Summer is a time for long walks and new discoveries for kids and their mothers. But are all discoveries safe? Among the smallest representatives of wildlife there are not only harmless bugs and butterflies, but also striped robbers - wasps. In hot weather, they accumulate near bodies of water, even flock to splashes of water during children's games with water pistols, and show interest in open pools.
Wasps love to build their nests in the most unexpected places, from a human point of view: under the canopies of entrances, in cans placed on a picket fence, brackets for satellite dishes or split systems. Biting neighbors are not averse to settling under the roof of the sandbox on the playground, while the speed of construction of wasp nests is such that just yesterday there was not a hint of uninvited residents under the “fungus”, but today a whole swarm is scurrying back and forth, bringing them to the “construction site” » new and new materials.
How do wasps bite?
Wasps are divided into many varieties, the most familiar to us are representatives of the paper species.
These insects are brightly colored with black and yellow stripes. Their bite is very painful for both children and adults. But even they cannot be compared with black and brown road wasps. After they sting, the victim may experience a real painful shock. And it’s not surprising, because these stinging insects feed on spiders, which are often several times larger than them. With their poison they can paralyze even tarantulas. Fortunately, such wasps are much less common than their counterparts, and can attack humans only for security reasons. Wasp venom contains histamine, enzymes, polypeptides, and biogenic amino acids. But some individuals are capable of injecting toxic elements under the skin that contribute to the destruction of cells in the victim. Since insects can feed on garbage and even carrion, a mass of pathogenic microorganisms accumulate on the sting. At the moment of stinging, microbes penetrate into the wound, which can cause the formation of pus.
Important! A wasp sting is especially dangerous for adults. Because susceptibility to the provocateur contained in wasp venom increases with each bite. Therefore, attacks of hypersensitivity can become increasingly worse, leading to serious complications.
In children, the symptoms of allergies are more tolerant, since the immune system has not yet had time to properly “get to know” the allergen. The cause of severe consequences is often the action of the poison, rather than the manifestation of a hypersensitive reaction. Therefore, pain and swelling remain, but allergic manifestations (fever or rashes) are rarely observed.
How can you prevent bites?
Teach your child not to bite. When the child is old enough to understand, teach him that biting hurts and can be dangerous for both the child and the person he bites.
- Do not pretend that you will bite the baby and do not allow the child to bite you in the game. Don't bite your baby back!
- Make a “no biting” rule and strictly adhere to it.
- Young children are still learning self-control. Show your child how to express anger and frustration by saying “no” or “I don't like that” rather than by biting.
- Distract your child if there is a problem with another child during play.
Wasp sting symptoms
Characteristic symptoms
First of all, when attacked by a stinging insect, it is necessary to determine whether a wasp or a bee bit the child. Unlike hardworking honey producers, wasps are very aggressive creatures and can sting not only for the purpose of protection, but for absolutely any reason. If a child is bitten by a bee, the sting gets stuck in the skin, and the insect itself soon dies. Wasps do not leave a sting when attacking: since it has a smooth shape, the insect can easily pull it out. Another danger is that these arthropods are capable of attacking the baby up to 4-5 times.
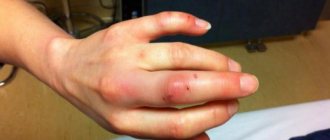
Immediately after a wasp sting, the damaged area on the child’s body looks like a small red swelling with a dot in the middle, which causes an unpleasant burning sensation and pain. There is also itching of the wound itself and the surrounding area. With severe inflammation from a bite in the arm or leg, swelling can spread throughout the entire limb, and the contours become blurred.
Important! It is especially dangerous if a wasp has bitten a child on the head - in this situation, the poison spreads faster through the blood vessels. The consequences may be: dysfunction of the central nervous system, spasms of the respiratory tract and the development of inflammatory processes due to increased production of histamine.
Symptoms usually disappear within a few hours. But if a wasp bites a child in the face, it may take 2 days for a full recovery. Sometimes the situation is aggravated by an allergic reaction and serious complications.
Allergy to bite
An allergic reaction to a wasp sting in a child is quite rare. Parents should be alert to:
- Redness reaching 1 cm in diameter or even more.
- Swelling that becomes extensive - for example, if a wasp has bitten a baby on the finger, the skin around it quickly turns red and swells, and eventually the entire hand may swell.
- Rash on the body that causes itching.
The risk group includes infants, toddlers under one year of age, and children who have not previously encountered a wasp sting.
First aid after a bite
It is important that adults do not start to panic, otherwise this will frighten the child even more and aggravate the body’s reaction to the bite. The worst troubles are severe swelling from a wasp sting and pain, which will begin to subside with treatment and will completely disappear after a few days. Despite this, your vacation will definitely be ruined.
You should not listen to various horror stories about instant allergic reactions, etc. Severe swelling and respiratory arrest, of course, can occur, but very rarely and most often this concerns a wasp bite of an adult. In this regard, you should not panic and think about the bad. A child’s body is not able to react this way to an insect bite. After the defeat, it is the toxins from the poison that provoke swelling and pain. Of course, the injury will be accompanied by inflammation and pain, but the body temperature will not change in any way and an allergic rash will not appear on the skin.
First aid will require quick and coordinated action on the part of an adult. What do we have to do:
- First, you will need to quickly, without sudden movements, leave the place where the wasp or several wasps are located.
- It is forbidden to kill an insect on the skin, as this can cause the sting to get stuck in the wound, and the poison contains a substance that makes the wasp even more aggressive. One crushed wasp can lead to an attack on an entire colony. To remain safe, you need to brush the insect away.
- The wound needs to be disinfected. To do this, you will need any liquid containing alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, iodine, or even plain water and soap. An aspirin tablet dissolved in water is ideal. The mixture is applied to the bite site and covered with a bandage or clean cloth, on top of which a cooled object is placed. If a cold compress is not available, your hand can be placed under cold water.
- When a child is bitten by a wasp, a tight bandage must be applied to the affected limb. This way, toxins will not be able to spread in the body.
- It is important to remove toxins as quickly as possible, so the child needs to drink a lot - mineral water, strong tea. But you shouldn't drink milk.
- After a bite, it is advisable to give the victim an antihistamine and show the child to a doctor.
Why is a wasp sting dangerous?
If bitten, parents need to monitor the baby’s condition throughout the day. Typical symptoms of the lesion are swelling, redness and pain. If a child suffers a wasp sting, complications and consequences may occur, such as:
- The appearance of blisters.
- Headache.
- Unbearable itching.
- Temperature increase.
- Fever.
- Loss of coordination.
- Sudden changes in blood pressure.
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea.
- Difficulty breathing, shortness of breath.
- Convulsions, fainting.
Therefore, from time to time, the mother should ask the baby about his well-being and check whether the child’s temperature rises after a wasp sting.
Important! If a wasp has bitten a child on the tongue or throat, you should immediately call an ambulance - swelling can block the airways and lead to suffocation.
You should not think long about what to do if a wasp has bitten a child in the eye or eyelid - you must urgently contact a hospital facility. The doctor will advise how you can remove the swelling and relieve swelling from the sting. Otherwise, inflammatory processes and suppuration of the eyes may occur. The risk of developing conjunctivitis increases. A wasp sting on the mucous membrane of the eye is more dangerous for children than just on the eyelid, since vision-related pathologies may later appear.
What can you get infected with during a bite?
Wounds from human bites, especially in small children, are usually not dangerous. However, some parents are concerned about more serious blood-borne infections, such as hepatitis B or C, and HIV (human immunodeficiency virus). The infection can be transmitted if a person is infected with any of these viruses and if the bite results in blood contact. This situation is unlikely in childcare settings, but it does happen.
Hepatitis B.
It is transmitted from person to person through blood and other body fluids. It can be transmitted through sexual intercourse, from mother to child, and by sharing needles and syringes. The virus is not transmitted by contact of saliva with intact skin. Only a bite that breaks the skin can transmit hepatitis B, and even then, spread is rare. A child with hepatitis B who bites another child and breaks the skin may expose the bitten child to hepatitis B infection. A child who bites a child who has hepatitis B may be infected with the virus if the bitten child's blood gets into the child's mouth.
Contact the clinic immediately if you are told that your child has bitten another child, or another child has bitten yours until it bleeds, and the baby has not been vaccinated against hepatitis B.
Hepatitis C.
It is also transmitted from person to person through blood or other body fluids. Hepatitis C infection is rare in young children. Hepatitis C infection from a bite by a small child is extremely unlikely; such cases have not yet been recorded in medical practice.
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
It is transmitted through sexual intercourse, from mother to child before or during childbirth. It is extremely unlikely that HIV will be transmitted through a child's bite, even when the skin is broken. Giving a child anti-HIV medications after a bite is not recommended.
When is a doctor needed?
Often, parents are aware of how to provide first aid for insect bites and how to carry out treatment at home. However, there are a number of signs that require urgent medical attention:
- While the child is breathing, whistling sounds are heard, which indicates a violation of bronchial obstruction and suffocation.
- The patient is an infant under 3 months of age.
- The presence of multiple bites.
- It becomes difficult for the victim to swallow and speak. Such symptoms may indicate swelling of the larynx, asthma attacks, or neurological manifestations.
- A feeling of pain in the chest indicates a disruption of the cardiovascular system due to exposure to toxic substances.
- Stinging in soft tissue (tongue, larynx) or in the eyes.
- Symptoms of severe intoxication: dizziness, fever, tachycardia or pulmonary spasms.
- A sharp deterioration in the child’s health.
What is forbidden to do if a baby is bitten by a wasp?
Every child needs to know what not to do when stung by a wasp, so as not to worsen the situation. If the baby is still too small, the parents themselves must monitor his actions. So, when bitten by a stinging insect, the following is contraindicated:
- Wipe the painful area with water from natural bodies of water (rivers, lakes). Such water contains pathogenic bacteria and, if they get into the wound, lead to various diseases.
- Look for a sting after a sting – unlike bees, wasps do not leave a sting in the skin.
- Squeeze out the poison - if the toxins come back out, it will be only in small quantities. And increased blood flow will provoke an even greater spread of poison in the tissues. An additional disadvantage will be the increased risk of secondary infection.
- Scratching the bitten area can cause infection and spread toxic substances.
- Take antihistamines without showing allergic symptoms. Hypersensitivity to wasp venom is rare in children, but medications (and even drunk without reason) may well lead to poor health in the baby. The exception is a predisposition to allergies.
- Kill a wasp - when a flying insect dies, it releases a secret that can be instantly sensed by its relatives. If the hive is located nearby, then the child may be attacked by a crowd of angry wasps.
- Use adult medications instead of children's ones. Incorrectly selected medications can cause serious complications.
And the most important thing for parents to remember is to try to control themselves even with strong feelings. Do not panic, do not lament or openly show your anxiety. This may make the child even more scared. You need to feel sorry for the baby and say that nothing terrible happened, and the pain will soon subside.
Allergy to bites
What to do if a wasp bites a child with allergies? Give your baby an antihistamine tablet to prevent the development of the disease. If a child is stung by a wasp, the doctor may prescribe: Suprastin, Zodak, Zirtec, Cetrin. For allergic rhinitis, nasal sprays are well suited: Tizin, Azelastine, Reactin.
Antihistamine ointments are used to reduce rashes and skin itching. According to numerous reviews from parents, two drugs are considered the most effective:
- Fenistil gel – has antiallergic and antipruritic effects. The positive effect appears after just a few minutes. The site of the wasp bite should be smeared 2 to 4 times a day: the more severe the child’s symptoms, the more times it will be required.
- Psilo-balm – eliminates allergies, pain and swelling. Pleasantly cools the skin, reducing unpleasant itching sensations to a minimum.
It is especially noticeable if a wasp has bitten a child on the lip or eye. The lip may become greatly enlarged and numb. With allergic edema, the eyelid often swells so much that it becomes almost impossible to open the eye. Therefore, treatment for increased susceptibility to bites should be carried out without delay.
Wasp sting in a child under one year old
If a wasp has bitten a six-month-old or one-year-old child, the itching and pain after the bite may go away faster, but the lump and swelling usually remain for a longer time. What to do if a wasp bites a child under one year old? First of all, distract the child from the pain (for example, with a cool bath) and give him an antihistamine: Zyrtec, Fenistil, Cetrin drops or Peritol syrup. You can also take ¼ of a Suprastin tablet, after crushing it between spoons to a powder state.
Helping a child not be allergic to wasp/bee stings
In most cases, a bee or wasp sting does not pose any particular danger to children. Doctors advise smearing the affected area with antihistamine ointments and: Soventol and Fenistil-gel .
You can also use special balms with natural oils and natural ingredients for this purpose.
These include:
- Insectline.
- Gardex.
- Moskitol.
- Feminine picnic.
These drugs help the child’s body cope with irritation, swelling, avoid secondary infection, and also perfectly soothe pain and discomfort.
You can also remove swelling using tinctures of calendula, propolis, ammonia with alcohol, dandelion extract, onion, garlic, plantain, and parsley.
If a child has a fever after a bite, you can lower it with paracetamol (reduce if it exceeds 38 degrees).
What should you do if a child is bitten by a wasp?
To provide first aid to a child for a wasp sting, you must act in a certain way:
- Immediately after the bite, suck out and spit out the poison before it has time to spread throughout the body. If you start acting immediately, the manifestation of symptoms will be smoothed out as much as possible.
- When providing first aid for a wasp sting at home, you need to press a swab soaked in vinegar or lemon juice onto the child’s reddened skin for 2-3 minutes. Wasp venom has an alkaline environment, and acid suppresses its negative effects. Therefore, you can apply any sour product to the swollen area - a piece of lemon, orange or green apple.
- Rinse the wound area with cold water to remove any remaining dirt and toxins.
- It is not difficult to remember how to treat a wasp bite on a child at home. Any disinfectant solutions will help here: Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, brilliant green.
- Take an antihistamine if the baby is susceptible to hypersensitivity or one of the parents has this disease.
- You can numb a wasp sting and relieve swelling in a child using such improvised means as a piece of ice wrapped in a cloth, or any frozen food from the refrigerator.
- Drink more liquid (tea or plain water) to quickly remove the poison from the body.
What is first aid?
If an insect has bitten your child, the first thing you need to do is calm down and not be nervous. This is especially true for those who are allergic to bees. Providing assistance should be carried out exclusively in a calm environment, since panic will only create chaos and lead to more disastrous consequences.
The algorithm of actions after a bite is as follows:
- find the bite site and remove the sting from there (if there is one);
- try to suck the poison out of this place;
- find any acidic product (apple, orange, lemon, etc.), cut it into a slice and apply it to the bite site so that the acid it contains begins to neutralize the remaining poison that could not be sucked out;
- after that, find something cold (food from the freezer, an ice pack, cold metal objects, etc.) and apply it to the wound surface.
If there are concerns that an allergic reaction may begin, you can give the child one tablet of Suprastin. It will block any manifestations of allergies in the body and prevent sudden reactions to a bite from developing. It is advisable to take the tablet as early as possible.
It is also very important, literally in the first hours after exposure to an insect, to treat the wound with external antibacterial drugs, in particular, after a wasp sting. This insect does not lead the cleanest lifestyle and can feed on carrion and decomposition products.
Moreover, children do not tolerate itching and scratch the wound surface. This further increases the likelihood that pathogenic microflora will enter the blood. To prevent such a situation, it is enough to take any antiseptic that is on hand (hydrogen peroxide, alcohol, iodine, brilliant green) and treat the bite site.
If the patient has a strong sensitivity to bee venom, the treatment should be slightly different. These people should carry an epinephrine auto-injector with them to administer in case of an allergic reaction. If the patient is prone to panic, it is recommended to teach loved ones how to use the product so that they can provide assistance if necessary.
To administer a drug to a patient whose life is counting down to seconds, it is necessary to act decisively and quickly. The protective cap is removed from the auto-injector, the side with the needle is pressed against the outer surface of the thigh and the button is pressed for 5 seconds to make the injection. In emergency cases, adrenaline can be administered even through clothing.
How can you help a child if he has been bitten by a wasp?
Medications
Before treating a wasp sting in a child, it is necessary to determine the extent and nature of the lesion. Most often, doctors prescribe medications that help eliminate itching, relieve inflammation and swelling.
If a small child has been bitten by a wasp or a bee, topical medications can help improve his well-being:
- Rescuer is a balm based on natural ingredients: beeswax, ghee, esters of sea buckthorn, calendula, tea tree and lavender. The product will help relieve swelling and promote rapid tissue restoration and pain relief. Approximate cost of the balm: 170 rubles.
- Balm Zvezdochka - “cools” the affected areas, thereby providing an analgesic and antipruritic effect. However, you should not apply too much balm to the skin - this can cause a burn. If after using the drug the child begins to complain of a strong burning sensation, the remaining product should be removed with water.
- Bepanten - used in the form of an ointment or cream. The main substance of the drug is dexpanthenol. Bepanten helps accelerate tissue metabolism, moisturizes the skin and relieves inflammatory processes. The medication has virtually no contraindications and can even be prescribed for the treatment of newborns.
If the pain after a wasp sting in a child becomes unbearable, it is recommended to use Soventol anesthetic gel or Menovazin ointment.
Alternative medicine
With the help of folk recipes for bites, you can get rid of itching, pain and relieve swelling. There are 5 most effective ways:
- Grind the leaves of parsley, plantain, Kalanchoe, celandine or dandelion and press onto the reddened area.
- Add a little water to the soda, apply the paste to the affected area and leave until completely dry.
- Dilute 1 tsp. table soda in 200 ml of water, moisten a cloth in the soda solution and apply to the affected area. A solution with salt, vinegar or citric acid is prepared in a similar way.
- Wipe the affected area with olive oil.
- Cut the aloe leaf lengthwise and keep it on the wound surface.
What does the bite site look like?
This article talks about typical ways to solve your issues, but each case is unique! If you want to find out from me how to solve your particular problem, ask your question. It's fast and free
!
After a bite, a person feels a burning pain. The wounded area immediately begins to swell, and the weaker the body, the more. Particularly severe swelling is observed in children, people suffering from allergic diseases, and people with health problems. Maximum swelling is observed on the face (especially on the lips and eyelids).
Tissue swelling with pronounced pain is not the only consequence of insect exposure. The following symptoms are also possible:
- skin redness;
- severe itching;
- blistering;
- rash all over the skin;
- headache;
- abdominal pain;
- heat;
- nausea, vomiting;
- in especially severe cases - convulsions.
Blisters on the skin due to a bee sting
If a person is completely healthy, he can easily withstand an insect attack. After a few hours, most of the symptoms no longer bother him. The exception is swelling of the face and other soft tissues, which take much longer to subside - about 48 hours.
Safety regulations
To protect your child from wasp attacks, it is recommended to follow a number of rules:
- Do not wear clothes in bright colors - such colors attract the attention of wasps.
- Do not use eau de toilette, especially those with a sweet or floral scent.
- If your baby gets dirty, dirty areas should be cleaned immediately using wet wipes.
- If a stinging insect is circling nearby, it is necessary to warn the child so that he does not take active actions, swing at the wasp or run away. It is best to take the baby by the hand and quietly leave the “dangerous place.”
- Explain to the child that it is impossible to kill the wasp, otherwise a whole swarm of embittered relatives may arrive.
- Do not allow the child to walk barefoot in the shade - these are the places where insects prefer to make nests.
- Do not leave jam or other sweet foods out in the open.
- Before going on a picnic, use special repellents that repel annoying insects.
When going outdoors with your child, you need to take repellents and medications for wasp stings with you. If there is a tendency to allergies, antihistamines should be added to them. If after a bite the symptoms are mild, parents can help the child with ointments or folk methods on their own. In case of severe intoxication, multiple lesions or a sharp deterioration in the child’s condition, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance.
Prevention is the best remedy against insect attacks
Do not use sweet toilet water - this smell attracts insects.
If you are bitten by a wasp, what to do is clear. But it is better to prevent an insect attack than to deal with the consequences later. To do this, you need to avoid actions that attract the attention of the wasp:
- Outdoors, cover various sweets, fruits, juices and other foods with something. Children may not notice wasps landing on them. As a result, the wasp bite occurs on the cheek, lip, larynx or tongue.
- Tidy up your child's long hair (braid it or tie it in a ponytail) when walking outdoors. Otherwise, the insect, entangled in the hair, may sting the child in the ear.
- Never panic or wave your arms when you see a dangerous insect. Just quietly and calmly move away to the side.
- Do not use sweet baby toilet water. Because of this smell, wasps attack the child and sting him in the neck.
- Use modern insect repellents if you stay outdoors for a long period of time.
If you adhere to the above recommendations, attacks and bites can be minimized.