiotics and started her on nebulizer treatment, and she soon showed signs of recovery.
Elliana’s mother remembered the tragic story of a boy who died from dry drowning. “I would never have done what I did if I had not heard about this incident,” Grace explained. And it's for this reason that she wants to share her story with other parents.
Symptoms of dry drowning
include: rapid, difficult breathing, chest pain, vomiting, extreme tiredness, behavior that is not typical, drowsiness or weakness, and irritability.
“I don’t want mothers to be afraid to take their children to the pool or to the sea,” Grace said. “But if you know your child has inhaled water... pay attention.”
Thank you for reading to the end! If the article was useful, please like and subscribe to the channel. I will be pleased to see feedback from you.
Prevention
It is very dangerous to leave children to play unattended in or near water. When a child is in the bathroom or near a body of water (near a pool, lake or river), he must be constantly supervised. This is especially true for children who can crawl or walk, for whom any containers with water pose a threat.
A harmless examination of a toilet or a bucket of water can end in tragedy. After your child bathes in a plastic children's pool, immediately drain the water or cover it. After washing your baby, empty the water from the basin. The toilet lid must be down. If your child is very active and curious, lock the bathroom door. Do not leave buckets containing even a few centimeters of water or cleaning solution within a child's reach. Never leave a child unattended near a running bathtub or in a bathtub filled with water.
Source: www.sweli.ru
Two types of water poisoning:
- Indirect . Water serves only as a conductor for bacteria and toxic substances;
- Direct. When there is an excess of it, it itself serves as a source of poisoning.
Water intoxication is associated with an excess of fluids in the body - the kidneys can process less than one liter per hour. Each person’s drinking norm is different and is regulated by thirst. It is also worth considering that in addition to water, the body also receives liquid in other forms - broths, drinks, juicy fruits.
The predominance of liquid in the water-salt balance leads to the fact that the body’s cells and their nuclei begin to be washed out, and the soft tissues and organs begin to swell. The heart and central nervous system are the first to suffer:
- The heart rate either increases or decreases until it stops completely;
- Lethargy, confusion, dizziness, faintness appear, and coordination is impaired.
The worst-case scenario is death due to cerebral hypoxia or edema of the lungs and other respiratory organs.
At risk are people who systematically violate the correct drinking regime - women on a water diet, in which all food is exclusively liquid, or those who often experience false thirst - athletes, dancers, supporters of an active lifestyle, drug addicts and alcoholics.
Water intoxication results from:
- Pathogenic microorganisms - salmonella, E. coli, staphylococcus, anthrax, cholera live in natural sources (reservoirs, ponds, wells, rivers and lakes);
- Chemical components - industrial waste, chlorine, pesticides, cause gastrointestinal upset, and provoke severe forms of intoxication;
- Overhydration is an excess of fluid when it goes beyond the cells and begins to penetrate other organs.
Causes
All possible causes can be divided into 2 groups:
- Infectious.
- Non-infectious.
Infectious factors
The children's body, due to its “imperfection” compared to the protection systems of adults, is more susceptible to the effects of infectious factors. The most common pathogens that cause diarrhea and fever are:
- Rotaviruses
Rotavirus is transmitted through nutrition, which is why it easily spreads in the external environment. The greatest danger is posed by canteen workers in kindergartens, since their failure to comply with hygiene rules can lead to infection of a significant number of children.
Severe cases of rotavirus infection occur specifically in preschool children, as it causes not only fever and diarrhea, but also the following symptoms:
- general intoxication - most often the first manifestation of infection is characterized by lethargy, refusal to eat, increased sweating, unmotivated crying; school-age children often experience headache and dizziness;
- vomiting is dangerous for infants, because the symptom manifests itself in almost 100% of patients, lasts up to 2 days, older children may not be bothered, usually lasts no more than 1 day;
- abdominal pain – characterized by moderation, increased pain during palpation of the lower abdomen.
The older the child, the less pronounced the clinical picture of rotavirus infection.
- Salmonella
This is a huge family of bacteria that a child becomes infected with in the following ways:
- transmissible (wild and domestic animals and birds that do not suffer from salmonellosis, but only transmit it);
- contact and household contact (dust, soil, feces or bird droppings left on the fingers of parents who picked up dirty eggs);
- nutritional (thermally poorly processed meat, milk, other dairy products, bird eggs, by water).
The chance of infection increases many times over if food is stored for a long time and under improper conditions before consumption.
Characteristic symptoms of salmonella infection:
- diarrhea, characterized by the presence of clots of mucus and blood;
- fever;
- nausea and vomiting;
- pain, rumbling in the stomach;
- dehydration (can be pronounced, causing loss of consciousness, orientation, profuse sweating and convulsions in the child).
- Shigella (causative agents of dysentery)
Distinctive features of dysentery infection:
- Symptoms of general intoxication. Just a few hours after infection, the temperature in children rises to 38-39°C and remains at this level for 3-4 days.
- Signs of damage to the gastrointestinal tract appear 2-4 days after infection. In children, you can observe frequent bowel movements from 5 to 20 times a day, which coincides with attacks of pain. At the beginning of infection, diarrhea is profuse, and after a couple of days the stool becomes scanty and may contain impurities of fresh blood.
- Dysentery affects the large intestine of both children and adults, which is why pain corresponds to the area of projection on the anterior abdominal wall of the lower intestine. At first the pain is dull, but over time it becomes more and more acute.
- Nausea, vomiting, and if the small intestine is affected, bloating.
- Dehydration, which is manifested by dry skin, mucous membranes, a feeling of thirst, and a decrease in blood pressure in the child.
- Group A hemolytic streptococcus (causative agent of scarlet fever)
Scarlet fever is transmitted only by airborne droplets and has an acute onset. The greatest danger lies in the absence of characteristic signs during the acute period of the disease that would distinguish it from measles and rubella, which are typical ailments in children. With any of these infectious lesions, the child may experience fever and diarrhea, so if you suspect scarlet fever, you should always call a doctor at home.
Non-infectious factors
Among the non-infectious factors that cause diarrhea with fever in children are:
- Teething. Baby teeth erupt in babies at the age of 6-8 months, in rare cases - a little later, but up to 1 year. All children have to go through this physiological phenomenon, but it may be accompanied by loose stools and moderate fever. Such clinical manifestations associated with teething usually last no more than 1-3 days. Diarrhea during teething.
- Food intoxication. Caused by poor quality of consumed products. A characteristic feature is a combination of fever, diarrhea, vomiting and hypersensitivity reactions such as skin rash, and less commonly, an allergic cough.
- Food intolerance. The enzyme systems that are responsible for the breakdown of proteins, fats and carbohydrates absorbed by humans are imperfect, which is why the consumption of unboiled cow's or goat's milk, fermented milk products, etc. by infants can cause a reaction accompanied by fever, diarrhea, and vomiting.
- Drug treatment. The use of this or that drug can cause an allergic reaction on the part of the child’s body, which is often manifested by fever, diarrhea, rash, and cough. If parents have discovered that such a clinical picture is associated with taking medications, they should stop using them and visit a specialist.
- Dysbacteriosis. It is more common in infants or children who have been on long-term therapy using antibiotics that inhibit intestinal flora. It should be taken into account that the disappearance of one’s own population of non-pathogenic or opportunistic microorganisms weakens the functioning of the body’s defense systems and provokes the emergence of pathogenic populations.
- Dyspepsia. In children, this phenomenon is associated with a functional or organic nutritional disorder and digestive disorders. In a child, dyspepsia is manifested by a feeling of discomfort or pain in the epigastrium, a feeling of fullness in the stomach after eating, early satiety, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn, fever.
Tap water poisoning
It would seem that drinking tap water is not scary, because it must be purified.
But in practice, the opposite is true - typhus, staphylococcus, salmonellosis, E. coli, anthrax, rust and chlorine impurities - this is what may end up in your glass.
In some regions, in addition to being harsh, it generally has an unpleasant smell and taste.
Intoxication with tap water is an example of chemical poisoning, when 300 ml of liquid contains more than 10 chemical compounds.
How to avoid poisoning from tap water?
Use a filter to clean or boil for 10-15 minutes over high heat. High temperature kills over 80% of harmful microorganisms. It is best to combine filtration with boiling: there will be no bacteria, and no heavy metals either.
How to identify poisoning from a tap?
Clinical symptoms appear both a few minutes after the entry of toxins and several hours later, it all depends on the extent of the organism and the individual characteristics of the person.
Main symptoms:
- Nausea, profuse vomiting with little relief;
- Pain in the abdominal cavity – cutting, stabbing;
- Diarrhea;
- General increase in temperature.
Skin fungus
Feeling flaking between your toes or under your arms? Did the skin turn red in these places, did the nails lose their shine, became deformed and began to peel? The symptoms are similar to a skin fungus infection.
A fungal infection is easily transmitted: sometimes accidentally touching an infected person or his swimming equipment is enough. By the way, many people do not even suspect that they suffer from this infection: the causative agent of onychomycosis can remain in the body for a long time and manifest itself only in the form of a slight tickle between the toes.
How to protect yourself: carefully remove moisture (sweat or water) between your toes. Do not walk on tiles barefoot: wear rubber shoes even in the shower.
Sea water poisoning: what is it? How to avoid and determine?
Sea water intoxication most often occurs due to harmful bacteria that multiply and produce decay products in the marine environment.
Salt and jellyfish diligently kill part of the pathogenic microflora, but they cannot cope with its volume completely.
Waste, garbage, animals are not all that provoke the occurrence of sea water poisoning; often people prefer to go to the toilet directly into the sea, and besides, not always healthy people swim.
How you can get poisoned by sea water:
- During swimming, underwater games, when it is accidentally swallowed;
- If its particles get into food or drinks;
- In the absence of basic hygiene after bathing - hand washing, washing.
Sea water poisoning symptoms:
- Nausea;
- Vomiting until the stomach is completely empty with temporary relief;
- Headache, dizziness;
- Loss of appetite;
- Pain in the peritoneum.
What to do? Stay calm and go to a dark, cool place. Seek medical attention. Drink distilled water; if the condition is too severe, rinse or induce vomiting.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Diagnostics should be carried out only if dizziness is suspected to be non-functional.
In the differential diagnosis of cephalalgia, a thorough history and neurological examination of the person plays an important role.
The survey determines:
- The nature of the pain (dull, throbbing, pressing).
- Localization of pain (one-sided, diffuse, in the eye area).
- Intensity and duration (seconds, hours, days, daily pain).
- Frequency of attacks (one or more times a month).
- The presence of other accompanying symptoms (phonophobia, photophobia, lacrimation, runny nose, cranial nerve palsies, hemiparesis, cerebellar symptoms, impaired consciousness) and provoking factors (physical activity (pain worsens during exercise), defecation, tilting or turning the head, stress, menstruation, medications, alcohol).
- The doctor also asks about current treatment and its effectiveness and consequences.
Caution - intoxication from the pool
Pool water intoxication is the ingress of life-threatening toxins through the liquid with which it is filled.
The main danger is chlorine and microbes from visitors (not everyone showers before swimming and goes to the toilet). Despite the fact that special substances are added to the pool that kill harmful microflora, sweat and urinary secretions activate a chemical reaction to convert chlorine into cyanogen chloride. A few milligrams of the substance are enough for severe intoxication and death.
Symptoms of intoxication:
- Wet or dry cough;
- Feeling of a lump and irritation in the throat;
- Tearfulness.
Signs:
- Stopping breathing;
- Weakening of the pulse, temporary cardiac arrest is possible;
- Fainting.
If the necessary assistance is not provided, and the concentration of toxins exceeds all normal limits, the person dies.
What to do? As soon as you feel unwell, leave the water. Wash and rinse your nose and mouth with clean water. If the eyes are red and irritated, apply eye antimicrobial gel, drop 2-3 drops of olive or other natural oil into the eyeball. If the condition only worsens, there is a possibility of loss of consciousness, call an ambulance.
How to protect yourself? Wear a special cap, gloves, swimsuit, nose clip, never swallow pool water, and always wash after swimming.
How dangerous is diarrhea with fever in a child?
It should be understood that if you do not pay attention to these 2 symptoms, then together they lead to the following complications:
- Dehydration. It develops more intensively if the child’s symptoms include vomiting.
- Cramps.
- Loss of consciousness.
- Changes in intestinal function, which lead to chronic constipation, flatulence, and diarrhea.
- If a child has suffered a rotavirus infection, there is a possibility of developing lactase deficiency.
- Dysbacteriosis. Occurs if infectious diarrhea has been treated with antibiotics for a long time.
- Rectal prolapse is a common complication of dysentery that has not been completely cured.
- Death. It may be associated with many of the above factors, since dehydration leads to a decrease in blood pressure, dysbiosis leads to the colonization of the intestines by pathogenic microflora, convulsions and loss of consciousness are manifestations of damage to various parts of the nervous system.
First aid for water intoxication
If you or another person suspects the development of water intoxication, you should urgently call an ambulance. It is worth rinsing the stomach and drinking water only if the possibility of overhydration is completely excluded, otherwise you can hasten the death of the patient.
In case of infectious poisoning - E. coli, typhus or chemicals, it is necessary to cleanse the gastrointestinal tract by rinsing. In case of poisoning that occurs in an aquatic environment - a swimming pool, pond or sea, it is necessary to wash, rinse the mucous membranes (oral cavity, eyes and nose), and induce vomiting to remove contaminated water.
Treatment of overhydration occurs under the strict supervision of a doctor, depending on how part of the organ system is affected, therapy is formed. The level of water-salt balance is also adjusted individually.
If you drink water correctly and only purified water, no problems will arise. In addition, do not forget that when used correctly, it is a source of vitality and health.
Treatment
If there are symptoms of poisoning with dirty water, the first step is to examine the victim by an infectious disease specialist. In case of severe poisoning with intoxication, before taking medication, to determine the pathogen, you need to submit biological material to the laboratory: feces, vomit, blood. Also, if available, a sample of drunk water will also be suitable for research. If a pathogen is detected, the patient in the infectious diseases hospital will be given antibiotic therapy with detoxification and symptomatic treatment.
As for overhydration, its mild form does not require any intervention: the body will gradually restore its water-salt balance on its own. In severe conditions, if necessary, doctors can resort to prescribing diuretics, sodium chloride, hemodialysis, hormonal, diuretic drugs, etc.
Folk remedies for diarrhea
There is a varied range of medications that are used to treat diarrhea. The choice of a particular medication depends on the cause that caused the disorder.
Diet therapy
Medicines for diarrhea are not a panacea at all. A range of interventions should be considered when treating diarrhea. The most important of which, as already mentioned, is the fight against dehydration. Let's look at medications for diarrhea in adults that are used most often.
All of them are divided into several pharmacological groups:
- sulfonamide drugs (“Fthalazol”);
- antibiotics (Levomycetin, Tetracycline tablets);
- nitrofurans (drug "Furazolidone");
- antimicrobial drugs (“Enterofuril”, “Sulgin”);
- antifungal (Intetrix) - used for amoebic dysentery;
- enterosorbents (Enterosgel, activated carbon);
- antiviral drugs.
Let's look at the most well-known remedies for diarrhea in adults. In what case is it advisable to take this or that drug?
Traditional medicine knows many ways to treat such ailments as diarrhea. Folk remedies for treating diarrhea have been proven for centuries.
Prevention measures
To significantly reduce the risk of a child encountering such a serious condition, it is necessary:
- Maintain hygiene. By teaching your child to wash their hands and food well, you will ensure your child’s safety.
- Provide your child with good nutrition. This means high-quality and fresh products containing vitamins and beneficial microelements.
- Protect the child during mass epidemics, limit his contact with sick and infected people.
It is worth remembering that indiscriminate use of multivitamins can lead to hypervitaminosis, which negatively affects the baby’s health.
Just two symptoms can cause enormous harm to a child’s body that is not yet fully formed, so be attentive to your child and try to provide him with all preventive measures. If you experience diarrhea with fever, contact your pediatrician immediately.