Poisoning with petroleum products is the most severe type of intoxication of the human body. Both the ingress of petroleum products into the esophagus and the inhalation of their vapors pose a danger to life and health.
In the first case, the size of the toxic dose of gasoline, diesel fuel or kerosene varies from 20 to 50 milliliters; the lethal dose of products such as toluene, benzene or xylene is generally only 15 milliliters.
Such poisonings are typical both in everyday life (in garages, inside individual vehicles, etc.) and at work. For example, personnel of oil industry and oil refining enterprises are constantly in contact with both crude oil and petroleum products, as well as other petroleum-containing harmful substances (solvents, catalysts, etc.).
The state of the air environment of such enterprises and the settlements surrounding them has a harmful effect on the human body. It contains a lot of hydrocarbon compounds, of which the most dangerous include: hydrogen sulfide, benzene, carbon monoxide and various sulfur compounds. The impact of a complex of such substances on the human body causes a strong toxic effect, which can lead to poisoning.
Harmful hydrocarbons can enter the body not only through the respiratory tract, but also through the skin.
Vapors from oil and its products can cause acute and chronic poisoning, as well as various skin diseases. Acute intoxication is typical when exposed to sulfur petroleum compounds, and can also be caused by high concentrations of hydrocarbons. Chronic poisoning is usually caused by exposure to high-sulfur oil over a long period of time.
Read also:
Russian standard - URALS oil
Symptoms
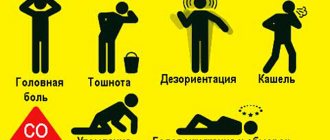
Symptoms of gasoline vapor poisoning occur almost immediately and depend on the degree of poisoning, which in turn depends on the dose of the toxic substance received and the time of its exposure to the victim. In this regard, acute and chronic forms of poisoning can be distinguished.
The main signs of gasoline vapor poisoning are as follows:
- weakness, dizziness,
- unsteady gait, poor coordination of movements,
- nausea, vomiting,
- mental excitement,
- headache,
- chest pain,
- rapid pulse,
- high body temperature,
The fumes from leaded gasoline are especially dangerous. If they are inhaled in high concentrations, you can instantly lose consciousness and even die.
If the substance gets into the lung, symptoms will be added: pain in the area of the affected organ, frequent shortness of breath, bluishness of the skin, cough with possible blood.
After a person swallows fuel, repeated vomiting, abdominal pain, and loose stools begin. The liver is also affected.
In severe acute poisoning, hallucinations, convulsions, impaired consciousness to the point of complete loss, coma, respiratory arrest, and death are also possible.
The phenomena of chronic intoxication with gasoline vapors are characterized by slightly different symptoms:
- weakness, increased fatigue,
- nervous system disorders,
- menstrual irregularities in women,
- indigestion,
- problems with sleep and sense of smell,
- memory impairment,
- low blood pressure,
- erectile dysfunction in men.
If gasoline comes into frequent contact with the skin, skin inflammation occurs and eczema may subsequently develop.
Treatment methods and care
For oral poisoning (ingestion)
Rinsing through the probe until clear water appears. Afterwards, an antidote is placed in the stomach - a solution of activated carbon (3-4 tbsp.), Vaseline oil and water (200 ml.). Next, you need to be treated in a hospital. Complications such as pneumonia and pulmonary edema are not uncommon. Therapy is carried out (treatment depending on the degree of damage to the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract), administration of intravenous glucose solution.
Bed rest must be strictly observed. You should take vitamins of group PP, C and B1, calcium, and iron-containing supplements (can be bought at the pharmacy).
After prolonged inhalation of vapors
Caffeine is injected subcutaneously. In difficult cases, an oxygen cushion is used. Further therapy is aimed at treating diseases caused by poisoning.
Substance abuse is the regular inhalation of gasoline vapors (acetone, solvents) in order to cause euphoria. The modern hobby of young people and adolescents leads to damage to the central nervous system. Main symptoms: weakness, hallucinations, dilated pupils (drug addiction has similar manifestations).
First aid
What to do if you are poisoned by gasoline vapors?
Providing first aid for gasoline vapor poisoning includes the following actions:
- It is necessary to interrupt contact with fuel fumes as soon as possible and remove the poisoned person to fresh air.
- Give warm drinks often. Liquids in case of poisoning always help the body naturally remove toxins,
- Organize pastel mode, cover with a warm blanket and ventilate the room well,
- Give/take sorbents: activated carbon, Enterosgel, Polysorb, Smecta, Laktofiltrum and others.
A mild form of poisoning can be treated with this method of treatment. In case of severe poisoning, or if children or pregnant women are poisoned, proper medical care must be provided in a special medical institution. The first step is to call an ambulance.
While the ambulance is on its way, it is recommended to provide first aid, the algorithm of which is described above. In case of loss of consciousness, place the victim on his side. If breathing stops, perform artificial ventilation.
If the petroleum product gets into the stomach, it should be rinsed quickly with a large volume of water and induce vomiting.
How chickenpox begins: how the initial stage manifests itself in children
Chickenpox is called that way because it can be spread by the wind, that is, by airborne droplets.
Let's figure out how chickenpox manifests itself in children. Someone sneezes contagiously next to you, you will already forget about this insignificant episode in your life. And after 1-3 weeks the temperature suddenly rises.
This is the initial stage of chickenpox in children. And if it were not for the almost simultaneous appearance of the rash, then chickenpox in children could be mistaken for an acute respiratory infection; in addition, the symptoms of chickenpox include headache and a feeling of weakness.
Now you know how chickenpox begins.
Prevention
The main preventive measures in the fight against petroleum product poisoning are mainly aimed at observing safety precautions both in enterprises, gas stations, and at home. It is necessary to ensure good ventilation/ventilation of the work space, use personal protective equipment (gloves, protective suit, gas mask). Persons who constantly work with gasoline are recommended to ventilate and wash their work clothes more often, as well as undergo regular medical examinations. If symptoms of chronic poisoning are detected, it is recommended to leave hazardous work or temporarily withdraw from it.
You need to be vigilant with difficult teenagers and, if anything happens, seek qualified medical help. All containers with toxic substances should be kept away from children.
It is not recommended to keep leaded gasoline at home, or to use the chemical for various household purposes.
Petroleum products include a large group of substances derived from petroleum. In terms of chemical composition, petroleum products are a mixture of hydrocarbons.
Various types of fuel (gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, fuel oil), lubricants, some solvents are all petroleum products.
In what cases can intoxication occur?
The International Classification of Diseases (ICD 10, code T52) contains a section “Toxic effects of organic solvents”, which lists the following substances: petroleum products (gasoline), kerosene, paraffin wax, petroleum ether, varnish gasoline, naphtha, benzenes (except toluene and xylene) and nitro- and amino derivatives of benzene and its homologues.
Hydrocarbon poisoning can occur through inhalation of vapors and ingestion. It also occurs chronically when working in oil refineries and other industries, and with substance abuse. Leaded gasoline, which contains tetraethyl lead, is dangerous and can lead to serious consequences.
Causes of petroleum product vapor poisoning
The most common causes of poisoning by vapors of petroleum products are accidents during the production of these substances, their storage and transportation. In everyday life, intoxication is possible when working with fuels and solvents in poorly ventilated areas. Often, petroleum distillation products are used by drug addicts as intoxicants. Poisoning can be acute or chronic.
Clinical picture of petroleum product vapor poisoning
Inhalation of oil vapors and products obtained from it has an irritating effect on the mucous membrane of the eyes and upper respiratory tract, which is manifested by pain and burning in the eyes, sore throat, and unproductive cough. The systemic effect on the body is manifested mainly by damage to the nervous system. Acute intoxication is manifested by headache, nausea, and ringing in the ears. Poisoning with gasoline and kerosene vapors resembles alcohol intoxication - mild euphoria and excitement occur, speech and coordination of movements are impaired, and hallucinations are less likely to develop. Severe poisoning with substances consisting mainly of aliphatic hydrocarbons is accompanied by depression of consciousness up to coma with areflexia. Inhalation of aromatic hydrocarbons, on the contrary, is characterized by the occurrence of muscle twitching and cramps. Severe poisoning can result in death due to paralysis of the respiratory center or fatal rhythm disturbances. When systematically inhaling petroleum product vapors, patients complain of headaches, dizziness, general weakness, fatigue, sleep disturbances, and depressed mood. Victims experience severe asthenia, neurotic disorders, polyneuropathy, progression of encephalopathy, and vegetative-vascular disorders. There is instability of blood pressure and bradycardia. On the part of the respiratory system, the development of mucosal atrophy, chronic pharyngitis, laryngotracheitis, and bronchitis is possible. Damage to the gastrointestinal tract is manifested by a decrease in acidity in the stomach, a decrease in the activity of the digestive glands, and toxic damage to the liver. Suppression of all hematopoietic germs is manifested in a general blood test in the form of anemia, leuko- and thrombocytopenia. Disturbances are also possible from the endocrine system. There is moderate hyperfunction of the thyroid gland, and sometimes menstrual irregularities. Women may have problems carrying a pregnancy. When inhaling highly concentrated aerosols of mineral oils, lipoid pneumonia develops. Typical symptoms of such pneumonia are sudden weight loss, fatigue, shortness of breath, a painful productive cough, and the sputum contains droplets of oil.
How to treat whooping cough in children?
Poisoning of children with petroleum products most often occurs due to negligence or curiosity. If fuel is stored at home in an easily accessible place, problems cannot be avoided: bright packaging attracts the baby's attention, despite the warnings of parents.
In most cases, poisoning with gasoline, vinegar and other household chemicals occurs in children who swallow out of curiosity. This all happens because parents leave such products within easy reach, without warning labels. Such things should be stored in a specially designated place that is inaccessible to the child.
The following page presents the new calendar of preventive vaccinations for 2020 in an easy-to-use form. Looking at the vaccination calendar for children for 2020, every mother will be able to determine the time when vaccination is necessary. Also, the national calendar of preventive vaccinations 2018 will indicate the period of revaccination, which should be strictly observed for the correct formation of immunity.
Particular attention should be paid to the vaccination schedule for children under one year of age - this category of babies is the most vulnerable to various infections. The vaccination calendar in Russia undergoes some changes every year, therefore, if vaccination began a year earlier, it continues according to the standard schedule.
The new national vaccination calendar in Russia begins to operate in January and applies to everyone who is vaccinated for the first time.
There are clinical periods of whooping cough in which symptoms and treatments can vary significantly.
The following periods of whooping cough in children are distinguished:
- catarrhal, which disguises itself as a typical acute respiratory viral infection with an accompanying runny nose, sore throat, dry cough and fever;
- convulsive with spasms of muscle tissue, clinically manifested in typical coughing attacks with a preceding aura in the form of anxiety and lack of air;
- The recovery period, during which symptoms subside and attacks become less frequent, can last up to 2 months.
The first signs of whooping cough appear after the end of the incubation period, which can last from 3 days to 2 weeks.
Timely diagnosis of whooping cough helps limit the spread of the pathogen. The chain of infection is naturally broken, and the number of affected children is reduced.
Equally important is the rapid diagnosis of whooping cough in children in relation to the patient himself and the prognosis for his life and health. As practice shows, earlier treatment of the disease with antibiotics reduces the recovery period by almost 2 times.
The primary diagnosis is established based on the clinical picture. The changes in the composition of peripheral blood are not significant. Leukocytosis and changes in erythrocyte sedimentation rate may be observed. The number of lymphocytes increases. During the spasmodic period, a decrease in hemoglobin and hematocrit levels may be detected.
To clarify the diagnosis, a bacteriological culture of sputum or a throat smear is performed. To more quickly establish a final diagnosis, a serological blood test can be performed to detect the presence of specific antibodies. The agglutination reaction is being studied. At an early stage, the intradermal test method helps to identify pathology.
Before treating whooping cough in children, differential diagnosis is necessary.
General treatment measures include:
- isolation of a sick baby;
- ensuring a high level of air humidity in the room where it is located;
- reducing the air temperature in the room to 20 degrees Celsius (this measure reduces the number of attacks);
- use of antibiotics and antitussives;
- use of specific globulins;
- restoration of immunity;
- eliminating negative consequences.
Next, the treatment methods and medications used are discussed in more detail.
Treatment of whooping cough in children necessarily includes antibacterial therapy. The duration of the disease and the severity of the baby’s condition depend on the correct choice of drug.
The most commonly used antibiotic for whooping cough is Levomycetin, which can be replaced by Ampicillin or Erythromycin. The drugs are prescribed for oral administration.
Intramuscular and intravenous administration of antibiotics for whooping cough is indicated only in severe cases of the disease and a pronounced gag reflex against the background of coughing attacks. The daily dosage is calculated based on the formula: 0.05 mg per kilogram of the child’s weight, divided into 4 single doses.
If there is no visible effect 48 hours after the drug is prescribed, the therapy regimen is changed by adding 1 or two drugs from the approved groups.
At an early stage of the disease, specific treatment with globulin with anti-pertussis properties is possible. The standard administration regimen is intramuscular injection three times a day, 3 ml.
An excellent remedy is oxygen therapy using oxygen pillows and masks. In parallel, it is necessary to use “Reopoliglyukin”, a “Glucose” solution for intravenous administration. These measures help stop pathological changes in the lung tissue and heart muscle.
Neuroleptic drugs for whooping cough are used exclusively during the spasmodic period of the disease. The most commonly prescribed drugs are Aminazine, Atropine, and Propazine. They affect the frequency and depth of coughing attacks.
The most effective antitussive agent is Sinekod syrup. Codelac Phyto, Libexin, Ambroxol and many others can also be used. Dosages are calculated based on the age and body weight of the child.
Complex vitamin therapy and the use of drugs that have an immunostimulating effect are indicated. Glucocorticosteroids are used only in extreme cases. The drug Prednisolone is strictly contraindicated, as it can have a stimulating effect on the respiratory center.
This article has been read 583,079 times.
The first signs of chickenpox are quite characteristic. At first, mild rashes appear on the skin, just flat pink spots. In just a few hours the number of rashes increases sharply. The spots become more convex and bubbles with liquid contents form. Under no circumstances should they be squeezed out. Chickenpox treatment in children is completely different.
During the first 3-4 days, chickenpox in children is accompanied by very severe rashes not only on the skin, but on the mucous membranes - the eyes, genitals, and mouth. These symptoms of chickenpox are typical and appear in all patients without exception.
Itching with chickenpox in children can cause a secondary bacterial infection. The most unpleasant thing is that this rash is also very itchy, but you cannot scratch it to avoid infection in the wound.
Some bubbles pass and new ones appear. Chickenpox in children occurs in waves.
New rashes usually appear within 3-4 days. Then the disease declines.
In place of the blisters, crusts remain, which gradually fall off on their own and, if you follow all the doctor’s recommendations, leave no traces.
Your local doctor will tell you how to treat chickenpox in children, but some basics are still worth knowing. First, you need to know that chickenpox is a virus, so it cannot be cured with antibiotics.
But why do some doctors still prescribe antibiotics? This is done in cases where chickenpox in children is accompanied by a bacterial infection, and the blisters begin to suppurate. This often happens due to constant scratching of the rash.
Almost always, treatment of chickenpox in children requires the close attention of parents. It is necessary to try by all means to distract the child from scratching the rash. Read a fairy tale to your child, play calm games.
Although the symptoms of chickenpox are not so unbearable for a child, it is still advisable to maintain bed rest for the duration of the illness (about a week). There is no specific treatment for chickenpox. There is no cure for it. But it is possible to minimize the discomfort caused by this disease. To prevent new rashes, change bedding and underwear frequently
By the way, you should not get the rash wet; this will only aggravate the discomfort and prolong the healing time of the blisters. This, in fact, is the answer to the question of whether it is possible to bathe a child with chickenpox.
Impact on the body
Workers in the oil and oil refining industry come into contact with both crude oil and its refined products, as well as the reagents used: acids, alkalis, solvents, catalysts.
The air environment of industrial enterprises processing sour crude oil contains a variety of hydrocarbons, the most dangerous of which are benzene, hydrogen sulfide, organosulfur compounds, sulfuric and sulfurous anhydrides, and carbon monoxide. The combined effect on the body of the working complex of various hydrocarbons and hydrogen sulfide enhances the toxic effect.
The impact of petroleum products on the body is possible by inhaling their vapors, as well as through the skin. Oil and products obtained from it can cause acute and chronic poisoning, as well as skin lesions. Acute poisoning can be caused by both sulfur compounds in oil and high concentrations of hydrocarbons. Long-term exposure to high-sulfur oil can cause chronic poisoning.
Liquid petroleum distillates
In the past, much attention has been focused on the association of chemical pneumonitis with ingestion of various petroleum distillates and essential oils.
We were talking primarily about small children swallowing kerosene, gasoline or red polish with mineral oil. Approximately 1 out of every 200 victims died due to pulmonary complications.
In studies conducted by Gerard on rats, mortality was inversely proportional to oil viscosity at SSU below 60 (the lower the SSU, the higher the mortality). (Examples of aspiration hazards from consumption of common hydrocarbons are given in Table 1.)
Other important factors that influenced the results included the length of the straight-chain molecules and their boiling point. Small molecules were more irritating to the lung; At the same time, rapid absorption of the substance was noted. The low boiling point causes the evaporation phase of the substance to begin at body temperature, which leads to a certain displacement of air from the lungs.
Table 1. Viscosity of some common hydrocarbon products
- Mineral insulating oil (varnish, refill for signal lamps)
- Petrol
- Turpentine (pine oil, paint thinner)
- Kerosene (coal oil, jet fuel)
- Heavy gasoline
- Solvents for varnishes and paints
- Petroleum ether (light gasoline)
- N-hexane (solvent)
- Aromatic hydrocarbons (xylene, toluene, benzene)
- Halogenated hydrocarbons (trichlorethylene, tetrachlorethylene,
- tetrachloroethane, carbon tetrachloride)
- White alcohol (Stoddard's solvent, Varasol)
- Naphtha (racing fuel)
- Motor oil and lubricating oils
- Fuel oil and diesel fuel
- Mineral oil (Vaseline oil)
- Rubber and plastic glue
- Petrolatum (Vaseline)
- Grease
- Tar
The question of the possible absorption of petroleum distillates in the gastrointestinal tract and their resecretion in the lungs remained open until Bratton and Haddow (1975), Mann et al. (1977) and Dice et al. (1982) did not show in an experiment on animals that naphtha and kerosene are absorbed in negligible quantities without causing pneumonitis.
Another question concerns the etiology of CNS depressive effects associated with exposure to petroleum distillates. Wolfsdorf in 1976, studying the effects of kerosene on the brain of primates, which was administered intrathecally, intracardially, into the carotid artery and into the portal vein, came to the conclusion that the central nervous system manifestations after ingestion of kerosene were due to hypoxia that occurs during aspiration pneumonia.
Most petroleum distillates are mixtures, so as production technology changes, the composition of the product or a specific ingredient, such as kerosene, also changes.
The variability of clinical manifestations may also be explained by different technologies for the production of petroleum products in different companies. In addition, even if the hydrocarbon content of any product ingredient is high, the aspiration potential and toxicity will be determined by the overall physical properties of the final product.
As a rule, substances with an SSU below 60 are distributed through saliva and enter the lungs during swallowing; chemical pneumonitis can be caused by even 0.2 ml of such a substance entering the trachea. In patients who cough, wheeze, cry, or spontaneously vomit after ingesting petroleum distillate or essential oil, aspiration is assumed until proven otherwise. Many of these foods burn your mouth and irritate your stomach.
The initial symptom of swallowing gasoline is often belching for many hours. Loose stools often occur until the petroleum distillate is completely eliminated from the gastrointestinal tract.
Patients with respiratory depression may not have early radiographic changes, and in asymptomatic patients, early signs are sometimes detected as early as the first radiograph or appear several hours later.
The typical distribution of infiltrates is bilaterally basal, right basal, or perihilar with clear lung bases.