The harm of magnetic resonance imaging is associated with the influence of the magnetic field. Obtaining highly sensitive sections is possible due to the resonance of hydrogen atoms under the influence of a strong magnetic field.
Excited hydrogen protons change radio frequency pulses, which are recorded by special sensors. The image is built by software. The 3D modeling mode creates a spatial reconstruction of the area under study.
Practical studies show that water is part of 90% of tissues. After exposure to a magnetic field, protons are activated. The effect lasts for the duration of the procedure. After magnetization stops, the structure of the liquid molecules is restored.
When answering readers whether MRI of the head is harmful, we note that there are no negative consequences in practice. Medical discussions regarding the likelihood of a strong magnetic field influencing the genetic apparatus years after the procedure continue.
When an MRI of the head and brain is prescribed, doctors first identify contraindications and indications.
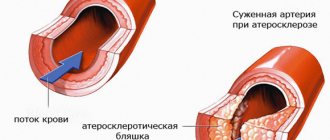
X-ray radiation is more dangerous. The rays damage the genetic apparatus and lead to chromosomal abnormalities. The effect of high doses of x-rays causes acute radiation sickness. Magnetic resonance imaging excludes genetic defects.
A radiology doctor will be able to determine whether it is harmful to do an MRI of the brain for a particular person after a preliminary analysis of the outpatient card and the results of diagnostic methods.
There are no other symptoms. The benefits of MRI many times exclude theoretical long-term changes in the genetic apparatus. Scientific research continues and medical discussions about the negative consequences are ongoing, but there has been a rapid expansion of MRI scanning by private clinics.
Is there a risk
MRI is based on the magnetic field that dominates the tomograph. The organs and tissues of the human body are partially assembled from hydrogen molecules, which react to the influence of magnetic waves. This reaction is recorded by equipment in the form of images, which are subsequently subjected to medical analysis.
Many may decide that magnetic tomography, based on the computer principle, is harmful to human health. However, radiation during MRI diagnostics has nothing in common with the x-ray load during CT, and therefore does not have an adverse effect on the body.
MRI may be harmful to those for whom this type of examination is contraindicated.
MRI: a quick look at the physics
The basis of MRI is the study of the proton composition of the body. Thus, the human body is hydrated, water makes up the vast majority of its mass. Water molecules are not found in the body “by themselves,” but in the form of ions (positively charged proton, negatively charged hydroxyl ion).
Water and protons are present in almost all tissues (bones contain a smaller amount). When a person is exposed to a magnetic field, protons line up in one of the possible directions (and not chaotically, as happens in normal situations - outside the influence of a magnet), forming a “response”, on the basis of which, after complex computer processing, an image is formed.
Did you know that MRI of brain vessels diagnoses almost all vascular diseases of the brain?
Learn about methods for diagnosing brain cysts, causes, symptoms.
Restrictions sheet
Magnetic resonance imaging, like other diagnostic techniques, has a number of absolute contraindications:
- the presence in the body of the person being examined of metal implants, foreign objects, a pacemaker, a hearing aid, etc.;
- mental illnesses, the development of which is expressed in the patient’s inability to remain motionless inside the tomograph;
- state of alcohol or drug intoxication.
In addition to absolute ones, there are also relative contraindications to MRI:
- diseases of the cardiovascular system (depending on the severity of the pathology and the patient’s condition);
- fear of closed spaces (an open type tomograph is used as an alternative).
Separately, it is worth touching on the issue of the possibility of conducting examinations for children and pregnant women.
Is it possible to diagnose children and pregnant women?
Radiation exposure during MRI diagnostics is zero, but experts try not to prescribe such a procedure to children. Examination is rarely used: to confirm the diagnosis and monitor the effectiveness of the therapeutic course.
Why is MRI diagnostics so rarely used in the case of children, especially young ones? Specific sounds of equipment, closed spaces, and unfamiliar surroundings can frighten the baby and disrupt the progress of the study. In such cases, doctors recommend using anesthesia.
Introduction of contrast
Harm during MRI of the brain, spine, pelvic organs and other anatomical structures in the absence of contrast is minimal, however, in the case of pregnant women, MRI is contraindicated in the 1st trimester.
At this time, the formation of all organ systems of the unborn child occurs; the degree of influence of the magnetic field on these phenomena is not fully understood, therefore MRI in the first 14 weeks of pregnancy is prohibited (examination is allowed only if serious pathologies of the fetus are suspected).
In the 2nd and 3rd trimester, you can undergo diagnostics, but without using a contrast agent, since it can harm the child’s body.
After the 1st trimester of pregnancy, MRI diagnostics are often performed to assess the condition of the fetus. The examination takes place without harm to the expectant mother and child.
Types of MRI machines and examination safety
MRI machines come in open and closed types. A closed-type magnetic tomograph is a classic-looking tube, open on both sides, into which a table for the patient slides like a tunnel. Many people feel scared at the thought that they will have to lie motionless for 40-60 minutes in such a pipe.
Magnetic elements in open-type tomographs are not located in a tube surrounding the patient’s body, but in a C-shaped arc, relative to which the work table moves. This design allows patients with claustrophobia to be examined without harm or negative consequences, because only the part of the body being examined is covered by the device, as much as required, so they are not afraid.
It seems that open-type tomographs are less harmful and more convenient for performing MRI of the brain. In fact, in both cases the research is not dangerous. The choice in favor of an open-type device is often made if examination in a classic tomograph is impossible due to claustrophobia or the patient is simply scared.
During pregnancy
The question of the harm of MRI during pregnancy is also one of the most popular. It is traditional to prohibit research in the first trimester of pregnancy. This limitation is caused by insufficient research into the influence of electromagnetic waves on the formation of the fetus. It is accepted that in the first months of intrauterine development, MRI is harmful to the embryo, since at this time it is most vulnerable to external negative influences.
In exceptional situations, doctors may allow scanning, objectively and comprehensively assessing the harms and benefits of refusing the study.
Prevention of complications during MRI
The person being studied needs:
- inform a specialist about problems with the urinary system;
- do not undergo examination if you have metal prostheses, pacemakers, or during pregnancy (especially in the first trimester);
- during the procedure, remove all jewelry;
- wear clothes without zippers, fasteners or other metal parts.
Effect of contrast agent
In some cases, diagnosis requires a more detailed look at a specific organ, such as the liver. To do this, doctors use a special contrast agent injected into the body. It is produced on the basis of gadolinium salts. The introduction of a contrast substance improves visibility in areas of tumors, neoplasms, metastases and simplifies the diagnosis of cerebral and cardiac blood flow.
In Russia, drugs that have passed clinical trials and are approved for use are used, such as Gadovist, Primovist, Datorem. They are completely harmless. Side effects of using such drugs can include extremely rare allergic reactions and difficulties in removing the drug from the body. To avoid such an outcome, “contrast” MRI is not prescribed to patients with renal failure.
How dangerous is magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)?
Low-frequency gradient and high-frequency radiofrequency magnetic fields result from the gradient coils required for imaging.
Their effects:
- impact on implanted products;
- creating a ring current and heating the tissue;
- magnetic phosphenes, cardiac stimulation, muscle stimulation.
Products of both a medical and non-medical nature (metal shavings) implanted into the patient’s body can move and heat up, and active implants (pacemakers, infusion pumps) may not work correctly in a strong magnetic field. There are many examples of such implants.
Most metal hip prostheses and spinal fixation devices are MRI-safe (however, they sometimes produce significant local artifacts, but this is a diagnostic issue, not a safety issue).
Most IUDs currently in use are not displaced by a magnetic field or heated by pulse sequences.
Metal shavings in the eyeball (usually the result of repair work) are an absolute contraindication.
Pacemakers in the presence of a strong magnetic field may stop working, reset, or go into asynchronous mode. MR-compatible pacemakers have recently appeared on the market. Neurostimulators (eg, vagus nerve stimulator) are most often MR-compatible.
MRI (even on systems with a field of 1.5 or 3 Tesla) is safe for most patients with other metal objects in the body. This primarily applies to patients with foreign non-magnetic bodies (for example, shot) or non-magnetic (titanium) medical implants. Metal teeth, steel staples, or wires used to suture the sternum after cardiac surgery are generally safe for MR examinations. The same applies to coronary stents and heart valves.
External metal objects - magnetic sphincters, colostomy bags for artificial ostomies, dentures should be removed before the study, if possible.
MRI with contrast
Contrast agent
The use of a contrast agent is often indicated as part of magnetic tomography. The essence of the technique is the preliminary administration of a dye to the patient. This approach helps in the detailed study of organs and tissues and is applicable in the diagnosis of blood vessels, tumors, spinal diseases, etc.
When it comes to MRI with contrast, the list of contraindications for tomography expands. Additional restrictions include:
- increased sensitivity to contrast;
- renal failure;
- the period of bearing a child (the entire period) and breastfeeding;
- multiple myeloma;
- pathological processes in the lungs;
- recent liver transplant.
Is there any harm from MRI with contrast? The substance used in the tomography process is based on gadolinium salts, which are characterized by a low toxicity index, and therefore are safe for health.
What are the consequences of using contrast?
When using a contrast component during MRI diagnostics, the possibility of an allergic reaction cannot be ruled out. If we take statistical data as a basis, we can say that such cases account for only 0.01% of the total number of MRI examinations.
To exclude even the minimal likelihood of developing an allergy to the contrast agent, the patient needs to undergo an allergy test. If allergic reactions are not identified during the procedure, the risk of occurrence after magnetic tomography is zero.
Among the alarming symptoms during the allergy test:
- redness, swelling of tissues in the area of injection of the component;
- slight itching;
- lowering blood pressure;
- dizziness;
- lacrimation, discomfort in the organs of vision;
- sneezing;
- cough;
- dyspnea.
Allergy test
The appearance of such symptoms is a reason to refuse contrast in the process of MRI diagnostics.
If a patient who belongs to the group of people with contraindications for diagnostics undergoes an MRI with contrast, the patient’s well-being is likely to worsen and the therapeutic dynamics will slow down, the development of anaphylactic shock and other side effects.
How does anesthesia affect a child and is it dangerous?
CT can rightfully be called one of the most important inventions in the field of medicine.
Appearing in the 70s of the last century, computed tomography became a revolutionary discovery, allowing early diagnosis of numerous human diseases, and its creators received the Nobel Prize. This device is based on the quantitative determination of the ability of tissues to absorb X-ray radiation. CT refers to a radiation diagnostic method. Ionizing radiation is not safe for the body, but only if the radiation dose exceeds the permitted threshold.
The maximum permitted dose per year is 150 mSv. According to statistics, a patient who regularly undergoes fluorography, mammography and dental imaging receives only 15 mSv. If we talk about CT, then when examining the skull and head, the radiation dose is 1-2 mSv, the chest, abdominal cavity - 6-11 mSv.
However, CT scanning has clear benefits that outweigh the possible risk of future cancer. Doctors use minimal power to reduce radiation exposure, and modern tomographs produce much less radiation than older machines.
Another popular question that patients ask is whether magnetic resonance imaging is harmful and how often can it be performed? This research method allows you to quickly identify the early stages of numerous ailments. An absolute advantage is the absence of ionizing radiation.
Many patients mistakenly transfer information about the dangers of X-ray radiation to MRI, which is fundamentally incorrect. The magnetic fields used, coupled with radio frequency signals, do not pose any threat either during the study or in the future. Currently, there is no medical evidence of harm from this procedure. Millions of people have had MRI scans and no negative effects have been found.
The only disadvantage associated with this study is its duration. The scan lasts from 15 minutes to an hour, and during this time the patient must lie still. He does not experience any unpleasant sensations.
These hardware diagnostic methods are among the most popular. It should be noted that:
- During X-rays, the patient is exposed to a stream of ions. It has low power, so one x-ray session cannot cause any harm. The radiation dose is too low.
- The specificity of X-rays is that the received radiation doses are added. It cannot be used repeatedly in a short period of time. Doses accumulate, and with repeated examination the negative effect intensifies. It is highly undesirable to repeat x-rays several times in a short period of time. The negative impact from the previous dose simply will not have time to wear off. Over time, tissues are restored, and if the ionizing effect is repeated frequently, cells and tissues can be damaged.
- X-rays are contraindicated in certain pathologies and pregnancy. Radiation can be harmful to the fetus.
- X-rays are also undesirable during breastfeeding. A nursing mother should be examined by other methods.
Some patients equate the magnetic resonance method with x-rays. It is not right. Both methods, although hardware-based, are based on completely different physical processes. With MRI, there is no risk of harm to health even with repeated procedures, and there is absolutely no ionizing radiation.
General anesthesia for a child during MRI is a reasonable and justified action, thanks to which negative consequences for the child’s psyche can be avoided. Very often, such a diagnosis leads to severe fear and unpleasant emotions in the child. When performing an MRI under anesthesia, the baby is not immune to the side effects of anesthetics.
The maximum permitted dose per year is 150 mSv. According to statistics, a patient who regularly undergoes fluorography, mammography and dental imaging receives only 15 mSv. If we talk about CT, then when examining the skull and head, the radiation dose is 1-2 mSv, the chest, abdominal cavity - 6-11 mSv. Obviously, these figures do not reach the maximum permitted number of 150 mSv, so several examinations can be done per year.
A woman’s condition, such as pregnancy, is a direct contraindication to CT scanning. It is recommended to discuss other testing methods with your doctor, such as MRI or ultrasound.
Many doctors prescribe this test for children only for serious reasons. The fact is that the susceptibility of a child’s body to the effects of radiation is several times higher than that of an adult. However, in some situations, the need for quick and accurate diagnosis outweighs the possible risk of CT.
This procedure is not recommended before 12 weeks of pregnancy. In the first 3 months, vital organs form in the fetus. It is at this time that the unborn baby is most susceptible to the negative influences of the environment. The only exception in which an MRI is performed before 12 weeks is if there is a suspicion of fetal pathology. In other cases, the study is postponed to the 2nd or 3rd trimester of pregnancy.
Women expecting a child are especially wary of the offer to undergo a tomographic examination. They are interested in whether MRI diagnostics are harmful to the health of the fetus? To date, there is not a single scientific study indicating that this form of scanning is harmful for pregnant women. But doctors, as
reinsurance, they still do not recommend undergoing tomography for women in the early stages of pregnancy. Since in the first months the formation and development of internal organs occurs in the fetus, even the slightest emotional stress for the mother can have a negative impact on the fragile organism. In this regard, MRI is not recommended before 12 weeks of pregnancy. But after three months of pregnancy, doctors begin to use this method to find out about the state of health
both mother and fetus along with ultrasound.
As for small children, magnetic resonance imaging is allowed for a child of any age due to its safety. However, sometimes tomography for children requires the use of medicated sleep. Not all parents immediately understand why their child is prescribed anesthesia to undergo an examination. This procedure can be used in cases where the baby has excessive mobility, and there is no other way to make him lie motionless.
radiography
Comparing the impact of two types of hardware diagnostics - radiography and magnetic resonance imaging on the human body, we note the following: during an X-ray examination, a person is exposed to ionizing radiation, albeit in small doses. In this case, X-rays have a cumulative effect (they tend to accumulate in the body). X-rays have a number of strict restrictions related to the health status of patients and are prohibited for pregnant women.
Many patients automatically transfer information about the dangers of X-rays to MRI, which is completely wrong. Since the characteristics of the magnetic fields and radio frequency signals used are such that they do not pose any threat to the patient’s health both during the procedure and in the distant future. There are no sources of radioactivity in the installation.
There is no harm from MRI even if it is necessary to repeat the examination several times at short intervals. Therefore, when answering the question, what is more harmful than MRI or X-ray, you should remember the features of these diagnostic methods and the undeniable advantage of magnetic resonance imaging.
So, is MRI harmful to your health? As we have already mentioned, during magnetic resonance imaging, the patient’s body is exposed only to a powerful electromagnetic field, and this frightens many. However, scientists have not established the fact that they cause harm to the human body during MRI.
Sometimes patients become ill during the procedure, but the reason for this is not the radiation, but the confined space. The MRI camera is very small; some patients find it very scary to stay in such a confined enclosed space for half an hour, and without moving.
If a person is too afraid, he should tell the doctor about this even before the diagnosis begins. For patients who are too afraid to undergo an unfamiliar procedure or are intimidated by limited space, the following options are available:
- Conduct scanning not in a closed, but in an open device. There are such methods, and recently they are being used more and more often.
- During the procedure, you can lie not on your back, but on your stomach. Many people like this position better.
- It is allowed not to place a special pillow under your head. To ensure that the patient receives more air, a special fan can be turned on.
- It must be remembered that the subject has a special panic button at his disposal. If problems arise, the procedure can be interrupted immediately.
- If the patient suffers from claustrophobia, he may be advised to take a sedative before the MRI.
Danger of contrast
MRI using a contrast agent is more dangerous. The procedure increases the information content of oncological lesions. Contrast is administered intravenously. A syringe or injector is used for this.
Contrasting is strictly contraindicated during pregnancy at any stage and while the baby is breastfeeding. The main complication that the substance can provoke is an allergic reaction. The disorder may be mild, moderate or severe.
With a minor allergy, the patient complains of:
- nausea;
- itchy skin rashes;
- change in skin color;
Some people complain of dizziness after an MRI with contrast.
- hearing loss;
- blurred vision;
- dizziness;
- drowsiness.
The initial stage of allergies does not require treatment and does not pose a health hazard.
In moderate and severe cases, difficulty breathing, loss of consciousness, intense vomiting and heart failure are added to the existing symptoms. We urgently need to call a doctor.
Allergic reactions after contrast are uncommon. Usually, negative symptoms are encountered by people prone to individual intolerance to a substance.
After watching this video, you will find out whether it is harmful to have an MRI:
Impact on the child's body
The harm of MRI often makes patients refuse to undergo examinations, but is there any negative impact in the method? The intense magnetic field forces inventors to make devices that are resistant to radio frequencies. However, electromagnetic interactions are actually completely harmless to the human body.
Doctors often prescribe tomography for diagnosis of the following symptoms:
- Frequent headache.
- Dizziness.
- Tumors of unknown origin.
Harm from MRI of the brain can occur if you do not follow simple rules. Like other procedures, this method has its contraindications:
- Installed pacemaker.
- Ferromagnetic or other electronic implants have been installed in the middle ear.
- Metal implants.
- A compression distraction device was installed.
The consequences of an MRI can be very serious if you have tattoos on your body. In most cases, this does not apply to modern tattoos, especially to those that were made more than 20 years ago. Back then, inks using metal enzymes were often used. If you try to undergo a tomography with such a tattoo, the harm of an MRI can be different: from light palpation to very severe pain.
Some patients were unable to complete the study due to unbearable pain. Even if there is no noticeable pain, in such cases the quality of the images deteriorates significantly. If you are sure that your tattoos contain metal components, you can replace the diagnostic method with CT or ultrasound.
Children are frequent guests in MRI rooms. They, like adults, are often prescribed this study. “Isn’t scanning dangerous for a fragile child’s body?” - worried parents ask.
Scanning does not impose any additional burden on the child. The only difference from diagnosing adults may be the use of light anesthesia on a restless baby in order to ensure his immobility. Children tolerate it well. It is only rarely recommended to reduce mental or physical activity in the first hours after an MRI.
Contraindications
MRI has relative and absolute contraindications. All restrictions are listed in the table.
| Relative contraindications | With relative restrictions, the procedure is postponed indefinitely or auxiliary means are used. Such contraindications include: • nerve stimulants; • prosthetic heart valves; • pregnancy up to 3 months; • fear of closed spaces; • tattoos. |
| Absolute contraindications | Absolute restrictions include: • the presence of a pacemaker; • metal implants; • ear designs. |
To exclude contraindications, you should first consult your doctor.
What is safer: MRI or X-ray?
radiography
It is hardly possible to compare the procedure of magnetic resonance imaging and conventional radiographs. First of all, the final data from fluoroscopy are inferior to organ scanning in terms of information content. In some cases, computed tomography provides sufficient results; its cost is much lower than electromagnetic diagnostics, but the harm to the patient’s health is much higher.
Of course, exposure to ionizing radiation, which is used to obtain an X-ray, is strictly regulated, and radiation dose standards are calculated for different age categories and depend on the state of human health. Medical specialists who refer patients for CT or X-rays calculate the doses of radiation and determine how many times the diagnostic procedure can be performed so as not to harm the patient.
Under certain circumstances (for example, if the patient has loose ferromagnetic implants or endoprostheses), an MRI may be unsafe, and a CT scan will solve this problem.
Benefits of MRI
MRI is one of the most accurate and safe diagnostic examinations. The procedure completely scans internal organs and tissues. For some diseases, magnetic resonance imaging has no alternative.
The examination makes it possible to assess the condition of the entire body. For some diseases, research is completely irreplaceable. Doctors confirm the usefulness of the method in diagnosing pathological processes. The only thing you need to do is make sure there are no contraindications.
What are the harms of MRI to health?
During the procedure, the patient’s body is exposed to radiofrequency radiation, which accompanies us every minute in everyday life. The high-frequency electromagnetic field is completely safe for our health, this is confirmed by many years of research by scientists.
Many people are interested in: is it dangerous to do an MRI of the brain and how can it affect mental activity?
In diagnostic practice, there is no evidence of harm caused to the patient’s health or deterioration in well-being after the examination.
If a doctor prescribes this test, it means that it is really necessary to undergo it in order to confirm the diagnosis or choose the optimal method of treatment.
How often can an MRI be done?
Since MRI does not involve talking about the effects of radiation on the patient’s body, examinations are carried out as often as specific clinical circumstances require. Before the study, the patient will have to take a referral from the attending physician. In some medical centers, you can undergo MRI diagnostics without a doctor’s referral.
Magnetic tomography is often prescribed for preventive purposes. The examination is carried out after surgery to evaluate the results of therapy.
Often, specialists decide to conduct the examination more than once. Sometimes MRIs are done twice a day. What should be the minimum time interval between consecutive diagnostics? With traditional MRI, there is no need to take a break at all. As for magnetic tomography using internal contrast, in this case the examination is carried out at intervals of at least 3 days.
The only disadvantage of frequent use of the method may be the cost of the examination. Too frequent appointments of magnetic tomography rightfully alarm patients.
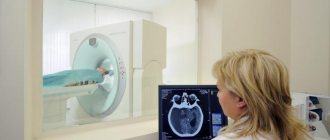
How is the examination carried out?
The MRI machine looks like a large cylinder into which the patient is placed. During the examination, the patient is placed on a pull-out couch and the limbs are secured with straps, this allows for a clearer image (the pictures turn out blurry when moving).
When examining the brain, a special device with wires is placed on the patient's head, which sends and receives radio waves.
After the patient is moved inside the capsule of the device, the diagnostic doctors go to another room, from where they observe the procedure, and a speakerphone is provided to check the patient’s condition.
The tomograph consistently produces a group of images of a layer-by-layer section of the examined tissues, with the help of which an accurate diagnosis can be made.
Is MRI harmful?
Magnetic resonance imaging is considered one of the safest diagnostic methods. Many patients are worried, believing that during the examination the body is affected by a strong electromagnetic field. The harm of MRI to the body has not been proven.
The procedure is most harmful for people who are afraid of closed spaces.
In this case, the method can leave an indelible imprint on the psyche. These people should first consult their doctor to:
- get a referral to an open tomograph;
- during the procedure, the patient was turned on inside the apparatus with a fan and the pillow was removed to alleviate the condition;
Before going for an MRI, you need to get an appointment with a doctor.
- if possible, obtain permission to conduct the examination while lying on your stomach;
- The doctor reported that there was a panic button to stop the examination.
During the procedure, the patient is placed on a moving platform. An electromagnetic field is created in the device. The image is obtained thanks to electromagnetic pulses. The described actions do not have any negative effects on the body.
MRI can be harmful only when combined with contrast. To eliminate possible risks, the doctor first checks with the patient whether he has any allergic reactions. The examination is not carried out if there are contraindications.
In order to protect yourself, you should first consult a doctor. You should inform your doctor about all individual intolerances and pathological processes.
An MRI begins with the patient being positioned correctly on the couch.
Some doctors argue that MRI should not be assumed to be 100% safe. That is why, like any other method, diagnostics should be done only thoughtfully and after a preliminary visit to the doctor.
What is a tomograph?
Diagnosing patients with tomography is justified in most cases, since this examination is very informative, is not dangerous and is not harmful to health, but at the same time allows you to obtain a layer-by-layer three-dimensional image of the organ being examined.
The popularity of computer scanning is due to the fact that this method provides extensive information about the organ being examined. But how does this information get on the screen? It's all about the tomograph, which reads information from magnetic waves. This is a device with a retractable table on which the patient is placed.
There are open and closed tomographs. MRI is equally safe for the body in any of them and is not harmful to health. The closed device is similar to a tunnel; the table slides into it and diagnostics are carried out directly inside. And in an open tomograph, a device is placed above the patient that reads data from magnetic waves passing through the body.
Nowadays, more and more often, doctors prescribe tomography of the body, this allows you to quickly assess the patient’s health status. There is a misconception that MRI is very harmful. To understand whether this is so, it is necessary to understand the operating principle of the apparatus that performs the examination.
The operation of the tomograph is based on certain physical processes, the occurrence of which is absolutely not harmful to health. When the patient is on the table, electromagnetic scanners are turned on, which affect the human body without harm, as a result of which hydrogen atoms begin to respond to the influence and line up in a certain way. Such positions of the smallest particles make it possible to read information layer by layer, translating it into a picture, which is sent to the diagnostician’s monitor.
Over the course of several years, various studies have been conducted on the effect of MRI on the human body, and the impact of electromagnetic rays or frequency radio waves through which the procedure is carried out was also assessed. The benefits and harms of magnetic resonance imaging were discussed and rechecked by specialists from various fields of science.
All data obtained did not reveal any dangerous effects on the body or health. Studies have shown that diagnostics in a magnetic tomograph certainly affects a person, but the radiation exposure from one procedure does not exceed the impact from talking on a mobile phone for an hour. Therefore, the harm of MRI is rather the fear of patients going for diagnostics.
Tomography does not pose any harm to the body or health. You can even find out whether it is harmful or not from your doctor. A professional will be able to describe in detail the mechanism of MRI, indicate all the consequences and diagnostic options.
Most often, tomography is prescribed after injuries and falls, as it can indicate the hidden consequences of the injury. Is MRI of the brain harmful in this case? Exactly as much as it is harmful to health to do MRI of the spine, tomography of blood vessels, MRI of joints, and diagnostics of the musculoskeletal system.