Cannabis (anasha, hemp, marijuana) is an insidious drug, the destructive consequences of which are hardly noticeable in the first months of use. At first, a persistent addiction does not even arise. But a couple of years pass, and the addict realizes that his habit is far from harmless, since the whole body suffers from the drug. Recently, the persistent myth that it is impossible to overdose on marijuana was destroyed. In 2020, the first case of death from exceeding the dose of this drug was officially recorded.
Dose for overdose
Marijuana is a narcotic substance of plant origin. In ancient times it was used to reduce pain. Currently used in some countries for medicinal purposes, but does not have a more intense effect compared to non-narcotic drugs.
The potency of marijuana is determined by the presence of a substance called tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). For a person, an overdose of cannabis is possible when consuming a dose exceeding 50 mg per kilogram of weight.
The maximum concentration of marijuana in the blood is reached six hours after consumption. An overdose develops when the permissible amount is exceeded three times.
The narcotic substance spreads through the bloodstream throughout the body and affects all organs and systems. First of all, the brain suffers from marijuana, mental activity is impaired, and the presence of mental disorders is noted.
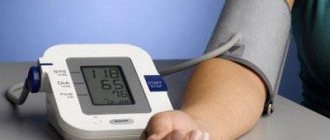
THC affects the functioning of the cardiovascular system, leading to an increase in blood pressure and the development of tachycardia.
After consuming marijuana, the release of toxic substances in the body occurs in two stages. The first is forty minutes after consumption, the second - over the next twenty-four hours. Therefore, an experienced specialist has the opportunity to accurately determine the period of marijuana use.
Is it possible to die from an overdose of this drug? Theoretically, this option cannot be ruled out, but the dose must be increased many times over.
Regular use of marijuana leads to addiction, disruption of the digestive tract, and the development of mental disorders.
Use in medicine
The medicinal use of marijuana goes back to ancient India and the Middle East, where cannabis was widely used as an analgesic, antiepileptic, anticonvulsant, and antiemetic.
The history of its use in medicine dates back to at least the 18th century BC.
The first mention of the use of marijuana in European medicine dates back to the period of colonization of India by England, in the mid-19th century, when army surgeons began to use marijuana preparations for pain relief, treatment of muscle spasms, epileptic seizures and rheumatism. It was thanks to the practice of military doctors of the English colonial corps that marijuana preparations became widespread in Britain and the USA in the nineteenth century.
According to modern data (2011), the use of marijuana in patients with chronic pain (in particular, cancer patients) can reduce pain while simultaneously reducing the dosage of opioid analgesics. The antiemetic effect of cannabinoids is extremely useful when combined with chemotherapy for cancer and AIDS. In a number of countries (Canada, Israel, Spain, Great Britain), the drug Sativex, consisting of a combination of natural cannabinoids (THC and CBD), is used in the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Indian hemp and hemp, as well as the preparations made from them, contain substances related to endogenous cannabinoids (endocannabinoids), in particular anandamide. In 2003, the journal Nature Medicine noted that the brain's endocannabinoid system is involved in a variety of processes in pain, memory, neurodegeneration, and inflammation, and that cannabinoids have significant clinical potential.
Marijuana and drugs made from it are successfully used to improve the conditions of cancer and AIDS patients. THC has been successfully used to combat nausea caused by the use of anti-cancer drugs; this substance is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the above purpose. In some countries (for example: Holland and Canada), marijuana is used as a medicine for cancer patients, as an antiemetic used in chemotherapy.
At the same time, it should be noted that pharmacological studies do not show the advantages of cannabis over other, more traditional antiemetics and analgesics. As a result, the prescription of cannabis preparations for pain relief is an exception, in case of individual intolerance to traditional drugs.
Scientists at a leading research center in Madrid have found evidence that cannabis can prevent memory loss in patients suffering from Alzheimer's disease, The Guardian reports. Their preliminary research showed that tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive component of marijuana, inhibits the activity of cells that cause damage to neurons in the brain. The mechanism of memory loss in such patients is not fully understood, but the problem is believed to be partly related to glial macrophages (microglia), which form a sheath around the nerve cells of the brain. In Alzheimer's disease, microglial activity goes out of control and damages neurons, destroying entire areas of the brain.
Meanwhile, in the United States, legislation prevents the conduct of full-fledged studies of the clinical effectiveness of marijuana. At the same time, in the UK, the government allowed one pharmaceutical company to grow various varieties of hemp for the purpose of clinical trials of marijuana obtained from it.
Signs of overdose
How does marijuana poisoning manifest? An overdose is characterized by certain symptoms that manifest themselves quite intensely.
Symptoms:
- Dilated pupils, lack of reaction to light,
- Rapid heartbeat
- Increased appetite
- Lack of voice, hoarseness, hoarseness,
- Redness of the skin on the face,
- Extreme thirst, dry mucous membranes in the mouth,
- Increased blood pressure,
- Feverish state, muscle spasm,
- Increased anxiety, nervousness, panic fear,
- Convulsions, convulsions,
- Depressed state, lethargy,
- Pathological sleep.
The condition can persist for up to several days. In case of severe poisoning and repeated excess of the permissible dosage, death may occur. The cause of death is often malfunctions of the cardiac and respiratory systems.
There is no official confirmation of possible death from marijuana intoxication, but a person can die from the development of pathological processes after an overdose. Inappropriate behavior during an overdose can cause suicide.
Formation of addiction
Research results from scientists show that regular smoking of weed leads to mental and physical dependence. A drug addict develops apatoabulic syndrome, its symptoms reminiscent of schizophrenia.
- At the first stage, a person constantly has the desire to take 1-2 puffs, but he can do without smoking if there is no marijuana. In this case, the smoker experiences only mild anxiety.
- The second stage takes a long time. At this time, after smoking, the addict experiences pleasure, relaxation, and euphoria. His mood rises, and all worries recede and even completely disappear from consciousness.
- At the third stage, after the next smoked portion, the addict still experiences euphoria, but it does not last long. Bliss quickly changes into a bad mood, apathy, lethargy sets in, and irritability appears. Gradually, those who do not smoke hashish disappear from the addict’s environment, because... he is much more interested in communicating with fellow smokers than with healthy people.
First aid and antidote
If signs of poisoning appear, first aid must be provided to the victim. First of all, it is recommended to call a medical team. Before their arrival, measures are taken to alleviate the condition of the overdose victim.
Measures:
- It is recommended to calm the victim and create a favorable environment for him.
- Provide access to fresh air, unfasten all tight clothing.
- If you are poisoned by weed while smoking, strong tea with the addition of lemon or honey will help cope with unpleasant symptoms.
- To reduce body temperature in case of overdose, it is recommended to wipe the body with a cloth soaked in cool water. It is permissible to place a wet, cold towel on your forehead.
- When using weed internally, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with plenty of clean water.
- It is allowed to give the victim of an overdose various sorbents to speed up the removal of the toxin.
- In the absence of consciousness, resuscitation is performed.
- It is necessary to maintain a conversation with the victim of an overdose, not to let him fall asleep or lose consciousness.
Treatment of poisoning is carried out in a medical facility. In rare cases, a specific antidote SR141716A is used.
Use
When orally consuming (that is, eating) cannabis products containing narcotic substances (such as hashish, managa, THC-containing oil, culinary products based on them, and the like), cases of significant excess dosages are possible.
Smoking is characterized by the combustion of plant fiber and the release of smoke with associated evaporation of drugs. To filter smoke from the carcinogenic substances it contains and cool it, a hookah with water or juice can be used.
It is also possible to evaporate the cannabinoids contained in dried marijuana without burning the fiber; for this, a stream of hot air at a controlled temperature is supplied to the substrate; the content of carcinogenic substances in such vapor is minimal. For this, a vaporizer is used - a device for evaporating active substances from a dry mixture.
Recreational use
Recreational use of cannabis is traditional for many peoples of India, the Himalayas, Central Asia, Indochina, the Middle East, Africa and Central America. In the 19th century this tradition began to spread in Europe and North America, and now exists almost everywhere.
Unlike alcoholic beverages, cannabis preparations cannot be dosed precisely and their effects are often unpredictable. Therefore, inexperienced consumers are not always able to stay on the line beyond which recreational use develops into an overdose.
Overdose
Overdose is the use of an excessive dose of a drug, leading to disruption of the body’s functioning. Recently, the term is often used in everyday life for the non-medical use of narcotic and psychotropic substances; in these cases, it means taking an amount of a substance that causes undesirable, unpleasant or dangerous effects.
Fatal overdose on cannabinoids is unlikely because the lethal dose of THC is 40,000 times the average effective dose. However, exceeding the individual effective dose by 3-4 times can give a number of unpleasant symptoms, both somatic (increased sweating, tremors of the limbs, tachycardia, nausea, dizziness, fainting) and mental (see “freezing”, “glitches”, “ betrayal”, “deadness”, “paranoia”, “obsessive ideas”), there is also a feeling that time is passing for a long time. After 10 minutes it may seem like an hour has passed. More severe overdoses usually cause impaired coordination of movements, difficulty thinking and speaking, complete or partial immobility and a half-asleep state, against the background of which oneiric hallucinosis can sometimes be observed.
Overdoses often occur when cannabis preparations are taken orally. When smoking, you can overdose if you consume a product with a very high THC content. In the absence of unpleasant physical manifestations, a cannabinoid overdose is usually perceived as a psychedelic experience and does not have severe consequences. If the overdosed person is concerned about his condition, he should take the same measures as in case of food poisoning (induce vomiting, rinse the stomach, drink hot sweet tea). In case of smoking, gastric lavage and vomiting are not effective.
Oral consumption
Oral consumption ( eating ), the oldest method of consuming psychotropic cannabis products, has partially lost its popularity due to the spread of smoking. When taken orally, the psychotropic effect begins to be felt after 40-60 minutes. This is a slight sensation of a change in the state of sensations (comparable to smoking low-grade marijuana). The full effect occurs 0.5-2 hours after taking the product, and there is usually no “arrival”. Changes in well-being increase and accumulate gradually, and at some point they become so clear that they can no longer be ignored. But there is also a sharp change in condition, after 30-40 minutes, the so-called “wave”. Intoxication from oral use is usually longer lasting (sometimes up to 6-8 hours) and deep, often accompanied by motor retardation and vivid visual effects (see oneiroid, pseudohallucinations).
Sweets
In the medical tradition of Ayurveda, sweets containing crushed bhang served as popular broad-spectrum medicines. The content of cannabinoids in them was low, and their psychotropic effects were neutralized by the addition of antidotes (in particular, calamus root). Sweets for recreational consumption (majun, dawamesque, etc.), popular in the East in the Middle Ages and Modern times, were distinguished by a higher concentration of psychotropic components. In addition to bhang and hashish, they often included datura, henbane and poppy sleeping pills. Such sweets took the form of jam, fudge or halva.
In 1860, the production of Hasheesh Candy lollipops, produced by the Gunja Wallah Company, was launched in New York. Sweets made from syrup with the addition of an alcoholic tincture of cannabis were advertised as “the most pleasant and harmless stimulant” and were sold for 40 years.
Currently, hemp lollipops are produced by some European companies, but do not contain cannabinoids, but are made on the basis of an aromatic extract.
Medical care and treatment at home
Therapy is carried out in the department of narcology or toxicology. Various medical procedures are carried out aimed at cleansing the body of toxic substances.
Procedures:
- Droppers and diuretics are prescribed for detoxification.
- Medicines are used aimed at normalizing the functionality of the cardiac system and restoring blood pressure.
- If necessary, use an artificial respiration apparatus.
- Neuroleptics are administered intramuscularly to reduce agitation and nervousness.
- If necessary, hemodialysis and forced diuresis are performed.
- The victim is under constant medical supervision.
During the recovery process, vitamin complexes are selected to support the immune system, and conversations are held with a narcologist and psychologist.
An overdose cannot be treated at home; adverse consequences may develop.
How does marijuana affect the body?
Since ancient times, weed has been used as a pain reliever. It was used as an infusion to relieve seizures. Today, as far as medical purposes are concerned, marijuana is used to stop vomiting (it helps well with chemotherapy), as well as to normalize the health of patients with multiple sclerosis.
The degree of activity of cannabis is determined by the content of tetradigrocannabinol. THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is a neurotransmitter that directly affects the body's neuromuscular responses. The substance also takes part in the functioning of internal organs. For this reason, after taking cannabinoids, an accelerated heartbeat, coldness in the extremities, and surges in blood pressure are sometimes felt.
As a result of ingestion, marijuana is immediately absorbed into the blood, absorbed by cells and released into the central nervous system. After this, the central nervous system is rebuilt, and the production of serotonin increases.
Consequences and prevention
What can happen during marijuana intoxication? An overdose of a drug can lead to the development of adverse effects in the body.
What is possible:
- Disruption of the nervous system, psychological disturbances,
- Memory loss, lack of attention,
- Heart attacks, pathologies in the functionality of the cardiac system,
- Liver dysfunction, toxic hepatitis,
- Sexual dysfunction
- Diseases of the lungs and other organs of the respiratory system,
- In rare cases, schizophrenia may occur.
Death from marijuana - myth or reality
In 2020, it became known that you can die not only from long-term complications caused by the use of increased doses of marijuana. Death can occur instantly. On November 17, the first case of overdose was reported in Colorado, which is described in a toxicology article in the medical journal Clinical Practice and Cases in Emergency Medicine.
A tragic incident occurred with a one-year-old boy who found a bag of marijuana hidden by his parents and consumed it internally. This led to toxic damage to the myocardium. The child’s heart could not stand it and stopped; the ambulance team was unable to save the baby.
The effect of the drug on the heart muscle has been known for a long time, but until 2017, only cases of the development of pathologies, but not instant death from cannabinoid poisoning, were known. This, unfortunately, was the appeal of defenders of the legalization of soft drugs. Confirmation that marijuana can kill you instantly has become a compelling reason to tighten controls on the sale and use of all types of cannabis products.
Video: is weed harmful to humans?
Read more:
Stages of cleansing the body after quitting smoking
The benefits of water and how to maintain water balance in the body
Hepatitis C, symptoms and treatment
Herbal remedies and treatment of attention deficit disorder without drugs
Food poisoning of microbial origin
Article rating:
Share with friends:
You may also be interested in:
Amphetamine overdose: signs and symptoms, first aid, consequences
Alcohol poisoning - how to treat it?
Opiate overdose - symptoms and first aid
Isopropyl alcohol poisoning⛔
Possibility of overuse
A person who uses hashish in large doses has a disrupted perception of the surrounding reality. The addict sees blurry objects and brighter colors around him. But sometimes things, on the contrary, become too clear. The smoker becomes tongue-tied and his thoughts lose track.
A person addicted to marijuana does not look the same in appearance as a healthy person: his movements are inhibited, his gaze is distant, his gait is unsteady. A drug addict perceives time incorrectly; for example, a couple of minutes seems like 2-3 hours to him.