Surely many of us will remember one or more situations when we felt ill after taking one or another medication, or after inhaling vapors of an unknown substance. But not everyone can boast of how to help the body cope with this kind of intoxication.
In medical practice, in such cases, detoxification is carried out - this is the implementation of physical, chemical and biological measures to destroy and remove toxins from the body. This will be discussed in our publication.
What is detoxification and who needs it?
Detoxification of the body
Detoxification means ridding the body of toxic substances. The term “toxins” is translated from Greek as “poisonous”. Toxins are toxic components that accumulate in organs, blood, and interstitial fluid. They can be of plant, animal or synthetic origin. Harmful substances disrupt the coherence of metabolic processes and lead to a decrease in the quality of operation of important systems of the human body.
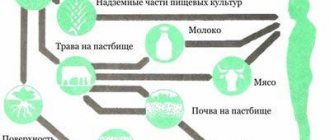
Toxins enter the human body from outside or are formed by the body itself. The main source of toxic substances is the environment. They enter the body with food, water, penetrate from the air, through the skin. Often the source of toxic poisoning is parasites that infect the human body. Helminths and protozoa live in different organs and poison the body with the products of their vital activity. In a normal state, the body gets rid of all dangerous substances on its own, thanks to the coordinated work of the liver, lungs and kidneys. Harmful substances are filtered in these organs and removed from the body through urine, feces, sweat and breath.
#2. Limiting the occasional intake of protein foods (protein inhibits autophagy)
Restriction for the same 24 hours on the intake of protein foods: meat, fish, eggs, cottage cheese, milk, etc. also has a beneficial effect on human health (body).
When we consume a lot of protein from outside (from food) = protein is deposited and intoxication increases.
This is because the body has no incentive to detoxify from harmful and disease-causing cells (because protein enters the body and it is in excess) and regeneration of new cells does not begin from eaten old cells.
Simply put, with increased protein intake = detoxification (autophagy) does not occur (does not start).
In general, regarding protein, I want to give several recommendations for daily use (on use)…
I recommend that you maintain a balance of plant and animal protein in your diet.
Personally, I have 20% vegetation (although I don’t even take it into account), and 80% animal.
Animal protein in my diet is 1.6 grams per kg of body weight = I do not consume and do not recommend more than these figures, because with excess, problems arise: a large load on the liver, the occurrence of diseases, for example, the formation of stones and much, much more.
Therefore, I eat no more protein + - 1.6 g/kg + from time to time I carry out autophagy.
And so, to conclude, autophagy is absolutely natural, simple, cheap, etc. method-process which:
- Self-renews, self-cleanses and makes the body more viable.
- Improves health - promotes rejuvenation - as a result, improved appearance.
- Slows down aging and prolongs life expectancy.
- Relieves chronic infections and inflammation (destroys bacteria and viruses)
- Renews cells and tissues of the whole body
- Increases brain efficiency
- Restores cells of the nervous system
- Eliminates damaged proteins and organelles, which helps prevent cancer, cardiovascular, neurodegenerative diseases (Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, dementia, etc.)
The need for detoxification
Previously, this term was used only by narrow specialists when it came to drug or alcohol poisoning. Recently, detoxification measures have become necessary even for people who lead a healthy lifestyle, do not abuse alcohol, and do not smoke. As a result of the negative environmental situation, the problem becomes very acute.
Soil, air and water pollution causes more than ten million deaths in our country every year.
In addition to chronic ill health as a result of the intake of harmful substances, there are conditions that require emergency medical care. Let's try to consider each of the conditions and draw up a plan of rational actions.
Methods of detoxification of the body
Endogenous and exogenous toxins are not located in one place, but constantly move through the body’s bloodstream. The intensity of spread depends on the chemical and physical characteristics of the poison.
Detoxification of poisons is the process of neutralizing toxins and accelerating their evacuation from the body. Options involve getting rid of toxins and evacuating dangerous substances from the digestive organs, cleaning the blood and intercellular fluid from toxins and their breakdown products. All options for detoxification measures can be divided into enhancing natural processes, artificial detoxification, and antidote therapy. Thus, methods are divided into natural and hardware.
Read
Rules for detoxification at home
Main stages of detoxification
Inducing vomiting
The order of assistance measures varies in each specific case, but regardless of the type of toxins, there is a general algorithm of actions:
- inducing vomiting and gastric lavage;
- use of adsorbents;
- forced diuresis;
- The next steps are chosen by health workers depending on the situation.
A full range of measures to reduce intoxication phenomena is carried out in a medical institution, if necessary, special equipment is used, and experienced specialists take part. Detoxification measures at home can only be carried out in isolated, “mild” cases. Even if there is no threat to life, the patient must be treated under the supervision of a doctor. Only a doctor can determine the severity of the disease by eye, so only he can prescribe the correct treatment. Untimely and inadequate assistance can aggravate the patient’s condition and cause serious consequences.
High volume hemofiltration
Experimental and then clinical studies conducted in recent years have revealed the advantages of using high-volume venovenous hemofiltration in patients with multiple organ failure and sepsis. Improvements in cardiac activity and hemodynamic parameters were noted in animal experiments at UV rates of up to 120 ml/kg/h.
Clinical studies have shown that increasing the dose of hemofiltration above the usual “renal dose” has a positive effect on survival. High-volume venovenous hemofiltration is a method that can significantly reduce the plasma concentration of most inflammatory mediators, thereby providing the ability to “manage” the systemic inflammatory response.
However, it is unlikely that filters and membranes used for HF in the treatment of acute renal failure, due to the size of the pores and sieving coefficients, will be of significant importance in the extracorporeal therapy of sepsis.
Hemofiltration using hemofilters with high-permeability membranes
To increase the clearance of “medium” molecules during extracorporeal detoxification procedures, it has recently been proposed to use hemofilters with highly permeable membranes (up to 100 kDa). The results of the first studies indicate a significant increase in the elimination of inflammatory mediators, and the clearance of these substances under convection and diffusion principles of mass transfer using highly permeable membranes was similar.
The clinical use of these hemofilters is alarming primarily because of the danger of high loss of protein fractions. However, a recent randomized prospective study comparing the effectiveness of using high-permeability and standard hemofilter membranes in patients with acute renal failure and sepsis showed no significant decrease in albumin concentration 48 hours after the start of the procedure in both groups of patients and a significantly higher clearance of IL-6 and IL-1ra by the end the first day in the group of patients who used highly porous filters.
Vascular access for continuous renal replacement therapy
When performing PAVGF, catheters of the largest diameter are used for catheterization of arteries and veins to ensure a sufficient gradient to promote the movement of blood through the extracorporeal circuit.
The problem of vascular access arises most acutely when it is necessary to carry out the procedure in newborns and children of the first year of life due to the small caliber of both arteries and veins. In children weighing up to 5 kg, catheterization of either the femoral or umbilical arteries and veins is usually performed using single-lumen catheters ranging in size from 3.5 to 5 Fr.
The use of double-lumen venous catheters has practically solved the problem of vascular access in patients in the ICU during both intermittent and permanent venovenous procedures.
Evaluation of the method of continuous replacement therapy
Is the method of continuous RRT so ideal for patients in the ICU? Despite more than twenty years of successful experience in using such therapy in intensive care practice, this technique is not without a number of disadvantages.
Firstly, the risk of bleeding increases significantly due to the need for constant use of systemic anticoagulation.
Secondly, there may be a significant reduction in the concentration of inotropes, antibiotics and other expensive drugs due to their constant ultrafiltration or adsorption on the filter membrane.
Third, chronic RRT is not always effective in correcting uremia, especially in patients with hypercatabolism.
Fourth, 24-hour RRT complicates a range of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, increases the need for sedation, and limits patient mobility.
Finally, the high cost and labor intensity of treatment cannot be discounted, especially in cases of severe sepsis and MODS, when high-volume procedures are required (UF more than 6 l/h).
Thus, despite the widespread popularity of continuous RRT methods in the intensive care unit, these RRT methods are also less than ideal for a number of reasons.
Signs of chronic intoxication
Decreased immune strength of the body
In addition to acute conditions that require medical intervention, there are conditions that do not have clear manifestations of pathology, but require correction. You need to think about detoxification measures if you notice the following manifestations:
- Decreased immune strength of the body. If you become hostage to all the cold seasons, reacting to a decrease in temperature with colds and ARVI, your immune system has stopped coping with its task in full.
- Constant fatigue and malaise. Fatigue and loss of strength are alarming symptoms. If your favorite activity does not bring satisfaction, and fatigue appears immediately after waking up in the morning, your body is polluted. A constant headache, discomfort in the muscles, cramps are a distress signal and a request for help.
- Hormonal changes. They manifest themselves in different ways: increased sweating, weight fluctuations, mood swings.
- Deterioration in appearance. When intoxicated, the quality of hair, nail plates, and skin changes. People note brittle hair and nails, peeling nail plates, and skin rashes.
- Digestive problems. A person complains of heaviness in the stomach after eating, alternating diarrhea with constipation, and the appearance of excess weight.
If such symptoms appear, it is necessary to exclude serious diseases. If no pathology is identified, you can begin detoxification.
#6. No large meals before bed
A heavy dinner turns sleep into a self-poisoning procedure.
When you have eaten heavily, the body does not activate the process (or does not activate it as effectively) of self-cleaning and cell renewal. As a result of this, intoxication (poisoning) of the body increases.
Read point #8. about sleep and you will understand a lot (why this point is very important).
A hearty meal should be before 18.00; after - something very, very light or nothing at all.
Methods of detoxification for mild poisoning
The choice of option depends on a lot of factors, the leading ones being the individual characteristics of the body, concomitant diseases, and the severity of the condition.
Diet food
Diet food
A diet can have two directions: to help get rid of excess weight or to cleanse the body of toxins and poisons. To evacuate harmful substances, it is recommended:
- Drink the required amount of water, at least three liters per day.
- Increase your fiber intake to improve the elimination of toxins. It is mainly recommended to give preference to plant foods.
- Try to reduce the amount of salt you consume. It promotes fluid retention and interferes with the full flow of metabolic processes.
- Eat only lean meats.
It is important not to reach the point of fanaticism: there is no need to look for the rarest products and kill yourself over the candy you eat.
How to reduce the risks of side effects
Rules for a healthy lifestyle
Liberation of the body from harmful substances should take place in a gentle manner and under the constant supervision of a doctor. Diet, properly selected methods and a healthy lifestyle contribute to the rapid elimination of toxins without consequences for health.
Herbal teas are used to improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, kidneys and liver. Their mild effect will not cause harm if the composition is correctly selected (without components that can cause allergies).
To completely cleanse the body of harmful compounds, you must stop smoking, drinking alcohol and drinking drugs. A balanced diet and fasting days reduce the load on the digestive organs and help avoid stomach upset and other unpleasant consequences after using detoxification drugs.
Physical activity and medicinal cleansing
Physical activity is extremely beneficial for human health. Sports are a great way to detoxify. Activity leads to increased sweating, hence the release of toxins and poisons. There is no need to exhaust yourself with excessive exercises, just walk more and find an exercise that is suitable for your strength. Medicinal detox allows you to remove toxins and poisons as effectively as possible. For cleansing, sorbents are recommended that have the ability to bind and remove toxins. The drugs are not absorbed into the blood, work in the digestive tract and do not disrupt the microflora.
Activated carbon
The best sorbents are recognized:
- Activated carbon. An inexpensive drug that helped our ancestors. Effective, but has a small area of activity. Exists in tablet form.
- Colloidal silicon dioxide. New generation drug. It is taken in the form of a suspension. Instantly affects the problem, quickly normalizing the condition.
- Smecta. It is taken in the form of a suspension. Recommended for digestive problems, poisoning, diarrhea. Indicated in pediatrics.
- Lingin. Plant sorbent. It is effective for a variety of pathological conditions and is prescribed as an additional component of antibacterial action for infectious diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
Read
What is the essence of the 7-day detox diet?
The drugs have contraindications, so it is important to consult a doctor before use.
Natural Detoxification Methods
Natural detoxification aims to stimulate the body's natural systems to speed up the elimination of toxic buildup. The body has systems that are responsible for this. The so-called natural filters remove toxins as they accumulate or enter: kidneys, liver, intestines, lungs.
Forced diuresis
Natural detoxification methods include:
- Forced diuresis.
- Use of enterosorbents.
- Blood purification with ultraviolet light.
- Liver support.
- Use of immune stimulants.
Vomiting and gastric lavage
Often, poison that has entered the body causes vomiting. Toxins are removed along with vomit. Vomiting does not always occur on its own, so it is recommended to artificially stimulate the process. You can provoke vomiting mechanically or by drinking a large amount of cleaning solution, but it is not allowed to provoke the gag reflex:
- If the patient is unconscious, the procedure is unsafe. A person may choke on vomit or water.
- Some substances can disrupt the integrity of the membranes of the digestive tract, and vomiting will only worsen the situation.
After emptying the stomach of food containing toxins, the organ is washed.
At home, it is carried out by drinking large volumes of water. In a hospital setting, liquid is injected into a person’s stomach through a tube. The procedure is carried out every three to four hours to remove toxins and prevent their spread throughout the body. Gastric lavage occurs in combination with previously induced vomiting. The chance that all harmful substances came out with vomiting is not high. It is forbidden to rinse the stomach if the body is affected by certain acids and poisons, as the pathological condition can significantly worsen.
"Classical" hemodialysis
Under experimental conditions, the possibility of extracorporeal blood purification using HD was first shown by J. Abel in 1913. But only 30 years later, in 1943, WJ. Kolff has designed a device suitable for clinical conditions.
The term “classical hemodialysis” should be understood as intermittent (lasting no more than 3-4 hours) therapy, with a frequency of 3 times a week, using high blood flow rates (250-300 ml/min), dialysate solution (up to 30 l/h) and dialysis dose (Kt/V at least greater than 1).
Regarding the justification of the use of “classical” hemodialysis in the ICU in patients with acute renal failure, which is one of the components of the treatment of multiple organ failure syndrome (MODS), there is still intense controversy among specialists, and the issue is far from a final solution.
First of all, this is due to the fact that the use of hemodialysis often had a depressing effect on the circulatory system. Hemodynamic instability when using standard hemodialysis in patients in the intensive care unit is most often due, on the one hand, to the speed and volume of ultraviolet radiation, and on the other, to a decrease in plasma osmolarity.
During the HD procedure, diffusion transport of osmotically active substances from the blood into the dialysate takes place due to a concentration gradient. Because this transport exceeds the transport of water during conventional hemodialysis, there is a decrease in plasma osmolarity, which causes an even greater decrease in the volume of extracellular fluid that rushes into the cell.
The temperature of the dialysate and replacement solutions plays an important role in stabilizing hemodynamic parameters during extracorporeal procedures. The use of cool (room temperature) solutions significantly affects the ability to prevent arterial hypotension due to the occurrence of moderate vasoconstriction and an increase in total peripheral vascular resistance. However, it should be taken into account that severe vasoconstriction can certainly impair tissue perfusion and cardiac performance.
The most justified use of intermittent HD is primarily in patients with symptoms of acute renal failure, when rapid and effective filtration of uremic toxins, correction of water-electrolyte balance and acid-base status are required.
“Classical” hemodialysis in the treatment of acute renal failure in patients in the intensive care unit who are in critical condition, unfortunately, is deeply unphysiological, since it involves, on the one hand, more intensive (aggressive), and on the other hand, short-term treatment, with large time intervals (more days) between procedures.
Moreover, the use of the “classical” HD technique in the ICU does not allow for adequate nutritional support due to the risk of severe fluid overload and the development of pulmonary edema during interdialytic intervals.
Finally, possible complications of this intensive dialysis technique include a rapid decrease in the concentration of solutes (osmotically active sodium and urea), which leads to significant changes in the water content of the brain tissue and increased intracranial pressure in patients at risk of developing or having already developed cerebral edema .
Thus, the use of “classical” HD is not the best option in the treatment of acute renal failure in an intensive care unit. There is no doubt that in the traditional version, this RRT technique cannot ensure either safety or proper effectiveness of therapy in patients in critical condition.
Continuous methods of renal replacement therapy (hemofiltration/hemodiafiltration)
The development and improvement of extracorporeal blood purification technologies have led to the formation of new principles and systems for the treatment of acute renal failure in the intensive care unit in patients in critical condition.
In 1977, Dr. P. Kramer et al. published the first results of a new treatment method, which they called continuous arteriovenous hemofiltration (CAVHF). The method is based on the use of a highly permeable membrane in a hemofilter, which is connected to the artery and vein using modified hemodialysis lines.
The arteriovenous pressure gradient makes it possible to move blood along the extracorporeal circuit without the use of a pump. PAVHF is based only on convection, that is, blood purification is achieved through UV and the replacement of fluid lost during filtration, while diffusion is not used.
The undoubted advantage of the method is the absence of a negative effect on the state of the circulatory system, with the possibility of adequate control over fluid balance. In addition, PAVGF makes it possible for patients with oligoanuria to receive adequate intensive treatment, including infusion-transfusion and drug therapy, parenteral and enteral nutrition.
However, this method also has certain limitations. A very important disadvantage of arteriovenous access is the unstable blood flow rate in the extracorporeal circuit due to a decrease in the arteriovenous gradient due to hypotension, often observed in patients in the ICU, or thrombosis of the circulating circuit and filter.
Thanks to the widespread introduction into clinical practice of double-lumen catheters and new generation perfusion modules for permanent methods of renal function replacement, continuous venovenous hemofiltration and continuous venovenous hemodiafiltration (CVVHDF) have become most widespread.
With these types of treatments, a perfusion module is used to ensure blood flow through the extracorporeal circuit, and their effectiveness, especially PVVGDF, is significantly increased through the use of convection, ultrafiltration, and diffusion.
Of course, PVVHDF, in comparison with “classical” hemodialysis, provides greater hemodynamic stability, unlimited control over fluid balance, allows for adequate nutritional support, control the concentration of even the smallest amount of dissolved substances, and correct or prevent the development of electrolyte imbalance.
Published in 2000 by C. Ronco et al. The results of a randomized controlled trial showed that with chronic RRT methods, increasing the volume of hemofiltration can improve the survival of patients with AKI and sepsis in the ICU.
Use of medications
Gastric lavage does not guarantee 100% removal of toxins and poisons. To minimize the risk of toxic substances entering the bloodstream, adsorbents are used. The drugs are able to absorb, bind and remove toxins naturally. There are many effective enterosorbents, among them are: Polysorb, Enterosgel, Polyphepan, Activated carbon.
Enterosgel
The drugs will be effective only if you quickly respond to problems and use the medicine before the massive penetration of toxins into the blood. If you take sorbents late, the result will not be good, and in this case it is necessary to carry out deeper detoxification measures. To cleanse not only the stomach, but also the intestines of toxic compounds, they practice the use of laxatives. This group of drugs is not used when acids and alkalis penetrate the body. If you take a laxative, the burn from the chemicals will spread to all parts of the gastrointestinal tract.
Read
How does ion detoxification of the body work?
Extracorporeal therapy based on sorbents
The use of traditional methods of dialysis therapy does not allow the removal of protein-bound toxins from plasma, since these methods provide control only of water-soluble molecules, and the use of sorption techniques, especially in combination with RRT methods, makes it possible to effectively remove albumin-associated hydrophobic complexes, as well as water-soluble substances.
Sorbents are divided into two large groups: specific and nonspecific. The former are based on specially selected ligands or antibodies that provide high target specificity. Nonspecific adsorption is usually based on the use of charcoal and ion exchange resins with the ability to bind toxins and hydrophilic properties.
Although the clinical use of sorbents was initially hampered by the frequent occurrence of leukopenia and thrombocytopenia, recent improvements in the design of the HD apparatus and the advent of biocompatible coatings have revived interest in this auxiliary blood purification technique.
In 2006, C. Ronco et al. a new combined technique was proposed - plasma filtration plus adsorption plus dialysis, which, according to the authors, can be of great practical importance in the complex therapy of MODS and sepsis.
Plasma sorption formed the basis of a new extracorporeal blood purification technique - combined plasma filtration-adsorption (CPFA). It combined the regeneration of filtered plasma by adsorption on a non-selective sorbent and hemofiltration of whole blood before its return to the bloodstream of patients, which allows increasing the clearance of sepsis-associated medium-molecular substances.
Non-selective removal of inflammatory mediators occurs through adsorption on a hydrophobic resin, which has significant sorption capacity for most inflammatory mediators and cytokines and a high degree of affinity for them. The CPFA technique is based on various mechanisms of mass transfer: diffusion, convection and adsorption, which together play an immunomodulatory role.
S. Ronco et al. were the first to describe the experience of the clinical use of CPFA and noted an improvement in hemodynamic parameters after just one procedure lasting 10 hours. Moreover, it was revealed that plasma monocytes that passed through the sorption column were again able to respond to the release of endotoxin.
Based on these data, it was proposed that CPFA is a blood cleansing procedure for septic shock that modulates the immune response and restores the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory mediators.
Despite evidence of improved survival, further, larger studies are needed to determine the potential of CPFA in the treatment of patients with sepsis.
Experimental studies have shown that the use of sorption techniques makes it possible to achieve effective elimination of endotoxin and significantly reduce the concentration of inflammatory mediators, which increases the survival rate of experimental animals compared to the control group. Moreover, a decrease in the circulating concentration of cytokines is combined with a decrease in the binding activity of nuclear factor kp, which indicates a regression of the activity of the inflammatory process at the tissue level.
Selective, biocompatible LPS adsorption cartridges manufactured by Alteco (Lund, Sweden) and columns (Toraymyxin™, Toray Japan) for endotoxin adsorption during hemoperfusion have recently appeared on the European market. Experimental work on the effectiveness of using the Alteco adsorber in modeling sepsis in animals, carried out in Sweden, showed a significant decrease in the blood concentration of lipopolysaccharide, inflammatory mediators, improvement in hemodynamic parameters and, above all, cardiac output.
In Russia, there is only a single experience of hemoperfusion procedures using endotoxin-selective columns in seriously ill patients with infectious and septic complications. The Alteco LPS adsorber is a sorption column consisting of 20 porous polyethylene plates, the total surface area of which is 3.3 m2, and the filling volume is 20 ml.
Toraymyxin PMX-F is a sorption column containing a fibrous adsorbent, where polymyxin B is covalently bonded to a-chloroacetoamidemethylated polystyrene and immobilized to polypropylene fibers. The high sorption capacity of the Toraymyxin column is explained by the large area of the fibers due to their small diameter (30-40 pm) and their high porosity.
A reflection of the microbial load is high titers of endotoxin in the blood when performing the LAL test (cascade enzymatic reaction method - gel-thromb test) and using a new method for biochemical diagnostics that assesses the level of endotoxin activity (EAA). Experimental studies have shown that an increase in EAA levels in vitro corresponds to an increase in the concentration of LPS in the blood.
According to a study by J. Marshall et al., a low level of endotoxin corresponded to a mortality rate of 11%, while with medium and high EAA it was already 13 and 17%, respectively. In carried out in 2007-2008. D. Klein et al. A prospective study among 53 patients with septic shock revealed a mortality rate of 16% with an EAA value of less than 0.4 and 34% with an EAA in the range of 0.4-0.59, while with an endotoxin activity level of more than 0.6, the mortality rate increased to 50%.
Forced diuresis
The procedure is aimed at activating the functioning of the kidneys in order to speed up the elimination of dangerous substances from the body. About two liters of a medicinal solution are injected intravenously into the patient, and diuretics are administered. The kidneys begin to work much more actively and excrete a large volume of urine. Often it reaches five to seven liters. The doctor monitors the patient’s condition and, if necessary, carries out concomitant therapy.
Diuresis shows different effects, depending on the poison entering the body.
The highest result is observed in case of poisoning with water-soluble poisons. The procedure is not suitable for everyone. There are conditions that are contraindications for diuresis: kidney disease, heart problems, old age.
Indications for use
A specialist may prescribe a procedure for intensive treatment of the following pathologies:
- antiphospholipid syndrome;
- rheumatological systemic diseases: vasculitis, arthritis, granulomatosis, lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis;
- in case of poisoning with medications, chemical compounds in production;
- poisoning with alcoholic drinks, narcotic substances;
- after environmental disasters;
- radiation damage to the body;
- toxicosis in pregnant women;
- rhesus conflict;
- development of genitourinary infections;
- glomerulonephritis;
- insufficiency of the cleansing function of the liver or kidneys;
- diabetes mellitus;
- autoimmune thyroiditis;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- skin diseases: psoriasis, eczematous process, neurodermatitis, furunculosis;
- myasthenia gravis;
- polyneuropathy or polyneuritis;
- Parkinson's disease;
- multiple sclerosis;
- liver cirrhosis;
- pancreatitis with areas of necrosis in the pancreas;
- disruption of intestinal microflora;
- focal inflammation or suppuration in the lungs;
- atherosclerosis;
- bronchial asthma;
- myocardial ischemia;
- increased blood pressure;
- hypertension.
Extracorporeal detoxification methods in intensive care are used urgently, without diagnostic procedures, in acute emergency conditions, for example, sepsis. In emergency abdominal surgery, the procedure can be performed for conditions such as ruptured appendicitis, peritonitis, acute diseases of the liver and pancreas.
In addition, the use of extracorporeal detoxification methods in dental surgery is known: for abscesses of soft tissues of the oral cavity, jaw bones, etc.
Methods of active detoxification
Artificial detoxification is carried out using equipment that cleanses the blood and lymph, and is characterized by the use of antidotes.
Hyperventilation
This option is used when inhaling dangerous vapors. The patient is connected to a ventilator.
Peritoneal dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis
There is a special device in the abdominal wall through which a large volume of a special solution is injected. This helps to cleanse not only the blood, but also the intercellular fluid. Contraindications to abdominal dialysis are the following conditions: adhesions in the peritoneum, pregnancy in the second and third trimester.
Blood transfusion
The point of the technique is to administer donor blood to the patient and remove the same volume of “poisoned” blood through the artery on the thigh. This option is used when affected by organophosphorus poisons. If you have heart disease, blood transfusions are prohibited.
Hemodialysis
Blood purification is performed using an artificial kidney apparatus. The effectiveness of the procedure depends on the response time: the sooner the procedure begins, the higher the effect will be. The method is much more effective than forced diuresis, but cannot be used at low blood pressure.
In what cases is it contraindicated?
Efferent therapy has contraindications:
- Hemodialysis is prohibited for patients with epilepsy, stage 3-4 oncology, active tuberculosis, schizophrenia, alcoholism and drug addiction, diseases with a risk of bleeding. Detoxification is not performed for elderly people (over 70 years old); the method is not used for diseases of the nervous system.
- Plasmapheresis is not prescribed to patients with bleeding disorders, anemia, or low protein levels in plasma.
- Cleaning using hemosorption is not indicated for cancer patients, patients with brain damage, or people at risk of bleeding. It is not recommended to use this method during menstruation, flu, or low blood pressure.
The article was approved by the editors
Hemosorption and plasmasorption
Hemosorption
This is the purification of blood (plasma) through a sorbent. Using a pump, the components are driven through activated carbon, which absorbs the poison. Since the procedure negatively affects platelets, measures are taken to protect blood elements. The procedure is effective only if poisons and toxins are located directly in the blood (plasma). The method is five times more effective than hemodialysis.
Consequences of removing toxins
Cleansing the body is a process that must be approached responsibly. After removing toxins, the following negative consequences may occur:
- Due to the uncontrolled use of drugs, abdominal pain appears, digestion is disrupted, and beneficial bacteria, which are necessary for proper digestion of food, die.
- Frequent colon lavage with an enema can not only remove toxins, but also damage the mucous membrane of the colon.
- Cleansing the liver using oil can cause liver colic.