The effect of this form of release occurs after 20-30 minutes, the maximum duration of the effect is 6 hours.
The modified release of morphine implies a longer lasting analgesic effect. These pills are called MCT Continus. The active ingredient is morphine sulfate. Concentrations are 10, 30, 60 and 100 mg. The duration of the effect is 12 hours, the action also begins 20-30 minutes after administration. This drug is used at intervals of about 12 hours.
There are other drugs that contain morphine. The substance usually contains various additives that determine the effect. These include Fentanyl, Omnopon, Nalbuphine. The latter is the only one approved for sale in some countries without a prescription, which results in a large number of drug-dependent patients.
How is morphine different from morphine?
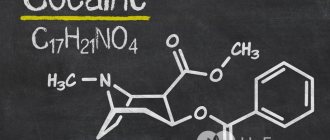
Chem. Morphine formula is C17H19NO3.
Chem. the formula of morphine (morphine hydrochloride) is C17H20ClNO3.
- Morphine is one of the derivatives of morphine, its hydrochloride salt or hydrochloride.
- Morphine dissolves well in alcohol and hot water, but is more difficult to dissolve in cold water. Morphine is slightly soluble in water.
- Morphine, unlike morphine, is easily oxidized.
Many people, including medical professionals, consider morphine and morphine to be different names for the same drug. At its core, morphine is a morphine derivative obtained by adding hydrogen chloride (HCl). This change in the structure of the molecule did not affect the effects and side effects.
Historical reference
Morphine - what is it? This is a drug with an analgesic, sedative and hypnotic effect. A medicine made from such a substance was actively used in medical practice back in 1805. Not a single hospital could do without it during the American Civil War. As a strong painkiller, it was administered intravenously and intramuscularly to wounded soldiers after surgery. This greatly alleviated their suffering. However, it should be noted that this remedy quickly became addictive. Soon, the condition to which the patient was exposed after prolonged use of the medication received the name “soldier’s disease.”
As you know, at the beginning of the last century, morphine was used not only by the military, but also by doctors who, with its help, wanted to get rid of the feeling of fatigue.
Mechanism of action of morphine
The effect of morphine on the body:
- causes a euphoric state;
- stimulates the release of vasopressin;
- activates opiate receptors;
- suppresses the transmission of pain impulses;
- increases the pain threshold for severe pain of various origins;
- increases the tone of the gastrointestinal tract muscles;
- stimulates opioid receptors;
- changes the emotional coloring of pain due to its influence on higher areas of the brain;
- has a depressing effect on the vomiting, cough and respiratory centers;
- relieves spasms of smooth muscles of organs;
- reduces the activity of the heat regulatory center;
- dilates the pupils;
- actively affects the center of the vagus nerve;
- increases bronchial tone;
- reduces both physical and psychogenic pain;
- causes inhibition of conditioned reflexes;
- has a sedative effect.
History of the drug substance and composition of preparations with morphine
Morphine is a complex organic chemical compound, an alkaloid. It has the appearance of white needle-shaped crystals, slightly yellowing or graying during storage. At the beginning of the nineteenth century, the German pharmacologist Friedrich Serturner described in detail the physical and medicinal properties of the drug. Because of its ability to cause intense drowsiness, the opiate was named morphine after the Greek god of dreams, Morpheus.
In the past, the only source of the alkaloid was the poppy plant, but only of certain varieties. Nowadays, for the needs of the pharmaceutical industry, morphine is obtained synthetically.
The following dosage forms of the drug are used in medicine:
- injection solution. As additional ingredients, domestic and foreign manufacturers use disodium edetate, glycerol, water and hydrochloric acid;
- pills. Their auxiliary composition is represented by potato starch, milk sugar, microcellulose, povidone, magnesium stearate, sodium carboxymethyl starch.
, another type of drugs containing morphine has appeared in the assortment of hospital institutions . The opioid alkaloid is reliably protected from aggressive gastric juice by a durable gelatin shell. The drug is released into the blood gradually, which provides a prolonged (long-lasting) analgesic effect.
After taking medications with codeine, its transformation occurs in liver cells (hepatocytes). It is metabolized to pure morphine. Therefore, for several years now, such drugs have been sold in pharmacies only with doctor’s prescriptions.
Effect of morphine
Narcotic effects of morphine:
- state of euphoria;
- feeling of flying or floating;
- warmth throughout the body;
- relaxation;
- relieving mental and physical pain;
- tranquility;
- absence of negative emotions and thoughts.
Side effects of morphine:
- dizziness;
- agitation;
- hallucinations;
- headache;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- convulsions;
- asthenia;
- irritability;
- tinnitus;
- blurred vision;
- anxiety;
- violation of movement coordination;
- tachycardia;
- bronchospasm;
- formation of mental and physical dependence;
- atelectasis;
- cardiopalmus;
- sudden jumps in blood pressure;
- short-term loss of consciousness;
- dry mouth;
- nausea and vomiting;
- stool disorders;
- decreased appetite;
- muscle stiffness;
- gastralgia;
- decreased amount of urine;
- cholestasis;
- paralytic ileus;
- ureteral spasm;
- allergic reactions (facial redness and swelling, rash, itching of the skin, urticaria, tracheal swelling, laryngeal spasm);
- compression of the bladder sphincter;
- decreased libido;
- erection problems;
- increased sweating;
- dehydration;
- reduction in body weight.
Pharmacokinetics
Most often, morphine (an anesthetic) is prescribed intravenously, subcutaneously and intramuscularly. However, rectal, oral, epidural or intrathecal use is also possible. This drug is absorbed quite quickly. About 20-40% of the drug is bound to plasma proteins. The drug "Morphine" crosses the placenta and can cause breathing problems in the fetus. It should also be noted that this drug is detected in breast milk.
When administered intramuscularly, the effect of morphine develops in approximately 15-26 minutes. Maximum distribution in the bloodstream is achieved after 35-45 minutes and lasts about 3-5 hours.
Symptoms of morphine poisoning
The minimum life-threatening dosage is 200 ml; in case of high sensitivity to the drug, 60 mg of the substance can lead to death.
In case of opiate addiction, a life-threatening dosage can be 2-3 g of the drug taken per day.
Signs of overdose:
- drowsiness;
- cold sweat;
- bradycardia;
- confusion;
- drop in blood pressure;
- decreased body temperature;
- nervousness, anxiety;
- urinary retention;
- delirious psychosis (loss of orientation in space and time);
- increased intracranial pressure;
- dry mouth;
- vomit;
- swelling of the face;
- ringing or noise in the ears;
- pallor alternating with blueness;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations;
- profuse drooling;
- slow, difficult breathing;
- severe weakness;
- very narrow pupils without changes with increasing/decreasing illumination;
- muscle stiffness;
- respiratory arrest;
- dilated pupils indicate the onset of agony;
- loss of consciousness;
- coma;
- death.
In most cases, symptoms of overdose appear very quickly - from 15-20 seconds to 10-16 minutes. Death generally occurs within a few hours.
Increasing dosages
If after a day there is no good therapeutic effect, the patient still feels pain, but there are no signs of overdose, it is allowed to increase the dosage by one and a half times. This step is repeated every day until the analgesic effect is achieved or the first signs of drug poisoning are achieved. An alternative option is to add additional injections to the basic treatment.
It is important to clarify with the patient how effective the intermediate dose was. Sometimes there is a need to re-evaluate pain because in some cases morphine may not work for a particular patient.
Another important point when prescribing this substance is that there is no maximum permissible dosage of morphine. The more pain a patient experiences, the higher the likely amount of drug they can tolerate.
The correct dosage is one that completely relieves the pain syndrome, while it does not provoke acute drug poisoning, and also does not cause any side effects.
In most CIS countries, the daily dose of morphine is estimated based on the amount of injection administration with a modified release tablet form. This is due to the fact that in many post-Soviet republics there are no normal release oral forms.
Help with overdose
The main medical treatment for morphine overdose is the administration of an antagonist - naloxone or nalorphine, as well as resuscitation procedures.
If you suspect an overdose of morphine, you must immediately call an ambulance and tell them what caused the overdose.
In case of overdose, it is important to know the following:
- Taking any pharmaceutical drugs during morphine poisoning is strictly prohibited, since the drugs will further enhance the toxic effect of the opiate substance. Therefore, it is impossible to independently prescribe medications to the victim, wanting to somehow alleviate the condition.
- Gastric lavage is carried out only in case of poisoning with tablets.
- A person who has been poisoned by drugs should not be allowed to fall asleep or lose consciousness. You should focus the victim’s attention with light slaps, pinching the ear, and shouting. It is necessary to talk with the victim, force him to give answers to the questions asked, and remind him to breathe.
- If nalorphine or naloxone is available (these are opium antagonists - a specific antidote), administer 1-2 ampoules in combination with cordiamine (a drug that stimulates blood circulation and respiration), preferably intravenously, otherwise - subcutaneously or intramuscularly. When taking morphine and a stimulant, the administration of cordiamine is prohibited.
- If breathing is lost, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration and chest compressions until the medical team arrives.
Dosages
To determine the required amount of the drug, you need to find out why a particular patient needs morphine. In case of emergency conditions - painful shock, pulmonary edema, cerebral edema, a single injection of 1 milliliter of morphine solution is first prescribed, which gives doctors time for the duration of its action to provide assistance.
Morphine has low (about 26%) bioavailability when taken enterally (by mouth). When administered intravenously, morphine is intensively absorbed by tissues; within 10 minutes after intravenous administration, 96-98% of morphine disappears from the systemic circulation.”
Wikipedia
In addition, the injectable form is used to relieve pain in cancer patients in the last stages of cancer in a hospital setting. Sometimes their relatives are given a prescription to purchase morphine during their outpatient stay. However, doctors often prefer oral therapy by administering the drug, so they describe a scheme for how to take morphine at home.
Normal release
The initial dose is 2.5-5 mg 1 time per 4 hours. Elderly or weakened by cancer intoxication patients need minimal doses at first. If they have a history of drug addiction or codeine use, then the starting dose is doubled. Before bedtime, the dosage is also doubled. This is necessary so as not to take another pill in the morning. Sometimes patients are allowed to add an early dose of the same amount at any time to relieve pain in the absence of a therapeutic effect. Doctors recommend administering such intermediate doses in the presence of severe pain. Increasing basic therapy is possible with frequent administration of additional tablets. In cases where pain increases with movement, it is recommended to take this intermediate dose approximately 30 minutes before the patient begins any activity.
Modified release
A switch to this form of morphine is allowed when it becomes clear how much of the substance the patient needs for 12 or 24 hours. This is due to the duration of action of the modified form. To calculate the required dosage of morphine MB, it is necessary to sum up the total number of normal-release tablets over the last day, and divide the resulting dosage by two. If it is not possible to prescribe a normal-release drug to the patient, he is prescribed a modified one at a starting dose of 10 mg twice a day.
Signs of desomorphine use
The main signs of desomorphine use are mood swings for no reason, resourcefulness, secrecy, and indifference to others. Such people have disturbed sleep, redness of the eyes and constriction of the pupils. A characteristic sign of a desomorphine addict is that he smells of iodine, and at a later stage a cadaverous smell clearly appears. Bruises and characteristic skin changes are detected on the body. Necrosis of brain cells and complete degradation occurs; disorders primarily affect the motor and speech centers.
Due to its high toxicity, for some drug addicts it becomes the first and last drug in life. The use of desomorphine is becoming a big national problem for the general health of the nation, since its users, on average, are no more than 24 years old.
Use with extreme caution
This remedy should be used with extreme caution for abdominal pain of unknown cause, emotional lability, attacks of bronchial asthma, arrhythmia, convulsions, drug addiction, alcoholism, suicidal tendencies, cholelithiasis, as well as during surgery on the urinary system and gastrointestinal tract. In addition, this drug should be carefully used for brain injuries, prostatic hyperplasia, liver or kidney failure, intracranial hypertension, urethral stricture, hypothyroidism, severe inflammatory bowel disease, epileptic syndrome, pregnancy, lactation and after surgery on the biliary tract . Morphine should also be used with extreme caution in severely ill patients, in the elderly and in childhood.
Development of morphine addiction
Dependence forms after two to three weeks of regular use of morphine. The first signs of the first stage of an already formed addiction are considered to be a painful desire to use morphine in order to experience the desired sensations. Against this background, sleep is disturbed, becomes shallow and short-lived, although overall well-being does not suffer from lack of sleep. Appetite is reduced. The patient is concerned about constipation and urinary retention.
Tolerance to morphine develops quite quickly. In this case, the reaction to the drug is significantly reduced . To achieve the desired effect, the drug addict injects increasingly large doses of morphine.
When the patient cannot use the drug, he experiences dissatisfaction and a depressed mood. All a person’s thoughts are occupied with thoughts about the drug, all everyday problems recede into the background. The patient's life revolves only around the search for morphine.
After three to four months of systematic use of morphine, the second stage of addiction forms . The individual dose of the drug increases several times. The development of the second stage of morphine addiction is indicated by the occurrence of withdrawal syndrome. Withdrawal syndrome manifests itself in the form of the following symptoms:
- Loss of appetite;
- Insomnia;
- lacrimation;
- Sweating, periods of heat and chills;
- Weakness;
- Yawning and sneezing;
- Muscle pain/cramps;
- Angry, irritable mood;
- Abdominal pain, diarrhea.
By this point, a persistent attraction to the drug has already been formed. The euphoric effect of morphine is noticeably weakened . The second stage of morphine addiction can last several years.
Then the final stage inevitably comes - the third stage of addiction development. The patient is already administering morphine only to maintain optimal functioning and prevent withdrawal symptoms . The euphoria associated with morphine use is completely absent. Without morphine, a person becomes lethargic, inactive, and lacks energy. Withdrawal syndrome is more protracted, during which severe cardiovascular complications occur. The patient is constantly depressed, has suicidal tendencies, and decreased performance.
Natural sources and extraction[ | ]
Morphine and other morphine alkaloids are found in plants of the genus poppy, stephania, sinomenium, and moonseed. They are less common in the genera Croton, Cocculus, Triclisia, and Ocotea.
The main route of morphine biosynthesis in plants:
L-tyrosine - L-DOPA - reticuline - salutaridine - thebaine - ein, transformations occur under the action of appropriate enzymes.
Morphine is obtained almost exclusively from the congealed milky juice (opium), released when unripe opium poppy pods are cut. The morphine content in raw opium reaches 20%, on average - 10% [1], the minimum concentration is about 3%. Other poppy varieties contain less morphine.
There are several methods for isolating morphine from biological material[1]. Extraction with water acidified with sulfuric or oxalic acid is used. Extraction with alcohol acidified with oxalic acid is also used.
For example[1], opium is treated with warm water, the aqueous solution is evaporated under vacuum to a specific gravity of 1.17 and mixed with an equal volume of alcohol. When an aqueous solution of ammonia is added to this extract, a mixture of morphine and narcotine precipitates, which is separated from the mother liquor. This mixture is dissolved in dilute hydrochloric acid, from which narcotine precipitates when sodium acetate is added. The precipitate is filtered off and morphine remains in the solution, which is precipitated with ammonia. The resulting technical morphine is purified from impurities and converted into hydrochloride, which is recrystallized from water several times.
Treatment of morphinism
Treatment of morphinism is carried out in a specialized drug treatment hospital . To relieve acute intoxication, the patient is administered an opiate receptor antagonist (Naloxone, Naltrexone) and detoxification agents. Sedatives, anticonvulsants, and cardiovascular medications are also prescribed. After relief of the acute condition, symptomatic treatment is started in the form of hepatoprotective, nootropic drugs, and vitamins. To cure a pathological craving for morphine, the patient must undergo long-term psychotherapy.
Grigorova Valeria, medical observer
10, total, today
( 184 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
Parkinson's disease: symptoms, causes, treatment and prognosis
MDMA (ecstasy) abuse: signs, consequences, addiction treatment
Related Posts
Notes[ | ]
- ↑ 1 2 3 4 Senov P. L.
Opium alkaloids // Pharmaceutical chemistry. — 7th ed. - M.: Medicine, 1971. - P. 447. - 543 p. - Klockgether-Radke AP. "FW Sertürner und die Entdeckung des Morphins." [FW Serturner and the discovery of morphine. 200 years of pain therapy with opioids]. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther
.
2002; 37
(5):244-9. doi:10.1055/s-2002-30132 - Jurna I. “Sertürner und Morphin - eine historische Vignette.” Schmerz
.
2003; 17
(4):280-3. doi:10.1007/s00482-003-0220-3 - Ein demethylation
- Marshall Gates, Gilg Tschudi.
The Synthesis of Morphine (English) // Journal of the American Chemical Society. - 1956-4. - Vol. 78, iss. 7. - P. 1380–1393. — ISSN 1520-5126 0002-7863, 1520-5126. - doi:10.1021/ja01588a033. - Total synthesis of morphine and related alkaloids (English) // Wikipedia. — 2019-03-08.
- Svetlana Borisevich.
Laboratory diagnosis of acute poisoning (Russian). - Litres, 2017. - ISBN 5040234627. - ISBN 9785040234622. - Morphine // Bulgakov Encyclopedia.
- List of narcotic drugs under international control (unspecified)
. International Narcotics Control Board (December 2012). Retrieved September 21, 2013. Archived July 24, 2013. - TGA - Therapeutic Goods Administration (unspecified)
(unavailable link). Retrieved February 10, 2007. Archived February 17, 2007. - ↑ 12345678
Morphine // Great Medical Encyclopedia, T. 15. - 3rd ed. - M.: "Soviet Encyclopedia", 1981. - P. 459-462.
Consequences
Morphine is a highly potent drug that is highly addictive when used. After taking the last dose, painful withdrawal symptoms begin to appear after 12 hours unless a new “portion” is taken.
The use of morphine leads to the following sad consequences:
- mental disorders
- brain damage
- problems with the cardiovascular system
- tooth loss
- amnesia
- confusion
- hair loss, peeling nails, skin turns yellow
- stomach problems
- acute psychoses
- dementia
- death
Impact on the psyche
The psyche responds to withdrawal syndrome with confusion, neurosis-like states and psychoses. Patients complain of insomnia or nightmares that torment them. Vivid hallucinations of a frightening nature and depersonalization are noted.
Lack of treatment or self-treatment can be the impetus for the development of delirium. Delirium tremens of morphine addicts resembles delirium delirium. During an attack, patients hear voices and talk to them, feel foreign objects inside their own body and try to remove them, sometimes causing serious injury to themselves. Delirium tremens hallucinations are personified. Creatures that are not really there talk to addicts.
The psychoses of morphine addicts have different expressions, but they are almost always very difficult. Overexcitement and good mood are sharply replaced by anxiety, wariness and suspicion. Parnoid psychosis is accompanied by delusions and hallucinations. A persecution mania develops. The patient feels the threat of death and sees the environment in a hostile light towards himself. All these manifestations cause aggression towards others and make the drug addict unusually dangerous.